Arctigenin attenuates paraquat-induced human lung epithelial A549 cell injury by suppressing ROS/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases-mediated apoptosis
Chao Liu,Zhao-rui Sun,Meng-meng Wang,Zhi-zhou Yang,Wei Zhang,Yi Ren,Xiao-qin Han,Rui Liu,Quan Li,Shi-nan Nie
Department of Emergency Medicine,Jinling Hospital,Medical School of Nanjing University,Nanjing 210002,China
BACKGROUND: Paraquat (PQ)-induced acute lung injury (ALI) and pulmonary fibrosis are common diseases with high mortality but without effective antidotes in emergency medicine.Our previous study has proved that arctigenin suppressed pulmonary fibrosis induced by PQ.We wondered whether arctigenin could also have a protective effect on PQ-induced ALI.METHODS: A PQ-induced A549 cell injury model was used,and the effect of arctigenin was determined by a cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) cell viability assay.In addition,terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)-mediated dUTP nick-end labelling (TUNEL) staining assays and mitochondrial membrane potential assays were performed to evaluate the level of cell apoptosis.The generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) was reflected by dihydroethidium (DHE) staining and a 2’,7’-dichlorodihy drofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) assay.Moreover,immunoblotting studies were used to assess the expression of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) and p38 MAPK.RESULTS: Arctigenin attenuated PQ-induced inhibition of A549 cell viability in a dosedependent manner.Arctigenin also significantly reduced PQ-induced A549 cell apoptosis,as reflected by the TUNEL assay and mitochondrial membrane potential assay,which may result from suppressed ROS/p38 MAPK signaling because we found that arctigenin dramatically suppressed ROS generation and p38 MAPK phosphorylation.CONCLUSION: Arctigenin could attenuate PQ-induced lung epithelial A549 cell injury in vitro by suppressing ROS/p38 MAPK-mediated cell apoptosis,and arctigenin might be considered a potential candidate drug for PQ-induced ALI.
KEYWORDS: Paraquat;A549 cells;Arctigenin;Reactive oxygen species;Mitogen-activated protein kinases;Apoptosis
INTRODUCTION
Paraquat (PQ,1,1’-dimethyl-4,4’-bipyridylium),also known as methyl viologen,has been widely used as a broad-spectrum,highly effective and inexpensive herbicide in agriculture worldwide.However,PQ is highly toxic to humans and animals owing to its high toxicity,which has aroused great concern from the public.PQ can be absorbed through a variety of ways,including oral,inhalational,and transdermal ways,leading to toxic effects on multiple organs.PQ primarily accumulates in the lungs (6-10 times higher than plasma concentrations)because it can be actively transported into lung alveolar epithelial cells and Clara cells by the polyamine uptake system.Without effective antidotes,PQ-induced acute lung injury (ALI) and subsequent progressive pulmonary fibrosis are the primary causes of death.
Although great attention has been given to PQ poisoning and some progress has also been made,the mechanisms of PQ toxicity remain to be further elucidated.Accumulated evidence has suggested that reactive oxygen species (ROS)play key roles in PQ poisoning.PQ,as an electron acceptor,can induce numerous ROS generated in cells,which further leads to direct oxidative stress.Additionally,ROS would also trigger cell apoptosis as signal transduction molecules.Thus,direct ROS inhibition by antioxidants might be a potential effective way to ameliorate PQ injury.Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs),including extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs),c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs) and p38 MAPKs,are a group of serine-threonine protein kinases.MAPKs are vital in signal transduction from the cell surface to nucleus in response to a diverse array of extracellular stimuli.In addition,MAPKs have been reported to be activated by ROS.Moreover,it has been proven that suppressing the ROS/p38 MAPK pathway could reduce PQ-induced lung injury.
Arctigenin,a natural lignan compound extracted from(),has attracted researchers’attention for its promising therapeutic effects in the past several decades.Numerous studies have reported the beneficial biological activities of arctigenin,including anti-oxidase,anti-inflammation,and ant itumor activities.More interestingly,our previous study demonstrated that arctigenin attenuated PQ-induced pulmonary fibrosis by suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the Wnt3a/β-catenin pathway.Additionally,arctigenin has been shown to protect against lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury in ratsand mice.However,whether arctigenin can attenuate PQinduced ALI and whether the ROS/p38 MAPK pathway is involved are still unknown.Thus,our present study was designed to investigate the effects of arctigenin on PQinduced ALI and the underlying mechanisms.
METHODS
Cell culture
Human lung epithelial A549 cells were purchased from Fudan IBS Cell Center,Shanghai,China.Cells were cultured at 37 °C in 95% air and 5% COin Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) (HyClone,South Logan,USA) with 10% (/) fetal bovine serum (Invitrogen,Germany) and 1% (/) penicillin/streptomycin (Invitrogen,Germany).Subculture was performed with 0.25% trypsin/ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) solution (Invitrogen,Germany) after washing the cell monolayers twice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS).Trypsin was then inactivated,and the cells were seeded into fresh T25 flasks.
Cell viability assay
Cell viability was assayed using a cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) kit (Beyotime,China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.Briefly,A549 cells were cultured in a 96-well plate and treated with PQ (Sigma-Aldrich,USA) at the indicated concentrations for 24 h with or without arctigenin (MedChemExpress,USA),while PBS was used as a control.After treatment,10 μL of CCK-8 solution per well was added.The cells were then incubated at 37 °C for another 30 min,and the amount of formazan dye generated by cellular dehydrogenase activity was measured by absorbance at 450 nm with a microplate reader.
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)- mediated dUTP nick-end labelling (TUNEL) assay
TUNEL assays were performed with the one-step TUNEL apoptosis assay kit (Beyotime,China) following the manufacturer’s instructions.Briefly,A549 cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS and then permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100,followed by incubation with TUNEL working solution.The 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole(DAPI) was used to stain and visualize all nuclei.Cy3-labelled TUNEL-positive cells were detected by fluorescence microscopy.
Mitochondrial membrane potential assay
Mitochondrial depolarization in A549 cells was measured using a 5,5’,6,6’-tetrachloro-1,1’,3,3’-tetraethyl benzimidazolocarbocyanine iodide (JC-1) probe (Beyotime,China) according to the information described previously.In brief,cells were incubated with JC-1 staining solution (5 μg/mL) at 37 °C for 20 min,followed by rinsing with JC-1 staining buffer twice.JC-1,a cationic carbocyanine dye,exhibits potentialdependent accumulation in healthy mitochondria,where it forms J aggregates (red),while it remains a monomer(green) upon mitochondrial depolarization.The fluorescence of red aggregates and green monomers was captured by fluorescence microscopy,while the fluorescence intensity was quantified using ImageJ software.
ROS measurement
To detect the level of superoxide anions,the dihydroethidium (DHE) (Beyotime,China) staining was performed following the manufacturer’s instructions.A549 cells were incubated with 5 μmol/L DHE at 37 °C for 30 min and then rinsed in PBS three times.Thereafter,the cells were analyzed by fluorescence microscopy,and the red fluorescence intensity was quantified using ImageJ software.Additionally,the 2’,7’-dichlorodihydrof luorescein diacetate(DCFH-DA) (Beyotime,China) assay was also carried out for the detection of oxidative species.
Immunoblotting studies
Immunoblotting studies were performed following procedures described in our previous reports with modifications.In brief,proteins were extracted from A549 cells using RIPA buffer (Beyotime,China) containing protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche,USA) and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (PhosSTOP™,Sigma-Aldrich,USA).Protein samples (50 μg) were separated by 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and then electrotransferred to nitrocellulose membranes.Then,the blocked membranes were incubated at 4 °C overnight with primary antibodies,including rabbit antibodies against p38 MAPK,phospho-p38 MAPK,ERK,phospho-ERK,JNK,and phospho-JNK (1:1000,Cell Signaling Technology,USA).Rabbit anti-GAPDH or anti-β-actin antibody(1:3000,Abways,China) was used as an internal control.The membranes were washed and then incubated with horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-labelled goat anti-rabbit or goat anti-mouse secondary antibody (1:10000,Jackson ImmunoResearch,USA) at room temperature for 1 h.The membranes were washed three times in tris-buffered saline with Tween-20(TBST),and the bands were detected using enhanced chemiluminescence reagents (Millipore,USA) with a Tanon 5200 Chemiluminescent Imaging System (Tanon Science &Technology,China).The images were analyzed by ImageJ software to obtain integrated intensities.
Statistical analysis
Data were presented as the mean±standard deviation(SD).Statistical significance was determined by analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by a post hoc Tukey’s test for multigroup comparison.Differences were considered statistically significant when a-value <0.05.
RESULTS
Arctigenin ameliorated PQ-induced A549 cell injury
To evaluate the protective effects of arctigenin,a PQ-induced A549 cell injury model was successfully established,and the results of the CCK-8 assay showed that A549 cell viability was inhibited by PQ in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 1A).Moreover,arctigenin showed no significant effect on the viability of A549 cells under control conditions (Figure 1B) but ameliorated PQ-induced inhibition of A549 cell viability in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 1C).Additionally,light microscopy indicated the protective effects of arctigenin on PQ-treated A549 cells,as reflected by cell number and morphology (Figure 1D).These data supported that arctigenin ameliorated PQ-induced A549 cell injury.
Arctigenin alleviated PQ-induced cell apoptosis
Cell death usually occurs upon toxic insults,and cell apoptosis plays an important role in PQ-induced lung injury.Thus,we further tested the effects of arctigenin on PQ-induced A549 cell apoptosis by TUNEL assay and JC-1 staining.The results of the TUNEL assay showed that arctigenin dramatically reduced the number of TUNEL-positive cells induced by PQ (Figure 2A).Consistently,the JC-1 staining results also revealed that PQ-induced mitochondrial membrane potential loss,a marker for early-stage apoptosis,was significantly ameliorated by arctigenin treatment (Figure 2B).The above data demonstrated that arctigenin alleviated PQ-induced cell apoptosis.
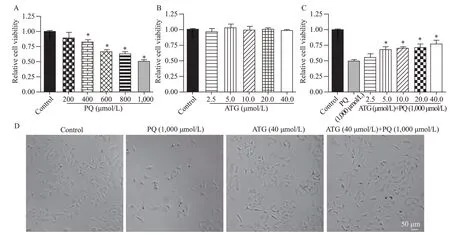
Figure 1. Arctigenin ameliorated paraquat (PQ)-induced A549 cell injury.A: PQ inhibited the viability of A549 cells in a dose-dependent manner,reflected by cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay (n=3,*P<0.05 vs.control);B: no dramatic effect of arctigenin was observed on the cell viability of A549 cells under control conditions,indicated by CCK-8 assay (n=3);C: the bar graph indicated arctigenin ameliorated PQ-induced A549 cell injury in a dose-dependent manner,determined by CCK-8 assay (n=3,*P<0.05 vs.PQ);D: representative light microscopy images indicated arctigenin ameliorated PQ-induced A549 cell injury,as reflected by more shrunken cells (scale bar=50 μm).
Arctigenin reduced ROS generation in PQ-treated A549 cells
ROS are vital molecules in pathophysiological processes after PQ injury.On the one hand,ROS can directly cause oxidative stress damage,and on the other hand,ROS would serve as signaling molecules to trigger apoptosis.Therefore,we explored the role of arctigenin on ROS generation in PQ-treated A549 cells by DHE staining and DCFH-DA staining.The representative images and statistical results indicated that the ROS level was dramatically increased in A549 cells after incubation with PQ for 24 h,but co-incubation with arctigenin remarkably inhibited PQ-induced ROS generation (supplementary Figures 1 A and B).These results showed that arctigenin reduced PQ-induced ROS generation in A549 cells.
Arctigenin inhibited p38 MAPK phosphorylation in PQ-treated A549 cells
Generally,increased ROS production in cells would lead to the activation of MAPKs,a family of serine/threonine protein kinases that mediate fundamental biological processes and cellular responses to external stress signals.Moreover,the ROS/p38 MAPK pathway has been reported to participate in PQ-induced cell injury.Accordingly,we further tested whether arctigenin would affect the activation of MAPKs,and the immunoblotting results showed that arctigenin significantly suppressed PQinduced p38 MAPK phosphorylation (supplemental Figure 2A).In addition,PQ also increased JNK but inhibited ERK phosphorylation,on which arctigenin had little effect(supplementary Figures 2 B and C).These data suggested that the inhibition of p38 MAPK was mainly involved in the protective effects of arctigenin.
DISCUSSION
Our study provides evidence that arctigenin protects against PQ-induced lung epithelial injury.Arctigenin ameliorated cell viability inhibition and cell apoptosis induced by PQ.Mechanistically,arctigenin may exert its protective effects by suppressing PQ-induced activation of ROS/p38 MAPK signaling (supplementary Figure 3).
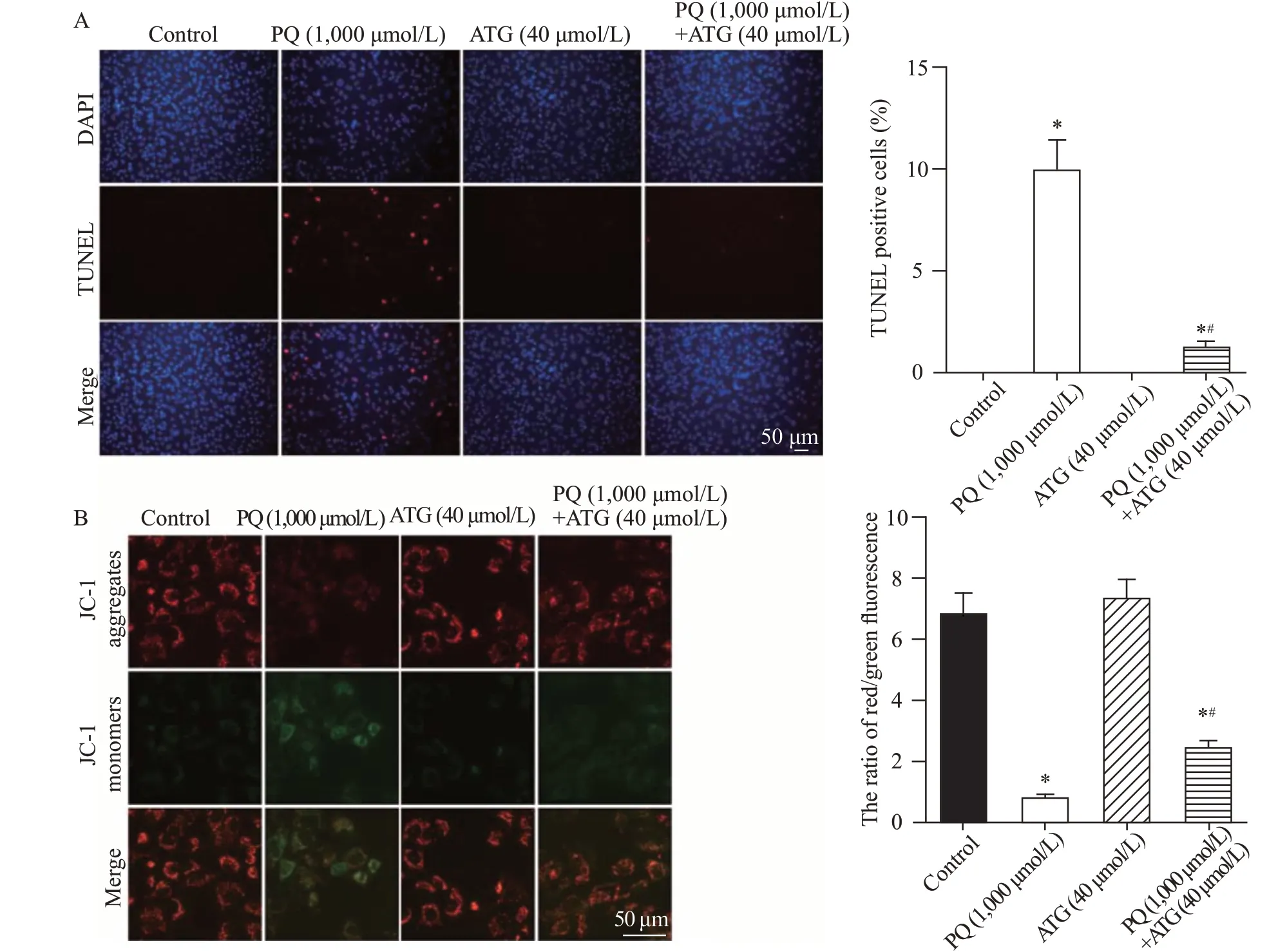
Figure 2. Arctigenin alleviated paraquat (PQ)-induced A549 cell apoptosis.A: representative images and statistical results of TUNEL staining showing arctigenin reduced A549 cell apoptosis induced by PQ (n=5,*P<0.05 vs.control;#P<0.05 vs.PQ;scale bar=50 μm).B: representative pictures and statistical results indicating arctigenin alleviated PQ-induced mitochondrial membrane potential loss in A549 cells.JC-1 exhibited potential-dependent accumulation in healthy mitochondria where it formed J aggregates (red) while it remained as monomer (green) upon mitochondrial depolarization.The ratio of red/green fluorescence of JC-1 dramatically decreased in PQ-treated A549 cells,which was relieved by arctigenin co-administration (n=5,*P<0.05 vs.control;#P<0.05 vs.PQ;scale bar=50 μm).
Arctigenin is the main active ingredient from,a herbal medicine widely used in China.In recent years,arctigenin has been extensively studied for its pharmacological properties,and numerous studies have reported the beneficial effects of arctigenin on antiinflammation,antioxidative stress,antitumor,and antineuronal degeneration.PQ poisoning has been frequently reported in recent years.As a highly toxic herbicide,PQ causes toxicity to multiple organs,including the lung,kidney,liver,and brain,among which the lung is the most targeted.However,there is still little effective treatment for PQ-induced lung injury and subsequent fibrosis,which leads to high morbidity and frequently to death.A previous experiment has proven that arctigenin can ameliorate PQ-induced pulmonary fibrosis via suppressing the epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Additionally,arctigenin has also been demonstrated to alleviate the lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury in ratsand mice.In line with these previous studies,our present work also supports the benefits of arctigenin against PQinduced lung epithelial injury,as reflected by the CCK-8 cell viability assay.This finding implies that arctigenin also protects against PQ-induced ALI and the early stage of PQinduced lung toxicity.Thus,arctigenin might be considered a potential candidate drug for the treatment of PQ-induced lung poisoning.
We next investigated the potential mechanisms by which arctigenin exerted its protective effect against PQinduced lung epithelial injury.It is generally considered that cell death would occur upon toxic insults,and apoptosis is one of the classical ways by which PQ causes lung epithelial cell death.Although arctigenin has been shown to induce apoptosis in several types of tumors and therefore has potential antitumor activity,the effect of arctigenin on PQ-induced lung epithelial cell apoptosis remains unknown.Thus,we tested the role of arctigenin in PQ-induced A549 cell apoptosis via a TUNEL assay and mitochondrial membrane potential assay,and the results showed that arctigenin dramatically reduced PQ-induced A549 cell apoptosis,which is not consistent with what has been found previously in tumors.This may result from the fact that these are two categories of diseases,the tumors and the organ injuries,because other studies in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injuryand brain injuryhave also demonstrated the anti-apoptosis properties of arctigenin.However,the underlying mechanisms of these differences remain to be further explored.
ROS,including the superoxide anion (O),hydrogen peroxide (HO) and the hydroxyl radical (HO•),are a group of chemical species that are formed upon incomplete reduction of oxygen.While PQ exerts its toxicity mainly through a process of redox cycling with superoxide anion production,ROS generation and oxidative stress have a central role in PQ poisoning.More importantly,excessive ROS would trigger the apoptotic signaling pathway.MAPKs,a group of serine-threonine protein kinases,play important roles in signal transduction in response to diverse extracellular stimuli.MAPKs have also been reported to be activated by ROS.In addition,it has been proven that PQ-induced activation of p38 MAPK plays a key role in the apoptotic pathway of A549 cells and that inhibition of ROS/p38 signaling could ameliorate PQ-induced lung injury.Thus,in our present study,we further checked whether ROS/p38 MAPK signaling was involved in the protective effect of arctigenin against PQ-induced lung epithelial injury.We found that arctigenin remarkably reduced PQ-induced ROS generation and p38 MAPK phosphorylation.This finding supports the previous concept that ROS/p38 signaling is vital in PQ toxicity.
However,we also realized that one of the limitations of our present work was the lack ofexperiments since only human lung epithelial A549 cells were used.It should be noted that what has been found in these cell experiments might not be equally applicable in animals or even in the clinic;thus,it would be more stringent to usestudies to verify the protective effects of arctigenin.
CONCLUSIONS
Our present study shows that arctigenin attenuates PQ-induced lung epithelial A549 cell injuryby suppressing PQ-activated ROS/p38 MAPK-mediated cell apoptosis,and arctigenin might be considered a potential candidate drug for PQ-induced ALI.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82172182 and 82102311);Social Development Projects of Jiangsu Province (BE2017720);Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20190247);Science Foundation of Jiangsu Health Commission (H2018039);and Jiangsu Postdoctoral Research Foundation (2018K048A and 2020Z193).
No animal or human subjects were involved.
None.
CL,ZRS,and MMW performed the experiments;ZZY,WZ,and YR provided help during the experiments;XQH,RL,and QL contributed to the manuscript revision and data curation;SNN supervised all experiments.
All the supplementary files in this paper are available at http://wjem.com.cn.
 World Journal of Emergency Medicine2022年5期
World Journal of Emergency Medicine2022年5期
- World Journal of Emergency Medicine的其它文章
- Intestinal microcirculation dysfunction in sepsis:pathophysiology,clinical monitoring,and therapeutic interventions
- Timing of brain computed tomography for predicting neurological prognosis in comatose cardiac arrest survivors: a retrospective observational study
- Development and evaluation of a predictive nomogram for survival in heat stroke patients: a retrospective cohort study
- Analysis of imaging characteristics of blunt traumatic aortic dissection: an 8-year experience
- Is rosuvastatin protective against sepsis-associated encephalopathy? A secondary analysis of the SAILS trial
- Hepatocellular carcinoma-derived exosomal miRNA-761 regulates the tumor microenvironment by targeting the SOCS2/JAK2/STAT3 pathway
