Research on the Status of Patent Protection of Prostaglandin Analogues for Glaucoma in China
Zhou Sheng’an,Dong Li
(School of Business Administration,Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,Shenyang 110016,China)
Abstract Objective To study and analyze the status of patent protection of prostaglandin analogues for glaucoma in China.Methods Patent literatures published up to April 7,2020 were retrieved by the keywords “PG” and “prostaglandin”on such patent information service platforms as SIPO,SooPat,and IncoPat.And then they were statistically analyzed by qualitative and quantitative means.Results and Conclusion A total of 300 patent literature related to prostaglandin analogues for glaucoma were obtained,and most of them were invention patents,including patents for composition and dosage form,indications and uses,related synthesis,the compound,and composition preparations.Prostaglandin analogues play an important role in the treatment of glaucoma.At present,China has a large number of patents applications,and the patent protection covers a wide range of technical fields,but the number of patents with valid legal status is relatively small.Therefore,China’s pharmaceutical enterprises and R&D institutions have more options in topic selection and project approval and patent protection strategies.
Keywords:glaucoma;prostaglandin;patent protection
Eyes are significant sensory organs for human to perceive the world.According to the classification stated in the “Clinical Diagnosis Guideline for Ophthalmology”,eye diseases involve many clinical branches,mainly including ocular infection,cataract,and glaucoma[1].The four common causes leading to blindness are trachoma,cataract,glaucoma,and fundus diseases,among which trachoma and cataract have been effectively controlled by anti-infective treatment and surgical treatment[2-4].However,glaucoma is easily ignored or mistreated by patients,resulting in misdiagnosis or failure to see doctors in time.Therefore,it still poses a serious threat to eye health[5].
Currently,the following drugs are commonly used for treating glaucoma,namely cholinergic drugs,β-receptor blockers,carbonic anhydrase inhibitors,and prostaglandin receptor agonists,etc.Prostaglandins serve as the first-line drugs and play an important role in the treatment of glaucoma[6,7].Clinically,major prostaglandins for glaucoma are latanoprost,bimatoprost,travoprost,tafuprost and other compound preparations with different compositions.
In the pharmaceutical industry,patent protection is vital to extend the life cycle of the product and increase the benefit of the enterprise.Due to the leading position of multinational enterprises in R&D of innovative drugs and their good intellectual property protection,they have advanced systems and concepts in patent protection and layout.In this regard,China’s pharmaceutical enterprises are still weak.This paper aims to provide suggestions for China’s pharmaceutical enterprises and institutions in developing strategies on patent protection by retrieving and quantitatively analyzing the patents of prostaglandin analogues for glaucoma published in China since the 1990s.
1 Data retrieval and screening
In order to avoid missing documents during retrieval,patent literatures published up to April 7,2020 were retrieved by the keywords “PG”,“prostaglandin” and “prostateamide” on such patent information service platforms as SIPO,SooPat,and IncoPat.
After searching,more than 1 800 patent documents were obtained.By preliminary analysis,it is found that prostaglandin analogues are widely used in the treatment of glaucoma,cardiovascular,reproductive and many other diseases.To ensure the accuracy of literature retrieval,the patent documents obtained during initial retrieval are screened.Only those related to glaucoma,latanoprost,bimatoprost,travoprost,tafluprost and their analogues are retained.Finally,a total of 300 patent documents were obtained.
2 Patent analysis
Patent documents obtained are statistically analyzed by the year of application,the nationality of the applicants,the nature of the applicants,the main applicants,legal status,and technical fields.
2.1 Year of patent application
The first patent related to prostaglandin analogues for glaucoma in China was applied on July 27,1990,by Allergen Aesthetics.As of April 7,2020,a total of 300 patent documents were found.And the average number of patents applied by institutions or individuals was 10 per year,except that no related patent was applied in 1991 and patent was not made public in 2020.The cumulative number of patent applications related to prostaglandin analogues for glaucoma in China each year are presented in Table 1 and Fig.1,respectively.
From the patent number presented in Table 1 and Fig.1,we can see that the patent applications of prostaglandin analogues for glaucoma in China mainly involve four stages.In the first stage between 1990 and 2000,the number of patents applied per year was between 0-5,which was relatively small.In the second stage between 2001 and 2006,the number of patents applied per year increased significantly,reaching 8-11.When the number of patents applied dropped to 6 in 2007,the third stage began in 2008.From 2008 to 2014,the number of patents applied increased significantly,reaching a maximum of 30 in 2012.In the fourth stage from 2015 to the time of this retrieval,the number of patents applied per year began to decline slowly.
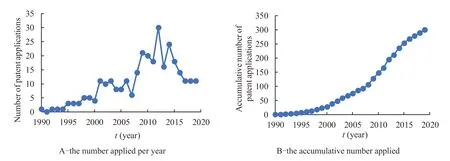
Fig.1 The cumulative number of patent applications related to prostaglandin analogues for glaucoma in China each year
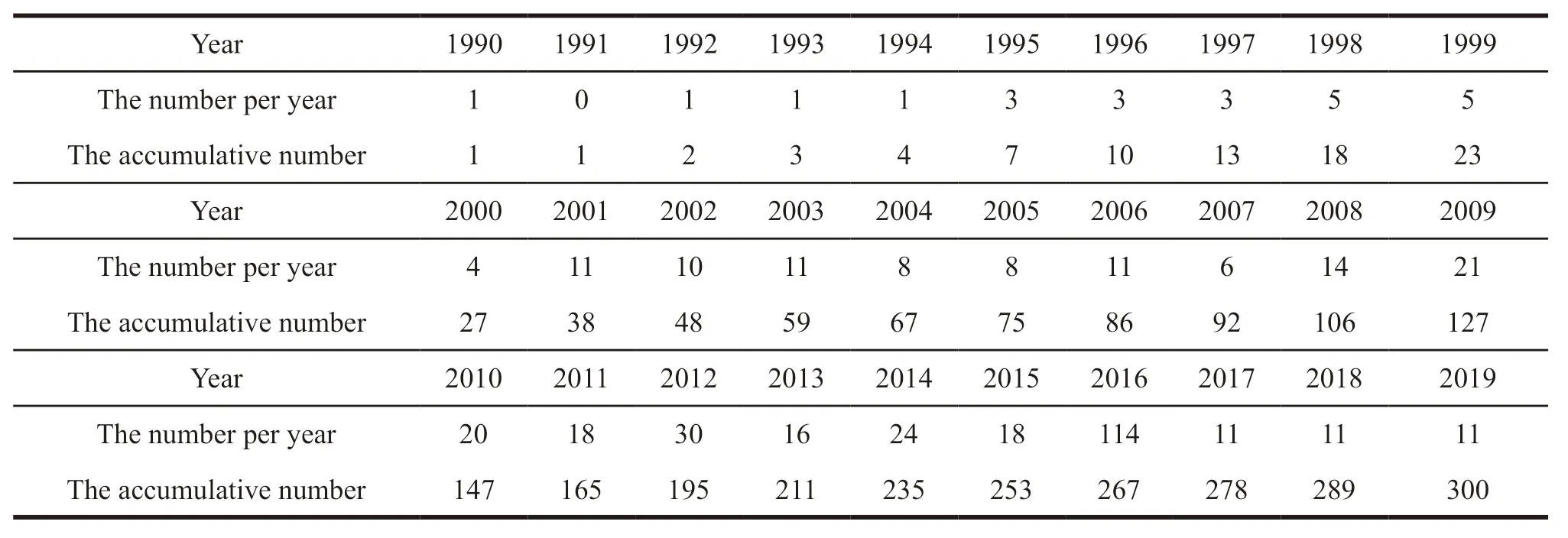
Table 1 The cumulative number of patent applications related to prostaglandin analogues for glaucoma in China each year
Based on the above data,the years can also be classified as four stages by inquiring the first approved marketing year of prostaglandin analogues used for glaucoma (8 single and compound formulations on the market).The first stage was from 1990 to 1999 and there was one on the market.The second stage was from 2000 to 2009,and there were 3.The third stage was from 2010 to 2014 with one.The fourth stage was from 2015 until now,no formulation has been approved.It can be seen that there is a strong correlation between the four stages by the approved year of marketing and by the number of patent applications.
2.2 Applicants’ country of origin
Statistics of 300 patents show that a total of 19 countries and regions have applied for patents related to prostaglandin analogues for glaucoma in China (Fig.2).To be specific,the United States and China dominate the market with 90 and 89 patent applications respectively,taking up 59.7%.Japan,Switzerland and France,which are in the second group with 39,17 and 15 respectively,take up 23.6%.For the rest 12 countries,the number of patents is less than 10,taking up 16.7%.The distribution of such patents among different countries is also closely related to the current pharmaceutical development across the world.The United States,Europe,and Japan have the biggest advantages in new drug R&D,while China is one of the largest countries in generic drug R&D and production in the world.
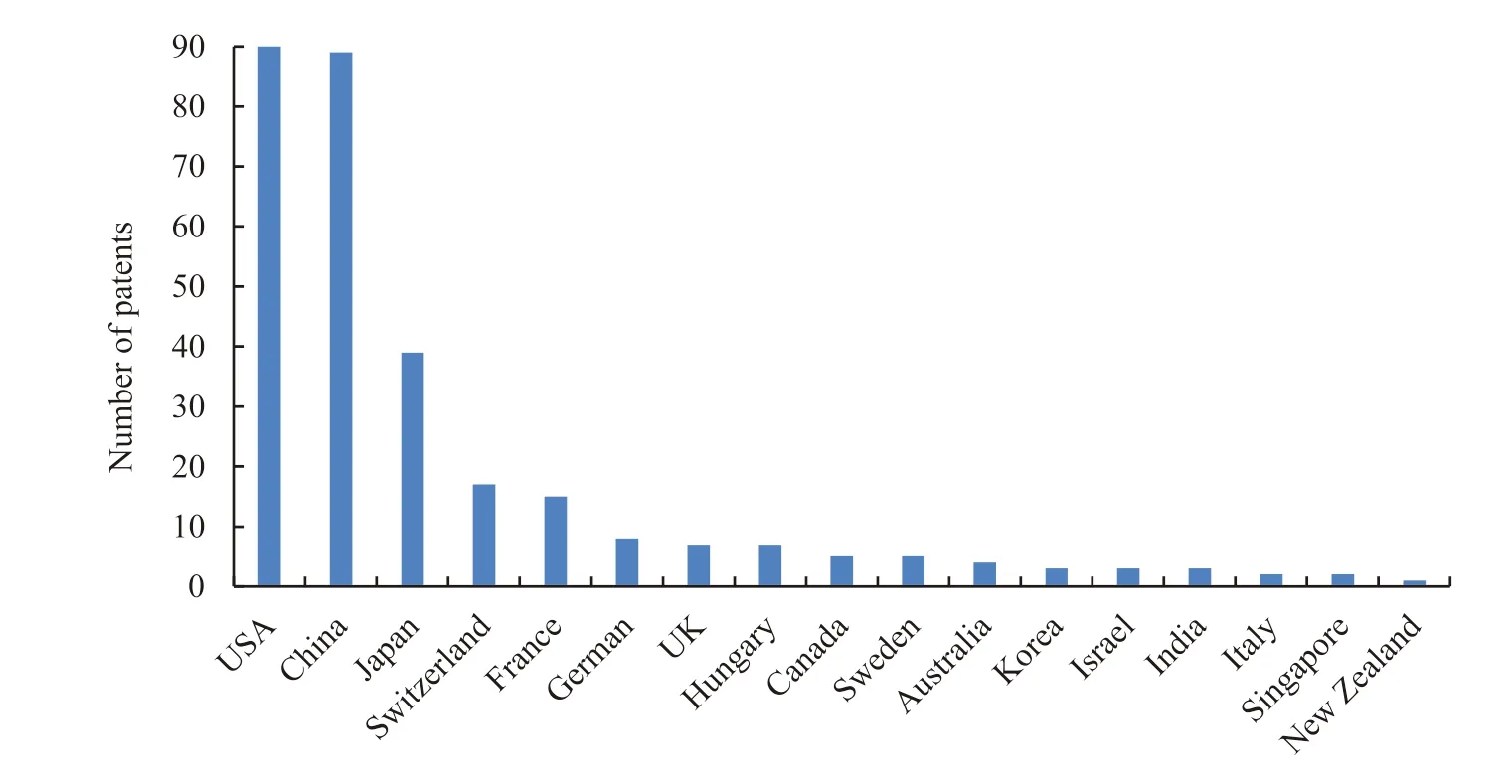
Fig.2 Patent application of prostaglandin analogues for glaucoma by country
2.3 Domestic applicants by province
Statistics of 300 patents show that a total of 16 provinces,regions,or municipalities directly under the Central Government have applied for patents related to prostaglandin analogues for glaucoma in China (Fig.3).To be specific,for the number of patent application,five provinces/municipalities directly under the Central Government including Shanghai,Jiangsu,Guangdong,Tianjin and Beijing list the top six in order,taking up 73.8%,and presenting a high regional concentration ratio.These five provinces/municipalities directly under the Central Government are in Beijing-Tianjin-Tangshan Region,Yangtze River Delta,and Pearl River Delta,respectively.These three clusters have the most advanced development in economy,medicine and health,sports and culture in China.All these performances are in line with the distribution of China’s pharmaceutical economy in various regions.
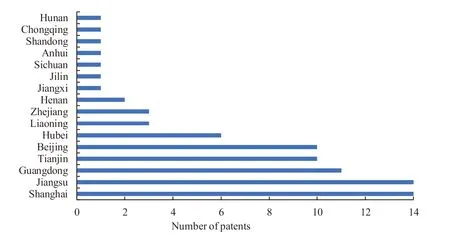
Fig.3 The distribution of patent application of prostaglandin analogues for glaucoma across Chinese mainland
2.4 Major applicants
Statistical analysis of 300 patents show that a total of 160 enterprises,institutions or natural persons have applied for patents related to prostaglandin analogues for glaucoma in China.The average number of patent applications per applicant is only 1.88,and the applicants are diversified.From the statistical analysis of the top 15 applicants in the number of patent applications (Table 2),they have applied for a total of 123 patents.Only three companies namely Allergen Aesthetics,Santen Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.,and Alcon Laboratories,Inc.applied for more than 10 patents.The other 12 companies have less than 10 patents applied.In addition,among the top 15 applicants,the United States and Japan have 5 and 3 respectively,and they are leading both in the number of applicants and the number of patents applied.In China,only Wuhan Wuyao Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.,(Mainland,China)and Chirogate International Inc.(Taiwan,China)entered the list with 4 patents,respectively.According to the distribution of patent applicants,it is found that the United States and Japan take the lead in R&D of prostaglandin analogues for glaucoma.
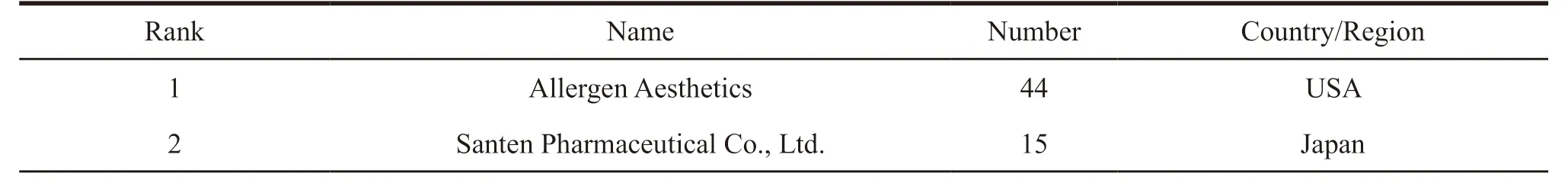
Table 2 Distribution of top 15 applicants for patents related to prostaglandin analogues for glaucoma
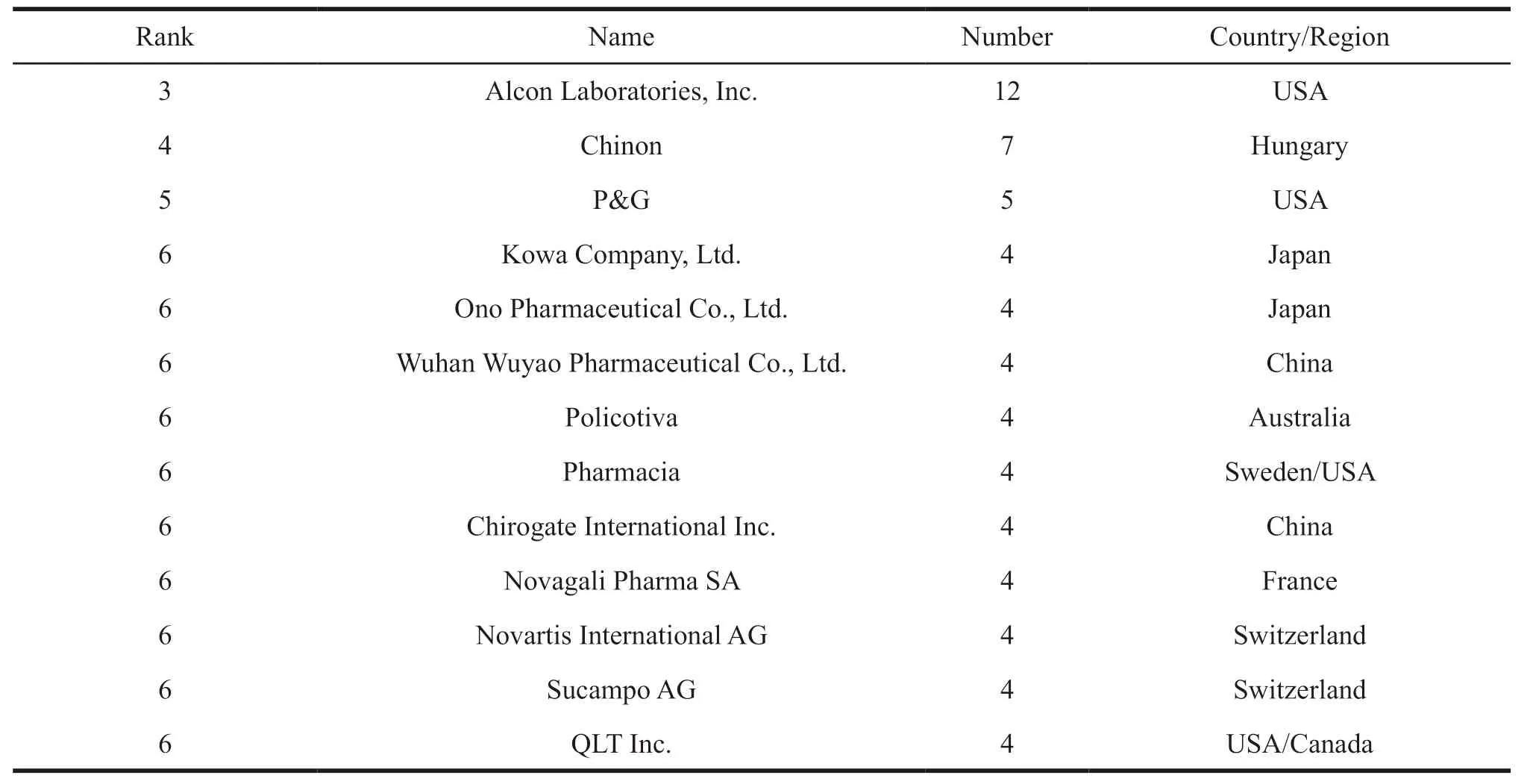
Continued Table 2
2.5 Legal status
Statistical analysis of 300 patent documents by current legal state (Fig.4) show that 79 patents are valid,taking up 26.2%,68 patents are open or being examined,taking up 22.9%.And the invalid patents are 153,accounting for 50.8%,of which 37 are rejected,5 are expired,73 are regarded as withdrawn or disclaimed,and 35 are overdue due to unpaid annual fees.It can be concluded that at present most patents are in a state of no right of protection in China,few patents are being protected.Efforts should be made in the future to enhance the right protection of this kind of patents.
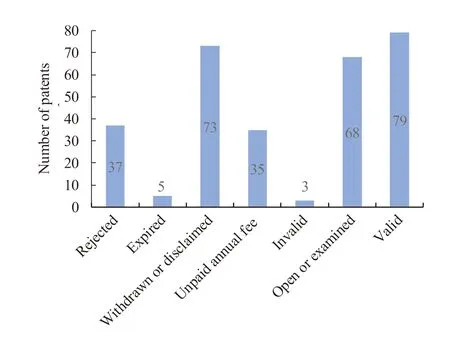
Fig.4 Legal status of patents related to prostaglandin analogues for glaucoma in China
2.6 Technical fields
An analysis has been carried out to the technical fields of the claims and inventions of 300 patent documents (Table 3 and Fig.5).And the following 8 categories are mainly involved,which include patents of compound,indication and uses,composition and dosage form,intermediate and synthesis process,composition preparation method,crystal form,quality control and analysis method,and utility model.Besides,most patents are associated with two or more technical fields.
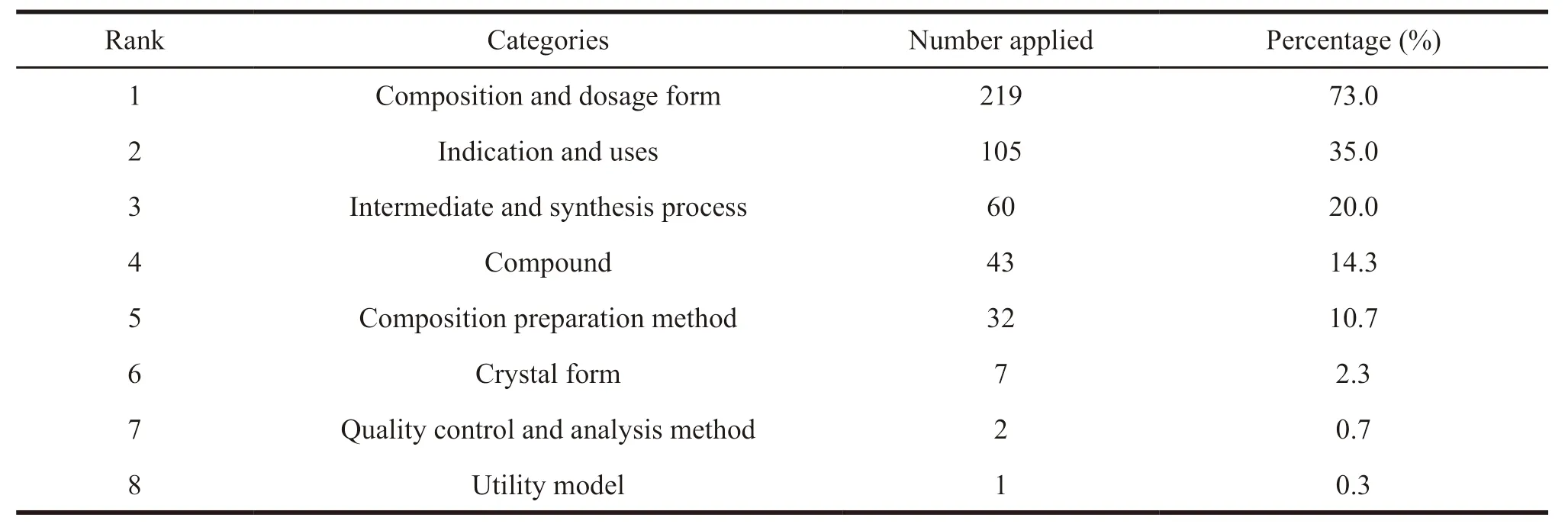
Table 3 Technical field distribution of patents related to prostaglandin analogues for glaucoma
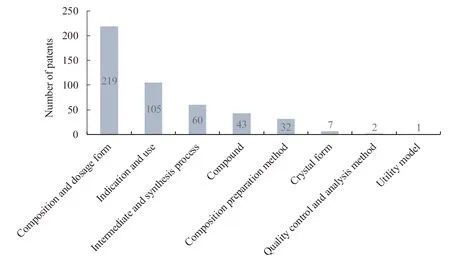
Fig.5 Technical field distribution of patents related to prostaglandin analogues for glaucoma
The statistical analysis of the data shows that the number of applications for compositions and dosage forms is the largest of patents related to prostaglandin analogues for glaucoma,taking up more than 70%.It mainly includes the followings.The first group is those used in combination with other drugs such asβ-blockers,carbonic anhydrase inhibitors,and Rho kinase inhibitors,etc.The second group is those used to make a variety of new dosage forms or new drug delivery systems such as semi-solid formulations,eye implants,nano-preparations,liposomes,and emulsions,etc.
In addition,for the patents related to prostaglandin analogues for glaucoma,patents of indications and uses account for 35%.Except for the treatment of glaucoma and high intraocular pressure,patent protection is also provided for a variety of other indications,such as corneal injury and other ocular surface diseases,treatment of alopecia and promotion of hair growth,fat metabolism,and peripheral vascular related diseases etc.
For compound patents,the chemical structure of traditional prostaglandin analogues is protected.And the published patents also protect compounds modified by special groups based on the original chemical structure to increase the curative effect,improve the bioavailability,prolong the action time,and reduce the adverse reactions.For example,polar groups such as nitro and phosphate are introduced to carry out esterification,acylation,deuteration,or polymer conjugation.
In comparison to other types of chemicals,patents of crystal form account for a low proportion.The analysis of the physical and chemical properties of such drugs shows the drugs on the market at present are oily liquids except for the solid powder of Bimatoprost.Therefore,there is no crystal form.
3 Discussion and conclusion
As the first-line drugs,prostaglandin analogues play an important role in the treatment of glaucoma.With the development of medicine and health in China,people pay more attention to eye health.As the diagnosis and treatment of eye diseases become effective,the number of patients increase by years.Therefore,the demand for clinical medication is rising.Since the first patent was applied in China in 1990,prostaglandin analogues for glaucoma have developed for 30 years.Although many original drugs have been approved for marketing in China,such approval is given to only 8 generic drugs.And most domestic enterprises are low-end imitator in the R&D of such drugs.To this end,a study on the patent protection of prostaglandin analogues for glaucoma in China was carried out,and following suggestions are put forward.
3.1 The trend in the treatment of glaucoma in the future
As the diagnosis and treatment of glaucoma are increasingly improved,the demand for clinical medication will be rising.Prostaglandin analogues for glaucoma will be widely used clinically for their efficacy and good safety.However,the statistical analysis of domestic patent literature shows that the combination of prostaglandin analogues for glaucoma with other drugs in the treatment of glaucoma may be the main direction of R&D in the future.
3.2 Transform from the R&D of low-end generic drugs to high-end modified new drugs for Chinese pharmaceutical enterprises
At present,only a few pharmaceutical enterprises in China (among which Everyday Bright Eyes,the parent company of Wuhan Wuyao Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.obtained the approvals of three products) have obtained the approvals of generic drugs like latanoprost,bemeprost and travoprost for marketing.The product line is relatively lowend,and the market share is small,too.Since the implementation of medical reform in 2015,China has vigorously encouraged enterprises to improve the innovation ability and market competitiveness.From the published patents,prostaglandin analogues for glaucoma can be improved and innovated to new drugs to meet clinical needs.
3.3 Focus on patent protection and layout by Chinese pharmaceutical enterprises
Based on the analysis of country of patent applications,among the published patent applications in China,the proportion of patents applied by domestic enterprises or institutions is low,less than 30%.Meanwhile,more than 70% of patents are applied by foreign enterprises,institutions,or individuals.As the number of products on the market and the number of patent applications are not compatible,the economic benefits of approved products are low for China’s pharmaceutical enterprises.Therefore,domestic enterprises or institutions should focus on the patent protection and layout of the products while improving their R&D strength and investment.
- 亚洲社会药学杂志的其它文章
- Drug Regulatory Science in EU and Its Enlightenment to China
- A systematic Review of the Safety and Effectiveness of Epidural Analgesia for Labor Analgesia
- Exploration on the Implementation of the Integration of Medical and Preventive Model in China’s Primary Health Care Institutions
- The Development of DTP Pharmacy and Its Impact on Pharmaceutical Enterprises
- Comparative Analysis of Social Forces Participating in Emergency Management of Public Health Events in China,Australia,Germany and the United States
- The Investigation and Research of the Performance Appraisal of R&D Personnel in R Company

