Metal-free directed C-H borylation of 2-(N-methylanilino)-5-fluoropyridines and 2-benzyl-5-fluoropyridines
Gorong Wu,Xiobo Xu,Shui Wng,Lu Chen,Binghn Png,To M,Yfei Ji,*
a Engineering Research Center of Pharmaceutical Process Chemistry,Ministry of Education;School of Pharmacy,East China University of Science and Technology,Shanghai 200237,China
b School of Chinese Materia Medica,Beijing University of Chinese Medicine,Liangxiang Campus,Beijing 102488,China
ABSTRACT A novel method for metal-free C-H borylation of 2-(N-methylanilino)-5-fluoropyridines and 2-benzyl-5-fluoropyridines has been reported.The 5-fluoropyridine directed borylation reaction exhibited high efficiency and site exclusivity.The useful protocol could be executed on a gram-scale easily and the borylated products showed good derivatization applications.Moreover,the practicality of the strategy was expanded by the fact that the directing group could be removed in an acceptable yield.
Keywords:Metal-free C-H borylation 2-(N-Methylanilino)-5-fluoropyridines 2-Benzyl-5-fluoropyridines BBr3
Organoborons play a major role in organic synthesis as their power in the conversion of functional groups coupled with the low toxicity and ease of handling.Among various C-H borylation strategies,one of the commonly known strategies is a metalcatalyzed directed approach[1–3].Owing to the extensive range of applications in natural products and drugs,the development of protocols for the functionalization ofN-methylanilines has attracted more attention in recent years.Traditional methods used for the borylation ofN-methylanilines were focused on noble transition-metal-catalyzed,such as Ir and Pd(Scheme 1a)[4–6].However,these works usually need ligands and harsh reaction conditions.From an economic and environmental perspective,the ability to achieve C-H borylation ofN-methylanilines under mild conditions by using cheaper boron reagents and avoiding the use of transition metals would be very significant.
At present,the use of strong Lewis acids such as B(C6F5)3or BX3(X = Cl,Br)for the C(sp2)-H bond borylation is considered to be a very effective method[7–25].Among these,BBr3is particularly prominent because of its strong reactivity,low cost and easy availability.In 2010,Murakami developed a seminal method to borylate 2-aryl-pyridines using BBr3[26].Two years later,Fu’s group had successfully developed an efficient metal-freeorthoC-H borylationviasequential borylation of substituted 2-phenoxypyridines with BBr3following esterification with pinacol[27].After that,other N-directing groups such as pyrazoles,pyrazines,pyrimidines,pyridines,imidazolones,imidazoles and quinolines were developed[28–36].In 2019,Shi group and Ingleson group described theortho-C-H borylation of aniline derivatives with an acyl moiety by using BBr3(Scheme 1b)[37,38].More recently,Chatani and co-workers reported the pyrimidine-directed metal-free C–H borylation of 2-pyrimidylanilines(Scheme 1c)[39].These researches provided outstanding strategies for the borylation of anilines.Although substantial progress has been made in the development of metal-free directed C-H borylation reactions with BBr3,the borylation ofN-methylanilines directed by pyridine under metal-free conditions has never been reported.
Inspired by these achievements and given the importance ofN-methylaniline derivatives,we hope to develop a new pyridine directing group to obtainN-methylanilines borates.Herein,we reported a novel route for directed C–H borylation of 2-(N-methylanilino)-5-fluoropyridines using BBr3.The reaction was also applicable to 2-benzyl-5-fluoropyridine derivatives as a substrate(Scheme 1d).Moreover,the obtained boronic esters exhibited good derivatization applications and the directing group could be removed in an acceptable yield,which provided a practical,efficient and simple pathway for synthesizing structurally diversifiedN-methylaniline and 2-benzyl-5-fluoropyridine derivatives.
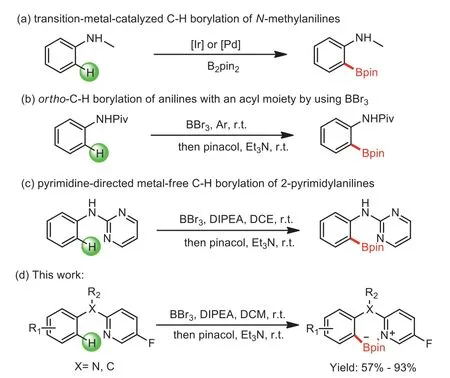
Scheme 1.Borylation of anilines and N-methylanilines.
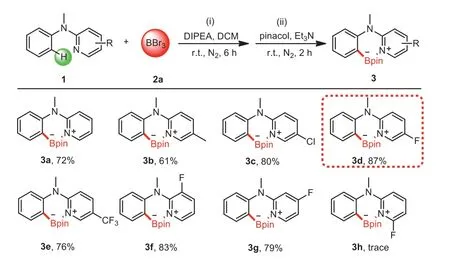
Scheme 2.Screening of directing groups.Reaction conditions:(i)1(0.2 mmol),2a(0.4 mL,1 mol/L in DCM),DIPEA(0.2 mmol),DCM(1.5 mL),N2,6 h;(ii)pinacol(0.4 mmol,dissolved in 1 mL dry DCM),Et3N(2.0 mmol),r.t.,N2,2 h.Isolated yields.
Our initial study focused on screening the directing groups(Scheme 2).First,a solution of 1a,DIPEA(N,Ndiisopropylethylamine)(1.0 equiv.)and 2a(2.0 equiv.)in dried DCM was stirred at room temperature under a N2atmosphere for 6 h,and then pinacol(2.0 equiv.)and Et3N(10.0 equiv.)were added and the mixture was stirred for another 2 h offering the desired compound 3a in 72% yield.Then we performed a brief survey of the electronic effects on pyridine ring.The results showed that,compared to 1a,5-CH3substituted substrate decreased the yield,but 5-Cl substituted substrate increased the yield,indicating that electron-withdrawing group on pyridine ring was beneficial to the reaction.Inspired by this result,stronger electron-withdrawing group 5-F and 5-CF3were conducted.To our surprise,3d was obtained in excellent yield(87%),but the yield of 3e was decreased,revealing the importance of proper electronic effects on pyridine ring.Finally,we investigated the influence of the position of the fluorine atom on the pyridine.3-F and 4-F substituted substrates lowered the borylation efficiency compare to 5-F.Besides,only a trace amount of 3h was obtained when the fluorine atom at the 6-position,possibly due to the steric hindrance that prevented the formation of N-B bond[40].Given that the fluorine atom played a crucial role in drugs and this reaction,5-fluoropyridine was identified as the optimal directing group for further surveys.
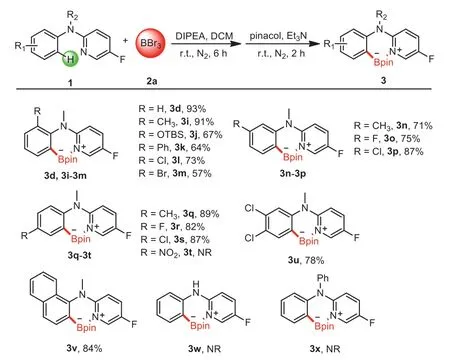
Scheme 3.Substrate scope of 2-(N-methylanilino)-5-fluoropyridines.Reaction conditions:1d,1i-1x(0.2 mmol),2a(0.6 mL,1 mol/L in DCM),DIPEA(0.2 mmol),DCM(1.5 mL),N2,6 h;then pinacol(0.6 mmol,dissolved in 1 mL dry DCM),Et3N(2.0 mmol),r.t.,N2,2 h,isolated yields.
Next,we evaluated the main parameters to optimize reaction conditions(Table 1).When the boron source was BCl3and ClBcat,no target product was obtained(entries 2 and 3).To our delight,increasing the amount of 2a to 3.0 equiv.,the yield of 3d was as high as 93%(entry 4).However,further increasing 2a did not give a higher yield(entry 5).Among various bases,DIPEA functioned as the best one(entries 6-8).Regrettably,we found that otherboronate esters could not be accessed when different diols were used instead of pinacol(entries 9 and 10).Changing the solvent to DCE and CFC-113a(1,1,1-trichlorotrifluoroethane)provided 21% and 83% yields of 3d,respectively.But the use of Lewis basic solvent THF was inefficient(entries 11-13).
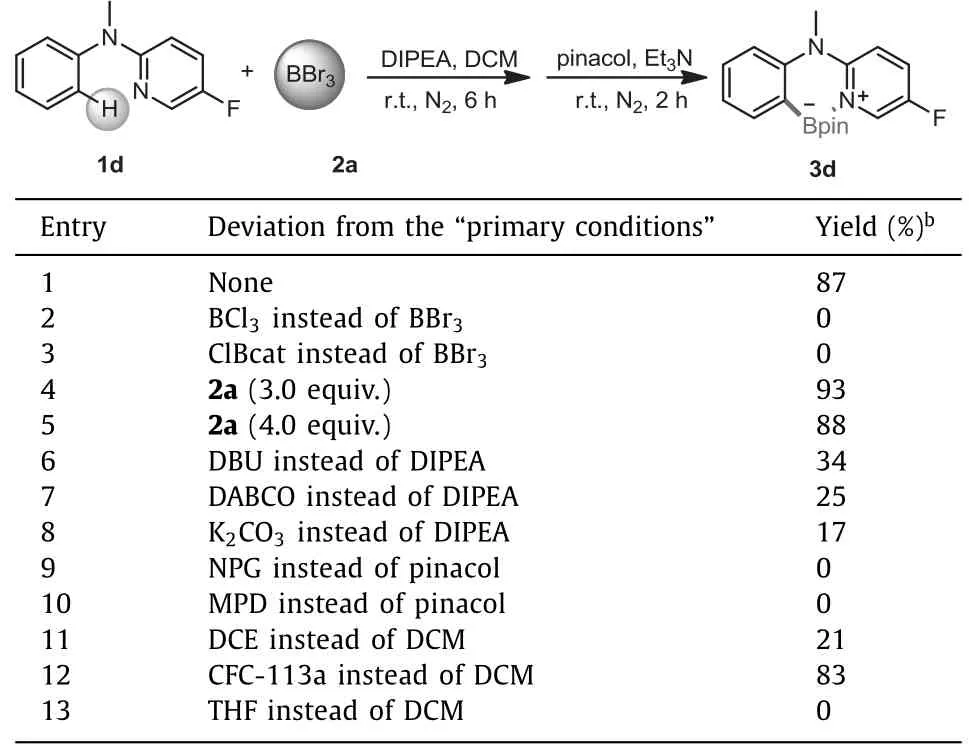
Table 1 Optimization of the reaction conditions.a
With the optimized reaction conditions in hand,the scope of 2-(N-methylanilino)-5-fluoropyridines was examined as shown in Scheme 3.To our delight,amines bearing electron-donating(Me,OTBS and Ph)or-withdrawing(F,Cl and Br)groups at theortho-,meta-andpara-positions afforded the corresponding borylation products in 57%-93% yields(3d,3i-3v).Generally,the yields of theortho-substitution substrates were lower than themetaandparaones.The large steric hindrance group OTBS(3j)at theorthoposition of the amine was also suitable to C-H borylation.In comparison with 3n-3p,amines containing CH3,F and Cl groups atpara-position(3q-3s)delivered relatively better yields.But stronger electron-withdrawing group NO2was not suitable for this reaction.Notably,3,4-dichloro substituted amine 1u worked well,affording the desired products in 78% yield.Moreover,treatment of 1-naphthyl-substituted substrate 1v could afford 3v in an excellent yield under the standard reaction conditions.However,no desired products were obtained with almost all starting materials intact when amines containing N-H or N-Ph substituents instead of N-Me,indicating that the great importance of the Me group.
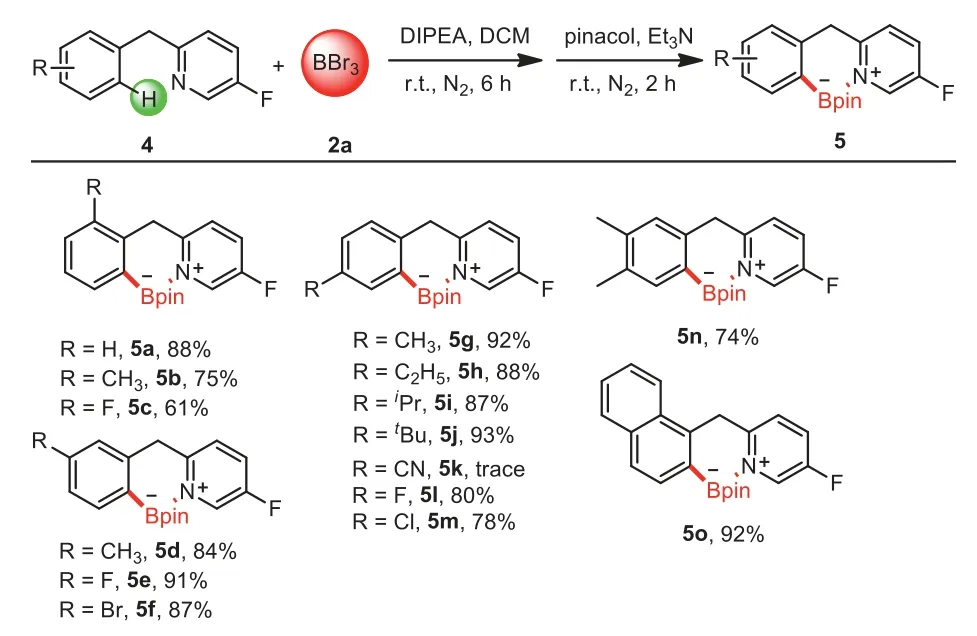
Scheme 4.Substrate scope of 2-benzyl-5-fluoropyridines.Reaction conditions:4a-4o(0.2 mmol),2a(0.6 mL,1 mol/L in DCM),DIPEA(0.2 mmol),DCM(1.5 mL),N2,6 h;then pinacol(0.6 mmol,dissolved in 1 mL dry DCM),Et3N(2.0 mmol),r.t.,N2,2 h.Isolated yields.
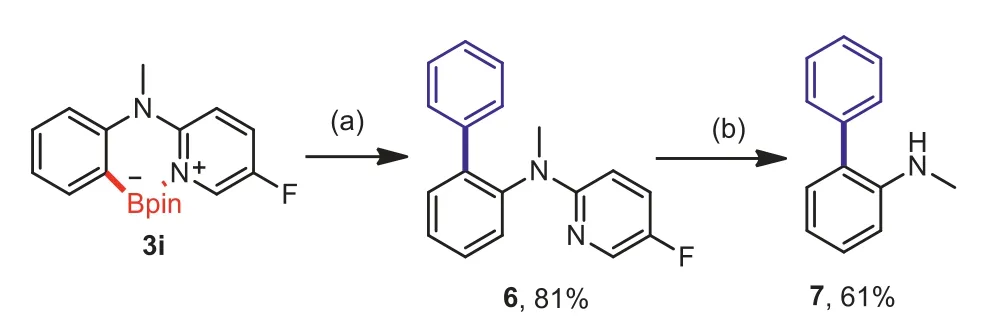
Scheme 5.Synthetic application of product 3i and removal of the directing group.Reaction conditions:(a)3i(0.2 mmol),PhI(0.24 mmol),Pd(PPh3)4(0.01 mmol),Na2CO3(0.6 mmol,2 mol/L in H2O),PhMe(1.5 mL),reflux,N2,12 h.(b)6(0.2 mmol),MeOTf(0.4 mmol),DCM(1.0 mL),r.t.,N2,24 h;then NaBH4(1.2 mmol),MeOH(1.5 mL),r.t.,air,6 h.Isolated yields.
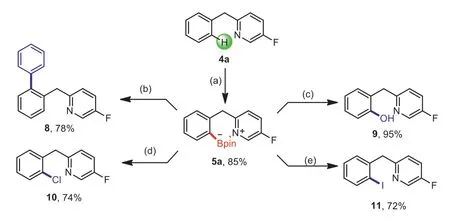
Scheme 6.Gram-scale reaction and synthetic application of product 5a.Reaction conditions:(a)4a(6.0 mmol),2a(18.0 mL,1 mol/L in DCM),DIPEA(6.0 mmol),DCM(15.0 mL),N2,6 h;then pinacol(18.0 mmol,dissolved in 10 mL dry DCM),Et3N(60.0 mmol),r.t.,N2,2 h.(b)5a(0.2 mmol),PhI(0.24 mmol),Pd(PPh3)4(0.01 mmol),Na2CO3(0.6 mmol,2 mol/L in H2O),PhMe(1.5 mL),reflux,N2,12 h.(c)5a(0.2 mmol),NaBO3.4H2O(0.8 mmol),THF(1.0 mL),H2O(1.0 mL),r.t.,12 h.(d)5a(0.2 mmol),CuCl2(0.6 mmol),MeOH(1.0 mL),H2O(1.0 mL),90 °C,24 h.(e)5a(0.2 mmol),NaI(1.0 mmol),Cu2O(0.02 mmol),NH3.H2O(0.5 mmol),EtOH,r.t.,air,20 h.Isolated yields.
The strategy was not restricted to 2-(N-methylanilino)-5-fluoropyridines;2-benzyl-5-fluoropyridines were also viable substrates for the reaction.The scope was investigated under the developed reaction conditions(Scheme 4).Most substrates exhibited high borate activity,especially 4e,4g,4j and 4o,and the yield of the corresponding products all exceeded 90%.In general,the compounds bearing electron-donating groups such as Me,C2H5,iPr andtBu gave the target products in higher yields than electron-withdrawing ones(such as F,Cl,Br,CN),indicating that the electron-donating groups were beneficial to the electrophilic borylation reaction by increasing the electron cloud density of the aromatic ring[41].Similarly,among theortho-,meta-,andparapositions substituted substrates,the borylated yields of theorthoposition substrates were relatively lower.However,the borylation of 4k became sluggish,in which the strong electronegativity affected the formation of C-B bond,thus leading to poor conversion.Subjecting compound 4n containing two methyl groups at the C3 and C4 positions could undergo C–H borylation.Besides,1-naphthyl-substituted substrate 4o generated 5o in an excellent yield(92%).
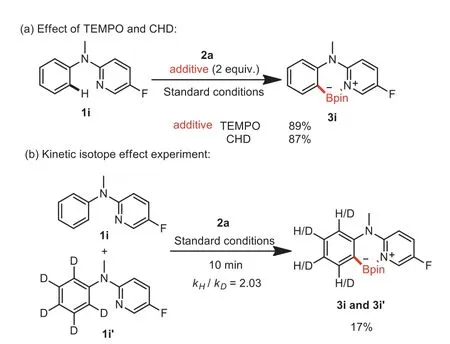
Scheme 7.Effect of TEMPO and CHD and kinetic isotope effect experiments.
To certify the potential utility of this method,we realized the arylation of 3iviaSuzuki-Miyaura coupling in 81% yield.Subsequent MeOTf-driven reductive removal of the pyridine directing group provided theN-methyl-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-amine in an acceptable yield(Scheme 5)[42,43].Importantly,this convenient,easily handled,synthetically useful protocol could be executed on a gram-scale without any difficulties.The borylated compound 5a could be transformed into a number of important compoundsviaa Suzuki-Miyaura coupling(8)and oxidation with NaBO3·4H2O(9)in good to excellent yields[42,44].Moreover,the synthesis of 2-(2-chlorobenzyl)-5-fluoropyridine(10)and 2-(2-iodobenzyl)-5-fluoropyridine(11)could be achieved by deborylative chlorination and iodination(Scheme 6)[27].
To elucidate the mechanism of this reaction,a control experiment was performed.Radical scavengers TEMPO and CHD were added into the reaction of 1i and 2a,respectively.As a result,the yield of 3i was almost unaffected,thus precluding the radical pathway(Scheme 7a)[45].Subsequently,the kinetic isotope effect experiment between equivalent 1i and 1i’with 2a under the standard conditions for 10 min was conducted(Scheme 7b)and gave a KIE value of 2.03 by1H NMR spectroscopic analysis(Supporting information).This result indicated that the cleavage of C(sp2)-H bond might be related to the rate-determining step[46].
On the basis of experimental investigations and literature precedents[9,10,14,24-26,39].We depicted a plausible mechanism in Scheme 8.First,a Lewis acid–base adduct was initially formed between BBr3and the N atom of 5-fluoropyridine group in 1i.Then Br transferred from A to another BBr3and generated a borenium species B.An electrophilic aromatic substitution proceeded readily to offer a Wheland intermediate C,because of the strong electrophilic nature of theN-methylaniline ring in B.Subsequently,proton abstraction by DIPEA gave the dibromoboron complex D.Finally,under the protection of pinacol,compound 3i was obtained.
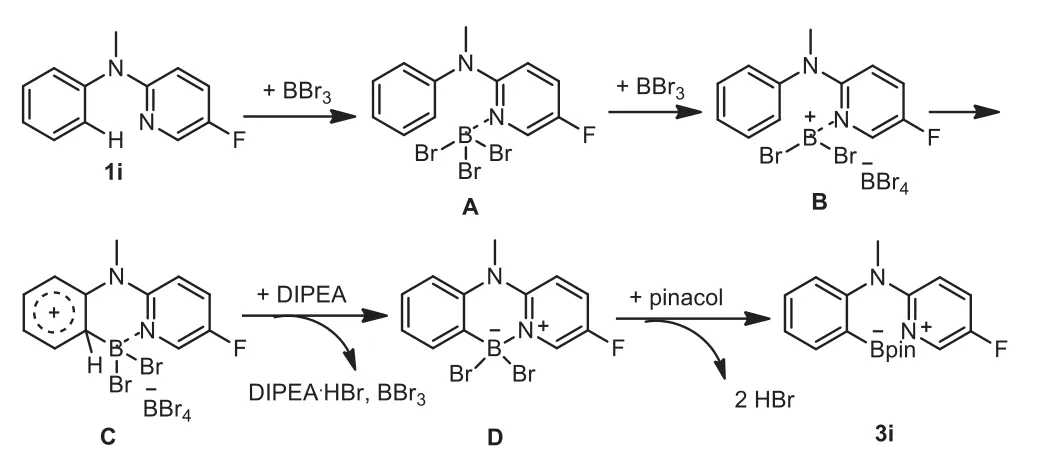
Scheme 8.Proposed mechanism.
In summary,we firstly reported the method for C-H borylation of 2-(N-methylanilino)-5-fluoropyridines and 2-benzyl-5-fluoropyridines under metal-free conditions.The obtained borylated products could be converted to various useful intermediates through common synthetic methods.Importantly,the directing group could be removed to enrich synthetic applications.Considering its simplicity and versatility,we expect that this novel borylation approach could show great promise in the screening of potential pharmaceuticals of 2-(N-methylanilino)-5-fluoropyridines and 2-benzyl-5-fluoropyridines.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgment
We gratefully thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China(No.21676088)for financial support.
Supplementary materials
Supplementary material associated with this article can be found,in the online version,at doi:10.1016/j.cclet.2021.09.081.
 Chinese Chemical Letters2022年4期
Chinese Chemical Letters2022年4期
- Chinese Chemical Letters的其它文章
- Key progresses of MOE key laboratory of macromolecular synthesis and functionalization in 2020
- Small nanoparticles bring big prospect:The synthesis,modification,photoluminescence and sensing applications of carbon dots
- Cell membrane-coated nanoparticles for immunotherapy
- Diketopyrrolopyrrole-derived organic small molecular dyes for tumor phototheranostics
- Exosome based miRNA delivery strategy for disease treatment
- Recent advances in targeted stimuli-responsive nano-based drug delivery systems combating atherosclerosis
