Quantification of Carcinoembryonic Antigen by Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry
HUANG Zi-li,HU Yue-li,LIU Jing,WU Yi,ZHAO Jin-yi,LIU Rui,LÜYi,2*
(1.Key Laboratory of Green Chemistry&Technology,Ministry of Education,College of Chemistry,Sichuan University,Chengdu 610064,China;2.Analytical&Testing Center,Sichuan University,Chengdu 610064,China)
Abstract:Cancer ranks as the leading threat to life expectancy all over the world,based on the latest estimations.Timely diagnosis and treatment of malignancies are still essential procedures to control the growing burden of cancer incidence and mortality.Single particle inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry(spICP-MS)is a detection method for single particles in time-resolved mode.Inheriting the advantages of ICP-MS,spICP-MS ensures the single-particle counting with high sensitivity and high element resolutions.For immunoassays by this mode,there are breakthroughs not only in improving the detection limits of heterogeneous immunoassay but also in achieving multiplex homogeneous immunoassays with a simpler procedure.In this work,a single particle counting strategy was achieved by spICP-MS for sensitive carcinoembryonic antigen(CEA)evaluation.Gold nanoparticles(AuNPs)with a diameter of 50 nm were synthesized by one-step sodium citrate reduction,which were further applied to CEA-specific capturing.Anti-CEA antibody labeled AuNPs were synthesized by electrostatic adsorption between disulfide bonds exposed on the anti-CEA antibodies and the surface of AuNPs.The strategy was based on sandwich immunoassay where anti-CEA antibody labeled magnetic beads(MBs)were applied to capture CEA and antibody labeled AuNPs.After separation by a magnet,MBs were enriched at the bottom of the centrifugal tube,while the remaining AuNPs in the supernatant were counted by spICP-MS.The more CEA occurred in the sample,the more AuNPs probes were captured on the surface of MBs,and the fewer numbers of detectable remaining AuNPs were found in the supernatant.The proposed method was more direct and facile without washing steps,compared with the traditional MBs strategy.The experimental conditions were optimized,including magnetic beads volume applied in immunoassay and dilution ratio of the sample in spICP-MS.Under the optimal conditions,spICP-MS could accurately determine the change of AuNPs numbers in the process of CEA immunoassay,with an efficiency of 2.1%.The proposed method provided a three-orders-of-magnitude linear range(0.05-20 ng/mL,r2=0.997)with a limit of detection(LOD)as low as 0.017 ng/mL for CEA quantification.The method was also successfully utilized in serum sample analysis with good selectivity,exhibiting a great potential in cancer diagnosis.
Key words:single particle ICP-MS;AuNPs;magnetic beads;CEA evaluation
In the past 2020,there were proximately 19.3 million new cases and 10 million deaths worldwide,making cancer a public health priority that needs efficient control[1].Early diagnosis of cancer which can give warning in time is still an efficient protocol to tackle this dilemma[2-4].Single particle ICP-MS(spICP-MS)based immunoassay,inheriting the advantages of ICP-MS where the revolution of absolute quantification has been massively achieved,is one of the state-of-the-art protocols for cancer diagnosis due to its high specificity(high resolutions among metal stable isotopes)and throughputs(noble metal and lanthanide nanoparticles can be tactfully applied)[5-8].Moreover,it is because that a gaseous ion cloud with large amounts of detectable ions can be counted per transient pulse after vaporized and ionized by ICP,spICP-MS concentrates on the numbers of particles instead of the ion itself,exhibiting potential on reaching higher sensitivity in immunoassay when applying nanoparticles counting[9-10].Gold nanoparticles(AuNPs)serve as the foremost studied nanomaterials with simple synthesis and adjustable morphology.Endowed with various properties that can be used for sensor and assay development,AuNPs have been widely adopted for multi-discipline research[11].In spICP-MS,the high abundance of+Au197(100%)guarantees a high signal response of AuNPs without other isotopic interference.In 2009,Zhang′s group firstly proposed a spICP-MS based competitive heterogeneous immunoassay for sensitive detection ofα-fetoprotein(AFP)using 45 nm AuNPs in 96-well microtiter plates[12].Later,they groundbreakingly reported an AuNPs based homogeneous DNA assay with dual data acquisition,widening the application of spICP-MS in other biological molecules[13].Having noticed the advantages of spICP-MS in evaluating signal changes within a homogeneous level,a series of homogeneous protocols,which are more facile than a heterogenous strategy based clinical practice without wash and separation procedures,have been reported for single analyte and multiplex assays by our group[14-16],following by Hu′s group[17-18]and Jiang′s group[19].Recently,we have paid attention to magnetic beads-based immunoassay,hoping to provide a more direct approach on molecules related nanoparticle counting,and extending the value of methodology in various fields of bioassay[20-22].
Herein,we proposed a magnetic beads-based single particle counting strategy for cancer biomarker quantification.Carcinoembryonic antigen(CEA),a 180 kDa glycoprotein that is clinically related to a series of malignancies such as colorectal cancer[23],was chosen as a model analyte.In the methodology,anti-CEA antibody labeled magnetic beads were applied for CEA capturing and subsequent antibody labeled gold nanoparticles(AuNPs)binding.After the magnetic separation of magnetic beads,the remaining AuNPs in the supernatant were diluted and counted by spICP-MS.Under the optimal conditions,the numbers of remaining AuNPs related to the concentration of CEA,providing a three-orders-of-magnitude linear range with a limit of detection(LOD)as low as 0.017 ng/mL.Desirable results were also found in selectivity and simulated sample analysis,making the proposed method promising in cancer diagnosis and prediction.
1 Experimental
1.1 Materials and apparatus
Chloroauric acid hydrate(HAuCl4·xH2O),trisodium citrate,sodium tetraborate,orthoboric acid,4-morpholineethanesulfonic acid(MES),and sodium phosphate buffered saline(PBS)were purchased from Adamas Reagent,Ltd.(Shanghai,China).CEA,capture anti-CEA antibody,and report anti-CEA antibody were purchased from Shanghai Linc-Bio Science Co.Ltd.(Shanghai,China).Bovine serum albumin(BSA),as well as normal fetal bovine serum(FBS),were purchased from Shanghai Sangon Biotechnology Co.Ltd.(Shanghai,China).DynabeadsTM(MyOneTM)carboxylic acid magnetic beads were purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.Ultrapure water with 18.24 MΩ·cm came from a Milli-Q water purification system.
Absorption of AuNPs was measured using a Cytation 5 Cell Imaging Multi-Mode Reader(BioTek Instruments,Inc.).Diameter characterization of AuNPs was implemented using a Malvern Zetasizer Nano ZS90(Malvern Panalytical Ltd.).All spICP-MS data were obtained using a NexION 350 inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer(PerkinElmer,Inc.).Transmission electron microscopy(TEM)images were obtained using a JEM-2010 microscope(JEOL Co.,Japan).
1.2 AuNPs synthesis
50 nm AuNPs were synthesized according to the direct reduction slightly modified from the previous literature[5].Briefly,100 mL 0.01%HAuCl4was heated to boiling for 15 min and was following mixed with 1 mL 1%trisodium citrate solution.Spherical AuNPs formed within 5 min.After keeping boiling for another 15 min and cooling down to room temperature within 6 h,AuNPs were finally purified with a 0.22μm filter and stored under 4oC for further use.
1.3 Preparation of antibody labeled magnetic beads and AuNPs
Carboxylic acid magnetic beads(MBs)were activated by 150 mg/mL EDC and 25 mg/mL NHS under MES buffer.After incubating for 25 min at 27.5℃,the MBs were redissolved with a 20μL CEA coating antibody and 100μL MES.14μL of 10%BSA was added for blocking.After three times washing,MBs were finally redissolved in 200μL PBS buffer containing 1%BSA.
In nanoparticle labeling,AuNPs exhibits a high affinity to disulfide bonds of antibodies.In this work,1 mL boric acid adjusted AuNPs were mixed with 25μg CEA labeling antibody for electrostatic adsorption and were incubated for 1 h at room temperature,then 10%BSA was added for one-hour blocking.As-prepared antibody-AuNPs were redissolved in 1 mL of 1%BSA after centrifugation.
1.4 Single particle counting based immunoassay
In single-particle counting based immunoassay,MBs, CEA,and antibody labeled AuNPs were successively added into a 200μL centrifuge tube.Then,the obtained mixture was settled on a thermal shaker and incubated under 27.5℃.After magnetic separation,the remaining AuNPs probes in the supernatant were diluted twice and introduced into the spICP-MS system for AuNPs counting and CEA quantification.The working instrument parameters were shown in Table 1.

Table 1 Working conditions
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Principle of the single particle counting strategy
Herein,a novel single particle counting protocol was proposed for CEA quantification.As shown in Fig.1,the antibody was immobilized on the surface of MBs for CEA capturing,while report antibody labeled AuNPs were applied for binding with CEA on MBs through sandwich immunoreaction. After magnetic separation,the bound AuNPs on MBs could be enriched at the bottom.The protocol concentrated on the remaining AuNPs in the supernatant which were directly diluted and introduced in the spICP-MS system without sample washing to achieve AuNPs counting.

Fig.1 Single-particle counting strategy for sensitive CEA quantification
2.2 Feasibility of sp ICP-MS based single particle counting strategy
In this work,AuNPs were synthesized and applied as stable tags for CEA quantification.As-prepared AuNPs were characterized by ultraviolet spectrum(UV),TEM,and dynamic light scattering(DLS).By Fig.2A-2C,AuNPs with a uniform size of 50 nm was observed.The UV peak of AuNPs was observed at 533 nm.
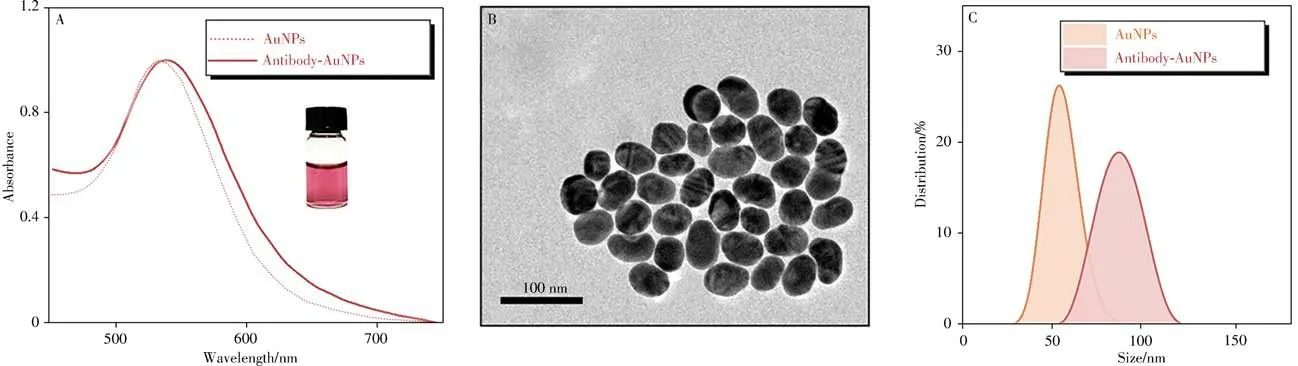
Fig.2 Characterization of AuNPs using UV spectrometry(A),TEM(B)and DLS(C)
The key of the proposed method lies in the numbers of AuNPs which can directly linearize with the concentrations of CEA.In other words,AuNPs with suitable diameters could provide not only distinctive signals above dissolved ion signals but also efficient immunoassay.In our previous work,nanoparticle diameter within 30-40 nm of AuNPs has been found to provide desirable homogeneous immunoassay[14-16],nevertheless the partially dissolved ion signals or AuNPs with diameter below 20 nm would increase the influence of background signals on the detective signals.Thus,we adopted 50 nm AuNPs in this work to provide efficient immunoassay with high precision.The relationship between the numbers of AuNPs and+Au197pulses in spICP-MS was investigated.As illustrated from Fig.3A to 3E,distinct Au signals were found above the background where each signal represented a detected Au nanoparticle.In addition,there was a good linear relationship between numbers of AuNPs and+Au197pulses(Fig.3F),meeting the requirement that+Au197pulses in spICP-MS could be utilized to count the numbers of AuNPs and further evaluate CEA concentrations.
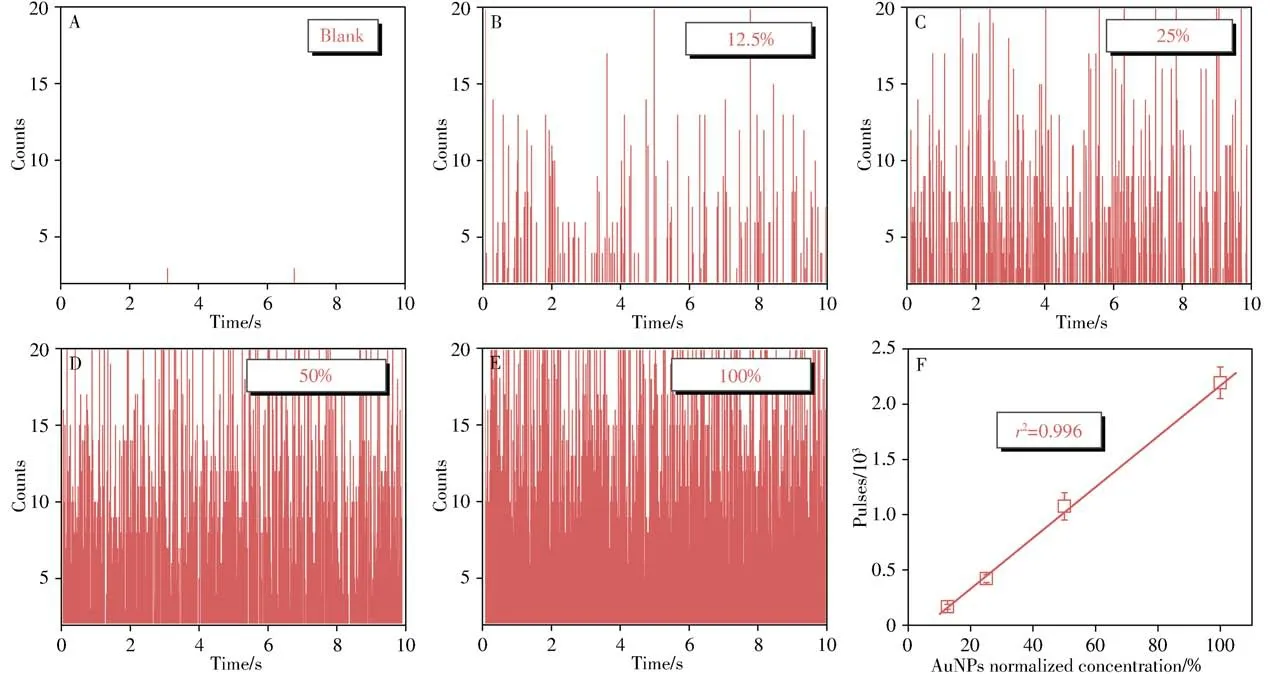
Fig.3 Transient signals of AuNPs with different concentrations in spICP-MS(A-E),and a linear relationship between frequency of spICP-MS and concentration of AuNPs(F)
Before immunoassay,AuNPs were labeled with the reported anti-CEA antibodies.UV,DLS,and spICPMS were applied for the characterizations of AuNPs before and after labeling.A gentle redshift of AuNPs peaks was observed in Fig.2A.A certain change of DLS results was attributed to the antibody on the surface of AuNPs which increased light scattering(Fig.2C)[24].Pulses and intensity of AuNPs were also measured by spICP-MS.When the numbers of AuNPs was controlled identical by spICP-MS,it is worth noting from the Fig.4A that the intensity which related to the size of AuNPs negligibly changed[14],demonstrating that there was no obvious aggregation of AuNPs before and after labeling,which could be exploited for upcoming quantification.And then,40 ng/mL CEA was mixed with MBs and antibody AuNPs to explore the immunoassay.Compared with TEM before and after the immunoassay shown in Fig.4B,4C,AuNPs were successfully captured to the surface of MBs through sandwich immunoassay,demonstrating the feasibility of the proposed method.
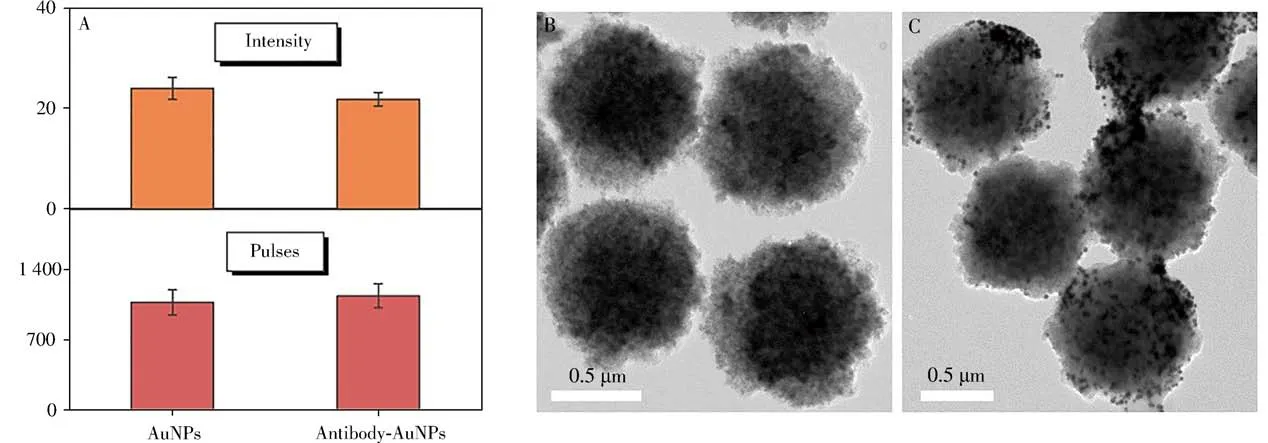
Fig.4 Pulses and intensity of spICP-MS before and after labeling(A),TEM images of MBs(B)and AuNPs captured on MBs(C)
2.3 Optimization of the immunoassay conditions
The volume of MBs is one of the crucial factors in the proposed immunoassay by spICP-MS and was investigated in this work.According to Fig.5A,10μL volume of MBs was selected to obtain the foremost analytical performance with the highest signal-to-noise ratio.
In this work,the remaining AuNPs probes in the supernatant after magnetic separation were diluted twice for single-particle counting.In the first dilution step,the supernatant was initially diluted 100 times.In the second dilution step optimization illustrated in Fig.5B,+Au197pulses increased initially with the elevation of sample volume and reached the top(100μL),while the intensity of antibody AuNPs(Counts)remained nearly unchanged during 10-100μL.Further increased volume could make several AuNPs counted in each dwell time in spICP-MS and cause pulse decrease as well as intensity increase.The efficiencies of spICP-MS were calculated in Table 2.After comprehensive consideration,a 50μL volume of sample was selected in our subsequent experiments.The total dilution ratio of two-step dilution was 8×103times.

Table 2 spICP-MS efficiencies under varied sample volumes
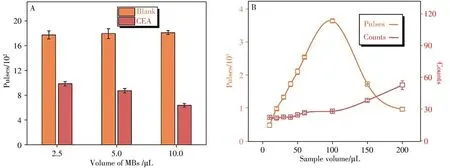
Fig.5 Optimization of MBs volume by frequency(A)and second dilution steep by both frequency and intensity in the immunoassay(B)
2.4 Quantification of CEA by single particle counting
Different concentrations of CEA were analyzed using the proposed strategy under the optimized conditions by spICP-MS.As depicted in Fig.6A-6B,higher CEA concentration could cause more antibody AuNPs captured on MBs and fewer antibody AuNPs remained in the supernatant,making+Au197pulses decrease.The relationship between pulses and CEA concentration was shown in Fig.6C where the linear range of detectable CEAconcentration was 0.05-20 ng/mL,with a limit of detection(LOD,3σ)as low as 0.017 ng/mL.

Fig.6 Transient signals of antibody AuNPs remained in the supernatant with different concentrations of antigen CEA(A-B),a linear relationship between pulses of antibody AuNPs and concentration of CEA(C),and the selectivity in the single-particle counting strategy
To further verify the selectivity of the proposed method,different interferences were used,and the results were illustrated in Fig.6D.It could be seen that the pulses of CEA were much lower than that of other antigens,indicating that the proposed single particle counting strategy has good selectivity,which was attributed to the antigen-antibody specific recognition.
2.5 Sample analysis
In order to evaluate the analytical capability of the established method in complex matrix,simulated serum samples using FBS were selected for analysis.Concluded from results shown in Table 3,the proposed single particle counting strategy had a comparable accuracy,indicating the capability in real samples analysis.Compared with other methods shown in Table 4,the proposed method was also exhibited desirable outcomes in CEA quantitation.

Table 3 Protocol accuracy in serum samples analysis

Table 4 Comparison of the proposed method with other methods
3 Conclusions
Cancer ranks as the leading threat to human health worldwide,making the in-time diagnosis and evaluation to control morbidity and mortality.Endowed with the ability of single-particle counting,spICP-MS based immunoassay exhibits great potential in sensitive assay within not only heterogeneous but also homogeneous levels.In this work,magnetic beads integrated single particle counting protocol was proposed for CEA quantification.The proposed method concentrated on the remaining antibody labeled AuNPs in the supernatant after immunoassay,which averted the acid digestions or sonication nanoparticles on magnetic beads for detection,providing a more facile procedure during measurements.Under the optimized conditions,the proposed method showed desirable outcomes on CEA detection and simulated sample treatments.We believed that the proposed method could have a promising clinical significance in cancer diagnosis,and serve as a more facile tool in ICP-MS based bioassays.
- 分析测试学报的其它文章
- 阿尔兹海默症生物标志物和早期诊断新技术
- 40周年刊庆 引 言
- 微管纸喷雾质谱法快速筛查血液中5种强极性毒物
- 基于核酸分子光开关的闭管可视化环介导等温扩增检测方法
- Detection of Broad Spectrum Bacteria Using a FITC-Lysozyme and Positively Charged AuNPs Constructed FRET Platform
- Detection of Biomarker Protein PDGF-BB in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Using a DNA Biosensor Based on Enzyme Cycle Amplification

