Analysis on Characteristics in Quanyou Series of High-quality
Hui XU Chunfeng LI Zhengmeng XU Fangchun SHI Lei XIE


Mid-season Rice Varieties Suitable for Planting in Hubei Province
Abstract In this paper, the basic characteristics of Quanyou series of high-quality rice varieties, suitable for planting in Hubei ecological areas (except Wuling Mountain Area) and approved by the provincial government in 2020, were analyzed. The result showed that, there were 12 suitable rice varieties. From the perspective of the main body of variety breeding, the varieties were mainly selected by enterprises; Quanyou series of high-quality hybrid combinations generally had large grains per panicle and high seed setting rate, but the effective panicle number was general, and the yield per panicle contributed more in unit yield. Quanyou series of high-quality hybrid combinations can be used for the selection and breeding of varieties with good rice quality and blast resistance, but breeding varieties resistant to bacterial blight and brown planthopper should be strengthened.
Key words Rice; Approved variety; High quality; Yield; Resistance
Received: July 7, 2021 Accepted: September 30, 2021
Supported by Rice Crop Research System Construction Project (CARS-01-79).
Hui XU (1974-), male, P. R. China, associate researcher, devoted to research about rice breeding and cultivation technology.
*Corresponding author.
Rice is an important food crop in China, and it is the basis for the country to implement its food security strategy. With the development of society and the improvement of people’s living standards, people have put forward higher requirements for rice quality, and there is an urgent need for breeders to be able to select high-quality, high-yield and adaptable rice varieties. Therefore, it is necessary to analyze and summarize the basic characteristics of newly approved varieties, such as quality, yield, and resistance[1]. At present, more varieties of Quanyou combinations (hybrid combinations with Quanyou 9311A as the female parent) have passed national and provincial approval, and more have been also used in production, with larger area of promotion and application[2], indicating that Quanyou series of varieties are popular in the market. In this study, basic characteristics of Quanyou series of high-quality rice varieties suitable for one-season mid-season rice planting in Hubei ecological areas (except the Wuling Mountain Area), approved in 2020, were analyzed based on the data from the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs and the provincial rice regional tests and production test, hoping to provide a reference for the breeding and production of new rice varieties.
Data Sources and Analysis Methods
Data sources
The data came from the Chinese rice varieties and their pedigree database established by the "National Rice Data Center" (http:∥www.ricedata.cn/variety/)[3].
Analysis methods
Chinese rice varieties and their pedigree database (http:∥www.ricedata.cn/variety/) was used to query the high-quality rice varieties of the Quanyou series approved by the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs and various provinces in 2020, and the yields, quality and resistance performance of various varieties in regional tests were analyzed.
The main quality indexes of rice referred to GB/T 17891-2017 High quality paddy, GB/T 17891-1999 High quality paddy, NY/T 593-2013 Cooking rice variety quality and provincial standards, and varieties with main quality indexes over level 3 (including level 3) are called high-quality varieties.
Data processing
Statistical analysis was performed on the data using Excel 2010 software.
Results and Analysis
Basic situation of variety approval
Through inquiries, in 2020, the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs and various provinces approved a total of 12 high-quality rice varieties of the Quanyou series suitable for one-season mid-season rice cultivation in Hubei ecological areas (except Wuling Mountain), of which 8 were nationally approved and 4 were approved by Hubei Province. The breeding units were mainly Anhui Win-all Hi-tech Seed Co., Ltd., Hubei Win-all Hi-tech Seed Co., Ltd., China National Seed Group Co., Ltd., Hubei Provincial Seed Group Co., Ltd., Shenzhen Jietian Model Organisms Technology Co., Ltd., Hubei Huazhan Seed Technology Co., Ltd., Chengdu Academy of Agriculture and Forestry, Zhenjiang Institute of Agricultural Sciences, Jiangsu Hilly Region, Wuhan CMP Super Seeds CO., Ltd., Hua’an Seed Industry Co., Ltd., Jiangxi Kewei Crop Research Institute and Guangzhou Jinyue Biological Technology Co., Ltd. The test varieties were mainly those selected and bred with the participation of enterprises, as shown in Table 1.
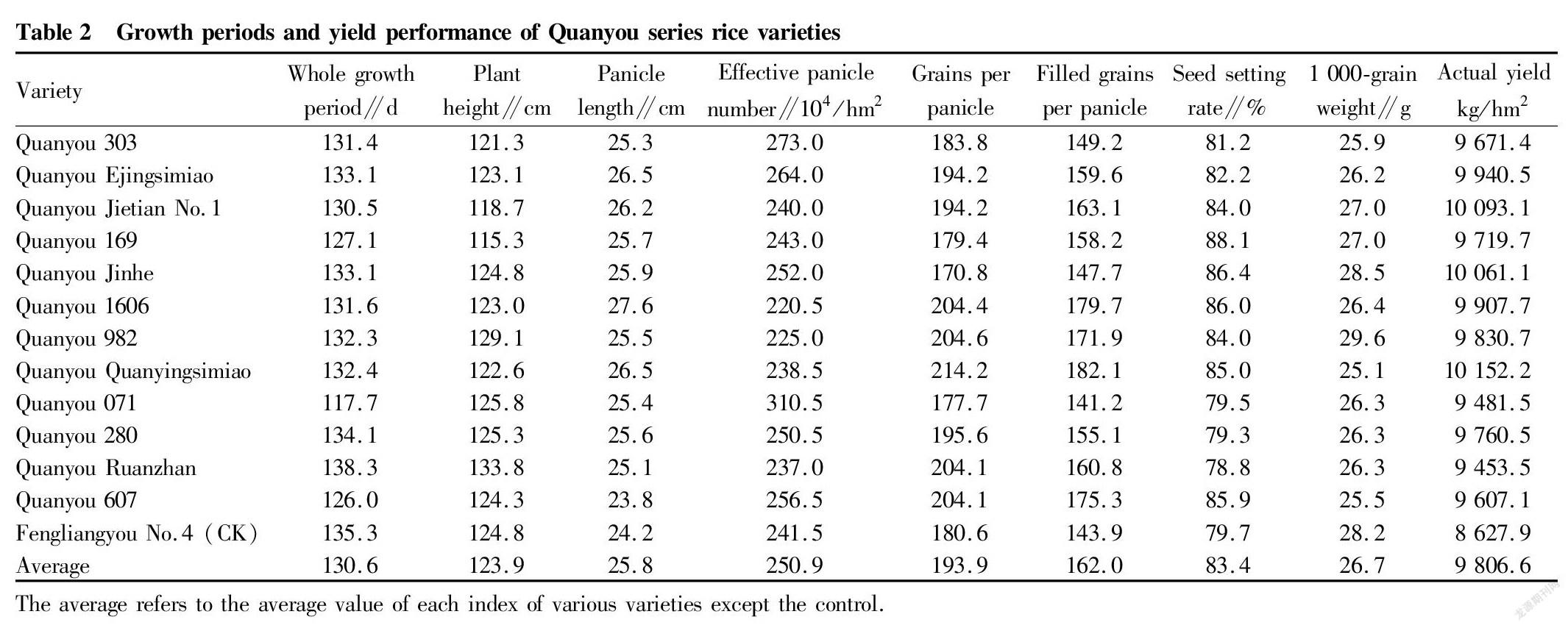
Growth periods and yield performance of Quanyou series rice varieties
It can be seen from Table 2 that the whole growth periods of Quanyou series of rice varieties were 117.7-138.3 d, with an average of 130.6 d. There were both long growth periods and short growth periods, which can meet different needs of Hubei ecological areas (except Wuling Mountain) for one-season mid-season rice, ratooning rice, shrimp rice, etc. Among them, Quanyou 303, Quanyou Ejingsimiao, Quanyou Jietian No.1, Quanyou Jinhe, Quanyou 1606, Quanyou 982, Quanyou Quanyingsimiao, Quanyou 280 and Quanyou Ruanzhan had a whole growth period more than 130 d, and can be planted as one-season mid-season rice; Quanyou 169 and Quanyou 607 had a whole growth period of 120-130 d, and can serve as ratooning rice; and Quanyou 071 had a whole growth period of less than 120 d, and can be used as shrimp rice. Compared with the control Fengliangyou 4, the plant heights of various varieties ranged from 115.3 to 133.8 cm, with an average of 123.9 cm, so the plant height was moderate; the panicle lengths were in the range of 23.8-26.5 cm, with an average of 25.8 cm, that is, the panicle length was larger; and the total number of grains per panicle ranged from 170.8 to 204.6, with an average of 193.9, that is, the total number of grains per panicle was relatively large. The grain lengths and the number of grains per panicle showed that Quanyou series of varieties had large ears and more grains. The number of effective panicles per hectare was between 2.205 million and 3.105 million panicles, with an average of 2.509 million panicles, that is, the number of effective panicles was average; the seed setting rates ranged from 78.8% to 88.1%, with an average value of 83.4%, so the seed setting rate was relatively high; and the 1 000-grain weights were in the range of 25.1-29.6 g, with an average value of 26.7 g, suggesting that the 1 000-grain weight was medium. The above analysis showed that Quanyou series of varieties generally have large panicles with more grains and high seed setting rate, but the number of effective panicles is average, and the single panicle yield contributes more to unit yield.
Rice quality performance of Quanyou series rice varieties
It can be seen from Table 3 that the head rice rates of the Quanyou series of rice varieties were in the range of 56.2%-70.9%, with an average value of 62.8%; and the chalkiness degrees ranked from 0.2% to 4.9%, with an average value of 2.7%, indicating that 9311A (the female parent of the Quanyou series of rice varieties) can be used for the selection of combinations with a low chalkiness degree. The amylose contents were in the range of 14.3%-19.1%, with an average of 15.9%; the gel consistency ranged from 50 to 81 mm, with an average of 72 mm; the alkali spreading values were in the range of 5.0-7.0, with an average of 6.2; and the length-width ratio were in the range of 3.0-3.3, with an average of 3.1, indicating that it is difficult for the length-width ratio of the combination 9311A to reach 3.6 or more. The above analysis showed that the 9311A can be used for the selection of combinations with excellent rice quality.
Hui XU et al. Analysis on Characteristics in Quanyou Series of High-quality Mid-season Rice Varieties Suitable for Planting in Hubei Province
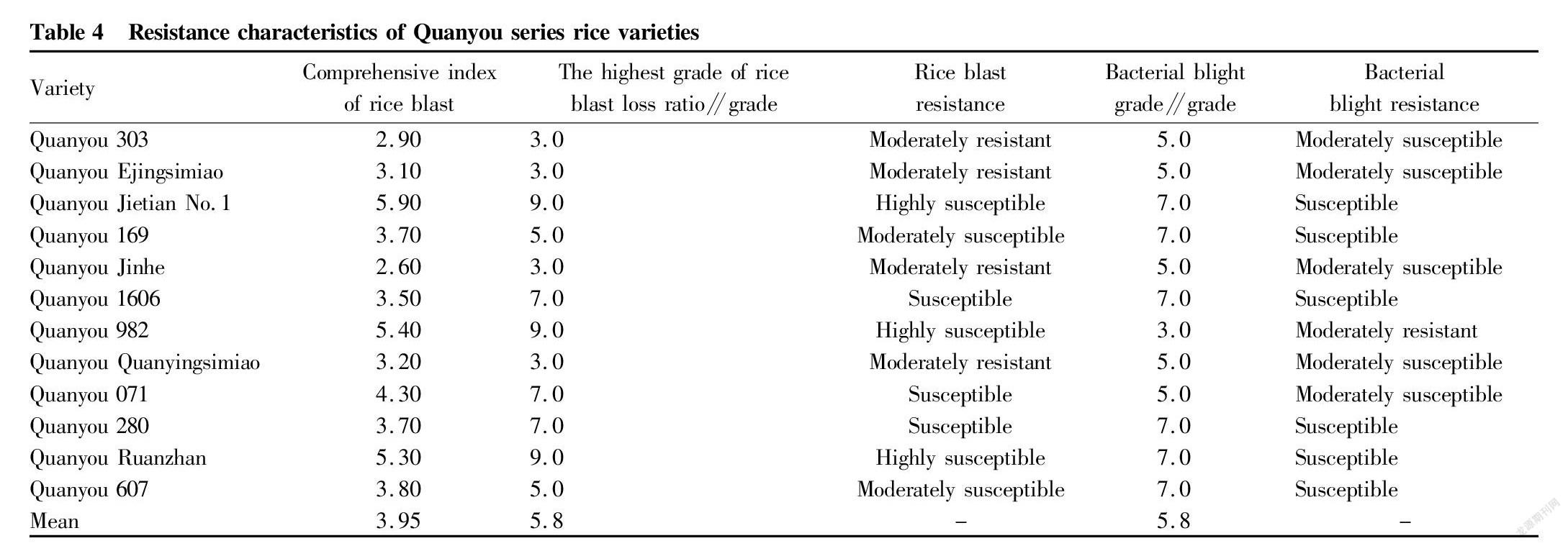
Resistance performance of Quanyou series rice varieties
It can be seen from Table 4 that the comprehensive indexes of rice blast in Quanyou series of rice varieties ranged from 2.60 to 5.90, with an average value of 3.95, and the highest grades of rice blast loss ratio were between 3.0 and 9.0, with an average value of 5.8. Rice blast resistance included medium resistance, medium susceptibility, susceptibility and high susceptibility. Among the various varieties, Quanyou 303, Quanyou Ejingsimiao, Quanyou Jinhe and Quanyou Quanyingsimiao were moderately resistant, indicating that the high-quality hybrid combinations of Quanyou series can breed varieties resistant to rice blast. The grades of bacterial blight ranged from 3.0 to 7.0, with an average value of 5.8. Only Quanyou 982 was moderately resistant, and the rest were susceptible and moderately susceptible. The above analysis showed that the selection of high-quality varieties resistant to bacterial blight using Quanyou combinations needs further study.
Conclusions and Discussion
Since 2014, the state has successively launched green channels and consortium test channels for variety certification, and variety test methods have become more diversified. It has led to a rapid increase in the number of rice varieties that have participated in regional tests and passed approval, and the replacement of new and old varieties has accelerated, requiring breeders to increase their efforts and output in improving rice quality, increasing rice yield, enhancing resistance, and adapting to simplified cultivation[4].
In recent years, more varieties of the Quanyou series combinations have passed national and provincial approval, and more have been also used in production with larger area of promotion and application, indicating that Quanyou 9311A is an excellent three-line sterile line with good yield and high combining ability. The number of high-quality varieties cultivated in the Quanyou series continues to increase, which has made great contributions to the supply-side reform of the rice industry. Through inquiries, in 2020, the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs and various provinces approved a total of 30 Quanyou series varieties suitable for one-season mid-season rice cultivation in Hubei ecological areas (except Wuling Mountain), including 12 high-quality rice varieties, which accounted for 40%, indicating that the proportion of high-quality varieties is not high. At present, with the development of social economy and the improvement of people’s living standards, high quality has become a new indicator of rice variety research and breeding[5], and the selection and breeding of high quality varieties is still an important task of current rice breeding.
Meanwhile, the overall resistance performance of the varieties is not enough. In terms of disease resistance breeding, in recent years, China has strictly controlled the rice blast resistance of tested rice lines, which has significantly improved the resistance of newly approved varieties to rice blast[6], and the research on resistance to rice false smut, sheath blight, and bacterial blight is also being gradually strengthened[7-9]. For the future breeding goals, we should pay attention to yield and quality, and also to the strengthening of mining and utilizing disease-resistant, insect-resistant, and stress-tolerant genes. In particular, pests, as an important factor affecting rice yield, should be paid attention to[10], we should gradually enhance the independent technological innovation capability of the seed industry, and promote the improvement of quality and efficiency of the rice industry.
References
[1] LIN H, WANG ZG, E ZG, et al. Analysis on characteristics of rice varieties registered in China in 2018[J]. China Rice, 2019, 25(6): 65-71. (in Chinese).
[2] LIN H, WANG ZG, E ZG, et al. Analysis on characteristics of rice varieties registered in China in 2019[J]. China Rice, 2020, 26(6): 16-22. (in Chinese).
[3] National Rice Data Center. Chinese rice varieties and their pedigree database[EB/OL]. http://www.ricedata.cn/variety/index.htm. (in Chinese).
[4] LIN H, PANG QL, WANG ZG, et al. Analysis on quality traits and yield of rice varieties approved in China in 2013[J]. China Rice, 2014, 20(4): 33-37. (in Chinese).
[5] MA XC, ZHANG ZG, FAN L, et al. Analysis on main characters of rice varieties approved by Anhui Province in 2008-2019[J]. China Rice, 2021, 27(1): 104-108. (in Chinese).
[6] HE X, DING ZH, HU LD, et al. Evaluation of blast resistance and identification of resistance genes of 48 rice cultivars in Hunan[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(1): 108-113. (in Chinese).
[7] ZHANG ZW, CHEN X, SHEN HM, et al. Research and application status of severity grading standards of the rice false smut disease in China[J]. China Rice, 2020, 26(4): 18-21. (in Chinese).
[8] HE M, YIN JJ, FENG ZM, et al. Methods for evaluation of rice resistance to blast and sheath blight diseases[J]. Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(5): 577-587. (in Chinese).
[9] CHEN FD, YAN BX, HE ZH. Mechanisms of disease resistance to bacterial blight and perspectives of molecular breeding in rice[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 2020, 56(12): 2533-2542. (in Chinese).
[10] LIU ZZ, XIONG ZQ, LI XM, et al. Rice varieties resistant to Nilaparvata lugens[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 35(6): 633-639. (in Chinese).
Editor: Yingzhi GUANG Proofreader: Xinxiu ZHU
- 农业生物技术(英文版)的其它文章
- Expression Analysis of Heat Shock Protein 70 Gene in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)
- Changes in Physiological and Biochemical Characteristics of Floral Organ
- Research Progress on Lonicera japonica Thunb. Affected by Environmental Stress
- Research Progress on Genetic Diversity of Snap Bean
- Allelopathic Effects of Cedrus deodara Needle Extracts on Seed
- Development Status and Countermeasures of Passiflora spp. Seedling Industry in Qinzhou, Guangxi

