Trust-Based Routing Optimization Using Multi-Ant Colonies in Wireless Sensor Network
Maryam hajiee,Mehdi Fartash,Nafiseh Osati Eraghi
Department Of Computer Engineering,Arak Branch,Islamic Azad University,Arak 38361-1-9131,Iran
Abstract:Nowadays,with the advancement of new technologies such as the Internet of Things,new applications and intelligent networks,the use of wireless sensor network increased considerably.They are prone to a variety of attacks.Thus,network security is of utmost importance to researchers.In the past,methods such as cryptography,authentication and hash function were used to create security in this type of network.However,due to the limitations of this type of network,trust-based methods are used today.Finding a secure route for transferring data among available routes greatly increases security in this network.In this paper,we present aTrust-based Routing Optimization using Multi-Ant Colonies(MACRAT)scheme which is based on the improvement of the ant meta-heuristic algorithm and an improved method for trust assessment which is presented.The simulation results illustrate that MACRAT is more efficient than existing routing protocols.The results show that MACRAT improved by 10% in black hole detection compared to ESRT protocol and by 4% compared to M-CSO protocol,the packet loss rate in MACRAT improved by 30.14% compared to ESRT protocol and 6% compared to M-CSO protocol.
Keywords:trust;wireless sensor network;secure routing
I.INTRODUCTION
One type of network widely used today due to its unique advantageous features is the wireless sensor network[1].Wireless sensor nodes are used in various applications such as emergency response[2],healthcare monitoring[3],military and agricultural fields[4],environmental monitoring.In the past,methods such as Cryptography,Authentication,and Hash functions[5–7]were used to create security in these networks.However,these methods are not very efficient due to limitations of wireless sensors including low computing capacity,memory and energy.As a result,these methods cannot separate malicious and selfish nodes from honest nodes.Today the concept of Trust and Reputation is used to create security in wireless sensor networks.The concept of trust is used in different areas of human relationships where two nodes communicate based on the degree of trust they have in each other.In previous research,trust has been expressed in different ways.In[8],trust is a degree of confidence considered for the future behaviors of a node based on its past behaviors.In other words,trust can be defined as the degree of confidence existing between two entities.Using trust not only assists in better identifying node behaviors but also improves network performance as nodes avoid communicating with malicious nodes and nor do they send or receive data[9].The trust management system has been implemented in various applications for security including secure protocol[10],secure data aggregation[11],trusted routing[12],and intrusion detection system[13].By studying previous research in the field of wireless sensor networks security,it was found that trust has played a major role in enhancing the security of wireless sensor networks and many studies have been carried out.However,because of its importance,there is a need for further studies in this field.Based on past studies,it is evident that these studies considered trust evaluation only at the communication level without even measuring trust at the data consistency level[14–16]and so unable to detect some internal attacks.Other studies,such as[17–20],consider different factors for calculating trust.One such research which enhances the security of the wireless sensor networks is the design of secure routing for this type of network.Thus,the data collected from the environment is sent to the base station through highly reliable nodes using a secure mechanism.The experimental results indicated that the efficiency of the proposed method is greater than state-of-the-art methods.The main contributions of the present research are as follows:
·A better method is used to gain trust at both communication and data levels.
·Routing perform in an improved way compared to the original ant colony algorithm.In this method,multi colonies is used instead of one.
·Simulation result show higher accuracy,greater detection rate of malicious nodes and routing perform with higher security.
·The amount of energy consume in the network is reduced leading to a prolonged life of the network.
·This method always attempts to select a shorter route to the destination.
The remainder of this article is organized as follows.Section II related work is examined.In section III,first,the concepts of trust and trust evaluation methods are presented and then the network structure and assumptions are described.The routing process and the selection of the optimal route are detailed in section III too.The performance of MACRAT is evaluated in section IV and concluding remarks are made in section V.
II.RELATED WORK
Because of the importance of trust in securing wireless sensor networks,much research has focused on this issue,each attempting to improve previous work.In some cases,trust is only calculated at the communication level.In other cases,trust is calculated at the data level in addition to level of communication.
In[14],a reputation-based framework for sensor networks(RFSNs)is provided.RFNS use a watchdog system to observe neighboring node behaviors and use a beta distribution to distribute reputation values.
In[15],an agent-based trust model(ATSN)is introduced.In this model,an agent node consider and store the positive and negative behaviors of nodes.Furthermore,it use only direct trust to calculate trust and the indirect trust method is not used to calculate the final trust.Thus,the accuracy of the calculation might be to some extent low.
In[16],a new light weight group-based scheme(GTMS)method which is clustered for sensor networks is proposed.The amount of trust is obtained from the communication behaviors of neighboring nodes.In this method,the amount of trust is calculated at three levels:at the node level,node level head and base station level.This method does not require large storage memory,undertakes few calculations and can detect attacks to a large extent.
In[21],a dynamic trust calculation method based on several factors is introduced.Trust is obtained by combining direct and indirect trusts.This method does not consider the process of updating trusts.
In[22],a trust-based routing scheme,Friendship based AODV(Fr-AODV),that detects black hole attacks is presented.Trust assessment is based on features such as node reputation and node identity.Each attribute is numerically stated and changes during the sending of packets.Fr-AODV also uses the path maintenance mechanism.
In[23],DSR is designed to secure the routing protocol mechanism and uses ”path rater”and ”watchdog”modules.This method can be used in routing protocols in which the origin determines the path of the packets.In the proposed trust management method,a credit system is added to the watchdog and path rater method and this credit system maintains a blacklist in the nodes and shares it with friend nodes.A combination of direct and indirect reputation and operational reputation based on observation of behaviors is used.
In[24],a secure on-demand routing protocol in case networks which prevent the manipulation of secure paths involving healthy nodes as well as many denial-ofservice attacks is presented.In[25],a pro-tocol called TERP is introduced.TERP was developed to support security and intrusion detection based on direct surveillance,indirect surveillance and a factor called increasing the accuracy of security calculations.Challenges associated with TERP include increased overheads due to recommendation sharing,vulnerability to intrusive nodes,and inability to detect some attacks.In[26]another protocol called TESRP is presented which aimed at protocol performance.The performance of this protocol was developed to improve the challenges and vulnerabilities of the TERP protocol based on beta distribution.Challenges of the TESRP protocol included security vulnerabilities against intruders with the intention of deceiving the intrusion detection system,inconsistencies in reliable assessments,increased overheads and delays in the routing process.[27]Introduced the TERP and TESRP protocols.In order to achieve the set goals and improved the issues of the two protocols,the performance of the mentioned two protocols was developed by increasing the transaction time interval criterion in intrusion detection assessments.
Interaction paths associated with poor TESRP performance in addition to support for reliability use the single-propagation of path failure packets only on paths to the source and multi-path routing with the aim of using backup paths.In[28],a Model and Reputation Bio-inspired Trust is provided for wireless sensor networks named BTRM-WSN.This article show how the effect of a pheromone emitted by ants helps other ants find a server that is more reliable.They also find a way to update pheromones and reward and punish.In[29],an ant algorithm is used and two models(EBTRM-WSN)are presented combining the Peer Trust System to increase performance.The results show that this model is more accurate in detecting reliable nodes and thus increases the level of security.Moreover,in[30],ant algorithm in the Mobile network Ad hoc was used to generate a QOS Mobility Aware ACO Routing Protocol(QMAA)to improve the performance of QOS.In[31],the ant algorithm which is in the routing of Vehicular ad hoc networks was used in conjunction with fuzzy logic to address challenges and problems.This method was shown to be highly effective and efficient.In[32],a routing framework based on Trust and opportunity in wireless sensor networks using a hybrid optimization algorithm is proposed.This hybrid optimization algorithm named,Monarch-Cat Swarm Optimization(M-CSO)which is the integration of Monarch Butterfly Optimization in Cat Swarm Optimization.This framework included two basic aspects,select safe nodes and select opportunistic nodes among secure nodes.In[33],a routing algorithm is proposed as a trust-based gravitational search approach(ETGSA)for wireless sensor networks.This algorithm optimizes the routing parameters with the gravitational search approach by considering the direct and indirect trust of the nodes as the problem of energy saving.
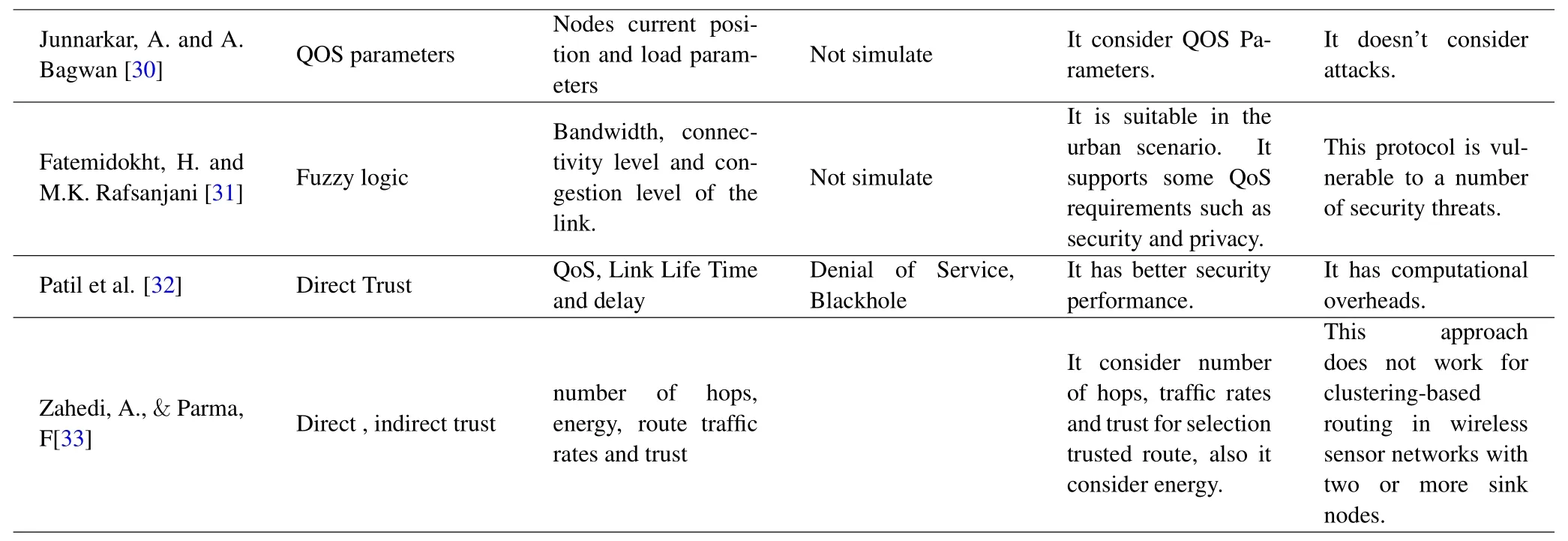
In this algorithm,the optimal route is selected based on the number of hops,energy,route traffic rates and trust.However,this approach does not work for clustering-based routing in wireless sensor networks with two or more sink nodes.Table 1,shows comparison of secure and trust-aware routing protocols.In the present article,an attempt has been made to identify Data integrity Attack and Black hole Attack by accurately calculating the trust and considering all aspects in addition to presenting a new method for improving routing.
III.THE PROPOSED MACRAT SCHEME:
This section details the proposed method.Assumptions made regarding the network are outlined below.
3.1 Assumption
1-All nodes in the network have the same resources in terms of energy,processing power and communication power.
2-The nodes are randomly distributed in the region and the location of the nodes and the location of the base station are fixed.
3-The destination of the transmitted data is the sink.
4-There are a small number of malicious nodes in the network that divert incoming packets from the path.
5-Malicious nodes do not collude with each other.
6-Each node maintains a list of its neighbors.
7-Each node can communicate with nodes that are in their radio range and are neighbors of the node.
3.2 Goals
The proposed method pursues the following goals:
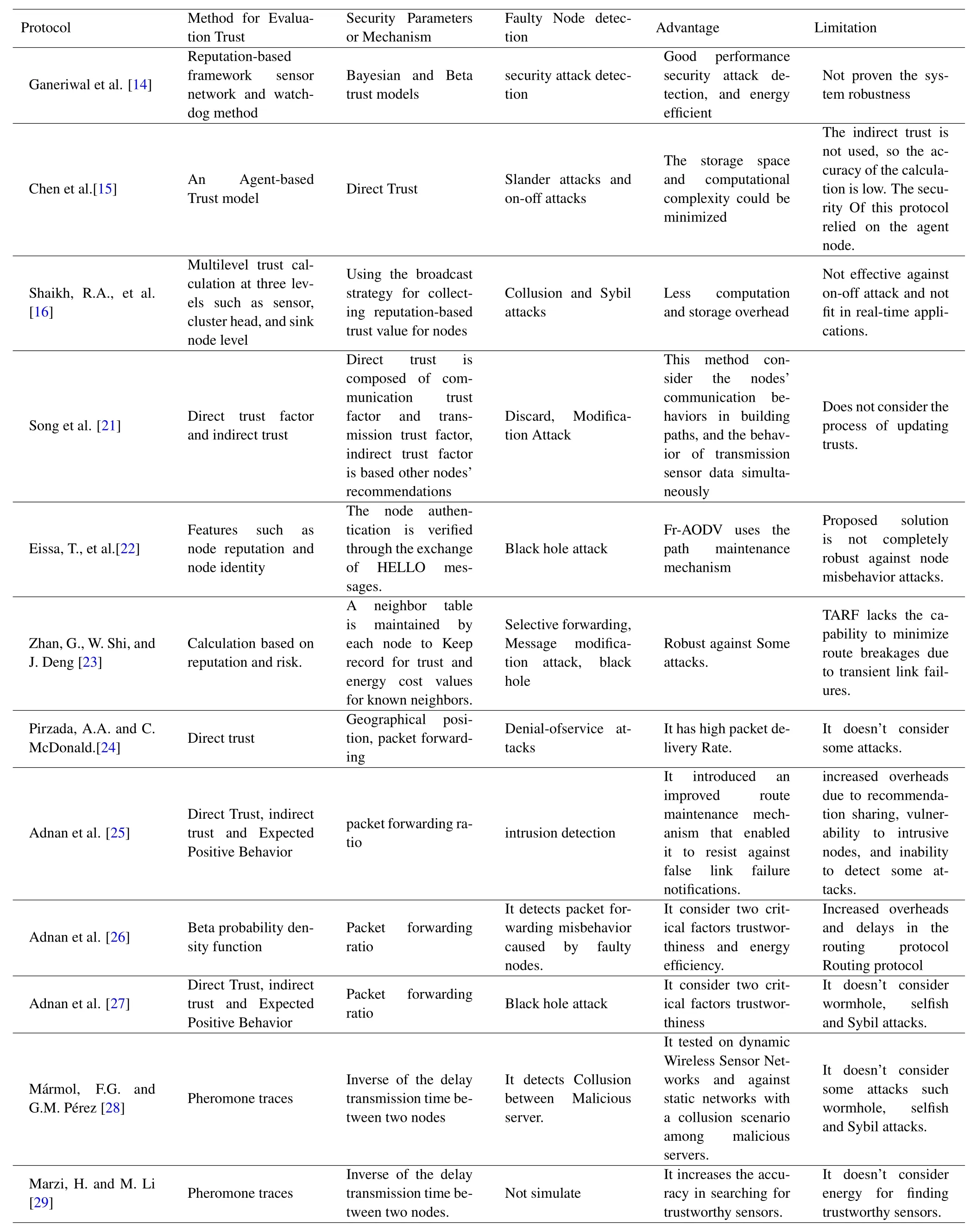
Table 1.Comparison of secure and trust-aware routing protocols.
1-Enhance security in wireless sensor networks using a concept called trust.
2-Increase network life.
3-Choose the path with the least number of hop to destination.
4-High throughput
3.3 Design of MACRAT
The proposed method includes the following sections:1)Trust Model,2)Make Multi Ant Colony,3)Route Discovery,4)Evaluation of the Rout,5)Election of the Trusted Rout,6)Rout Maintenance.
Trust Model evaluates the level of trust of the nodes in the wireless sensor network according to the direct trust and indirect trust observations and the beta evaluation function.Make Multiple Ant Colony makes multi-ant colonies for optimal routing and finds the best path.Routed Discovery is responsible for finding route in colonies created in the previous step using ant colony algorithm.In Evaluation of the Rout step,the paths that created in the previous step are evaluated.In Election of the Trusted Rout stage,a higher quality path is selected using the results of the route evaluation stage.In the Rout Maintenance stage,the path is replaced by the new path if the previous path does not have its previous quality.
3.3.1 Trust Model
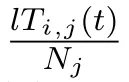
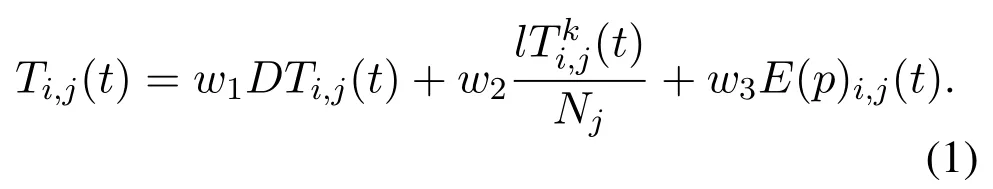
Initially,the network setup to each node in the network is given an initial level of security(0.5)as the average of the initial trust,and then based on the behavioral performance of the node,this rate will increase and decrease according to Equation(1).If the security level of the node is 0.5 the status of node is indecisive.If the security level of the node decreases below the malicious node detection threshold value(Tij(t)<0.5),the node will be identified as a malicious node,added to the blacklist and placed in the quarantine network(the package will not be received from the node and will not be sent to that node).If the security level of the node is greater than 0.5(Tij(t)>0.5)the node will be identified as a trusted node.The degree of trust of the nodes in the proposed protocol varies from zero to 1(zero meaning complete distrust and 1 meaning complete trust).
Evaluation of direct observations:Node selfobservations should be used to calculate direct trust.When node i wants to calculate the direct trust of node j,the amount of direct trust of node j is obtained by monitoring the behaviors of node j.To calculate the direct trust of a node,the concepts of variable credit over time and variable credit with the position of interaction and variable credit with the type of behavior should be used.The variable credit over time indicates the value of the concept of time in detecting erroneous nodes.In fact,the value of each interaction will vary according to the time of its occurrence as interactions in relation to proximity to the present time will be of greater value and importance.Equation(2)presents how to evaluate and calculate the validity of a variable over time.The relation Change Credittime(i,j)shows the validity of the variable over time from the evaluator node i to the evaluated node j,n shows nth interaction between the two nodes i and j,F(n),shows the type of behavior of node j in the nth interaction with node i(in case of correct behavior the value of 1 and in case of incorrect behavior the value of zero is assigned to this variable),and z is the number of interactions between the two nodes of i and j.
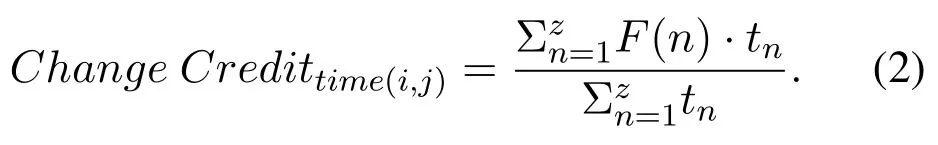
Variable Credit with interaction positionrefers to the position of interaction and its effect on malicious node detection.For instance,control package and information package or military data and ordinary data have different values.Therefore,it is necessary to value each interaction in relation to its position.Equation(3)is the developed Equation(2)for evaluating calculations of the variable’s credit with the interaction position.Thus,in the provided equation,Change Creditt(i,j)is variable valuation over time and the desired interaction position is between evaluator node i and the evaluated node j,σ and τ are relative valuation coefficients(so that τ+ σ=1)and Q is the value of the nth interaction.
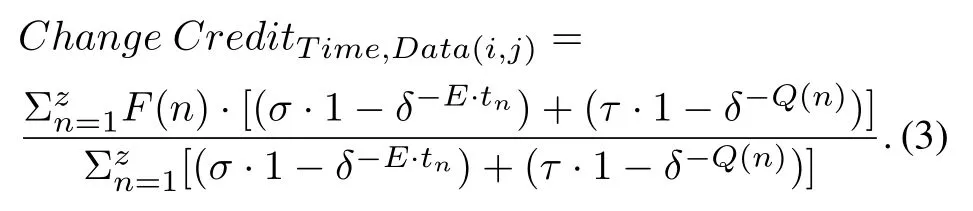
Variable credit with the type of behavior refers to type of behavior of interaction and its effect on malicious node detection.Therefore,it is necessary to give a variable value to any behavior in relation to its position.As a result the capability of applying destructive behaviors based on the validity obtained from the positive behaviors is discarded from the malicious nodes.
Equation(4)is the developed Equation(3)which provides a variable with the position of behavior with respect to the type of behavior and calculations.
Therefore,in the equation provided,Change CreditTime,Data,Behavior(i,j)),variable valuation over time,the position of the interaction and the type of desired behavior between the evaluator node i and the evaluated node j,and σ,τ,φ are the relative valuation coefficients(so that τ+ σ +φ=1)where according to the value of each factor in the malicious node detection,a higher or lower value can be given.M is the value of the type of nth behavior(for positive behaviors it has a value larger than negative behaviors and will vary between zero to one)stimulating negative behavior in the credit(if negative behavior occurs,value will be one and otherwise zero),∂encourages negative behavior in the credit(in the case of negative behavior value will be 1,otherwise 0),and p is the relative valuation variable of the behavior encouragement in the amount of credit,ω is the fine factor control and k is the number of inappropriate behaviors.
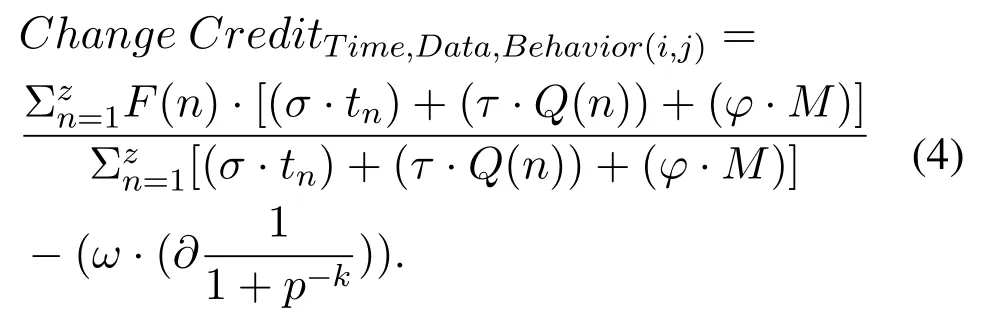
As mentioned above,the evaluation of the direct observations in Equation(1)is carried out based on Equation(4)in order to increase the accuracy in the calculations and the malicious nodes detected in a desirable form during direct observations.The following Equation(5)shows evaluation of direct observations by the evaluator node i for the evaluated node j.
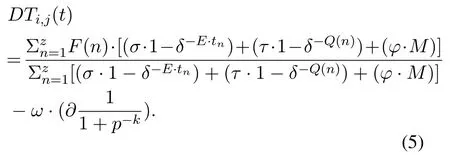
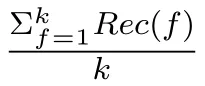
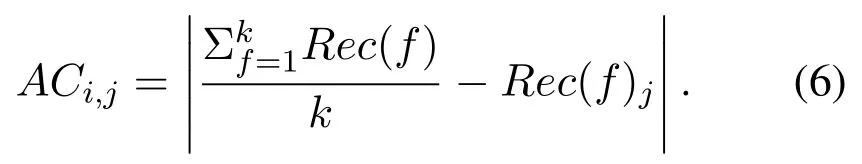
If based on Equation(6),jth node is identified as a suspicious node in the validation of indirect observations,the node which receives the recommendation evaluates the suspicious node in order to detect malicious nodes.In order to identify and detect malicious nodes in this process,the ith evaluator node asks recommendation from ith evaluated node for the nodes with enough knowledge and trusted nodes.Subsequently,the recommendations received by the ith evaluator node are evaluated according to Equation(7)related to indirect observations and if the deviation of the received recommendations exceeds one value of threshold,the node will be added to the blacklist as malicious node.In Equation(7)presented,ERi,is Detection Indicator,T(a)iis the value of the trust of the node i to the ath node,m is the total number of nodes for which the recommendation is asked,RT(a)jis the recommendation received from the jth node under evaluation in relation to the ath node.
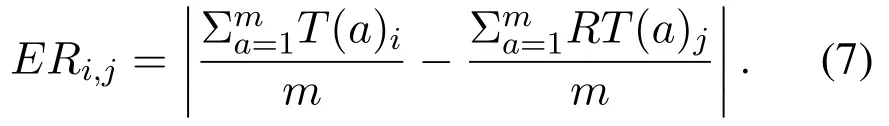
Furthermore,based on the validated recommendations of the indirect factor,evaluation will be calculated using Equation(8)and considered in malicious nodes detection of Equation(1).As in Equation(8),DTi,is the credit of node k for node i and DTk,j is the credit of node j for node k.
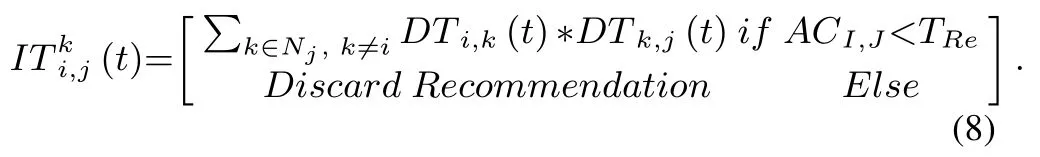
Beta distribution-based analysis:Beta distribution analysis is the third component of the malicious node detection relationship and is another practical factor in evaluating node behavior.This factor and its improvement are used to improve malicious nodes detection evaluations and increase the accuracy of computations in the proposed MACRAT protocol.For this purpose,the theory of DempsterShafer[19]and its extension to beta distribution was used in the proposed protocol.Equation(9)refers to how the beta distribution-based analysis is used for malicious node detection evaluations.In the presented equation,a is the correct behaviors of node j for requests arisen by node i,b is the wrong behaviors of node j for node i’s requests,p is the valuation factor,ISiis the uncertainty criterion of the node i to j based on the sequence of node j behaviors obtained from Equation(10):
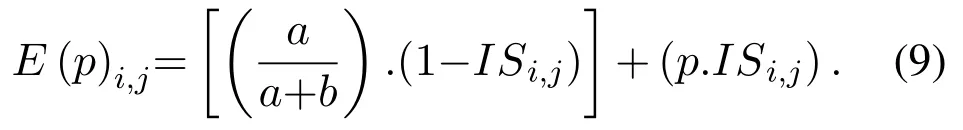
In Equation(10),ISi,jis the uncertainty criterion of node i to node j.
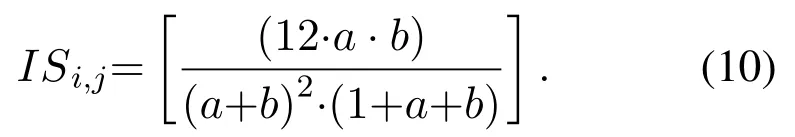
A result of the value of(p)will be used as a beta distribution-based analysis in order to participate in malicious node detection evaluations.
Trust update:The main nature of the trust is its dynamics.This means that the amount of trust increases or decreases over time,and it does not always have a fixed value.In fact,the amount of trust varies according to the number of transactions and the type of transactions[32].Due to the rapid and unpredictable behavior of a node,a node that was previously a faulty node might behave as a malicious node or a node that was previously normal becomes a faulty or malicious node after a while.Therefore,in order to have a secure network,the trust has to be updated after an event or over time.The direct trust of a node is updated by observing the direct behavior of nodes that are one-hop neighbor of nodes.Indirect trust is updated by recommendations from other nodes that observe the desired node behaviors and the update value of the beta distribution function is also carried out based on the data rate that is sent.Updating the trust value at time intervals Δt is undertaken as follows[27]:
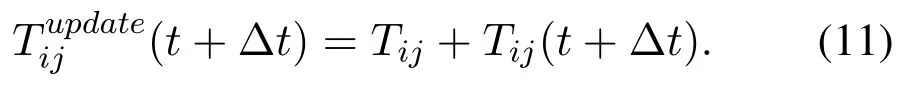
3.3.2 Multi Ant Colony and Rout Discovery
Humans have always looked to their environment for inspiration which is exemplified by the Ant Colony Algorithm.This algorithm is one of the best routing algorithms that works well in networks.The Ant Colony Algorithm is a type of metaheuristic algorithm used for problem optimization.Despite all the obstacles in nature,ants always choose the best way to find food.A moving ant leaves some pheromones on the surface of the earth determining the path with its smell.Subsequent ants are more likely to choose a path that has more pheromones when choosing a random path further amplifying the pheromones of this pathway.Thus,the probability of choosing a route increases.Ants also use a reaction called pheromone evaporation which refers to the evaporation and decrease of the amount of pheromone on the path over time.If previous ants select the wrong path,this pheromone will evaporate after a while resulting in subsequent ants not selecting the wrong path.This improves the choice of the final path[34].
The structure of network:To implement the current research,a network with n nodes randomly distributed in an n*n space was considered.The network can be represented as a nondirectional graph G(V,E)where V represents the set of all nodes in the network(V0,V1,V2,···,Vn)and E represents the set of edges.Each edge has instant weight which includes the amount of pheromone between two nodes.Each node contains information on for instance its neighbors and stores each neighbor’s ID in a list.It also includes communication and computational information,initial and residual energy,routing table,and neighbors’trust level.In this section,first,the routing process for a colony is described and then this method is implemented for several colonies.
Rout discovery:It was assumed that M ants work on the source node,initially all paths have the same initial pheromone,and all nodes have the same initial energy and trust.A node that wants to send data to a base station should choose a path that consumes less energy and has a higher trust.Initially,at node i,ant k selects node j to send data based on the following rules[28].
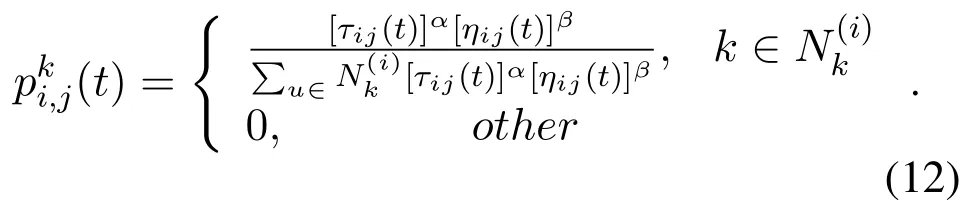
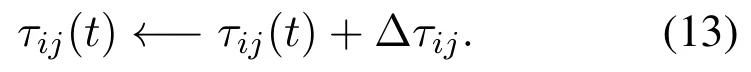
All the steps described are undertaken for all colonies resulting in the best paths in the colonies.In each colony,the best local path is created.The proposed algorithm re-evaluates the best paths found in each colony and finally,the best global route is chosen.After finding the best global route,the process of updating the pheromone(increasing the pheromone)is performed according to Equation(13).
Finally,the pheromone evaporation step is performed to prevent the rapid convergence of all ants to a suboptimal path.The concentration of pheromone paths is automatically reduced by the value ρ in each iteration.This causes the paths with less residual energy or misbehavior nodes to have less chance of being elected at the next step.This is Equation[28]for evaporation pheromone.
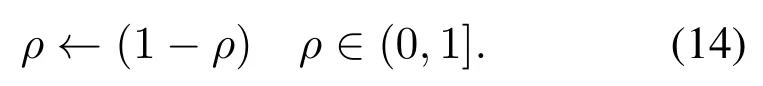
Rout evaluation and election of trusted rout:Evaluation of the found paths is obtained according to the CRF relationship where Ti,(t),the amount of trust for intermediate nodes of path is,Energy is the amount of remaining energy,and Hop count indicates the delay in the desired path.The best route is selected based on Equation(15).The other paths are stored as backup routes in the routing table source node.
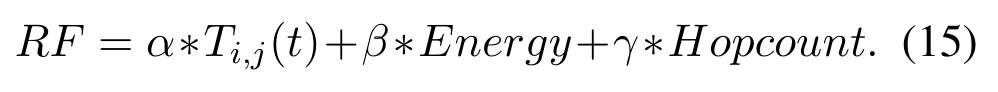
Then,the routing process will start from the main route.
Rout maintenance:At this stage,the path is replaced only if the previous path did not have its previous quality for reasons such as trust decreasing below the threshold caused by finding malicious nodes in the path or losing nodes in the path due to defective or exhaustion of energy.Thus,the new path already stored in the routing table must replace the previous path.
IV.SIMULATION
The proposed method(MACRAT protocol)was implemented in Matlab R2018b software in order to simulate and evaluate its performance compared to the ESRT protocol used in[27]and M-CSO protocol[32].MACRAT was compared and measured based on evaluating the changes of dependent variables.
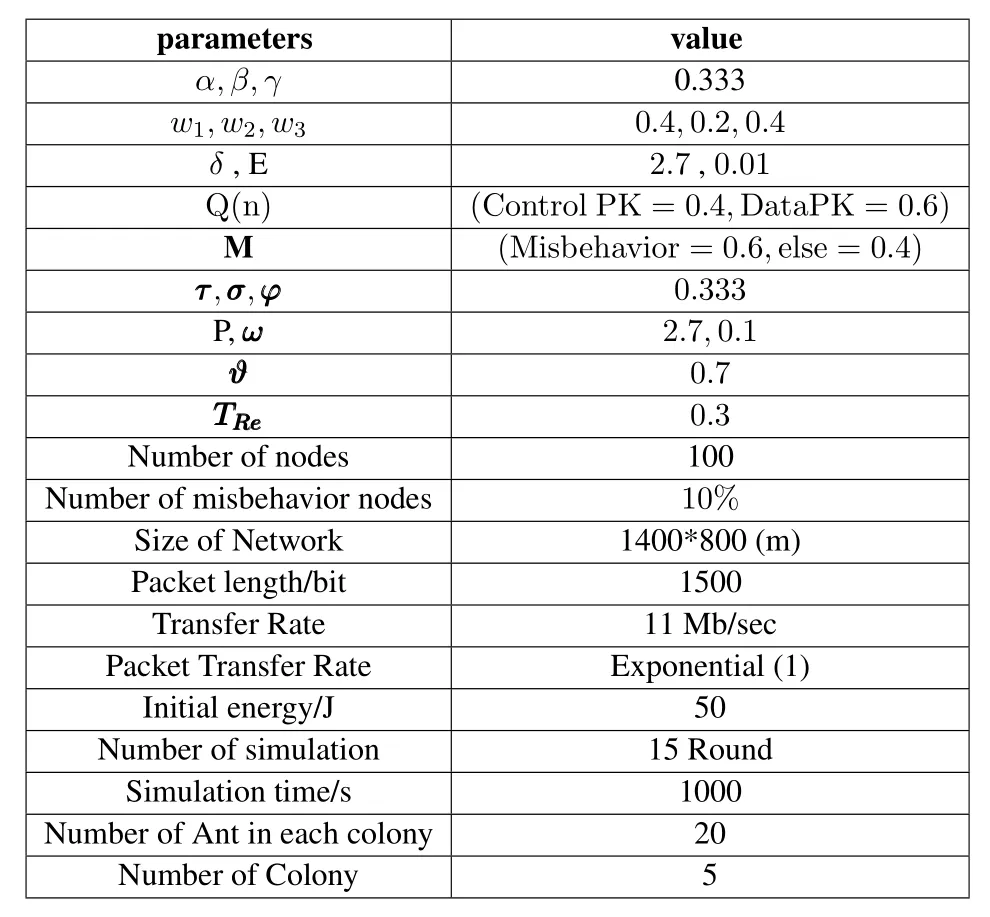
Table 2.Parameters for simulation.
In order to demonstrate the efficiency of MACRAT in implementing trust and detection and prevention of intrusive nodes,the performance of this protocol was evaluated and simulated with the presence of malicious nodes in wireless sensor networks.Indicators of packet loss rate,exchange latency,malicious nodes detection rate,error rate,transmitted data receiving rate,and wireless sensor networks throughput rate to measure the performance of the MACRAT protocol was compared to those of the ESRT protocol and M-CSO Protocol which presented as the simulation results.
Routing process latency means average of the time required by a data packet is generated by the node to reach the destination.Figure 1 shows the routing process latency in the proposed MACRAT protocol compared to the ESRT protocol and M-CSO protocol in the simulator.The proposed MACRAT protocol is based on how it operates in assessing and accurately detects malicious nodes and corneas in the network,and prevents disturbances related to these nodes during the routing process.The proposal MACRAT is based on self-organization that analyzes and examines the behavior of intermediate network sensors of important components such as variable trust over time,variable trust in the type of behavior and variable trust in the type of interaction.This appropriately identifies malicious nodes and excludes them from network operations in order to prevent negative consequences and occurrences of related failures in the interaction paths as much as possible.The average routing process latency in MACRAT, ESRT and M-CSO respectively are 34.47(ms),45.52(ms)and 35.71(ms).
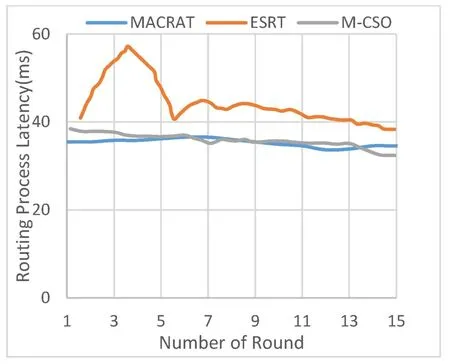
Figure 1.Routing process latency.
Figure 2 illustrates the error rates and failures of network interaction paths in the proposed MACRAT protocol compared to the ESRT and M-CSO protocols.This criterion specifies the number of errors found in the network while packet sending.The error rate increases when an attack occurs in the network.When one node is malicious and other nodes receive data from it,the error rate goes up and the path is damaged.The degree of errors encountered during data transmission over a communications or network connection.The higher the error rate,the less reliable the connection or data transfer will be.In the proposed method,the error rate is reduced compared to ESRT and MCSO protocols in the simulator.And that means improving in the proposed method.The average error rate in MACRAT,ESRT and M-CSO respectively are 29.19(bps),41.41(bps)and 35.71(bps).
Figures 3 and 4 show the packet loss rate and network interaction latency in the proposed MACRAT protocol compared to the ESRT protocol,respectively.
Packet loss rate means the fraction of sent data packets not received at their destination.Due to the fact that the proposed protocol uses a special mechanism to gain the trust of the nodes,so,trusted routes for sending data are selected and fewer malicious nodes are placed in the route,and as a result,the packet loss rate is lower.The average Packet loss rate in MACRAT,ESRT and M-CSO respectively are 32.41%,42.40% and 34.44%.
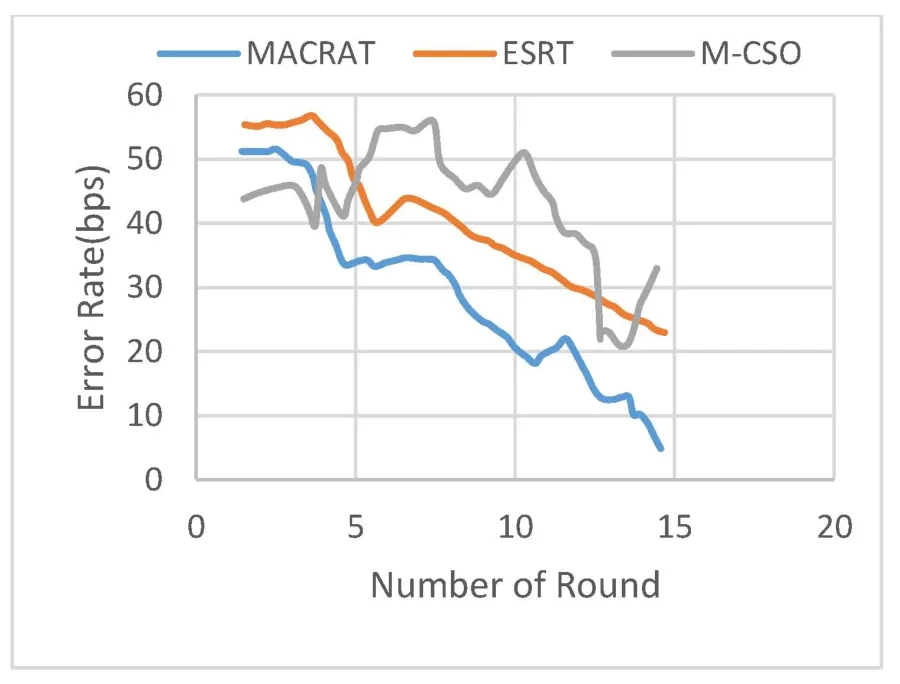
Figure 2.Error rates and failures of network interaction paths.
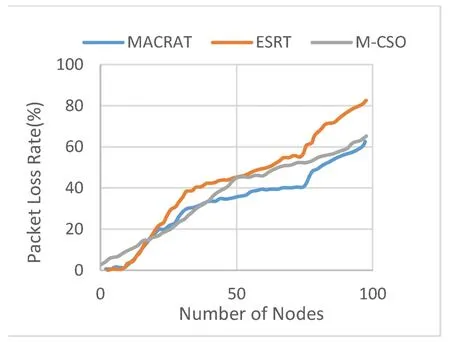
Figure 3.Packet loss rate.
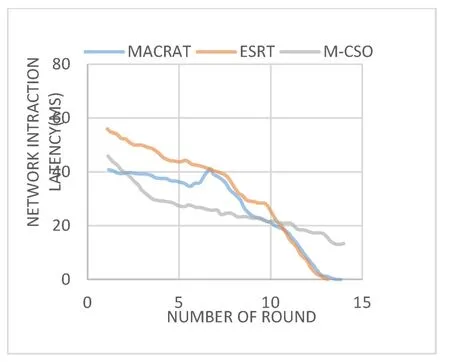
Figure 4.Network interaction latency.
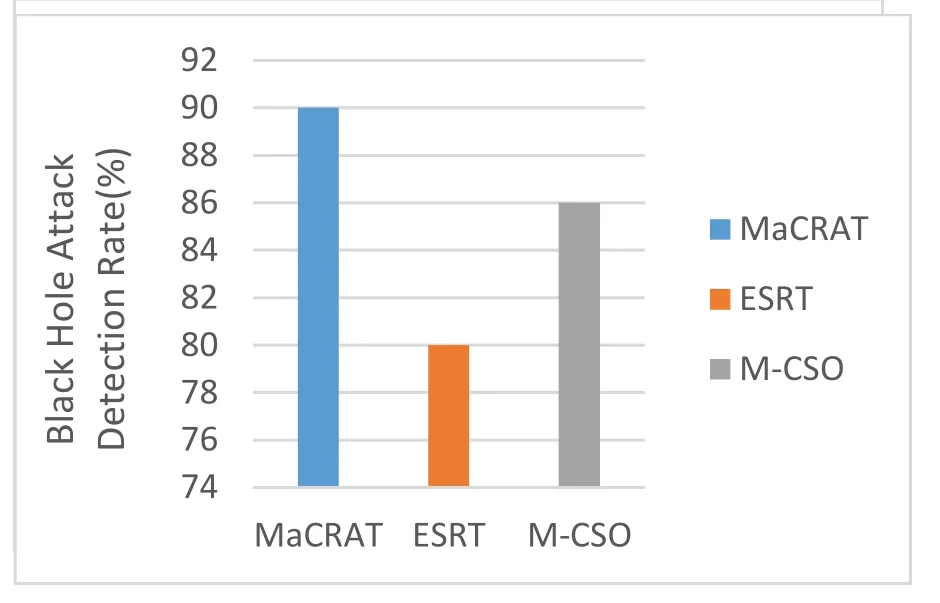
Figure 5.Percentage and detection rate of malicious nodes.
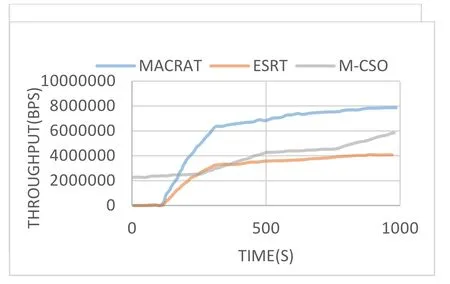
Figure 6.Network throughput rate results.
Network interaction latency means the average time of interactions that one node needs with other nodes to evaluate the value of trust of neighboring nodes.The average Network interaction latency in MACRAT,ESRT and M-CSO respectively are 27.33(ms),34.02(ms)and 26.87(ms).MACRAT is designed and organized as per its performance in relation to direct observations.It evaluates direct observations in a variable and adaptable way with time,place of interaction,punishment and encouragement of the variable,and negative intrusive behaviors.Recourse to past trust,relying on low-value interactions and positive behaviors are avoided well.It also provides the degree of certainty of the calculations relative to the relative knowledge associated with the indirect observations received,increases its capability for identifying malicious nodes by sending conflicting recommendations related to exchanges and sharing of indirect observations.Finally,on the centrality of the beta distribution,the comparison of the routing tables obtained in the ant movement provides the correct behavior of the nodes with double accuracy based on measuring the accuracy of the behavior and not determining the behavior.The existence of the mentioned factors and the design of the proposed protocol according to the introduced principles led to the best possible identification of malicious nodes with knowledge of how to attack these types of nodes and the characteristics of trust in the network.The diagrams shown in Figure 5 demonstrate the percentage and detection rate of malicious nodes in the proposed MACRAT protocol compared to the ESRT and M-CSO protocols in the simulator.As you see,according to the solution that the proposed method uses in identifying malicious nodes,the percentage of malicious nodes detection in this method is higher than the compared methods.The Network throughput rate results are shown in Figure 6 for the three protocols being compared.Throughput is one of the critical metrics to assessment the performance of the network.As you can see,the proposed method shows better results compared to the two mentioned protocols,and this is due to the efficiency of the proposed method in calculating the trust of nodes and detecting malicious nodes,as well as using multi colonies instead of one colony in routing.As a result,by identifying malicious nodes,they are isolated and no data is sent to them,thus increasing the efficiency of the entire network in routing using trusted nodes.The average throughput in MACRAT,ESRT and M-CSO respectively are 5052695(bps),2597746(bps)and 3725757(bps).
V.CONCLUSION
Due to the importance of the two factors of routing and security in wireless sensor networks,in this paper,a high security routing algorithm using a multicolony model is presented.In the proposed algorithm,using the detection of malicious nodes and the improvement of variable validity parameters over time,the validity of variable interactions,and mechanisms to investigate the history of positive and negative behavior of nodes are presented.The general steps of the MACRAT protocol are categorized as the evaluation of direct observations,indirect observations,beta distribution analysis and development routing function based on the construction of several colonies of the ant algorithm.The findings the proposed protocol evaluations demonstrate that the error rate and path failure in this algorithm significantly decreased compared to ESRT.In addition,the packet reception rate increased.Utilizing the benefits of techniques such as fuzzy sets for routing decisions and measuring trust is also recommended for future research due to the multi-criteria decision-making factors.
- China Communications的其它文章
- A Key Management Scheme Using(p,q)-Lucas Polynomials in Wireless Sensor Network
- Pilot Allocation Optimization Using Enhanced Salp Swarm Algorithm for Sparse Channel Estimation
- Put Others Before Itself:A Multi-Leader One-Follower Anti-Jamming Stackelberg Game Against Tracking Jammer
- DCGAN Based Spectrum Sensing Data Enhancement for Behavior Recognition in Self-Organized Communication Network
- On Treatment Patterns for Modeling Medical Treatment Processes in Clinical Practice Guidelines
- Hybrid Recommendation Based on Graph Embedding

