路径化床边健康宣教在结核性胸膜炎患者中的应用效果研究
林立华 傅根莲 沈炎琴 石燕 周日花


[關键词] 临床路径;健康宣教;结核性胸膜炎;应用研究
[中图分类号] R473.5 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)22-0172-04
Application effect study of pathway bedside health education in patients with tuberculous pleurisy
LIN Lihua FU Genlian SHEN Yanqin SHI Yan ZHOU Rihua
Department of Tuberculosis,Zhejiang Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine,Hangzhou 310003, China
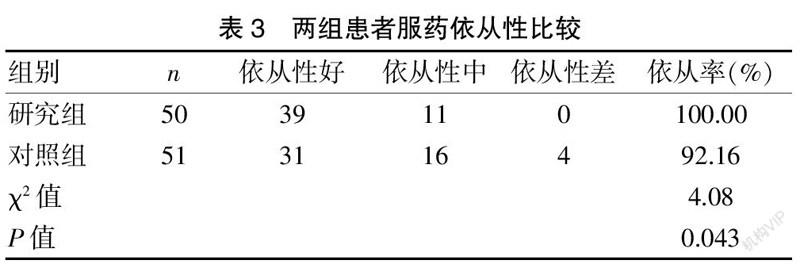
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the application effect of pathway bedside health education in patients with tuberculous pleurisy. Methods A total of 106 patients with tuberculous pleurisy admitted to the Department of Tuberculosis in our hospital from February 2018 to October 2019 were selected as the research objects,and were divided into two groups according to the convenient sampling method,with 53 patients in each group.The control group was treated with the traditional health education method and routine nursing,while the research group was treated with systematic health education according to the time on the pathway bedside health education execution sheet on the basis of routine nursing.The incidences of unplanned extubation, mastery of health education knowledge,patient satisfactions,and medication compliances after discharge were observed in the 2 groups. Results The incidence of unplanned extubation was 0 (0/42) in the research group, which was lower than 5.71% (2/35) in the control group, and no statistically significant difference was observed between the two groups (P>0.05). The mastery rate of health education knowledge in the research group was 98.11% (52/53), which was higher than 86.79% (46/53) in the control group,and the difference between the two groups was statistically significant (P<0.05). The satisfaction rate of the research group was 96.23% (51/53), which was higher than 84.91% (45/53) of the control group, and the difference between the two groups was statistically significant (P<0.05). The drug compliance rate of the study group was 100.00% (50/50) after discharge, which was higher than 92.16% (47/51) of the control group,and the difference between the two groups was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion The application of bedside health education alone to carry out pathway health education for patients with tuberculous pleurisy can improve the satisfaction of inpatients, the mastery of health education knowledge, and the compliance of medication.

