A Counterexample on H1 ⊊ in Martingale Theory
Tian Hongli Long Long
(School of Mathematics and Statistics,Central South University,Changsha 410083,China)
Abstract As we have already known that when 1 Key words Martingale space Levi martingale Hardy space Apply this space as a transition,Burkholder and Gundy[1,8]proved the following relationship Burkholder-Gundy’s result shows that the martingale maximal operatorMand the martingale square function operatorShave equivalentLpnorms when 1 And this will make it a little bit easier to talk about the properties of these spaces in the future whenp=1. At the end of this section,we make some conventions.Throughout this paper,Z and N denote the integer set and nonnegative integer set,respectively.We denote byCthe absolute positive constant,which can vary from line to line.The symbolA≲Bstands for the inequalityA≤CB.If we writeA∼B,then it stands forA≲B≲A. In this section,we introduce some standard notations from the martingale theory.We refer to [7,16,19]for the classical martinale space theory.Suppose that(Ω,F,P) is a complete probability space.Let (Fn)n≥0be an increasing sequence of subalgebras ofFsuch thatF=σ(∪n≥0Fn),and let Endenote the conditional expectation operator relative toFn.An adapted sequence of measurable functionsf=(fn)n≥0⊂L1(Ω)is called a martingale with respect to(Fn)n≥0if En(fn+1)=fnfor everyn ≥0.For a martingalef=(fn)n≥0,denote△nf=fn −fn−1,n ≥0(with conventionf−1=0). Example 2.1The dyadic martingale is a typical and important example of martingale theory.Let([0,1),B,dx)be the Lebesgue probability space,with the family{Fn}n≥0generated as Then all the martingales with respect to such(Ω,F,µ,{Fn}n≥0)are called the dyadic martingales.They are nothing but the 2n-partial sum of the Walsh expansion where the dyadic expressionxt=(y1,y2,···),x=(x1,x2,···),t=(t1,t2,···)satisfyyj=xjtjfor allj,withaddition module 2,and Thus,we have We have connected the dyadic martingales with the Walsh expansions. This connection remains ture for the Rademacher system{rn(t)}n≥1 Let(an)n≥1be a sequence,and It is obvious that (fn)n≥0is an adapted process with respect to{Fn}n≥0.From En(rn+1(t))=0,we have So,(fn)n≥0is a martingale with respect to{Fn}n≥0. Finally,we have which implies thatfH1. In this section,we give the the weak type results forp=1. Let (Ω,F,P) be a complete probability space.As is well-known,the weakLpspace,denoted bywLp,is defined as the set of allP-measurable functionsfsuch that and the wake spacewL∞is justL∞.It is easy to see that thewLpis a quasi-normed linear space for 0 Now,we introduce the definition of martingale weak spaces as follows:1 Introduction
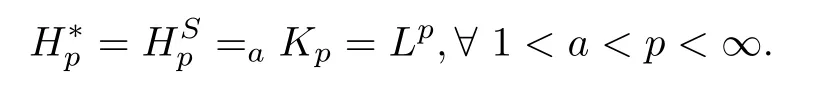

2 Preliminaries
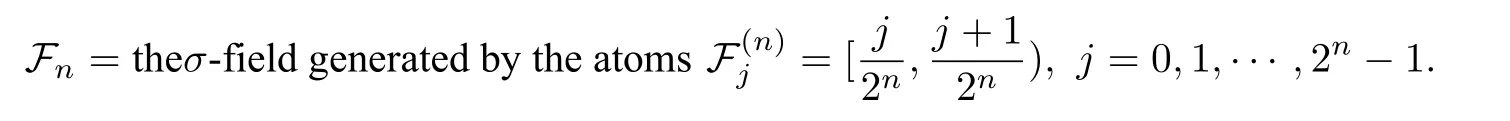



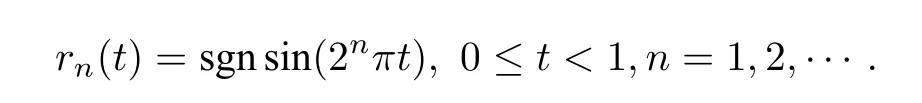
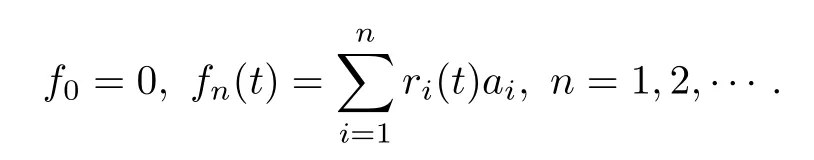



3 The main result




4 Weak type results for p=1




