Looped,Broad,and Deep Buried Suturing Technique for Wound Closure
Xuwen TANG ,Yong ZHANG ,Liu YANG,Dongyun YANG
Department of Chongqing Kewei Scar Medical Institute/Dongshang Medical Aesthetic Clinic,Chongqing 400038,China
# XW T and Y Z contributed equally to this work and shared co-authorship.
ABSTRACT This study explores the clinical application of the circular wide and deep (looped,broad,and deep buried,LBD) suture technique for scar resection and examines its clinical effectiveness for scar treatment.From June 2017 to March 2019,a total of 68 patients with scars were sutured using LBD technique,and recovery was achieved 24 months postoperatively.In all 68 patients,postoperative scars were slightly evident in two cases of cervical scar,one case of leg scar,and one case of chest scar.In addition,the remaining 62 patients were completely satisfied with the outcome.The LBD suturing technique could provide sustained and stable tension-reducing effects postoperatively and significantly improve scar formation in patients.This method is most applicable to incisions with tension.Therefore,it should be more widely used for clinical scar treatment.
KEY WORDS Suture technology;Looped,broad,and deep buried suturing technique;Scar resection;Cosmetic technology
INTRODUCTION
Wound closure is one of the most common surgical procedures.Among the factors affecting the quality of wound healing and scar formation in later stages,wound tension is one of the most critical factors.Therefore,many scholars have already developed methods to reduce wound tension[1];however,these methods are still insufficiently effective.
The traditional wound closure method involves a layered suture of the subcutaneous tissue and dermis,with the skin edge closed before suturing the skin surface.However,the tension is mainly concentrated near the wound,which likely causes local pigmentation,widening,and even hyperplasia.
To address this issue,a new type of suture technique,the looped,broad,and deep buried (LBD),was applied.The innovation of this technique comes from horizontal mattress sutures[2-3]with the following surgical procedures:Ⅰ) A blade is used to pierce the skin at the marked point.The distance between the points on the same side is approximately 0.5-1.0 cm,and the distance between each point and the wound is approximately 0.5-1.0 cm;Ⅱ) 3-0 or 4-0 absorbable sutures are selected according to the skin tension,and the needle is entered from the wound,exited from the marked point at one side,and then inserted into the original position from the exit point.The needle is inserted into the entire skin layer into the lower layer of the dermis and then back to the second point on the same side to exit the needle,which is then inserted in situ from this point,penetrating the entire skin layer to the lower layer of the dermis;Ⅲ) the same procedure is performed between two points on the opposite side of the cutting edge to form a rectangular-like trajectory (note:between the two points on the same side,the needle is arced in the shallow layer of the dermis to disperse the skin tension and minimize the skin depression at the needle point) (Fig.1);Ⅳ) the sutures are pulled on both sides to tie the knots.Care should be taken to ensure that bilateral skin edges can be completely tightly aligned,and thus,a slight tendency for eversion may occur.The suture knot is buried deep under the skin after the suture;Ⅴ) after making the skin on both sides of the wound completely tension-free,butted,subcutaneous,intradermal,and epidermal sutures are routinely performed.
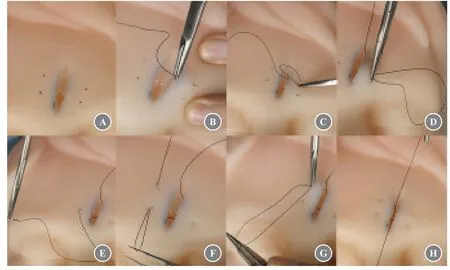
Fig.1 LBD suture technique.(A) Use a blade to pierce the skin at the marked point.(B) Enter the needle from the wound.(C) Exit the needle from the marked point on one side,enter the needle into the original position from the exit point,and then penetrate the entire skin layer to the lower layer of the dermis.(D) Return to the second point on the same side to exit the needle,enter the needle in situ from this point,and then penetrate the entire skin layer to the lower layer of the dermis.(E) Exit the needle from the marked point on the other side.(F) Penetrate the entire skin layer to the lower layer of the dermis and then return to the second point on the same side to exit the needle.(G) Enter the needle in situ from this point and then penetrate the entire skin layer to the lower layer of the dermis to form a rectangular-like trajectory.(H) Pull the sutures on both sides to tie knots.The suture knot is buried deep under the skin after suturing.
CASE PRESENTATION
A total of 68 patients with scars underwent LBD suturing.This prospective split-scar clinical trial was conducted between December 2017 and September 2020.The follow-up time was 24 months,and 62 patients were satisfied with the procedure.This technique is suitable for areas with high tension and wide scars.The use of LBD suture technology can effectively prevent long-term scarring caused by excessive tension and improve suture exposure and pigmentation.This method can effectively shorten the operative time and minimize postoperative scar hyperplasia.If combined with other comprehensive treatment methods postoperatively,the patient will achieve satisfactory improvement.
Case 1
A 31-year-old man developed a long scar on the left side of his face after a trauma that lasted for nearly 21 years (Fig.2A).The surgery used multilevel hypertension reduction sutures,including the LBD suturing technique.The patient voluntarily participated in this study.According to the preoperative agreement,he would not perform any postoperative care to relieve tension but relied on natural recovery.The suture was removed 5 days postoperatively,and the incision healed well at the time of suture removal.The following figure shows the recovery effect at the 24-month follow-up postoperatively (Fig.2B).The patient was very satisfied with the results and did not receive any photoelectric treatment postoperatively.
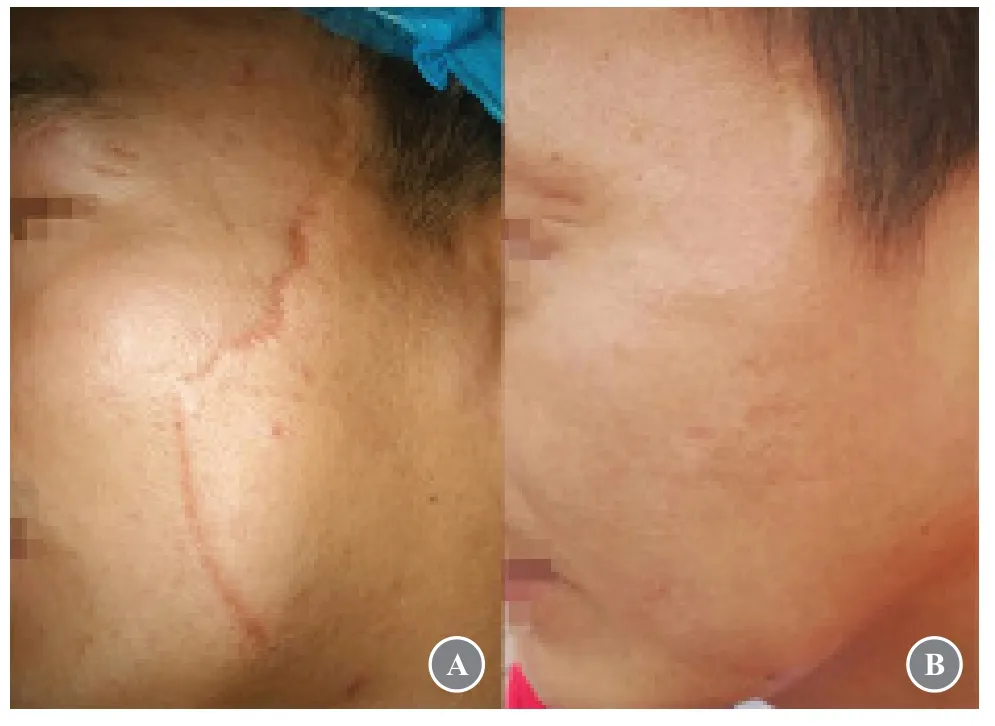
Fig.2 Application of LBD suture technique in wound suture.(A) Preoperative appearance.(B) Appearance after 24 months.
Case 2
A 40-year-old man developed a long scar on the left side of his face after a trauma that lasted for nearly 10 years (Fig.3A).The surgery adopted multilevel hypertension reduction sutures,including the LBD suturing technique.The patient also voluntarily underwent the procedure.According to the preoperative agreement,he would not perform any postoperative care to relieve tension but relied on natural recovery.The suture was removed 5 days postoperatively,and the incision healed well at the time of suture removal.The following figure shows the recovery effect at the 24-month follow-up postoperatively (Fig.3B).The patient was very satisfied with the results and did not receive any photoelectric treatment postoperatively.

Fig.3 Application of LBD suture technique in wound suture.(A) Preoperative appearance.(B) Appearance after 24 months.
Case 3
A 32-year-old woman developed a long scar on the right side of her face after a trauma that lasted for nearly 5 years (Fig.4A).The surgery adopted multilevel hypertension reduction sutures,including the LBD suturing technique.The patient voluntarily participated in this study.According to the preoperative agreement,she would not perform any postoperative care to relieve tension but relied on natural recovery.The suture was removed 5 days postoperatively,and the incision healed well at the time of suture removal.The following figure shows the recovery effect at the 24-month follow-up postoperatively (Fig.4B).The patient was very satisfied with the results and did not receive any photoelectric treatment postoperatively.
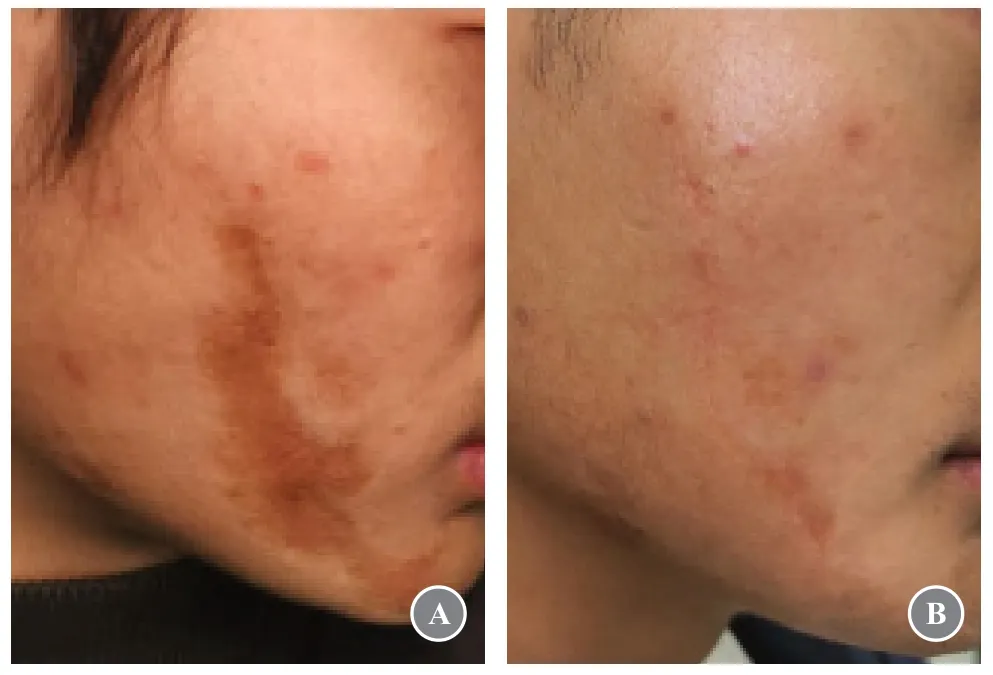
Fig.4 Application of LBD suture technique in wound suture. (A) Preoperative appearance.(B) Appearance after 24 months.
DISCUSSION
Incision sutures are the most common surgical procedures.If the suture technique is not good,it may lead to poor healing and obvious scar hyperplasia in later stages.Among the factors that affect the quality of incision healing,the degree of tension around the postoperative incision is the most important factor affecting incision healing and postoperative scar formation[4].If the tension on both sides of the wound cannot be effectively reduced,the continuous tension acting on both sides of the wound aggravates the local inflammation,induces the proliferation of new blood vessels,accelerates the collagen synthesis,and causes scar widening and redness.This pathological process can continue for several months or more[5-6].Therefore,improving the tension reduction suture technique and minimizing the tension around the postoperative incision are the focus of research on the prevention and treatment of scars.
To reduce the tension around the incision postoperatively and to prevent scar re-proliferation and widening postoperatively,necessary and sufficient subcutaneous sutures must be performed intraoperatively.In the traditional layered suture,tension mainly concentrated around the incision,which can easily cause scar hyperplasia.Therefore,this condition has been improved by several surgeons.Zhang et al.[7]further improved this technique:by embedding the stitches at the junction of the dermis and the subcutaneous layer and preventing the sutures from being exposed,the incisions can be better aligned,resulting in better results.Liu et al.[8]applied a modified buried vertical mattress suture to relieve wound edge tension.These studies have revealed that the recovery effect of subcutaneous implant sutures is better than that of simple intradermal sutures[9].
Nevertheless,for incisions with high tension,these methods have certain limitations.In the case of high tension,the subcutaneous tension-reducing suture has a certain“cutting”effect on the soft tissue within a certain period of time after the suture,resulting in weakened tension reduction of the suture.To overcome the shortcomings of the existing tension reduction methods,the author began to apply a new tension reduction suture technology-LBD tension reduction suture technology since 2017,that is,the deep-embedded annular mattress suture technology.The idea of LBD tension-reducing suture technology originated from the horizontal mattress-type tension-reducing suture in general surgery[10].The stitched part passes through the dermis to retain the original horizontal mattress,which effectively reduces tension and simultaneously prevents skin damage and secondary scar formation caused by external stitching.It can absorb the use of sutures and greatly extend the indwelling time[3];thus,it can be more effective and sustainably reduce the tension of the incision,reduce the wound surface,and improve the long-term outcomes of scar repair surgery.The three typical cases in this article were followed up for 24 months,during which no radiotherapy was performed.The patients were satisfied with their current recovery status.
As surgeons continue to innovate in clinical practice,more and better scar repair techniques are applied to scar plastic surgery and treatment[11].This study believes that the LBD technique has a stable and reliable effect of reducing tension and simple operation and can provide a more sustained and stable effect of reducing tension,especially for wounds with greater tension,which has a more significant effect on the formation of postoperative scars.
ETHICS DECLARATIONS
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
The need for ethical approval was waived as it was a case report.All participants provided written informed consent before study enrolment.
Consent for Publication
All the authors have consented to the publication of this article.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.The authors state that the views expressed in the submitted article are their own and not the official position of the institution of funder.
 Chinese Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery2021年2期
Chinese Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery2021年2期
- Chinese Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery的其它文章
- The Practice of China’s Cosmetic Medicine Dated Back to 3 800-4 800 Years Ago
- Progress in Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction:What Do We Know?
- Electric Field:A Key Signal in Wound Healing
- Mechanisms and Management of Postparalysis Facial Synkinesis
- A Novel Composite Skin Graft Technique with Fat Derivatives
- A Case of Congenital Syringocystadenoma Papilliferum
