A Novel Composite Skin Graft Technique with Fat Derivatives
Yixiang ZHANG,Bin FANG,Yun XIE
Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital,Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine,Shanghai 200011,China
ABSTRACT Skin grafting,although a relatively classic and well-known technique,still has multiple disadvantages such as secondary contracture of the skin graft,sunken depression,poor elasticity,and color mismatch.Adding adipose tissues significantly improved the graft appearance compared to traditional skin grafting methods.Herein,we report two cases of modified skin graft procedures,both showing positive outcomes.In case 1,a mechanically processed fat-derived product was injected into the lower half of the skin graft area.In case 2,left upper eyelid blepharoplasty was performed,and the orbital fat strip was transferred and placed under the recipient area on the right side.Hair growth was observed only in case 1,whereas the extent of sunken depression was significantly reduced in both cases.Compared to traditional skin grafting methods,adding fat components to the skin graft recipient area improved the appearance and blood supply,together with enhancing the regenerative rate.
KEY WORDS Skin grafting;Fat derivatives
INTRODUCTION
Skin grafting,a classic plastic surgery technique,is used to treat skin defects that cannot be covered by direct draw sutures.Two common skin graft procedures are available:split-thickness skin graft (STSG) procedures,which involve the entire epidermis and only a variable thickness of the dermis,and full-thickness skin graft (FTSG) procedures,which involve the epidermis and the whole thickness of the dermis,resulting in less secondary contraction than that in STSG procedures.STSG procedures are indicated for resurfacing large wounds,cavities,mucosal defects,muscle flap coverage,and temporary wound closure after tumor extirpation.They also reduced donor-site morbidity and relatively fast regrowth of the new skin.Conversely,FTSGs are indicated for small,uncontaminated,and well-vascularized wounds,which are generally preferred in cosmetic and functionally sensitive sites.Although skin grafting is a relatively well-known technique,several issues such as secondary contracture of the skin graft,sunken depression,poor elasticity,and color mismatch still occur.Improved skin grafting outcomes have been reported by preserving the adipose tissues and applying stromal vascular fraction (SVF) to skin grafts[1-2].Here,we present two patients who underwent skin grafting to which adipose tissues were added.Case 1 patient was injected with a mechanically processed fatderived product,and case 2 patient had a free septum orbital fat strip placed under the free skin graft.A brief account of these two techniques is given below.
CASE PRESENTATION
Case 1
Case 1 was that of a 29-year-old man with skin defect on his left arm requiring skin grafting.A mechanically processed fat-derived product,similar to nano-fat but preserves more live adipocytes,was injected under the skin graft into the lower half of the skin graft area.As compared to the upper half of the skin graft area not injected with the mechanically processed fat-derived product,the resultant skin color closely matched that of the recipient area and more hair growth was observed (Fig.1).
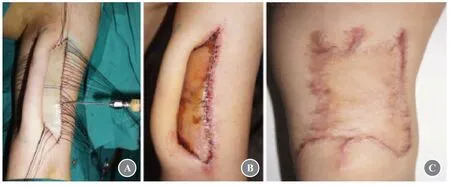
Fig.1 Photos of case 1.(A) Mechanically processed fat-derived product was injected into the lower half of the full-thickness skin grafting area.(B) Appearance after skin grafting.(C) Appearance 6 months postoperatively.
Case 2
Case 2 was that of a 19-year-old girl who presented to the hospital with a contracture scar at the right frontal and eyebrow areas.The right eyebrow and right upper eyelid were raised.Blepharoplasty of the left eyelid was performed under local anesthesia.Left orbital fat and excess skin (approximately 30 mm × 4 mm) were removed.The frontal scar at the upper board of the right eyebrow was released to correct the raised right upper eyelid,which showed a defect of approximately 30 mm × 4 mm,requiring a skin graft.The free orbital fat strip and FTSG from the left upper eyelid were transferred separately to the recipient area.Sutures and secure pressure bandaging were applied over the surgical site to hold the skin graft and fat tissues in place.After one week,the skin graft showed positive signs of survival (Fig.2).
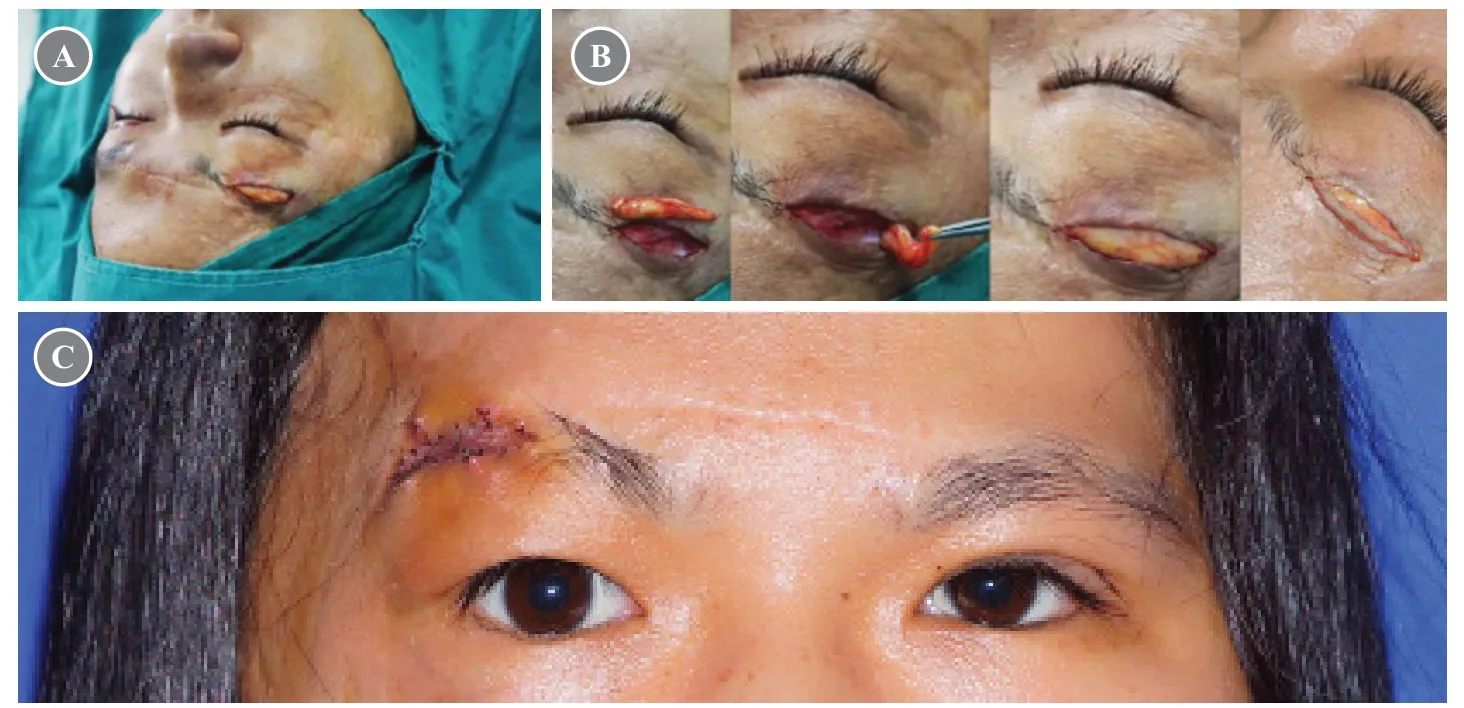
Fig.2 Photos of case 2.(A) The frontal scar from the upper board of the right eyebrow was released to correct the raised right upper eyelid,which showed a defect of approximately 30 mm × 4 mm,requiring a skin graft.(B) The free orbital fat strip and a full-thickness skin graft from the left upper eyelid were transferred separately to the recipient area.(C) Appearance after stitch removal.
DISCUSSION
In both cases,fat tissues were placed under the skin graft,yielding satisfactory results.Despite a slight difference between the two cases,improved skin elasticity,texture,and color were observed.However,the outcome of case 1 was superior due to signs of increased regeneration.The survival of skin grafts requires sufficient blood supply.Some common complications such as skin necrosis or partial necrosis may occur if the blood supply is adversely affected by the subcutaneous hematocele and effusion;if the recipient area lacks blood supply,such as bones or tendons;or if the recipient area has been subjected to radiotherapy.Hypoxia caused by insufficient blood supply can lead to cell necrosis and immune cell activation,which release a series of pro-inflammatory factors.However,the addition of fat derivatives can regulate the microenvironment via growth factors and cytokines,thus playing a therapeutic role in the ischemic model.This was confirmed by injecting fat derivatives,resulting in significantly increased vascular endothelial growth factors,transforming growth factor beta,and fibroblast growth factors.Furthermore,adipose-derived stem cells in fat derivatives can differentiate into endothelial cells,activate the interleukin 6 (IL-6) pathway,and promote angiogenesis[3].Nano-fat,a fat derivative,has abundant stem cells and SVF successfully isolated by Tonnard et al.Angiogenic factors and stem cells in nano-fats contribute to the formation of new blood vessels and promote skin regeneration[4].In addition,recent studies have shown that nano-fat can promote collagen production in the dermis,increasing the microvessel density,promoting epidermal cell proliferation,and thus enhancing the survival rate of fat transplantation[5].However,wound blood vessels may directly penetrate the skin graft from the wound due to the nano-fat diluted liquid rather than the semi-solid and semi-liquid state of general fat.Characteristics of the mechanically processed fat-derived product used in case 1 were similar to those of the combination of nano-fat and micro-fat.It not only has abundant SVF,stem cells,and angiogenic factors,but also protects adipocytes that act as a filler.These factors,as a result of co-transplantation with mechanically processed fat-derived products,enhance the survival of skin grafts.Free fat tissues require sufficient blood from the recipient site for survival.Given that orbital fat itself contains blood vessels and the blood supply of orbital fat is superior to that of other types of fat,it may sustain itself and supply blood to the superficial graft.The success of both cases depends on adequate blood supply.
This novel composite skin graft technique is recommended to improve the texture of the skin graft recipient area,especially where pit and scar contractures are likely formed.
ETHICS DECLARATIONS
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
N/A
Consent for Publication
All the authors have consented to the publication of this article.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.The authors state that the views expressed in the article are their own and not of the official position of the institution or funder.
 Chinese Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery2021年2期
Chinese Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery2021年2期
- Chinese Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery的其它文章
- The Practice of China’s Cosmetic Medicine Dated Back to 3 800-4 800 Years Ago
- Progress in Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction:What Do We Know?
- Electric Field:A Key Signal in Wound Healing
- Mechanisms and Management of Postparalysis Facial Synkinesis
- Looped,Broad,and Deep Buried Suturing Technique for Wound Closure
- A Case of Congenital Syringocystadenoma Papilliferum
