Novel technique of extracorporeal intrauterine morcellation after total laparoscopic hysterectomy: Three emblematic case reports
Antonio Macciò, Elisabetta Sanna, Fabrizio Lavra, Piergiorgio Calò, Clelia Madeddu
Antonio Macciò, Elisabetta Sanna, Fabrizio Lavra, Department of Gynecologic Oncology,Businco Hospital, ARNAS G. Brotzu, Cagliari 09100, Italy
Piergiorgio Calò, Department of Surgical Sciences, University of Cagliari, Cagliari 09100, Italy
Clelia Madeddu, Department of Medical Sciences and Public Health, University of Cagliari,Cagliari 09100, Italy
Abstract BACKGROUND In the presence of a large uterus, total laparoscopic hysterectomy (TLH), always requires morcellation to allow removal of the tissues from the abdominal cavity.However, uncontained morcellation has been scrutinized because of the possible spread of occult leiomyosarcoma. Therefore, in-bag extracorporeal morcellation has been developed. However, tissue containment and extraction are extremely challenging, especially when considering the increasing uterine size to be removed through minimally invasive surgery.CASE SUMMARY Herein, we describe a novel technique for extracorporeal intrauterine morcellation using the uterus outermost layer as a bag to achieve tissue extraction of very large uteri with suspected occult leiomyosarcoma after TLH. The study enrolled patients who were planned for TLH for large uteri (weight > 500 g). TLH was performed following the procedure reported in our previous studies. The novel technique has been described step-by-step in a video, which representatively describes the preoperative imaging and morcellation procedure of three very large uteri weighing 1500 g, 1700 g, and 3700 g, respectively. The procedures were performed without any complications. The patients had an uneventful postoperative course, and in all cases, the pathology was benign leiomyoma.CONCLUSION Extracorporeal intrauterine morcellation using the uterus outmost layer as a bag was found to be a feasible technique that allows a careful diagnosis and safe removal of suspected occult malignancies. The technique herein presented may be adopted in surgical practice, by adding it to the other available techniques of contained morcellation. It may represent a valid and feasible alternative,especially useful in cases of very large uteri exceeding the capacity of specimen retrieval bags.
Key Words: Laparoscopy; Minimally invasive surgery; Morcellation; myomas; Large uterus; Total laparoscopic hysterectomy; Case report
INTRODUCTION
In the presence of large uteri, minimally invasive surgeries, always require morcellation to reduce the uterine size and thereby allowing removal of the tissues through small incisions or with laparoscopic instruments. Over time several approaches have been developed for morcellation. It was at first executed manually utilizing scissors or scalpels throughout vaginal and mini-laparotomy approaches; thereafter, in 1993 an electromechanical morcellator was introduced and gained popularity for its efficiency and time and cost-saving[1]. Different techniques have been also reported to aid uterine tissue removal including bivalving, wedge resection, coring, and the “EXCITE”or “extracorporeal C-incision tissue extraction” technique[2,3]. Transvaginal morcellation or by a posterior colpotomy has been additionally described and can represent a suitable option[4]. However, the uncontained morcellation of the uterus and myomas have been inspected owing to the potential dissemination of occult leiomyosarcoma[5]. Given this potential risk in 2014, the Food and Drug Administration warned against the utilization of laparoscopic power morcellation in case of laparoscopic hysterectomy or myomectomy for presumed benign uterine myomas[6] and recommended the use of contained morcellation systems[7]. The employment of containment bags as a supplement to power morcellation has been recommended to restrict tissue spreading during the tissue extraction[8]. Such procedure was firstly described by Shibley[9] that used power morcellation to remove a uterus inside a bowel isolation bag. Different authors described feasible variants of such procedure,without major complications[10-14]. Retrospective studies showed that contained power morcellation necessitates an extra operative time of 20-26 minutes in comparison to uncontained power morcellation, with similar postoperative results[15,16]. A lot of these studies on contained power morcellation utilized bags not strictly developed for this specific intention[17]. Then, different containment tools have been developed to aid laparoscopic power morcellation, such as the Pneumoliner, the More-Cell-Safe[18] and the MorSAfe[19] in-bag contained power morcellation systems. Also,in case of manual morcellation the use of containment bag is important to limit tissue spillage and a variety of tissue containment bag have been employed with feasibility[4,13,20,21]. However, the majority of containment bag have not been specifically labeled for the indication of manual morcellation[17].
Then, the tissue containment and extraction have become extremely challenging,especially when considering the increasing uterine size to be removed through minimally invasive techniques. Notably, for some large masses, there are not large enough endobags to fit them in for extraperitoneal morcellation. Consistently, the American Association of Gynecologic Laparoscopists (AAGL) Practice Report highlighted that the use of specimen retrieval pouches should be investigated further[22]. With this background, here we aim to describe a new technique for extracorporeal intrauterine morcellation utilizing the uterus outermost layer as a bag to achieve tissue extraction of large myomatous uteri.
CASE PRESENTATION
Chief complaints
Case 1:The patient referred progressive increase in abdominal circumference.
Case 2:At admission patient referred progressive increase in abdominal circumferences associated with constipation and swallowing problems
Case 3:The patient came to our attention complaining symptoms related to an enlarged uterus,i.e., constipation, swallowing difficulties, increasing dyspnea, and pain, accompanied by ongoing enlargement of abdominal circumference.
History of present illness
Three patients were candidates to undergo total laparoscopic hysterectomy (TLH) for large fibromatous uteri (weight > 500 g) and were referred to our tertiary referral center, Department of Gynecologic Oncology, Azienda Ospedaliera Brotzu, Cagliari.The study was carried out following the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.According to the Italian Regulatory Agency for observational trials not involving drugs, the protocol was disclosed and authorized by the Institutional Ethics Committee of “Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria di Cagliari”, Cagliari, Italy. The patients gave written informed consent for the study enrolment, surgical procedure,and publication of the data and imaging.
History of past illness
In all cases patients’ past medical history was unremarkable.
Personal and family history
In all cases patients’ personal and family history was unremarkable.
Physical examination
Physical examination and bimanual pelvic examination at admission showed enlarged uterus accompanied by enlarged abdominal circumference in all three cases.
Laboratory examinations
Before the surgery each patients underwent cervicovaginal smear, and endometrial sampling based on endometrial thickness: In all cases malignancy was excluded.
Imaging examinations
Before the surgery, each patient underwent abdominal and transvaginal ultrasonography, as well as magnetic resonance (MR) or computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen. Specifically, the video 1 reports in detail the findings of the preoperative diagnostic imaging (computed tomography and magnetic resonance) of three emblematic cases.
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
In all three cases the diagnosis was very large fibromatous uteri (weight > 500 g) with suspected occult leiomyosarcoma. In detail, the uterine weight was 1500 g, 1700 g, and 3700 g in case 1, case 2 and case 3, respectively (Video 1). In all cases, pathological examination revealed benign leiomyoma.
TREATMENT
All cases underwent TLH, that was carried out following a procedure already described in our previous studies[23]. The description of TLH technique is outside the scope of the study and it is not reported in the video. All three patients underwent extracorporeal intrauterine morcellation according to the technique described below.The video 1 describes in detail the procedure carried out in each patient.
Detailed description of extracorporeal intrauterine morcellation technique
An accessory abdominal very-low or periumbilical transverse mini-laparotomy port site incision ranging from 4-9 cm depending on the uterine size was made. The uterine cervix was extracted from the mini-laparotomy and a wide trachelectomy was completed. Four traction forceps were placed at the four corners of the uterus to gradually extract the uterus through the minilaparotomy during the procedure. Then,we proceeded to gradual manual morcellation with cold scalpel, using the outermost layer of the uterus as a bag. The uterine myomas/tissue was gradually morcellated with caution and repeatedly exploring the depth of the uterine cavity. Morcellation continued till the uterus could be safely and entirely extracted by the minilaparotomy.During the procedure, the removed specimens were also sent immediately for an extemporaneous histological examination, which is routinely being performed during our surgical procedures. To verify the maintenance of the integrity of the uterine wall during morcellation, once removed the uterus was filled with water, thus confirming its capacity of a safe containment as a bag (video 1 and Figure 1). Following the suture of the accessory low mini-laparotomy, we laparoscopically assessed the abdominal cavity for any blood loss and organ injury and many times washed it carefully to remove any potential remaining tissue.
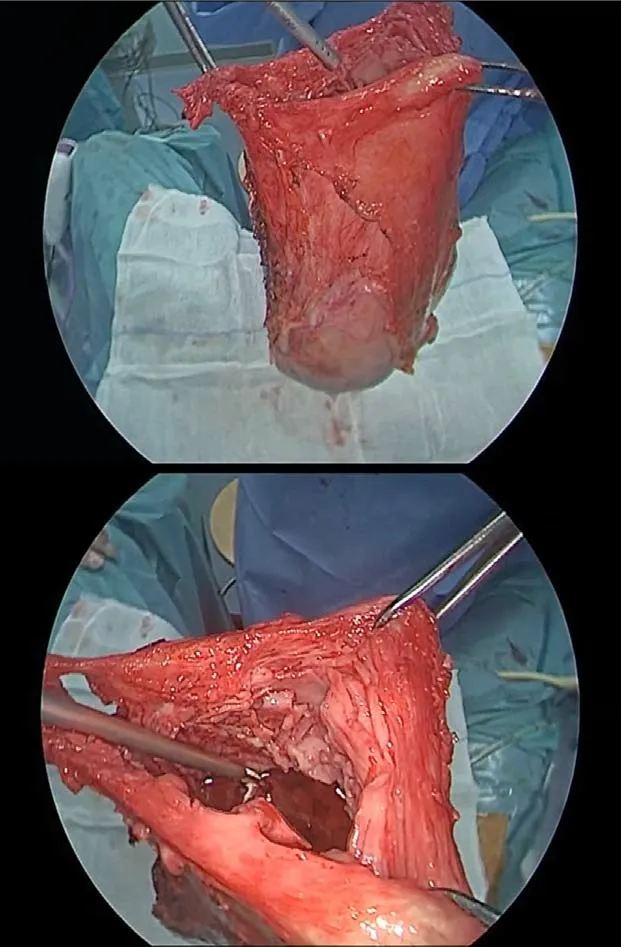
Figure 1 Evaluation of uterine wall integrity after uterus removal.
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
The procedures were performed without any complications in all patients. All three patients had uneventful postoperative courses. Pathological examination revealed benign leiomyoma in all cases.
DISCUSSION
A crucial condition for TLH in the presence of a large uterus is morcellation, during which larger specimens are broken into little fragment to remove them from the abdominal cavityviasmall incisions. However, intracorporeal uncontained morcellation may lead to unintentional peritoneal dissemination of occult cancers. To avoid such risk, the utilization of contained in-bag morcellation has been developed[3,19,24-26]. However, the usage of containment bags is limited to a determined uterine weight[27]. At this regard, a study reported successful in-bag contained procedures of power morcellation for samples varying from 300 to 2134 g, with no bag rupture or bagassociated complications[14]. To date, few studies tested the use of in-bag contained extracorporeal manual morcellation for large uteri after TLH, with the largest specimen weighing 1930 g[20,28]. In case of very large specimen, mostly single case reports, educational video articles and retrospective series with different technique and investigational devices have been reported[13,29,30]. To address these concerns,we developed an additional alternative technique of extracorporeal intrauterine morcellation carried out within the uterus utilizing its outer wall as a bag. The present video shows that such a technique is safe, feasible, and reproducible. It may allow to maintain the advantages of a minimally invasive approach while trying to lessen the risk of spreading throughout TLH. The final step of the procedure reported in the video confirmed the capability to preserve the integrity of the uterine wall during the cautious manual intrauterine morcellation and gradual uterus extraction. Our technique is comparable in term of outcomes (spillage, visually detectable rupture of containment system, or complications) with the other contained extracorporeal manual morcellation approaches described in literature[20]. The main challenge of our procedure could be the longest timing needed to perform the morcellation and extraction. Thus, our technique may represent a valid alternative to the other procedures of contained morcellation and be especially useful in cases of very large uteri exceeding the capacity of specimen retrieval bags. It cannot represent the only method applicable for morcellation and the gynecological surgeons should be also familiar with the other techniques.
CONCLUSION
We believe that such a novel technique presented herein may be useful to the readers who may consider adopting it in their practice, by adding it to the other available methods of contained morcellation. Further scientific evaluation of this technique in larger prospective studies is warranted.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors thank Dr. Martina Mura for her technical support.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2021年20期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2021年20期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Obesity in people with diabetes in COVID-19 times: Important considerations and precautions to be taken
- Revisiting delayed appendectomy in patients with acute appendicitis
- Detection of short stature homeobox 2 and RAS-associated domain family 1 subtype A DNA methylation in interventional pulmonology
- Borderline resectable pancreatic cancer and vascular resections in the era of neoadjuvant therapy
- Esophageal manifestation in patients with scleroderma
- Exploration of transmission chain and prevention of the recurrence of coronavirus disease 2019 in Heilongjiang Province due to inhospital transmission
