Expression and molecular mechanism of PCNA,Caspase-3,IL-6 and Survivin proteins in chorionic villi and decidual tissue of early embryo damage
Xiu-Rong Wang,Zu-Dong Teng,Xue-Xue Li and Wen-Ming Cao
Abstract— Objective: This study aims to explore its role in embryo damage and the relationship between them by testing the expression of PCNA, Caspase-3,IL-6 and Survivin protein in the chorionic villi and decidual tissue of patients with unexplained early embryo damage and normal early pregnancy at the same time voluntarily requested uterine aspiration abortion in order to clarify the pathogenesis of early embryo damage from the cellular and molecular perspectives, and provide theoretical basis for the diagnosis and treatment of embryo damage. Methods: From July 2018 to July 2019, 30 patients with unexplained embryo damage were selected as embryo damage group, thirty normal early pregnancy patients with aspiration abortion were selected as the normal early pregnancy group.The decidual tissue and chorionic villi of the two groups were collected to observe the structural and pathological changes. Immunohistochemical method was used to detect the distribution of PCNA,Caspase-3, IL-6 and Survivin in the chorionic villi and decidual tissue, as well as the expression changes of the above four proteins. Results: Compared with the normal early pregnancy group, the chorionic villi in the early embryo damage group were obviously dysplasia, degenerative changes, structural disorders, homogeneous destruction,obvious reduction or even disappearance of trophoblast cells,inflammatory cell infiltration, more neutrophils and lymphocytes,interstitial edema and cell atrophy,accompanied by hemorrhage;The decidual tissue of the intima was not good, most of the cells were spindle-shaped, the structure was disordered, the stroma has edema, inflammatory cells can be seen, and hemorrhage existed. The results of immunohistochemistry showed that the expression of PCNA protein in chorionic villi and decidual tissue of early embryo damage group decreased significantly(P <0.05),while the expression of Caspase-3 protein increased significantly(P <0.05). The expression of IL-6 protein decreased significantly(P <0.05), and the expression of Survivin protein decreased significantly (P <0.05). Conclusion: During early pregnancy,due to the down-regulation of the expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen PCNA and apoptosis inhibitor protein Survivin in chorionic and decidual tissues, the balance between proliferation and apoptosis is broken, which has an increase in Caspase-3 expression and a decrease in IL-6 expression. It may be that the balance of Th1/Th2 in chorionic and decidual tissues inclines to Th1,which leads to excessive apoptosis of chorionic and decidual tissues and the cessation of early embryo damage.
Keywords: Decidual tissue, chorionic villi, PCNA, caspase-3,IL-6,Survivin
I. BACKGROUND
With the full liberalization of China's two-child birth policy,the smooth birth of healthy babies plays a more important role in maintaining family stability, women's health and fertility.At present, the etiology of early embryo damage is not only related to the known chromosome abnormality, endocrine factors, infection factors, immune factors, environmental factors and other factors.There are still 50%of patients withunknown reasons. Embryo damage seriously affects women's physical and mental health. Research[1,2]shows that the incidence rate of embryo damage and spontaneous abortion is on the rise.Spontaneous abortion caused by embryo damage accounts for 10%-20% of the total number of pregnancies. Some studies have found that successful pregnancy depends on necessary trophoblast apoptosis, and embryo damage may be related to excessive trophoblast apoptosis[3,4].
Cell proliferation is one of the important physiological functions of living cells and an important life feature of organisms. It is used to supplement aging and dead cells in vivo and is the basis of growth, development, reproduction and heredity of organisms. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen(PCNA),an autoantigen discovered and purified by Miyachi et al.[5]in the serum of systemic lupus erythematosus patients in 1978,is a cell cycle regulatory protein, an auxiliary protein of DNA polymerase, and an essential factor for DNA synthesis.Its expression varies from cell cycle to cell cycle, and starts to rise in the early stage of G1, reaching the highest level in S phase, which is 2-3 times that of G1 phase. G2 and M phases show continuous decline. Its quantity change is consistent with DNA synthesis. It also plays an important role in promoting cell proliferation and is a good and reliable indicator for reflecting cell proliferation state[6,7].
Apoptosis refers to the response to changes in the environment. In order to maintain a stable state, cells trigger prestored death procedures in cells,which initiates automatic selfdestruction and death of cells[8]. The downstream caspases(Caspase-3) are activated by Fas antigen, TNF and TNF-α related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), which results in cell death. Studies have confirmed that there are two main apoptosis pathways, namely extracellular signaling pathway and intracellular signaling pathway[9]. The characteristics of extracellular signaling pathway are: through the mediation of related apoptosis-inducing ligands(Fas antigen,TNF-α and TNF), downstream Caspases are activated and cell death is triggered; The characteristic of intracellular signaling pathway is that cytochrome C is released from mitochondria to cytoplasm under the stimulation of apoptosis signal, thus stimulating apoptosis. Both pathways eventually activate Caspase-3,and then promote DNA cleavage through Caspase-3 substrate actin and PARP,which results in irreversible apoptosis of cells.It is believed that Caspase-3 is the main inducer of cell apoptosis[10].
During pregnancy, Th1 Th2 system plays an important role in regulating the cytokine balance network at the maternalfetal interface. At the maternal-fetal interface, immune cells,decidual tissue cells and trophoblasts secrete a large number of Th1 Th2 cytokines, which promote the mother to achieve immune tolerance and maintain normal pregnancy smoothly.IL-6 is a cytokine produced by Th2.IL-6 in uterus during pregnancy mainly comes from endometrial epithelial cells, which mediates humoral immunity and makes the body cooperate with immune tolerance. Survivin is an apoptosis suppressor gene with strong anti-apoptosis effect. It was first isolated by hybridization screening of Altieri experimental group of Yale University in 1997.Survivin is highly expressed in tumor tissues, but silent in normal tissues. Survivin is a newly discovered member of the family of inhibitor of apoptosis family of Proteins(IAPs),which is the most powerful inhibitor of apoptosis so far. Its tissue distribution has obvious cell selectivity. In recent years, it has also been considered that pregnancy is a special allograft phenomenon,and the behavior of trophoblast growth, infiltration and endometrial vascular construction is similar to the invasive growth process of tumor tissue. It has been reported that IL-6 (IL-6) and survivin play an important role in the process of early trophoblast growth and infiltration, blastocyst implantation and placenta formation.
This study explores its role in embryo damage and its relationship by testing the difference in the expression of PCNA, Caspase-3, IL-6 and Survivin in the chorionic villi and decidual tissue of patients with unexplained early embryo damage and normal early pregnancy voluntary aspiration abortion at the same time in order to clarify the pathogenesis of early embryo damage from the cellular and molecular perspectives, and provide theoretical basis for the diagnosis and treatment of embryo damage.
II. MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Sample selection
From July 2018 to July 2019, 30 patients with unexplained embryo damage were selected as embryo damage group,and 30 patients with normal early pregnancy abortion were selected as normal early pregnancy group. The decidual tissue and chorionic villi of the two groups were collected. Both groups of patients voluntarily underwent negative pressure uterine aspiration to terminate pregnancy. All the selected cases had regular menstrual cycle, and the memory of the last menstrual time was accurate;Good health,no genetic diseases,normal development of internal reproductive organs; The age was between 20 and 35 years old. There was no endocrine disorder during pregnancy, no use of steroids, no history of placing intrauterine devices,no trauma,no history of exposure to radiation toxicants, no history of smoking and long-term medication, no infectious diseases, no internal and surgical complications and pregnancy complications
2.2 Reagents
Recombinant Anti-PCNA antibody and recombinant Anti-Caspase-3 antibody were purchased from Abcam Company of the United States, Rabbit Anti-IL-6 antibody and Rabbit Anti-Survivin antibody were purchased from Bioss,and SP two-step immunohistochemical detection system was purchased from ZSGB-BIO.
2.3 HE stain
Decidual tissue and chorionic villi 1.0 cmx1.0 cm x 0.3cm were taken and fixed with 4%paraformaldehyde solution(pH=7. 4), washed, dehydrated, transparent, soaked in wax and embedded in paraffin.Wax blocks were sectioned for 5µm,baked at 58°C overnight,stained with hematoxylin-eosin(HE),and the structural and pathological changes of chorionic villi and decidual tissue were observed under ordinary optical microscope.
2.4 Immunohistochemistry stain
Paraffin sections were dewaxed into water,repaired by heat antigen, blocked by 3% hydrogen peroxide for 30min and 10% sheep serum for 30min, and added with recombinant Anti-PCNA antibody (1: 500)/recombinant Anti-Caspase-3 antibody (1: 100)/Rabbit Anti-IL-6 antibody (1: 300)/Rabbit Anti-Survivin antibody (1: 300), incubated at 4°C overnight.Incubation with secondary antibody, DAB color development,dehydration transparency,neutral gum sealing,photographing.IPWIN60 medical image analysis software was used for analysis. After the cells to be tested in the section to be tested are located under a microscope, the image is displayed on an image monitor, the IOD value and area value of the cells in the area are detected, and then 10 visual fields ( x 400)are observed according to the random principle. The content value of the measured receptor in this group is expressed by the average value of each section, and the relative intensity of this protein expression is expressed by the average value of the whole group.
2.5 Statistical processing
All the experimental values were analyzed by statistical software SPSS25.0. The experimental values were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (x ± s). The measurement data were compared by corrected t test.P<0.05 means the difference is statistically significant, andP<0.01 means the difference is statistically significant.
III. RESULT:
3.1 Morphological differences of uterine decidual tissue and chorionic villi between early embryo damage group and normal early pregnancy group
Compared with the normal early pregnancy group,thevillus dysplasia in the early embryo damage group was obvious with degenerative changes, structural disorder, homogeneous destruction, obvious reduction or even disappearance of trophoblast cells, inflammatory cell infiltration, more neutrophils and lymphocytes, interstitial edema and cell atrophy, accompanied by hemorrhage; The decidual tissue of the intima is not good, most of the cells are spindle-shaped, the structure is disordered, the stroma has edema, inflammatory cells can be seen, and hemorrhage exists. See Figures 1 and 2.
3.2 Distribution and expression of PCNA, Caspase-3, IL-6 and Survivin in chorionic villi of early embryo damage group and normal early pregnancy group
3.2.1 PCNA was mainly expressed in the nucleus of villus cytotrophoblast cells, which has brown-yellow granules,while the expression of syncytiotrophoblast cells was not obvious,and it was expressed in the nucleus of decidual tissue epithelial cells, showing brown-yellow granules. Compared with the normal early pregnancy group, the expression of PCNA in cytotrophoblast cells and decidual tissue cells in the embryo damage group was significantly lower(P<0.05).See Figure 3,Table 1.
3.2.2 Caspase-3 was mainly express in that cytoplasm of villous trophoblast and decidual tissue epithelial cells, which had brown-yellow particles. The nuclear expression was not obvious. There was a little expression in the cytoplasm of interstitial cells, and the cytoplasm of trophoblast cells in embryo damage group was strongly expressed. It was dark brown yellow, and the expression was also brown yellow in the cytoplasm of decidual tissue epithelial cells. In the normal pregnancy group, there was a small amount of expression in the cytoplasm of villus trophoblast cells, light yellow, or no expression, and a little expression in the stroma. Compared with the normal early pregnancy group, the expression in the chorionic villi and decidual tissue of the embryo damage group was significantly enhanced (P<0.05). See Figure 4, Table 1.
3.2.3 Survivin was mainly expressed in the nucleus and cytoplasm of villous trophoblasts and decidual tissue epithelial cells, which had brown-yellow granules, and the nucleus and cytoplasm of interstitial cells were also expressed. Compared with the normal early pregnancy group, the expression of survivin in the chorionic villi and decidual tissue of the early embryo damage group was significantly weakened (P<0.05).See Figure 5,Table 2.
3.2.4 IL-6 was strongly expressed in the nucleus and cytoplasm of villous trophoblasts and decidual tissue epithelial cells in the normal early pregnancy group, showing brownyellow granules, and also expressed in the nucleus and cytoplasm of interstitial cells. Compared with it, the expression intensity in chorionic villi and decidual tissue of the early embryo damage group was significantly weakened (P<0.05).See Figure 6,Table 2.
IV. DISCUSSION:
There is a certain degree of trophoblast apoptosis in the physiological activities of normal women during pregnancy[11], which mainly occurs in syncytiotrophoblast cells. In the process of embryo development, the balance between apoptosis and proliferation plays an important role in maintaining pregnancy[12], which is conducive to the formation of blood vessels and branches in chorionic villi and the maintenance of related invasion ability. Some studies have found that successful pregnancy depends on necessary trophoblast cell apoptosis[13-14], and embryo damage may be related to excessive trophoblast cellapoptosis[15-18].
This study found that the chorionic villi in the early embryo damage group were obviously dysplasia,degenerative changes,structural disorders, homogeneous destruction, obvious reduction or even disappearance of trophoblast cells, inflammatory cell infiltration, neutrophils and lymphocytes, interstitial edema and cell atrophy, accompanied by hemorrhage; The decidual tissue of the intima is not good, most of the cells are spindle-shaped, the structure is disordered, the stroma has edema,inflammatory cells can be seen,and hemorrhage exists.This is consistent with the results of Fang xiantao[19].
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) plays an important role in the process of DNA synthesis, and is generally only synthesized and expressed in proliferating cells.Immunohistochemistry showed that PCNA was mainly expressed in the nucleus of villus cytotrophoblast cells, which had brownyellow granules, while the expression of syncytiotrophoblast cells was not obvious, and it was expressed in the nucleus of decidual tissue epithelial cells, showing brown-yellow granules. Compared with the normal early pregnancy group, the expression of PCNA in cytotrophoblast cells and decidual tissue cells in the embryo damage group was significantly reduced. This was consistent with the finding of Mochizuki et al.[20]that a large amount of PCNA expression was detected in villus cytotrophoblasts of normal early pregnancy,and Du xiaomei[21]et al. that PCNA expression intensity of cytotrophoblasts in villus and decidual tissues of patients with early spontaneous abortion was weaker than that of normal early pregnancy women.
The results of this study showed that compared with the normal early pregnancy group,the expression of Caspase-3 in chorionic villi and decidual tissue of embryo damage group was significantly increased.Survivin was mainly expressed in the nucleus and cytoplasm of villous trophoblasts and decidual tissue epithelial cells,showing brown-yellow granules. The nucleus and cytoplasm of interstitial cells were also expressed.Compared with the normal early pregnancy group, the expression of survivin in the chorionic villi and decidual tissue of the early embryo damage group was significantly weakened.This is consistent with the research results of He Junmei[22].
Survivin is an IAPs, which is abundantly expressed in embryonic and developing fetal tissues,but not in normal adult tissues. When cells undergo transformation, they can be expressed to varying degrees. In cytoplasm,Survivin binds to Caspase-3 and Caspase-7 through multiple pathways to

Fig.1.Morphological changes of villus and decidual tissue(HE staining,200X)Note:A:Chorionic villi of normal pregnancy B:Chorionic villi of embryo damage C: Decidual tissue of normal pregnancy D: Decidual tissue of embryo damage

Fig.2.Morphological changes of villus and decidual tissue(HE staining,400X)Note:A:Chorionic villi of normal pregnancy B:Chorionic villi of embryo damage C: Decidual tissue of normal pregnancy D: Decidual tissue of embryo damage

Fig.3.Distribution of PCNA in villus and decidual tissue(200X)Note:A:Chorionic villi of normal pregnancy B:Chorionic villi of embryo damage C:Decidual tissue of normal pregnancy D: Decidual tissue of embryo damage
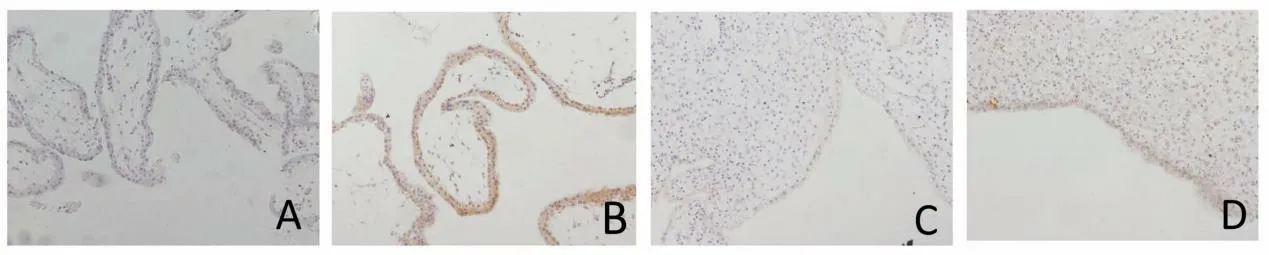
Fig.4.Caspase-3 distribution in villus and decidual tissue(200X)Note:A:Chorionic villi of normal pregnancy B:Chorionic villi of embryo damage C:Decidual tissue of normal pregnancy D: Decidual tissue of embryo damage
TABLE I EXPRESSION OF PCNA AND CASPASE-3 IN CHORIONIC AND DECIDUAL TISSUES BY IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY

TABLE II EXPRESSION OF SURVIVIN AND IL-6 IN CHORIONIC AND DECIDUAL TISSUES BY IMMUNOHISTOCHE MISTRY

Fig.5. Distribution of survivin in chorionic and decidual tissue(200X) Note:A:Chorionic villi of normal pregnancy B:Chorionic villi of embryo damage C: Decidual tissue of normal pregnancy D: Decidual tissue of embryo damage
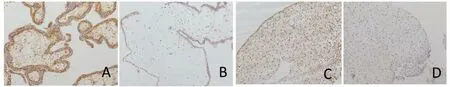
Fig.6. Distribution of IL-6 in villus and decidual tissue(200X)Note:A:Chorionic villi of normal pregnancy B:Chorionic villi of embryo damage C:Decidual tissue of normal pregnancy D: Decidual tissue of embryo damage
block the apoptosis process[23];In the nucleus, Survivin binds to CDK4, which releases oncogene protein P21 from CDK4 complex. P21 further binds to mitochondrial Caspase-3,inhibits its activity and prevents apoptosis[24].Feng M[25]et al. showed that survivin was highly expressed in normal early pregnancy chorionic villi and decidual tissue. Survivin can bind to Caspase-9 via a cofactor, inhibit the occurrence of apoptosis through endogenous pathways,or by binding to the spindle microtubules of mitotic cells and specifically binding to Caspase-3 and Caspase-7, the downstream terminal effectors of apoptosis,the activity of Caspase-3 and Caspase-7 is directly inhibited, thus inhibiting cell apoptosis, promoting cell mitosis, regulating cell cycle, shortening cycle,promoting proliferation, thus inhibiting apoptosis. Therefore,high expression of Survivin can inhibit apoptosis induced by various factors, while low expression of Survivin will reduce its ability to inhibit apoptosis, which would lead to excessive apoptosis of trophoblasts and lead to spontaneous abortion. Caspase-3 is the main inducer and effector of apoptosis. Mitochondria, cytochrome c-mediated apoptosis, Fasmediated apoptosis and other pathways all activate Caspase-3 to initiate Caspase cascade reaction and lead to apoptosis.The mechanism of survivin inhibiting apoptosis is also related to caspase-3. Liu Z[26]et al. believed that Caspase-3 was expressed in syncytiotrophoblasts and cytotrophoblasts in the study of mouse placenta. When 100000 workers of interferon U were injected into mice, the expression rate of Caspase-3 increased by 0.68 times, which caused apoptosis of placental tissue cells and abortion.
During pregnancy, there is a complex and special relationship between mother and fetus. The balance of paracrine or autocrine network system composed of various cytokines,hormones and proteins in the mother is extremely important for the growth and development of embryos. Once its unique microenvironment is destroyed, it may lead to adverse consequences such as abortion. The immune microenvironment at the maternal-fetal interface is composed of immune cells in decidual tissue and cytokines secreted by them; According to their functional cytokines, Th1 cytokines (IL-2, IFN-γ, TNFβ, etc;) can directly damage the placenta or activate cytotoxic effects such as NK cells to induce fetal abortion; The other is that Th2 cytokines (IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, etc.) induce maternal immune tolerance, which is beneficial to the establishment and maintenance of pregnancy. Reproductive immunity holds that normal pregnancy depends on immune tolerance,which is mainly reflected in the maternal-fetal interface-decidual tissue immune response[27]. During embryo implantation, Th1 type immune response of helper T cells is characterized by immune killing, inhibiting embryo implantation and trophoblast growth. Overexpression is not conducive to pregnancy maintenance, while Th2 type immune function plays an immune protection or immune nutrition role, which is beneficial to pregnancy[28].
The research results of Ju Zhongliang et al[29]. showed that the secretion of Th2 cytokines in normal pregnant women increased and the secretion of Th1 cytokines decreased.IL- 6,as a Th2 cytokine, was dominant in the maternal-fetal interface, especially during embryo implantation. It downregulated cell-mediated immune response, inhibited maternal rejection, promoted the generation of adhesion molecules and embryo implantation, which was beneficial to maternal-fetal tolerance and maintenance of pregnancy. Th2 cytokines (IL-4,-6 and-10) in patients with habitual abortion decreased significantly, Th1 cytokines increased significantly, and the ratio between Th1 cytokines and Th2 cytokines was out of balance [30,31].
We found that, IL-6 was strongly expressed in normal early pregnancy chorionic villi, which was suggested that IL-6 plays an important role in promoting embryo implantation and pregnancy maintenance. Compared with normal early pregnancy group, the expression intensity of IL-6 in chorionic chorionic villi and decidual tissue of early embryo damage group was significantly weakened,which further indicated that the occurrence of early embryo damage was related to the inclination of Th1/Th2 balance to Th1 in chorionic villus and decidual tissue of early pregnancy.It was consistent with Song Yueqing[32]research results.
The above results suggested that, during early pregnancy,the balance between proliferation and apoptosis was broken due to the down-regulation of the expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen PCNA and apoptosis inhibitor protein Survivin in chorionic and decidual tissues,showing an increase in Caspase-3 expression and a decrease in IL-6 expression. It may be that the balance of Th1/Th2 in chorionic and decidual tissues inclines to Th1, which leads to excessive apoptosis of chorionic and decidual tissues and the cessation of early embryo development.In a word, early embryo development is a particularly delicate process, which changes some sensitive indexes and makes them become a potential variation factor,resulting in abnormal phenomena of embryo development.
Acknowledgments:
The author did not receive any funding for this study.
Competing interests:
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Citation:
Wang XR, Teng ZD, Li XX, Cao WM. Expression and Molecular Mechanism of PCNA, Caspase-3, IL-6 and Survivin Proteins in Chorionic villi and Decidual Tissue of Early Embryo Damage.PrecMedRes.2021;3(2):9.doi:10.12032/PMR20210608004.
Executive editor:Na Liu.
Submitted:15 Marth 2021,Accepted:3 June 2021,Online:4 June 2021.
© 2021 By Authors. Published by TMR Publishing Group Limited. This is an open access article under the CC-BY license(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/BY/4.0/).
 Precision Medicine Research2021年2期
Precision Medicine Research2021年2期
- Precision Medicine Research的其它文章
- Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as a therapeutic target in lung cancer
- Targeting mitochondrial protein transport system:a promising treatment strategy for heart failure?
- Expression and clinicopathologic significance of RASSF1A and WT1 in recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer
- The predictive value of preoperative albumin-to-globulin ratio in patients with hilar cholangiocarcinoma
