Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as a therapeutic target in lung cancer
Jianwen Li,Zhanxia Zhang,Haibin Deng,and Zhan Zheng
Abstract—Abstract : Lung cancer has the highest incidence and mortality rate among all cancers. It is also one of the most threatening malignancies to people's health and lives. In recent years, tumor immunotherapy has received increasing attention,which was awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine in October 2018.There is growing evidence that marrow-derived suppressor cells(MDSCs) play an important role in the progression and metastasis of lung cancer. This article summarises the characteristics of MDSCs, preclinical studies of MDSCs in lung cancer cells and clinical studies in lung cancer patients. The novel combination immunotherapy of MDSCs is discussed. At present,some progress has been made in the antitumor treatment of MDSCs,and many unknowns in this field still need to beclarified by a large number of basic and clinical studies.
Keywords—Lung cancer, MDSCs, Immunosuppression, Tumor immune microenvironment
I. INTRODUCTION
Lung cancer has the highest mortality among cancers and is a challenging health problem(1). In the past 50 years, many developing countries reported that the incidence of lung cancer increased significantly, and the age of onset became younger,which seriously threatened people's health(2). A total number of 18 million new cases was diagnosed in 2018.The top three are lung cancer, breast cancer, and prostate cancer(3). Currently, chemotherapy remains the standard treatment for firstand second-line management of lung cancer,but the effectsare unsatisfactory. Tumor immunotherapy has become more and more effective and gradually accepted by everyone. However,More and more evidence show that MDSCs are not only closely related to the growth and progression of lung cancer but also hinder the success of lung cancer chemotherapy and immunotherapy.MDSCs can not only inhibit T cell activity but also form premetastatic niche and promote vascular endothelial formation.Given the significant role of MDSCs in lungcancer,MDSCs could be used as prognostic or predictive biomarkers for lung cancer.Moreover modulating the immunosuppressive properties of MDSCs may be an important approach for the treatment of lung cancer.
II. MDSCS AND THEIR CHARACTERISTIC
MDSCs is derived from marrow progenitor cells in the bone marrow. Under normal circumstances, in the body's immune response against bacteria or viruses, myeloid cells can quickly differentiate into mature granulocytes, DC or macrophages.However, under pathological conditions, especially when tumors occur, the bone marrow cavity is continuously stimulated by abnormal signals. A large number of MDSCs accumulate in tumors and peripheral lymphoid organs. The ability of MDSCs to differentiate into mature myeloid cells(mature granulocytes, DC, and macrophages) is reduced.MDSCs in mice are divided into two distinct subgroups according to differences in expression levels of LY6G and LY6C(two different epitopes of GR1), granulocyte-like MDSCs with CD11b+LY6GhiLY6Clowphenotype; monocytelike MDSCs with a phenotype of CD11b+Ly6GlowLy6Chi(4),which showed the different functions of these two types of MDSCs(5). In different animal models, both types of MDSCs were amplified. However in most models, the expansion of granulocyte-like MDSCs was obvious. The phenotypic markers of MDSCs in tumor patients are more diverse. On the one hand, MDSCs with different phenotypic characteristics are found in different tumors.On the other hand, the existing MDSCs are also different in the peripheral blood and tumor tissues from the tumor patients. The main criteria for identifying MDSCs are still derived from bone marrow cells and inhibition of T cells.The human myeloid suppressor cell surface mainly expresses both CD11b and CD33 proteins but lacks the markers of mature myeloid cells(6). Some scholars have proposed the myeloid cells (Lin−CD11b+)in human blood and tumorbearing tissue can be divided into four types, namely mononuclear/macrophage-like, neutrophil-like, eosinophil-like and immature myeloid cells according to phenotype and morphology, and the corresponding phenotypes are CD14+,CD14−CD15hi, CD14−CD15int, CD14−CD15−(7). Also,human solid tumor-induced MDSCs can be divided into two subgroups, CD33+HLA−DRlowHIF1α+/STAT3+and CD11b+HLA−DRIOWC/EBP β+,according to the phenotype and inhibiting immune cells of molecular channels (8).As far as lung cancer is concerned, various phenotypes of MDSCshave been reportedinthe peripheralblood of NSCLCand SCLCpatients,includingCD33+CD11b+,HLA−DR−Lin−, CD14+HLA−DR−, CD33+HLADR−Lin−,CD33+HLADR−Lin−CD15−,CD33+CD11b+CD15+,CD14+S100A9+and CD33+CD11b+HLA−DR−.Identifying specific prognostic markers of lung cancer is critical to selecting patients who are most likely to respond to treatment options. We believe that the phenotypic characteristics of MDSCs will become clearer with the discovery of new subgroups.
III. THE ROLE OF MDSCS IN PRECLINICAL STUDIES OF LUNG CANCER
MDSCs are one of the main members of immune escape.On the one hand, MDSCs not only suppress T cells and NK cells but also increase the number and proportion of Treg cells.On the other hand, several preclinical studies have indicated that MDSCs not only have immunosuppressive functions,but also facilitate tumor invasion, formation of pre-metastatic ecological sites and formation of stem cell properties.In short,MDSCs have a significant role in the development of lung cancer(Figure1).
A. The role of MDSCs in the tumor immune microenvironment
MDSCs are thought to be the major mediator of tumor immune escape. MDSCs are important nodes in the cellular immune regulatory response network, and the amplification and activation pathways are related to many factors. Under the induction of some pathological factors and related signalling pathways, MDSCs are activated and amplified to obtain immunosuppressive functions. MDSCs can inhibit the immune function of T cells and NK cells by producing inhibitory cytokines such as Reactive oxygen species(ROS)and Arginase-1(Arg1).
ROS are the main factor of MDSCs regulating immunosuppression. ROS molecules participate in a variety of signal transduction pathways and control a series of biological activities. ROS not only activate the antioxidant pathway but also modulates MDSCs. Studies have confirmed that MDSCs can also inhibit T cell activation via ONOO-(9). In tumor-bearing mice and tumor patients, ONOO- is significantly increased in the site of myeloid suppressor cells, which may be caused by the direct contact of myeloid suppressor cells with T cells,resulting in ONOO-induced TCR and CD8 nitrification, making T cells do not respond to specific antigen stimulation. The research results showed that (10)the tumor-related fibroblast immunosuppression increases by inducing ROS monocyterelated MDSC tumor-related fibroblasts in lung squamous cells. A recent study suggested that (11)the overexpression of S100A8 and S100A9 in macrophages not only leads to increased extracellular ROS production but also increases IL-10 mRNA expression. Other factors such as transforming growth factor-β(TGF-β), granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor(GM-CSF), IL10 and IL-3 can also induce the production of ROS by MDSCs.
L-Arg is an important factor in T cell function. MDSCs produce Arg-1 to increase the metabolism of L-arginine (LArg) and inhibit T lymphocyte response. In addition, Arg-1 modified by peg can increase the number of MDSCs and promote tumor growth in related mice. Carnosic acid (12)inhibits MDSCs, reduces iNOS2, Arg-1, and MMP9 mRNA levels,and enhances the anti-lung cancer effect of cisplatin. iNOS2 and Arg-1 are important functional markers of MDSC, and it is of great significance to help targeted MDSCs therapy.
The expression level of oxygen nitrite in MDSCs increased significantly. The expression level of Oxygen nitrite is proportional to the number of MDSCs and inhibits the function of T cells. Studies have found that(13) the two subtypes of MDSC (M-MDSC and G-MDSC) inhibit T cells through two different NO pathways.G-MDSC mainly uses gp91 and ENOS to produce PNT and damage T cells. M-MDSC is mainly affected by the release of NO. However, a factor that hinders one pathway has no effect on the other pathway and the level of related factors. In addition, studies have shown that(14)iNOS can not only regulate the secretion of VEGF butalso up-regulate the expression of Stat3 and ROS in MDSC. iNOS can participate in the recruitment and induction of MDSC.
Both Treg and MDSCs are subgroups of immunoregulatory cells, which have an important contribution to the immune microenvironment and are the target of immunotherapy(15).MDSCs promote Treg differentiation through the release of cytokines or cell-cell contact. Studies have proven(16)the interaction between M-MDSCs and Tregs induced by virus in vivo.MDSCs and Treg have increased significantly in tumor patients and tumor-bearing mice,and they are increasingly an important indicator for us to judge the progress of the disease(17). MDSCs can induce Treg to produce IDO to promote immune escape and tumor progression(18).
At the same time,the recruitment and expansion of MDSCs are regulated by some factors secreted by TME cells and cancer immunosuppressive pathways and substances. It is generally believed that(19,20) cytokines and inflammatory factors produced by tumor cells such as GM-CSF, VEGF,COX2, and PGE2 will promote the expansion of MDSCs.MDSCs are recruited to the tumor site by Chemokines.MDSCs stimulate immunosuppressive activity throughSTAT1,STAT,STAT6 and NF-κB transcription factors(21). Activated STAT3 can up-regulate the expression of a series of cytokines and inflammatory factors in tumor cells (IL-10, IL-6, VEGF,FGF2,COX2,CXCL12,IL-11,IL-23,IL-21,IL-17)(22), And these cytokines are STAT3 pathway activators of MDSCs.The activated MDSCs, in turn, produce ARG1, iNOS2, IDO,NADPH oxidase and immunosuppressive cytokines, forming a lung cancer immunosuppressive microenvironment and affecting T cells and other immune cells. S100A8/9 as a proinflammatory proteins(23),plays an important role in promoting the recruitment and activation of MDSCs. S100A8/9 can not only organise the differentiation of myeloid cells but also down-regulate T cell function.HIF-1a(24)is another important factor in promoting the differentiation of MDSCs. At the tumor site, HIF-1a promotes the differentiation of MDSCs into TAM and up-regulates NOS and Arg1 to increase the immunosuppressive function of MDSCs.
B. Non-immune role of MDSCs in lung cancer
MDSCs not only have immunosuppressive effects but also enhance tumor invasion and help form the pre-metastatic niches(PMN)of lung cancer, vascular endothelial regeneration to promote the development of lung cancer.Tumor invasion and metastasis are not internal functions unique to tumors, but require the involvement of immune cells and molecules. The role of MDSCs in promoting metastasis has beendemonstrated animal models and in many clinical studies.

Fig. 1. Role of MDSC in the tumor immune microenvironment. MDSCs can be recruited and activated through a number of cytokines, immunosuppressive substances and pathways. MDSCs suppress T-cell function mainly through Arg1, NO, and ROS. The infiltration and invasion of MDSCs are accelerated through blood circulation,and the formation of PMN promotes tumor growth and metastasis.Eventually the tumor may metastasize to the lung,liver and brain.
Extensive metastasis is the main cause of lung cancer death,and the formation of niche before metastasis is the key to metastasis. A series of evidences prove that(25)MDSCs accumulate in the peripheral blood, spleen, tumor, and lung metastases of tumor-bearing mice and clinical tumor patients.Through blood circulation, PMN (26)will form to promote tumor progression. The expression of MMP9 and M-MDSCs increase during tumor progression, thereby promoting the formation of niches before metastasis. In addition, it has been reported that (27)miR-494 may induce the expression of MMPs in CD11b+Gr-1 MDSCs and promote tumor invasion and metastasis in mouse models of lung cancer.Recent studies have shown that(28) MDSCs induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition by activating ERK and AKT signalLing pathways via CCL11. Angiogenesis is now increasingly recognised as a hallmark of cancer and a necessary process for tumor growth and metastatic spread. Several studies have demonstrated(29)the direct and indirect roles of MDSCs in tumor angiogenesis and angiogenesis. Splenic MDSCs have been reported to be directly involved in tumor angiogenesis through differentiation into endothelial progenitor cells. Tumor-secreted G-CSF and VEGFA are the main regulators of vascular endothelial cell mobilisation,proliferation and differentiation(30).Overall, MDSCs play an important role in tumorigenesis and metasta-sis.
C. Treatment Strategies for MDSCs in Preclinical Lung Cancer Studies
Because of the importance of MDSCs in lung cancer, the inhibition on generation, activation and function of MDSCs has gradually become the primary mode of treatment. There have been certain progress in the current anti-tumor therapy targeting MDSCs.
1) Inhibition of MDSCs related pathway:The first is the development of corresponding inhibitors for the abnormal amplification, transport and activation properties of MDSCs.A recent study revealed(31) the CCR2/MCP-1 pathway in MDSC-related tumor progression, demonstrating that CCR2 antagonists can promote anti-tumor immunity and limit tumor growth in lung cancer. As a matter of common knowledge,radiotherapy resistance is an important obstacle to clinical radiotherapy treatment. Because MDSC sensitizes NSCLC to RT, causing infiltration of MDSCs can promote radiation therapy resistance. LXR agonists(32) were found to partially eliminate the immunosuppressive effects of radiotherapy. In addition, studies have reported that(33) CXCR 1 and CXCR 2 small molecule inhibitor SX-682 can block the recruitment of tumor MDSCs, enhance T cell activation and anti-tumor immunity after various immunotherapy. The researchers used three known models of MDSC accumulation(34).They discovered the inhibitory effect of histamine on MDSC and improved the anti-tumor effect of PD1 immune checkpoint inhibitors. In addition, Prim-O-glucosylcimifugin, valproic acid, and TAM family receptor kinase inhibitors also can resist MDSC by enhancing anti-PD1 immunotherapy(34-36). Although we have found a lot of MDSCs-related inhibitors,the efficacy ofsingleuse is limited. The types and forms of inhibitors still need to be continuously discovered and innovated to find more and better inhibitors and strive for greater progress.
2) Knockout of MDSCs-related genes:Another way is to use knockdown genes to activate or inhibit related pathways.It was found that(37) lung oncogeneGprc5aknockout (Ko)mice are prone to tumorigenesis and metastasis. However,the PGE2PTGES inhibitor inhibited MDSC recruitment, restored T cells,and significantly inhibited lung metastasis.Inaddition,studies have shown that(38) IL-33 upregulates the number of CD8+T cells and NK cells through the MyD88 pathway and enhances tumor immune function, thereby inhibiting the proliferation of lung cancer cells. Caspase recruitment domain protein 9 ( CARD-9 ) is an adapter protein highly expressed in myeloid cells.It was found that(39)CARD9-/-mice were much heavier than wild-type mice, and the reductionof MDSCs by anti-Gr1 antibody could significantly reduce the tumor burden of CARD9. More surprisingly, there is a CARD 9-NF-κB-IDO pathway in MDSCs, which can inhibit the inhibitory function of MDSCs and prevent the occurrence of lung cancer. Mitigation of immune escape by knocking out MDSCs-related genes is now a relatively mature and popular technology, which is expected to be improved in the future.
3) Innovation of MDSCs-related drug materials:Although many clinically used chemotherapeutic drugs can inhibittumor growth to a certain extent,they have the disadvantages of high toxic side effects,low drug utilisation rate and high cumulative dosing. However, the nano platform constructed by loading small molecule anticancer drugs with nanomaterials has the advantages of targetable drug delivery and high drug release at the lesion site, which can reduce normal tissue damage and improve the therapeutic effect. As a novel tumor treatment strategy, organic photosensitive molecules or inorganic nanomaterials with photothermal conversion capability can be converted into heat under near-infrared light irradiation to exert various anti-tumor effects thermal ablation, overcoming chemotherapy resistance and inhibiting tumor metasta-sis.A study(40) prevented PMN formation by building a lowmolecular heparin butyl succinate micelle (LMWH-TOS)nanoparticle(LMWH-TOS)that interferes with G-MDSCsand a self-transporting nano system. This study could not only prevent cancer metastasis but also increase drug targeting. In addition,The development of nano emulsions(41)is beneficial to reduce the infiltration of MDSCs with few side effects.It provides a new dosage form for nano-drug targeting MDSCs. The study (42)design introduced biocompatible MDSCtargeted nanocarriers(NCS)into the microenvironment of lung cancer and showed efficient tumor ablation under near-infrared(NIR) irradiation, demonstrating a targeted nature of the nano system. Cross-fertilization between disciplines provides new ideas for the treatment of lung cancer.
4) Epigenetic modifications related to MDSCs:Cancer cells are continuously remodelled at the genetic, epigenetic and metabolic levels to resist apoptosis, reducing the immune recognition ability and achieve immune escape.There is an important bidirectional regulatory mechanism between metabolic remodelling and epigenome in cancer. Thus,regulation of epigenetic modifications of MDSCs not only alters the differentiation and metabolism of MDSCs themselves but also effects the metabolism of other TME cells, causing these cells to undergo metabolic reprogramming. There are also researchers who use epigenetic approaches to inhibit tumor development and metastasis. Studies have demonstrated that(43) adjuvant epigenetic therapy using low-dose DNA methyltransferase and histone deacetylase inhibitors 5-azacytidine and cilastatin can disrupt this pre-metastatic microenvironment and inhibit metastasis. Although the PD-1 pathway has been clinically more effective, individual efficacy varies widely because of heterogeneity between diseases and patients. Recent studies have found that (44)damage to the immune cycle can be repaired through epigenetic modifications. A rational combination of PD-L1/PD-1 blockade and epigenetic factors can greatly improve cancer treatment outcomes. Epigenetic modifications suppress MDSCs by modifying chromatin histones and non-histones to regulate the expression of genes involved in cell growth,differentiation and apoptosis.
5) Combination therapy of MDSCs:The immune microenvironment is complex, and the roles and immunosuppressive mechanisms of MDSCs are diverse. Many clinical and basic experiments have proved that MDSCs infiltration has a great impact on patients' immunotherapy, chemotherapy and radiotherapy. However,a reasonable combination of treatment methods can effectively treat lung cancer and prolong the survival time of patients.In addition,since MDSCs can inhibit T cells and NK cells, many studies have found that it is conducive to the treatment of lung cancer by affecting immune cells and intercellular transporters related to MDSCs. It is said that(45)MDSCs were co-cultured with Lewis lung cancer and differentiated into M2 macrophages, which facilitated the polarisation of M2 macrophages.In conclusion,there are great discoveries in the therapeutic strategies for MDSCs, but more breakthroughs and innovations are needed.
IV. THE ROLE OF MDSCS IN THE STUDY OF LUNG CANCER PATIENTS
MDSCs, a major member of immune escape, are a major obstacle to immunotherapy in clinical treatment. They not only promote the development of cancer metastasis but also affect the effectiveness of therapies such as chemotherapy,radiotherapy and immunotherapy. It is because of the unique role of MDSCs that MDSCs can now be one of the markers for clinical diagnosis of lung cancer. A variety of treatment strategies targeting MDSCs have also emerged(Figure2).
A. MDSCs hamper the clinical efficacy of lung cancer chemotherapy and immunotherapy
MDSCs not only affect the progression and metastasis of lung cancer but also have an important impact on clinical chemotherapy and immunotherapy. The number of MDSCs is inversely proportional to the responsiveness of chemotherapy and is positively correlated with the number of patients with low survival rate of lung cancer. Recent studies have also found that(46)MDSCs can also cause drug resistance and high recurrence rate. The increase in M-MDSCs subgroups is associated with poor response to first-line platinum chemotherapy.A clinical prospective study showed that (47)CD11b+CD14+S100A9+M-MDSCs may significantly reduce the clinical response of cisplatin chemotherapy. Another study showed that(48)in non-small cell lung cancer,CD15+CD11b+CD33+HLA-DR-Lin-is associated with poor efficacy of cisplatin chemotherapy. carboplatin resistance is associated with CD11b+/Ly6C+ myeloid release and upregulation of TIGIT and LAG3/CD160 depleted T cells(46). It is reported that Carnosic acid enhances the anti-lung cancer effect of cisplatin by inhibiting MDSCs(12). Studies have also found that the combination of targeted MDSCs and primary breast tumor resection can reduce metastatic lung growth(49).
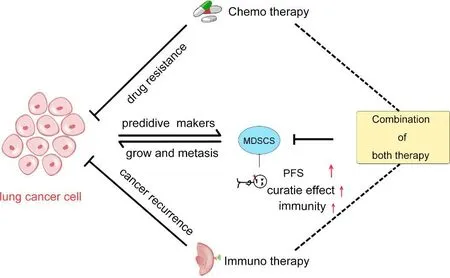
Fig.2.MDSCs in clinical lung cancer patients.MDSCs not only promote tumor immunosuppression,but also promote lung cancer development and metastasis.MDSCs affect chemotherapy and immunotherapy of lung cancer, and also promote drug resistance and cancer recurrence. Meanwhile, MDSCs can be used as a predictive marker for lung cancer diagnosis and treatment. The combination of chemotherapy and immunotherapy can increase the survival of patients,enhance immunity and improve the efficacy of anti-lung cancer treatment.
B. MDSCs in lung cancer can serve as prognostic or predictive markers
MDSCs may provide predictive and prognostic information in lung cancer patients.clinical studies to date suggested that MDSCs are important signs of clinical diagnosis andtreatment of lung cancer.The proportion of MDSCs in the blood helps judge the prognosis of the disease(50).In clinical practice,NSCLC occupies 85%of lung cancer,and its phenotypes mainly include B7-H3-CD14+HLA-DR-/lo−w,CD14+HLADR−/low,CD14+S100A9+,CD11b+/CD14−-/CD15+/CD33+,CD14+CD15+CD11b+CD33+HLA-DR−-L in −;SCLC accounts for 15% of lung cancer, and its phenotypes are mainly CD11b+CD33+HLA-DR− and CD14+HLA-DR− /low.The existence of subgroups of MDSCs has an important relationship with clinical results. Some of these studies have proved that elevated levels of MDSCs are predictive factors for the treatment of lung cancer patients. This is essential for patients who respond to treatment options. Therefore,MDSCs can be used as a marker of potential recurrence of lung cancer or a surrogate marker for the treatment effect of lung cancer. For example, a recent study showed that(51)the level of nitric oxide (NO) increased and the activity of MDSCs increased, which is an early sign of incomplete treatment of non-small cell lung cancer and subsequent potentialtumorrecurrence. The increasein the number of CD14+HLA-DR−/lowMDSCs in the peripheralblood of NSCLC is related to metastasis, chemotherapy response and progression-free survival. In addition,the increase in the frequency of CD14+HLA-DR− /low MDSCs in the peripheral blood of SCLC is related to the tumor cycle(52).The findings of these phenotypes provide us with important guidance and direction for the treatment of lung cancer, but their sensitivity and specificity still need to be fully elucidated.
C. Treatment Strategies for MDSCs in clinical Lung Cancer patients
MDSCs are the important immunosuppressive components of the tumor microenvironment. It becomes a target for intervention in the tumor microenvironment and effective treatment. Several studies have shown that the inhibition of MDSCs from different aspects is effective, which play an important role in the treatment of tumors.
1) Promotion of Myeloid Cell Differentiation:Promoting the differentiation of immature MDSCs into myeloid cells is a popular treatment for targeting MDSCs. Vitamin A is thought to help the myeloid precursor cells to DCs and giants a class of drugs that differentiate into phagocytes.CD11b+/Gr-1+ myeloid cells in the blood will mature and amplify if it lacks Vitamin A. Recent studies have shown that all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA), a derivative of vitamin A is important in promoting the differentiation of MDSCs into mature granulocytes(53). Researchers found that(54,55) the stem cell factor(SCF)can promote the expansion of MDSCs in tumor-bearing mice.Therefore,SCF can be inhibited by blocking the binding of SCF to its receptor KIT guided signals,thereby reducingthe expansion of MDSCs and formation of tumor vascular shape.Inhibition of SCF signalLing with tyrosine kinase inhibitors such as sorafenib and sunitinib in lung cancer reduces MDSC numbers. Although there are many factors that affect the amplification of MDSC, we are constantly researching and exploring. I hope there will be more useful discoveries.
2) Blockade of Immune checkpoints:Immune checkpoint inhibitors are currently the latest and most cutting-edge active immunotherapy methods.Programmed death-ligand 1(PD-L1)immunosuppressant has an important role and outstanding contribution in the treatment of lung cancer. There is a lot of research evidence to prove the important role of PD1 inhibitors in tumor immune escape. It is reported that (56)Entinostat enhances PD-1-targeted antitumor activity by inhibiting MDSCs.In addition, combined use of PD-1 inhibitors and platinum chemotherapy can increase the sensitivity of PD-1 inhibitors to tumor cells and inhibit tumor progression(57). Studies have shown that (58)PD-1 treatment improves the level of Tregs in NSCLC patients, and the level of M-MDSC is related to the anti-tumor effect of PD-1 treatment. Enhancing the efficacy of PD-1 from M-MDSC is also an important direction. Recent studies have shown that(59,60) cytokine-induced killer cells( CIK ) combined with PD-1 blocking antibody can improve the efficacy of advanced non-small cell lung cancer bed.
3) Elimination of MDSCs:Elimination of MDSCs has increasingly become a hot spot in immunotherapy. Studies have shown that(61-63) administration of small doses of 5-fluorouracil, paclitaxel or gemcitabine can selectively reduce the number of MDSC .These MDSC-depleting chemotherapeutic doses have no toxic effects on other leukocyte subpopulations, but have significantly enhanced antitumor efficacy. It has also been reported that(64) MDSC all express CD33 protein and that the use of Gemtuzumab Ozogamicin monoclonal antibody can specifically and toxically eliminate MDSCs, lift immunosuppression and increase the ability of T cells to attack tumor cells. SMAC mimetic Debio 1143 is used in conjunction with ablation radiotherapy to enhance Antitumor Immunity against Lung Cancer. Debio 1143 enhances antiretrovirals(Art)-induced tumor-specific adaptiveimmunity and reverses the infiltration of host immune suppressor cells in the tumor microenvironment, such as CD8+T cells, TNFα,and IFNγ(65). CDDO-Me not only eliminates the inhibitory activity of MDSCs but also significantly enhances the antitumor effect of tumor vaccines. It is an attractive treatment option by improving the effectiveness of cancer immunotherapy(66).Therefore,the elimination of MDSCs is an important means for us to treat lung cancer.
V. DISCUSSION
In short, MDSCs play an important role in tumor immune escape.Targeting MDSCs provides many new ideas for lung cancer immunotherapy,but there are still some problems.
First, MDSCs are a group of heterogeneous cells .the subpopulations of cells and related molecules that specifically inhibit T cell immune responses are not clear, especially the specific markers of human MDSCs are not clear. In clinical practice, we cannot precisely target MDSCs. Therefore, we need to further study the mechanisms and connectionsbetween sub-cells and find the biomarkers of human MDSCs as soon as possible.
Second, MDSCs can inhibit T cell-mediated specific antitumor immunity and NK and macrophage-mediated natural anti-tumor immunity. Whether MDSCs inhibit T cell immune response is antigen-specific, further confirmation is needed,and the mechanism of non-T cell immune response needs further research. With a better understanding of the mechanism,we can better master and use MDSCs.
Third, Although MDSCs play an important role in immunotherapy,inhibition of MDSCs has a good effect on many immune cells in the immune microenvironment. However, in order to better treat lung cancer, it can be coordinated with other treatment methods or therapeutic targets to strive for better the therapeutic effect.
Forth, how MDSCs migrate from bone marrow to another place. Is there any MDSCs in the spleen, peripheral blood,lymph nodes and tumor tissues, other tissues and organs? Is it related to the organ-specific metastasis of the tumor?Adoptive reinfusion of MDSCs for autoimmune diseases or transplant rejection is promising and promising, but obtaining MDSCs in clinical applications in vitro is still a problem.
Finally,in recent years,the immune target has found bottlenecks,and there are not many new targets and innovations.The tumor microenvironment is a complex whole, but it also gives us more opportunities to break through in multiple directions.At present,the relatively new research field mainly focuses on the regulation of non-coding RNA in MDSCs (67).
In summary, we should pay attention to how to target MDSCs in the treatment of tumors in the clinic, and use MDSCs to treat autoimmune diseases or transplant rejection.For the double-edged sword of MDSCs,we should master and seek a better balance.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS:
The present study was funded by the Natural Science
Foun-dation of Shanghai,China(No.20ZR1459200)and Scientific Research and Innovation Project of
Shanghai Education Com-mission(2017-01-07-00-10-E00064).
Competing interests:
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Citation:
Li JW,Zhang ZX,Deng HB,Zheng Z.Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as a therapeutic target in lung cancer.Prec Med Res.2021;3(2):7.doi:10.12032/PMR20210608002.
Executive editor:Na Liu.
Submitted:17 February 2021,Accepted:18 May 2021,
Online:19 May 2021.
©2021 By Authors.Published by TMR Publishing Group Limited.This is an open access article under the CC-BY license(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/BY/4.0/).
 Precision Medicine Research2021年2期
Precision Medicine Research2021年2期
- Precision Medicine Research的其它文章
- Targeting mitochondrial protein transport system:a promising treatment strategy for heart failure?
- Expression and molecular mechanism of PCNA,Caspase-3,IL-6 and Survivin proteins in chorionic villi and decidual tissue of early embryo damage
- Expression and clinicopathologic significance of RASSF1A and WT1 in recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer
- The predictive value of preoperative albumin-to-globulin ratio in patients with hilar cholangiocarcinoma
