Identification and morphological featuresof telocytesin endometriosis*
XUTing,ZHUZhi-ling,WUCai-qin,KEJun-ya,ZHANGHong-qi
(1Department of Obstetricsand Gynecology,Obstetricsand Gynecology Hospital of Fudan University,Shanghai 200090,China;2School of Nursing,Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Shanghai200031,China;3Department of Anatomy,Histology&Embryology,School of Basic Medical Sciences,Fudan University,Shanghai200032,China;4Key Laboratory of Medical Imaging Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention of Shanghai,Shanghai200032,China.E-mail:zhanghq58@126.com)
[ABSTRACT] AIM:To investigate the distribution and morphological features of telocytes(TCs)in the tissues of patients with ovarian endometriosis(EMs).METHODS:The tissue specimens from patients with ovarian cyst were harvested,and diagnosed as EMs by hematoxylin-eosin(HE)staining.Simultaneously,ultrathin sections of the tissues were observed under transmission electron microscope(TEM).RESULTS:The ectopic endometrium was observed in the focus of the ovarian cyst by HE staining,so that EMs was diagnosed.The results showed that TCs were indeed present in ovarian EMs under TEM.TCs with small cell bodies extended specific long,thin and moniliform telopodes(Tps)which had thick and thin parts(namely podoms and podomers,respectively).Moreover,podoms contained many organelles,such as endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria.It was found that TCs in EMs had significant autophagosomes and lipid droplet.Furthermore,TCs formed a network through direct contact via long Tps and indirect contact via vesicles.CONCLUSION:The TCs exist in ovarian EMs and their morphological features were demonstrated by TEM.This study provides an original structural and functional perspective for the cellular components of ovarian EMs and improves our comprehesion of the pathological aspects of EMs.
[KEY WORDS]Endometriosis;Telocytes;Transmission electron microscopy
Endometriosis(EMs)is a common gynecological disease,which has biological behaviors of tissue invasion and angiogenesis,and involves the migration of endometrial tissue fragments to the uterine cavity[1].EMs commonly occur in many parts of the body,while ovarian EMs is most common.In EMs,the endometrial-like tissue acting as endometrial tissue would thicken,break down and bleed with the menstrual cycle.The surrounding tissue may become irritated,and eventually form scar tissue and adhere to abnormal fibrous tissue bands,leading to adhesions between pelvic tissues and organs.The pelvic pain and reproductive disorders related to EMs have been reported in many researches.It is estimated to affect 6%~10%of women at childbearing age[2].The pathogenesis and pathophysiological characteristics of pelvic EMs are complex.Sampson′s theory of transversal blood counter current planting is the most mainstream to explain the pathogenesis of EMs[1].Retrograde menstruation refers to the reflux of menstrual debris containing living endometrial cells through the fallopian tube into the peritoneal cavity.The theory of reverse flow implantation once provided favorable evidence for the occurrence of EMs.There are some other typical theories which have also been suggested for the pathogenesis of EMs.Coelomic metaplasia of peritoneal epitheliumin situis also the source of EMs possibly,which means that the peritoneal mesothelium is transformed into the glandular endometrium[3].Metastasis of endometrial cells through lymph and blood vessels is considered to be another source of extrapelvic EMs[3].However,none of the proposed theory alone accounts for the cause of EMs in all patients.Therefore,we should make more research for the accurate mechanism of EMs.
Telocytes(TCs)[4],which was first confirmed by Prof.Popescu in 2005,was officially named as a new class of mesenchymal cells in 2010.The cell body of TCs was small and varied in shape,with a large nucleolar ratio.There was a large amount of heterochromatin under the nuclear membrane[4].The essencial features that distinguished TCs from other cells were small cell bodies and especially long,bead-like processes(telopodes,Tps).Tps issued by cell bodies range in length from tens to hundreds of microns and their numbers vary.Tps are alternately formed by thick segments(podoms)and thin segments(podomers)[5-6].Endoplasmic reticulum,Golgi bodies,and microbubbles can be seen in podoms.Tps also form a 3D network with other cells anchored by hetero-and homo-cellular junctions[6].As far as reproductive system is concerned,the existence of TCs has recently been demonstrated in vagina,uterus,fallopian tube,ovary,mammary gland and placenta[7].Many researchers pointed out their role in the regulation of local microenvironment,myogenic contractile mechanism,bioelectrical signaling,immunomodulation and regulation of blood flow[8].Additionally,previous research suggested that TCs might act as sex hormone level sensors and were related to pregnancy maintenance[9].TCs also played an important role in the maintenance of endometrium under physiological state and the dynamic changes of endometrial microenvironment during pregnancy[7].As the morphological characteristics and the number of TCs change under pathological conditions,such as preeclampsia and ovarian failure,there is a chance that they may contribute to treatment of above mentioned conditions[7].TCs are key component to maintain the normal structure of the female reproductive tract and play a unique role in the physiological and pathological processes of various gynecological diseases[10-14].Recent report indicated that TCs enhanced the proliferation,adhesion and motility of endometrial stromal cellsin vitro[15].Endometrial cells especially endometrial stromal cells flowing back through the fallopian tubes and into the pelvic cavity was widely accepted as the mechanism of EMs.Hence we hypothesized that TCs may be involved in EMs.In the study,we contribute to a deeper comprehending of TCs,showing evidence that TCs exist in ovarian EMs and might be involve in the pathogenesis of ovarian EMs.
MATERIALSAND METHODS
1 Patients
Five patients with ovarian EMs,(26.5±2.8)years old,were scheduled for elective surgery(laparoscopic oophorocystectomy)and selected for the research.Oophorocystectomy was performed according to the standard procedure.Tissue samples from ovarian EMs were acquired for further research.All patients were surgically treated at Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital of Fudan University,Shanghai,China in 2019-2020.The research was implemented in accordance with the ethical,moral,regulatory and scientific principles governing clinical study.All surgical samples were approved by the Ethic Committee of Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital of Fudan University(No.2018-76).
2 Tissue harvesting and ultrastructure observation
2.1 Hematoxylin-eosin(HE)stainingThe endometrial tissues were fixed in 4%formaldehyde for 72 h,which was dehydrated in a gradient of ethanol,and embedded in paraffin.Then,the tissues were cut into pieces and stained with HE staining.Pathological changes were observed with an optical microscope(BX51;Olympus).
2.2 Transmission electron microscopy(TEM)The ovarian EMs specimens were cut into small pieces and fixed overnight in 2.5%glutaraldehyde in 0.1 mol/L phosphate-buffered saline(PBS,pH 7.4)at 4℃.Then,the fixed samples were rinsed in PBSfor 10 min×3 times,and incubated for 1 h in buffered 1%osmium tetroxide(Polysciences)at room temperature.After washing in 0.1 mol/L PBS(pH 7.4),the samples were dehydrated using ascending concentrations of ethanol(50%,70%,80%and 100%),permeabilized with a propylene oxide-Araldite mixture,and then embedded in Araldite.Ultrathin sections(thickness:50 nm)were cut using an ultramicrotome(Reichert-Jung)and mounted on copper-coated grids.The specimens were stained with 1%uranyl acetate and Reynold′s lead citrate for 20 min.The processed specimens were observed under a transmission electron microscope(TECAI G2 Spirit Bio TWIN)and photographed using a high-resolution 16 mega-pixel digital camera connected to the microscope.
RESULTS
EMs is characterized by the presence of endometrial-like tissue and stroma in extra-uterine locations.The ectopic endometrium was detected by HE staining(Figure 1).
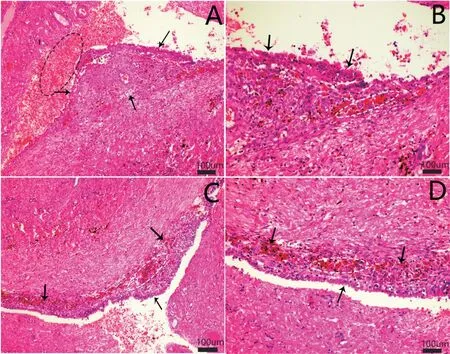
Figure 1.The histopathological changes in ovarian cyst detected by optical electron microscopy with HE staining(scale bar=100μm).A:the ectopic endometrium was observed(indicated by black arrows),and the ovarian cyst contained a large number of substantial red blood cells(the dotted black circle);B,Cand D:ectopic endometrium was in the focus of the ovarian cyst(indicated by black arrows),and the cells engulfing blood pigment were observed in or adjacent to ectopic endometrium(the dotted white circle).
Then,the patients with ovarian cysts were diagnosed as EMs by pathological diagnosis.The ultrastructural features of the TCs were observed in the tissues of patients with ovarian EMs.The TEM images showed morphological changes in capsule wall in ovarian EMs(Figure 2).The glandular configuration,collagen fibers(CFs),and red blood cells(RBCs)were observed by TEM(Figure 2).
We also observed TCs that demonstrated slender,long,moniliform cytoplasmic prolongations in ovarian EMs(Figure 3A and B).Tps contained abundant lipid droplet,autophagosome and endoplasmic reticulum(Figure 3C).
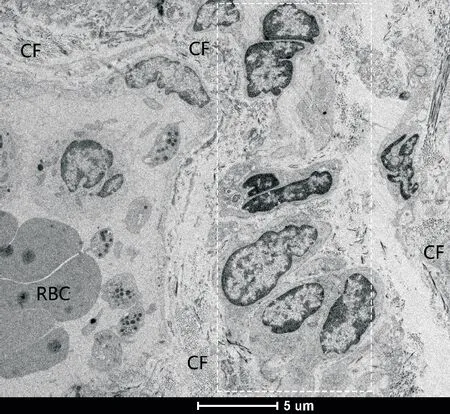
Figure 2.Morphological characteristics in capsule wall of ovarian endometriosis(EMs)under transmission electron microscope(scale bar=5μm).The typical glandular configuration(within the white rectangle),collagen fibers(CF),and red blood cells(RBC)were seen.
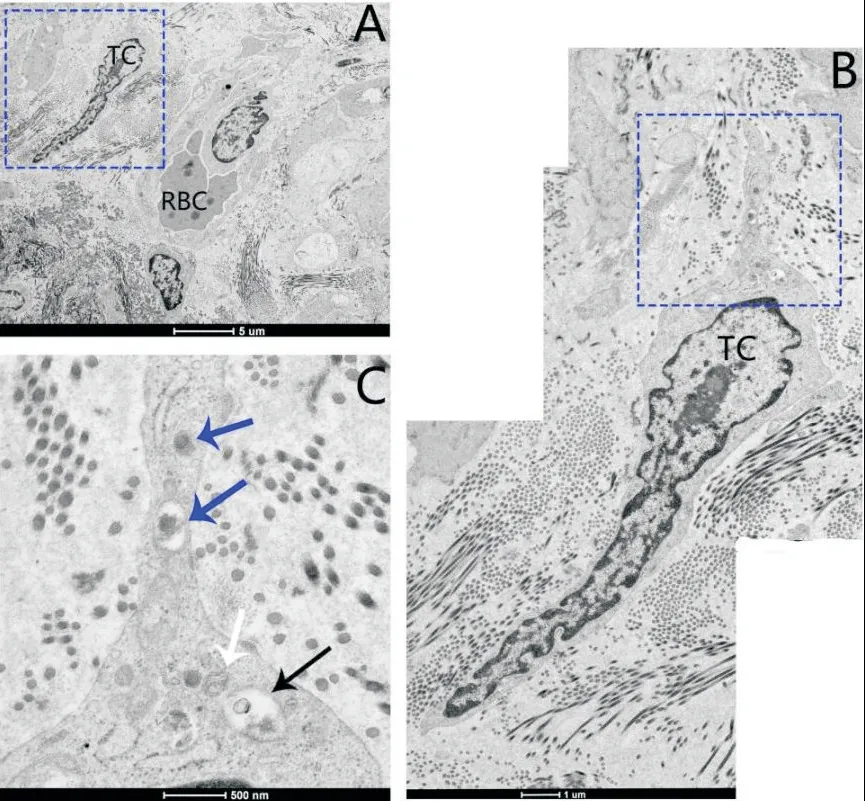
Figure 3.A new interstitial cell,the telocyte(TC),was found in the patient with ovarian EMs under transmission electron microscope.A:the cell body of TC had a large nucleus and very small amount of cytoplasm(scale bar=5μm);B:the image of high power of rectangle in figure A[scale bar=1μm;the TC showed a fusiform body,and a slender,long and moniliform cytoplasmic process(telopode,Tp;merged image)];C:the image of high power of rectangle in figure B[scale bar=500 nm;the Tp contained autophagosome(black arrow),endoplasmic reticulum(white arrow)and lipid droplet(blue arrows)].
The cell with long projections exhibited features that were in accord with the standard of classic TCs proposed by Popescu(Figure 4A).Plentiful lipid droplets were observed between the TC and CF(Figure 4B).Tps had overlapped structure and punctate contact(Figure 4B).
Figure 5 showed a typical TCwith a large,triangular nucleus and a long Tp containing mitochondria and lipid droplet.Such more lipid droplets among CFs and TCs were also observed(Figure 5B).
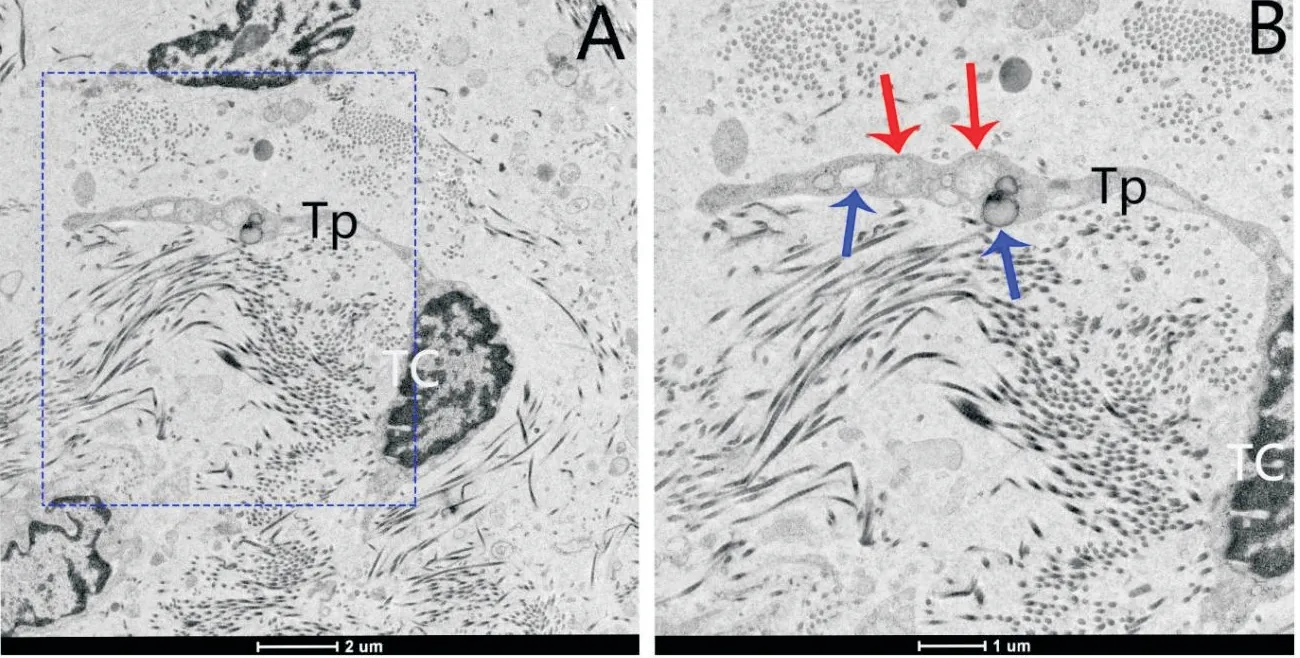
Figure 5.Ultrastructure of podom of Tp in the tissue of patients with ovarian EMs.A:the TC showed distinctly triangular nucleus with a small amount of cytoplasm(scale bar=2μm);B:the higher magnification of blue rectangle in figure A(scale bar=1μm)showed that the dilated segment of Tp podom had an irregular shape,with plentiful lipid droplet(blue arrows)and mitochondria(red arrows).
We further observed that these TCs touched and connected with each other(Figure 6A).The Tps were in direct contact with neighboring cells(Figure 6B and C).Tps among the neighbouring TCs formed various types of junctions.Vesicles were discovered between the Tps.It suggested that the adjacent TCs may use secretory vesicles to form homo-cellular communication or exchange of intracellular material(Figure 6B-D).
TCs were observed,and podoms accommodated plentiful lipid droplet and autophagosome(Figure 7).
We also discovered the TC which showed a large,specially-shaped nucleus with long protuberance(Figure 8).
A wide variety of fusiform TCs and their Tps were observed.The TCs and Tps established contact with other endometrial stromal cells(Figure 9).
These results indicated that TCs were present in EMs and had more significant autophagosomes and lipid droplets than normal TCs.Furthermore,TCs formed a network through direct contact via long Tps and indirect contact via vesicles.
DISCUSSION
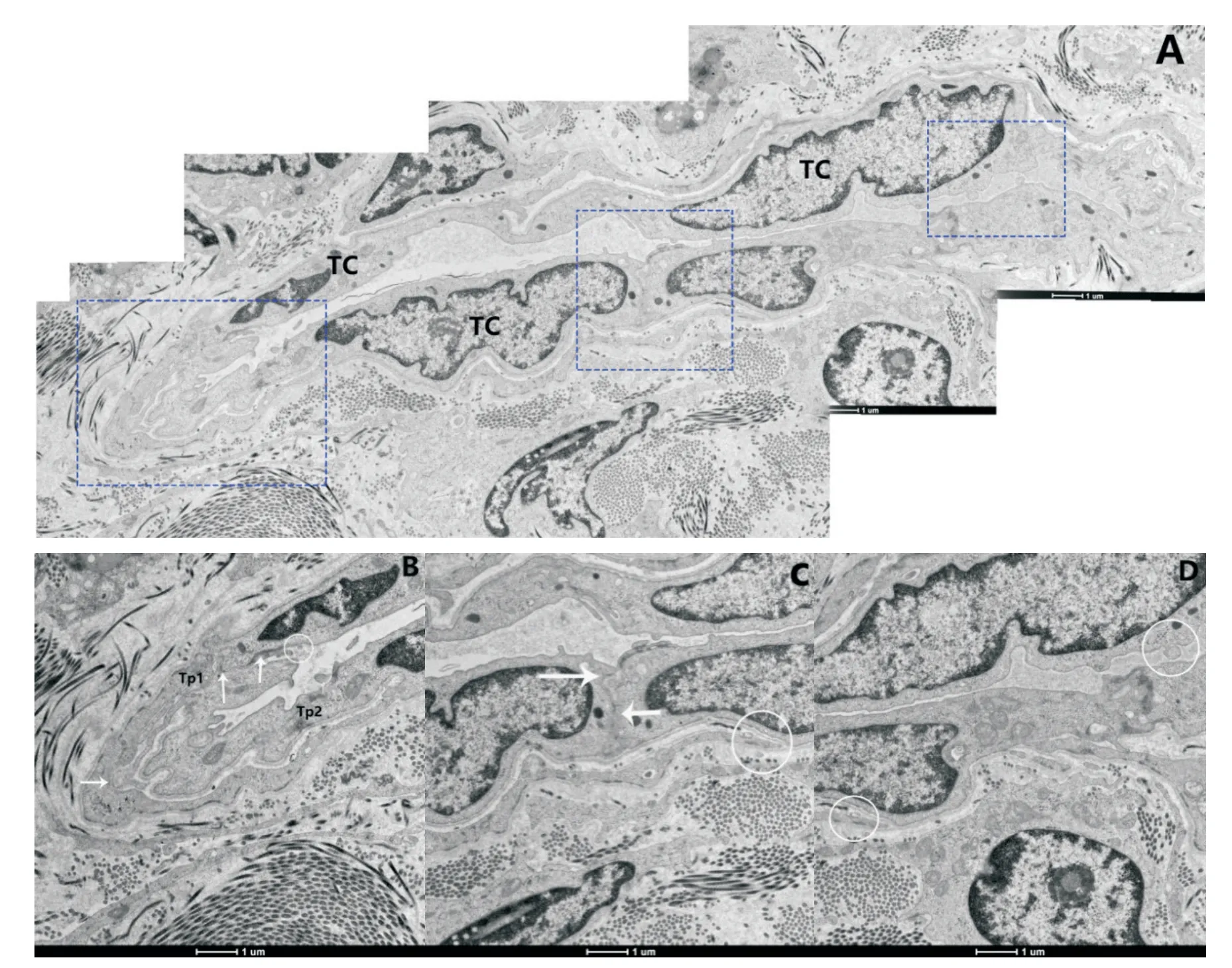
Figure 6.Cell communication between different TCs.A:several TCs and Tps were seen(merged image;spindle-shaped cell bodies of TCs had relatively large euchromatic nucleus surrounded by thin cytoplasmic layers accommodating cisterna;TCs formed a network);B:the local content of figure A[left rectangle;the end-to-end junction among Tps formed close contact among TCs;the ultrastructural feature of the Tps was shown;long cytoplasmic processes with thin segments(podomers)and dilations(podoms,white arrows)were characterized];C:the local content of figure A[middle rectangle;the cell bodies of 2 TCs formed directly contact each other;homo-cellular junctions(arrows)were seen];D:the image of right rectangle in figure A(the ultrastructural feature of the Tps was shown).Vesicles were discovered between the Tps(white circles in B,Cand D).The scale bar=1μm.
TCs are recently discovered cell population in reproductive system,characterized by a small cell body with very long,slender prolongations,termed Tps.TCs perform multiple biological functions in the female reproductive system.EMs is a gynecological disease which involves an interaction of endocrine,immune,proinflammatory,and proangiogenic processes[16-17].Previous studies have shown that TCs may be involved in EMs in a number of ways.Researches identified that TCs obviously enhanced thein vitromotile and invasive capacity of endometrial stromal cells,thus increasing the likelihood of EMs with unexplained infertility.The identified TCs might be involved in the maintenance of structural and functional integrity of oviduct tissue.TC damage might participate in structural and functional abnormalities of oviduct in the rat model of EMs-affected oviduct tissue.Decreased activity of TCs in EMs causes disorders of a transport function through the uterine tubes resulting in infertility in the rat model.Previous results indicated that TCs play functional role in the activation of peritoneal macrophages,which likely through indirect paracrine effects trigger and maintain the immune response in mice.However,all of these studies have been done in animals orin vitro.We directly expounded the existence and the ultrastructural features of the TCs in the tissues of patients with ovarian EMs in the present study.The results indicated that TCs in EMs displayed the representative morphological characteristics defined by Popescu,and formed a network through direct contact via long Tps and indirect contact via vesicles.The finding was also in accord with previous researches that Tps had direct membraneto-membrane contacts through nano-contact,and gap junctions.Autophagosomes are double-membrane sequestering vesicles,which are the symbol of the intracellular catabolic process called macro-autophagy.The cargo molecules targeted by autophagosomes ranges from redundant organelles and long-standing proteins to invading pathogens.Autophagosomes finally deliver the sequestered material in the interior of these organelles by fusing with lysosomes.Autophagy represents an essential survival mechanism because it eliminates the cytoplasm from potentially and unwanted toxic structures,and the autophagosomes are its central stage[18].The lipid droplet,which consists of a heterogeneous macromolecular assembly of lipids and proteins,is a dynamic cytoplasmic organelle.Lipid droplets may play a part in lipid storage and metabolism,and they are involved in the regulation of signal transduction and intracellular trafficking[19].The results of this study indicate that TCs in EMs contain abundant and large autophagosomes.There are grounds for believing that TCs may be involved in the process of EMs through cell-to-cell communication,shed vesicles,autophagosomes and lipid droplets.This research provides an original structural and functional perspective for the cellular components of EMs,and improves our comprehesion of the pathological aspects of EMs.However,the potential functions of TCs and the mutual effect among different cells in the EMs need further research.
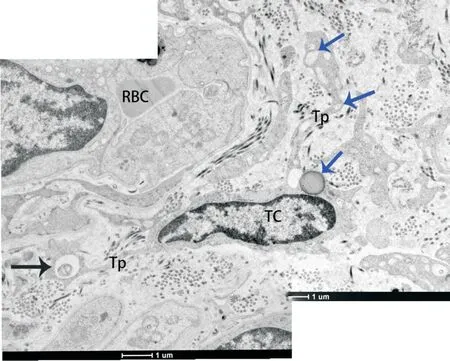
Figure 7.The ultrastructural feature of the Tps was shown(merged image).Long cytoplasmic processes with thin segments(podomers)and dilations(podoms)were characterized.Abundant cytoplasm was rich in some organelles and thick and short processes.Podoms accommodated plentiful lipid droplet(blue arrows)and autophagosome(black arrow).The scale bar=1μm.
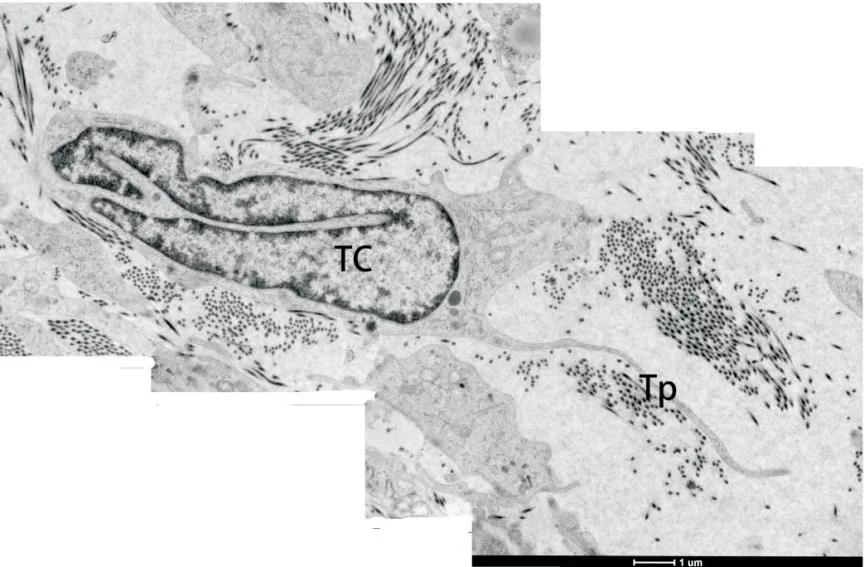
Figure 8.The TC which showed a large,specially-shaped nucleus with long protuberance was also discovered(scale bar=1μm).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
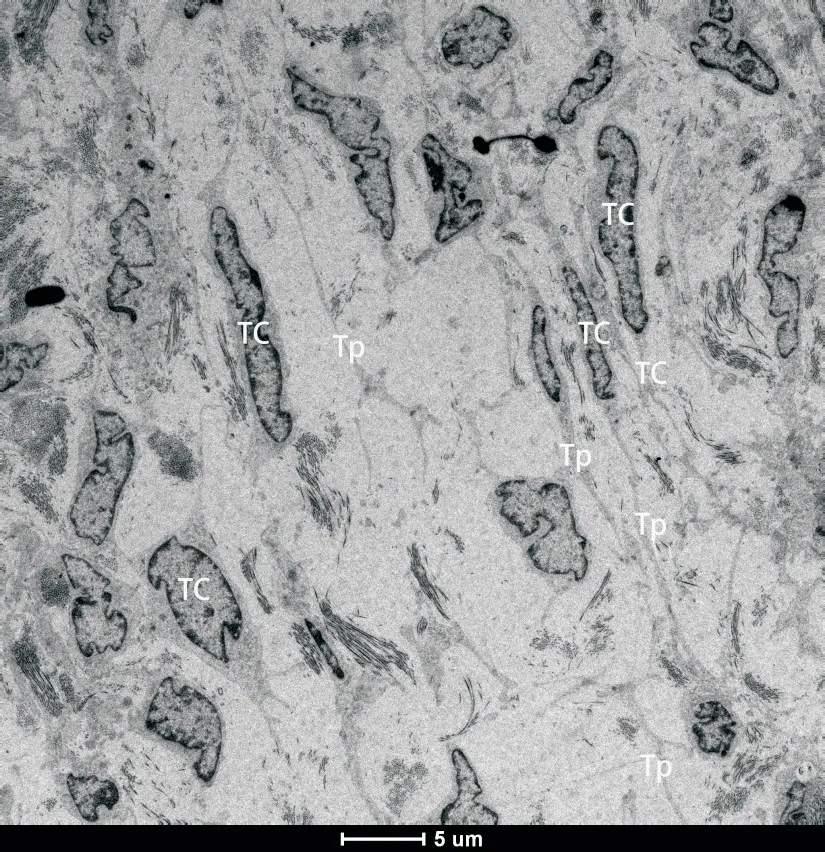
Figure 9.A wide variety of fusiform TCs and their Tps were seen(scale bar=5μm).TCs and Tps established contact with TCs of other endometrial stromal cells.
We thank Mrs.Nai-ying YANG from Department of Electronic Microscopy,Shanghai Normal University,for her technical assistance with the transmission electron microscope.

