The Calculation Method for the Volume of Landslides and Dammed Lake Sediments Triggered by a Strong Historical Earthquake in the Loess Plateau:A Case Study of Qiuzigou,Gansu Province,Northwest China
DU Peng,XU Yueren,LI Wenqiao,TIAN Qinjian and CHEN Lize
Key Laboratory of Earthquake Prediction,Institute of Earthquake Forecasting,CEA,Beijing 100036,China
The quantitative calculation of the volume of large earthquake-triggered landslides and related dammed lake sediments is of great significance in the study of secondary disasters and focal parameters of strong historical earthquakes.In this study,the dammed lake induced by Qishan M7 earthquake (Lingtai County,Gansu Province,Northwest China) is selected as the research object.Based on the information collected from the 4 boreholes in the dammed lake area,we further take advantage of the lowlevel Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) photogrammetry and the morphology recovery method,to calculate the volume of the dammed lake and landslides,respectively.Finally,major conclusions are obtained as follows:①the AMS-14C age at the bottom of the Qiuzigou Dammed Lake sediments is 2 890 ± 30 BP,which coincides with the 780 BC Qishan earthquake; furthermore,the Qiuzigou Landslides seem to have been triggered by the earthquake,forming an enclosed dammed lake deposition environment after the upstream sediments accumulate;②the Qiuzigou landslides are opposite-sliding landslides that have blocked the river valley; in detail,landslide volumes at the right and left banks are 235 × 104 m3 and 229 × 104 m3,respectively.The length of the dammed lake is 2.6 km,with a thickness of approximately 43 m near the landslides,and the total sedimentary volume is 573 × 104 m3; ③the erosion rate of Qiuzigou Landslide Dammed Lake is 0.44 mm/a,the accumulation rate is 15.05 mm/a,and the soil erosion modulus is 593 t/(km2/a),characterized as slight erosion.Quantitative research on the formation of landslides and dammed lakes from strong historical earthquakes is vital for increasing our understanding of the vibrational characteristics and surface action processes of these types of earthquakes.
Key words:Earthquake-triggered landslides; Earthquake dammed lake sediments;780 BC Qishan earthquake; Qiuzigou; Loess Plateau
INTRODUCTION
The tectonically active peripheral area of the Ordos block is considered as a strong earthquake-prone zone.However,owing to the remote geological history and less detailed earthquake recordation,the study of some historical earthquakes is challenging.Therefore,several parameters such as the magnitude,macro-epicenter and epicenter,extreme earthquake zone,and seismogenic structure of these challenging earthquakes have long been controversial,thereby causing uncertainties in the assessment of regional seismic activities and analysis of seismic hazards (Du Fang et al.,2018; Xu Xiwei et al.,2017).However,based on the description of earthquake damage,the spatial distribution of secondary disasters caused by earthquakes can help us determine the macro-epicenter,extent,and intensity of the extreme earthquake zone(Shi Zhigang,2011;Yuan Daoyang et al.,2017).In addition to the information provided by the limited historical records,a large number of co-seismic landslides and dammed lake sites remain in the peripheral area of the Ordos block,such as the HongtongM8 earthquake in 1303,HuaxianM8 earthquake in 1556,and LixianM8 earthquake in 1654.In particular,the TongweiM7earthquake in 1718 and HaiyuanM8earthquake in 1920 (Jia Jie,2016; Xu Yueren et al.,2018a,b) have retained numerous landslides,and there is a clear record of earthquake damage in the historical documents.Among these landslides,except for several small-scale co-seismic landslides which are almost disappeared,the larger earthquake landslides are still clearly visible.Particularly,the QishanM7 earthquake that occurred in 780 BC is the first systematically recorded destructive earthquake in Chinese history.The“Book of Songs” and“Historical Records” precisely record the occurrence time of the earthquake as 780 BC.Earthquake damage records include notations such as “three rivers exhaust,Qishan collapse;” “numerous rivers boil,hills collapse;” and “high banks become valleys,deep valleys become hills”.According to these records,this earthquake has triggered several co-seismic landslides and should be a strong earthquake event.This historical earthquake has always attracted the attention and consideration of researchers; however,in-depth comprehensive and systematic research is lacking.In this study,we select the typical Qiuzigou landslide dammed lake in a dense landslide distribution area,which is one of the significant historical landslides in Qishan and its northern plateau.UAV survey and drilling are performed to determine the volume of the landslide and deposition of the dammed lake.Additionally,quantitative calculations are performed,and the age of the landslides and the dammed lake are measured using14C dating.Finally,the relationship between the earthquake record and corresponding dense landslide body is established.
Mountain collapses,landslides,and mud-rock flows caused by external forces,such as heavy rains and earthquakes can block a river (valley),thereby forming a dammed body where backwater accumulates and forms a dammed lake (Yu Guoan et al.,2010).Through consulting historical documents and landslide data in China as well as conducting field investigations,Chai Hejun (1995) identified 147 river-blocking landslides and gathered valuable data revealing that strong earthquakes and heavy rain are the two primary factors that induce landslides to form barrier lakes.Current research on barrier lakes has mainly focused on the identification of ancient barrier lakes and their causes (Zheng Benxing,1994; Tao Yingke,2004; Ma Jianqing et al.,2009; Li Qiankun et al.,2011; Chen Chao et al.,2016; Li Jia et al,2018),including environmental effects (Chai Hejun et al.,2000; Yu Guoan et al.,2010; Li Jia et al.,2018),geological disasters (Cui Peng et al.,2009),stability analysis (Yan Zuwen et al.,2009),and other aspects.The still water sediments residing in dammed lakes are called dammed sediments.Wang Lansheng et al.(2012) obtained important paleo-earthquake and paleo-climate data in the study area through detailed research on the sediments of the ancient dammed lake in Diexi of the Minjiang River area,which is of great value to the study of paleo-geological environment changes and paleo-climate evolution.Xu Hongyan et al.(2015) investigated changes in the sedimentary grain sequence and bedding of the dammed lake at Diaolin in Maoxian County,Sichuan and performed analyses of optical luminescence and dating using the sporopollen concentration.The author indicates that the dammed lake may have been formed in 638 AD by an earthquake.The grain size change of the continuous lacustrine sediments and soft sediment deformation structures in the tectonically active area may contain records of the occurrence of ancient earthquakes and even the average recurrence interval (Jiang Hanchao et al.,2014,2016).Regarding the volume of ancient dams,a majority of recent studies have only conducted simple estimates,and therefore,it is of great significance to accurately compute the volume of dammed sediments.
As a key supplementary method for satellite remote sensing and conventional aerial photogrammetry,UAV has been increasingly utilized in various fields,owing to its strong maneuverability,high flexibility,low-altitude flight,low cost,and high resolution (He Jing et al.,2017; Lv Lilei,2016; Han Jie et al.,2008; Wen Qi et al.,2012).It has also become the primary means to obtain high-precision digital elevation model (DEM) data in the field of geoscience.With regard to geological disaster surveys,UAV provides extremely important data for quantitative analysis and research on landslides and other geological disasters; this has enabled the accurate calculation of various landslide parameters.The UAV image data have exceptionally good timeliness,and the accuracy meets the needs of rapid disaster assessment.At the same time,high-resolution UAV image data can serve as supplements for seismic damage investigation and remote sensing interpretation of strong historical earthquakes.
The Qiuzigou landslide dammed lake is located in Puwo Township,Lingtai County,Gansu Province (107.51°E,34.95°N).This lake is formed by a pair of “hedging” loess landslides in the north-south loess valley in the upper reaches of the Jinghe River.The landslide on the right bank of the valley is in the shape of a dustpan with a width of 365 m,and the height difference of the back wall of the landslide is 101 m.By comparison,the landslide on the left bank of the valley is chair-shaped,377 m wide,with a height difference of 112 m.These two landslides are both cut-layer landslides,and the main sliding surface cuts off the loess layer,paleosol layer,and calcareous nodule layer of different ages.As of 1975,according to a historical image,the dam was silted up,and the dam body was eroded.The image clearly shows that the flowing water gutter behind the lagoon has eroded the dammed lake sediments.In 1976,after artificial reconstruction,the barrier lake was restored,and the current reservoir was formed,which is now the primary source of drinking water in Puwo Township.The original longitudinal slope of the valley where the landslide occurred is 3.73%,the catchment area of the basin above the landslide is 5 km2,and the dam deposit area is 0.43 km2.Through UAV low-altitude photogrammetry of the landslide-dammed lake and its adjacent watersheds,high-resolution DEM and orthophotos are obtained,and the dammed sediments are drilled to obtain the columnar shapes of the four boreholes.Finally,high-resolution DEM and borehole data are used to estimate the volume of the landslide body and dammed-lake sediments.
1 IMAGE AND DRILLING DATA
In this study,a detailed examination of a typical historical landslide-dammed lake—Qiuzigou —is performed in the dense landslide distribution area (Fig.1,Fig.2,Table 1).Low-altitude photogrammetry of the Qiuzigou landslide-barrier lake and adjacent watersheds is performed using a UAV.

Figure 1 Interpretation landslide distribution map and the location of dammed lakes in the study area

Figure 2 Google Earth image of typical landslide dammed lake in the study area
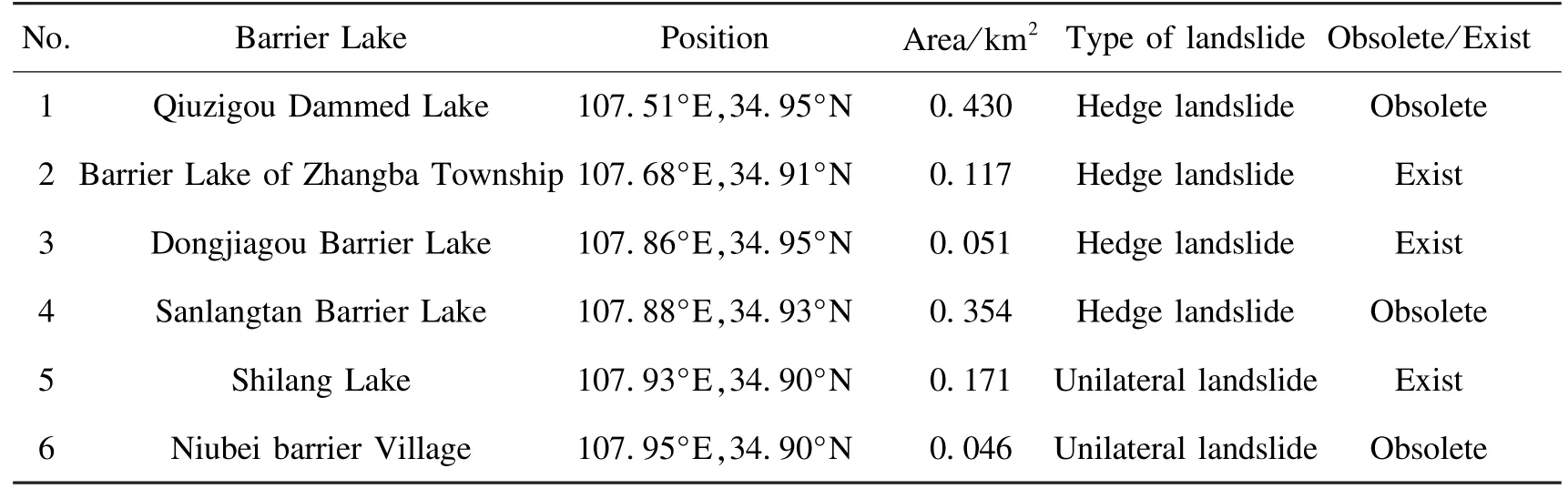
Table 1 Typical landslide dammed lake information in the study area
To minimize the impact of vegetation,the large-scale digital orthophoto collection operation is conducted in March when vegetation is scarce.The measurement area is approximately 7 km long from north to south and 4 km wide from east to west,corresponding to a total area of approximately 28 km2.Therefore,the measurement area is divided into two areas—north and south—and two take-off points are selected for two flights.The flight altitude is 300 m,and 4 124 photos are collected.The orthophoto is processed indoors using the Photoscan software.The final ground resolution of the orthophoto is 0.15 m,and the DEM accuracy is 0.5 m (Fig.3,Fig.4).In addition,the 1975 keyhole strip-shaped historical satellite images of the study area are collected to determine the shape of the dam before the reconstruction of the reservoir.The erosion of the dammed lake by flowing water gullies is insignificant,demonstrating that the dam failure of the barrier lake has a relatively short history and the abandonment time of the barrier lake(discussed below) is 1975.

Figure 3 UAV side view of Qiuzigou Landslide barrier lake

Figure 4 Historical image,drone image,and DEM of Qiuzigou Landslide and Dammed Lake
After preliminary reconnaissance and low-altitude aerial surveys,we drille the dammed lake sediment body and obtain a complete core.The four boreholes are all located in the middle of the dam body,penetrating the dam body to the loess at the bottom of the original valley.These processes are able to ensure that the maximum thickness of the dam at the borehole is revealed.The dammed lake sediments cover the loess in the valley,and calcareous nodules are observed at the bottom of boreholes 1 and 2.The dam sediment is gray-black silty clay with occasional calcareous nodules.In addition,three layers of yellow silty clay are sandwiched in borehole 3.The diagram of the boreholes is depicted in Fig.5.The total footage of these four boreholes is 128.5 m (Table 2).

Table 2 Drilling basic information
The bottom sediments of the dams are the first deposits after the blockage of the gully by the landslide deposition.Thus,the age of the sediments can be considered to represent the age at the beginning of dam sedimentation,which is approximately the time when the landslide occurred.Therefore,we collect14C isotope chronology samples from the core.Among them,a gray-black sludge sample containing carbon chips and organic matters is collected from a depth of 20 m from the top to bottom of ZK1,and the age is determined to be 2 200 ± 30 BP.Samples with carbon fragments are collected from the top of ZK2at a depth of 4.5 m and from the bottom of ZK2at a depth of 30.4 m.The gray-black sludge samples of dust and organic matters are determined to be 160 ± 30 BP and 2 890 ± 30 BP,respectively (Fig.5).These samples are measured by American Beta Laboratories using an accelerator mass spectrometer.
2 VOLUME CALCULATION METHOD
2.1 Volume of Landslide (Deficient Area)
The barrier dam is composed of materials from landslides or collapses that result in the blockage of the corresponding river.The scale of the barrier dam is equivalent to the empty volume of the landslide or collapse materials and thus,can be evaluated by calculating the landslide volume.Currently,there are three main methods for calculating the volume of a landslide.The most commonly used method for calculating the volume of a landslide is to multiply the area of the landslide by its average thickness.This method is simple and fast.However,owing to the uneven thickness of the landslide,the result of the calculation is quite different from the actual value.For example,in the study of seismic landslides,a certain number of seismic landslides and area sample points are generally selected for the estimation of the landslide scale in a single seismic area,and a power-law relationship between the two is established according to the relationship between the volume and area(Guzzetti F.et al.,2009).Using the landslide “area-volume” power-law formula,the landslide area is converted to volume (Parker R.N.et al.,2011).The average thickness estimation is subjective and the calculated area includes the source area,accumulation area,and sometimes even the area of the landslide circulation region.As a result,the calculation results may have a large error.A more accurate calculation method is to identify the sliding surface of the landslide.Field measurement methods mainly include drilling on the landslide body,as well as various other geophysical exploration methods (Jongmans D.et al.,2007).According to drilling or geophysical data,a binary polynomial is used to fit the sliding and upper surface of a landslide with a short slip distance.The Single Value Decomposition (SVD) method is used to fit the landslide perimeter,and the double integral algorithm can be used to accurately calculate the volume of the landslide (Li Song,2013).Despite of high accuracy,calculating the landslide volume with the use of the sliding surface information obtained by drilling methods has other disadvantages,including huge workload and high cost.The base structures of landslides explained by geophysical exploration methods are uncertain or diversified,and the methods are costly and timeconsuming,which is not conducive to a timely response to sudden landslide events.The landslide volume can also be calculated based on DEM/digital terrain model (DTM)subtraction before and after sliding (Chen Zhengchao et al.,2014; Tseng C.M.et al.,2013; Chen S.C.et al.,2019).
Figure 5 Borehole histogram and core photo
The “Cut-Fill” tool provided by the ArcGIS platform can calculate the volume change before and after the cut-fill process and the highlight cut-fill position using the renderer;meanwhile,the tool treats the positive and negative volumes as excavated and filled positions,respectively.The volume calculation principle is as follows:for a single pixel,the volume calculation formula is

where ΔZ=Zbefore-Zafter,representing the elevation difference of the two images at a given pixel location before and after (Fig.6).The total volume is the sum of the corresponding volume of each pixel.
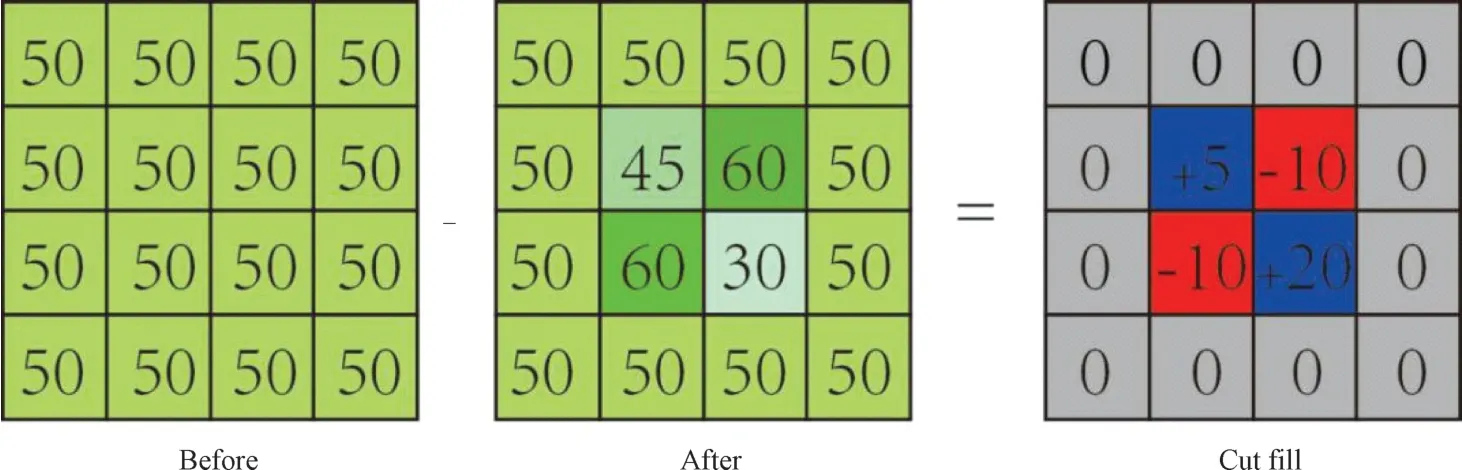
Figure 6 ΔZ calculation principle
With the popularization of Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) technology and low-altitude drone photogrammetry,it is easy to obtain a high-precision post-landslide DEM; however,a high-precision DEM before sliding is often not available.The volume of the landslide calculated by a low-precision DEM before sliding is quite different from the actual volume.To solve this problem,the high-resolution post-landslide DEM obtained by the drone is utilized to generate contour lines with a spacing of 5 m,based on the shape and gradient of the adjacent slope on the platform.Upwardly curved contour lines are generated at the landslide,close to the contour of the sliding front slope.Then,the contour lines are used to generate the TIN irregular triangle network.Finally,the TIN irregular triangle network DEM can be converted to the DEM before sliding (Fig.7).Using the fill and excavation tool “Cut-Fill” provided on the ArcGIS platform,the two main landslides that led to the formation of the Qiuzigou dam body-the right bank landslide deficit areaV1and the left bank landslide deficit areaV2-are calculated at approximately 185 × 104m3and 179× 104m3,respectively (Table 1).The real landslide volume is the sum of the deficit areasV1andV3(left bank landslide) and the sum of the deficit areasV2andV4(right bank landslide) (Fig.8).The volumesV3andV4are estimated based on their respective lengths,widths,and thicknesses,approximately 50 × 104m3.

Figure 7 Process of calculating the volume of the landslide deficit area using a high-resolution DEM

Table 3 Calculation results of landslide volume
2.2 Calculation of Dam Volume
Taking advantage of a high-resolution DEM,we obtain the cross-section of the dammed lake,as well as the cross-sections of the upper and lower reaches of the corresponding valley (without deposition) and the adjacent valleys (Fig.9(d)) The cross section results suggest that the dammed sediments belong to the type of V-shape gully(Fig.9(b)).We then construct the longitudinal section of the DEM along the valley and combine the depth of the original valley at the four drill holes to fit the longitudinal section of the original valley before the landslide (slope drop was 3.73%),thus determining the thickness of the sediment bodies.In detail,the thickness of the sediment body in contact with the landslide deposit (dam body) is approximately 60 m,and the distance from ZK01 is 615 m.Fig.9(a) shows the longitudinal section of the dam sediment.Finally,a threedimensional map of the sediment is drawn according to the “V” shape of the cross section,the thickness of each 100 m point on the vertical section,and the corresponding plane width(measured from the UAV high-resolution orthophoto) (Fig.10).

Figure 8 Model diagram of Qiuzigou Landslide

Figure 9 Topographic profile of Qiuzigou
The irregular dammed lake sedimentary body is divided into several regular bodies for a simpler calculation.With an interval of 100 m,the dammed lake sediment body is cut into 26 sections.Each section is approximately regarded as a triangular prism with cross section S1as the bottom surface,cross section S2as the top surface,and segment lengthL(100 m)as the height (H).The volume of the dammed lake sediments is the sum of the volume of 26 triangular prisms,which totals 5 724 338 m3(Table 4) (cross sectionSis regarded as a triangle,S=segment width×corresponding thickness×0.5,and the calculation formula for the volume of a triangular prism isV=H/3[S1+S2+SQR(S1×S2)]).

Figure 10 3-D display of dammed lake sediments
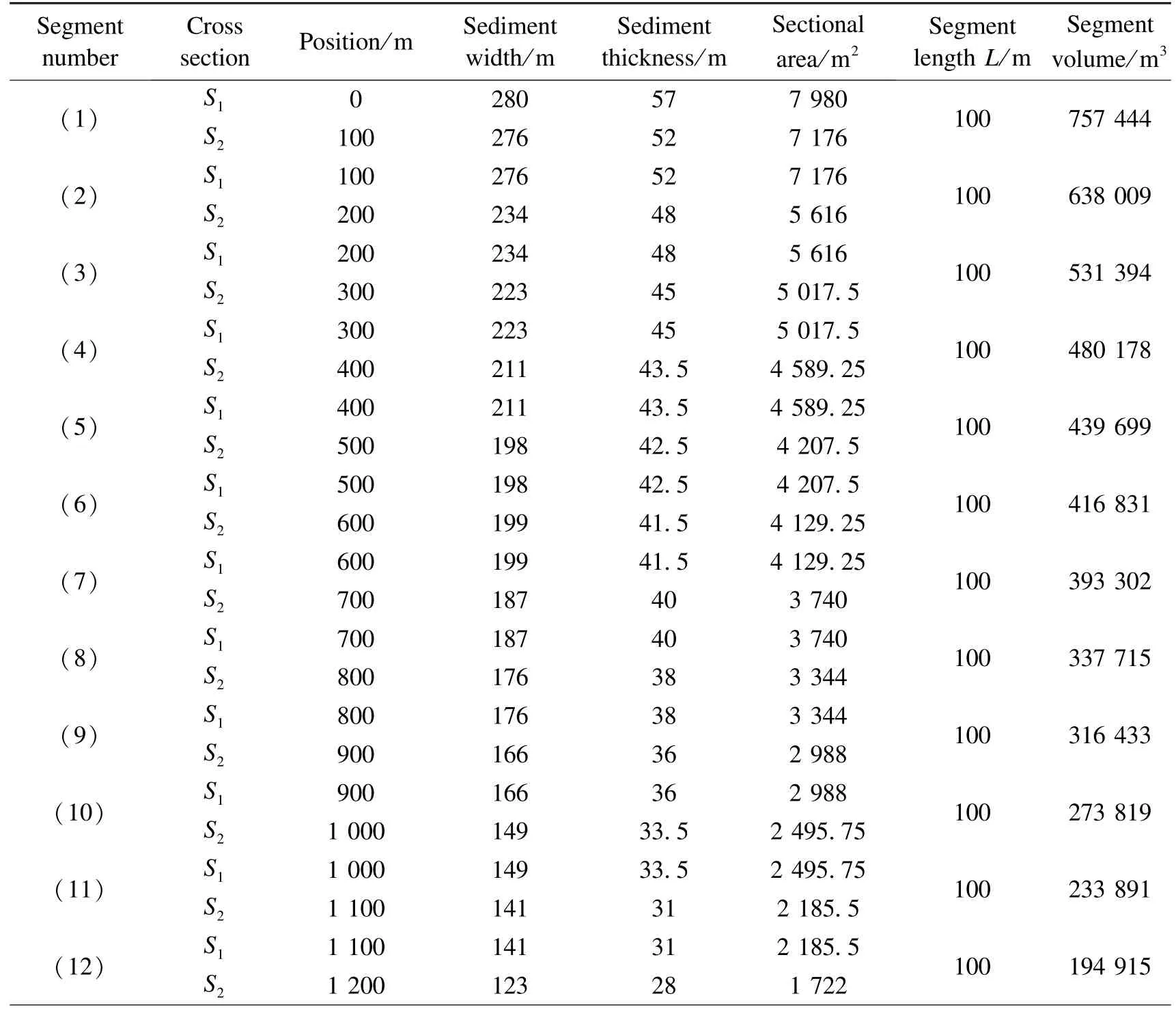
Table 4 Calculation of the volume of dammed lake sediments

Table 1
3 DISCUSSION
Two opposite-sliding loess landslides occurring on both sides of a deep-cut gully is a unique developmental form of landslides in loess areas.Based on the UAV DEM and the restored pre-sliding DEM,the Qiuzigou Landslide Dammed Lake formation model is assumed,as shown in Fig.8.Earthquakes have triggered two simultaneous landslides on both sides,blocking the valley consequently.As a result,the valley dries up and forms the current Qiuzigou Dammed Lake.The materials that forms the barrier dam are mainly derived from the two sliding deficit areas,meaning that the volume of the barrier dam is equal to the sum of the landslide deficit on both left and right sides.In order to calculate the volume of the two landslides,a high-resolution DEM provided by UAV is used to generate contours with a spacing of 5 m.Because the natural slope of the contours of this valley is relatively straight,the contour lines of the slope on both sides are in the shape of “round brackets”.Therefore,the contour lines are manually restored to approximate the relatively straight contour of the slope before the sliding,generating a pre-sliding DEM.The sliding deficit of the landslide on the right bank of the valley is estimated to be approximately 185 × 104m3,while the sliding deficit of the landslide on the left bank of the valley reaches approximately 179 × 104m3.The volumes of the landslide bodies on the right and left banks are estimated as 235 × 104m3and 229 × 104m3,respectively.The scale of the dam is found to be equal to the sum of the landslide volumes on the left and right sides (approximately 464 × 104m3).The landslides on both left and right sides of the Qiuzigou Dammed Lake are classified according to their sizes; the results indicate they both belong to large-scale landslides (Zhang Xiaoyong et al.,2013).Xu Yueren et al.(2020) compared the image characteristics and attribute parameters of several loess landslides and rainfall landslides generated by historical earthquakes,suggesting that the large-scale rainfall landslides occurred on the Loess Plateau are small in scale and short-lived.Such landslides are often hard to be recognized on high-resolution satellite images due to vegetation recovery and human activities.Hence,we argue that the large-scale counter-landslides in Qiuzigou is less likely induced by rainfall.The high-resolution DEM indicates that the cross sections of the upper reaches and lower reaches,as well as adjacent valleys shows a “V-shape” pattern.Therefore,it is inferred that the cross-section of the dammed sediment is triangular.Based on the high-precision DEM longitudinal profile along the gully,the longitudinal profile of the original gully before the dam is fitted by the vertical profile trend of the upper and lower reaches of the dam without deposits,and the original gully depth is exposed by the four drill holes.This guarantees accurate calculation of the dam body volume.Finally,a threedimensional map of the sediments is drawn according to the thickness and corresponding plane width at each 100 m point in the cross and longitudinal sections of the “V-shape”pattern (measured from the UAV high-resolution orthophoto).The volume of each 100 m segment (total of 26 segments) is calculated from the dam-deposition contact point,obtaining a volume of 724 338 m3.For comparison,the volume of the dam body is calculated at an interval of 50 m (that is,52 segments) (Fig.11),obtaining a volume of 5 725 091 m3.The results indicate that smaller intervals correspond to more segments and larger volumes; however,the results are in close agreement at the same time.Therefore,the volume of the Qiuzigou Dam is estimated to be approximately 573×104m3,and the total length of the dam body to be 2.6 km.Starting from the contact between the dam body and the dam deposit,the volume of the dammed lake deposit within 0-1 km is 460.15×104m3,accounting for more than 80% of the total volume.The volume of the sediment within 0.6 km from the end of the dammed lake is 6.04×104m3,which is only 1.06% of the total volume.Thus,from the contacting point,40% of the total distance corresponds to more than 80% sediments,generally representing the overall scale of the dammed body.On the other hand,the contribution of the volume corresponding to approximately 20% of the distance from the tail of the dammed lake is insignificant (Fig.11).
The sediments at the bottom of the dammed deposition can be assumed to represent the age of the landslide.A gray-black silt sample containing carbon fragments and organic matters is collected from the bottom of borehole 2.The dating result shows an age of 2 890± 30 BP,corresponding to 780 BC when the Qishan earthquake occurred.Therefore,the landslide is speculated to have been caused by the “780 BC Qishan earthquake”.“Historical Records” record the following sentences:“In the Second Year of King You’s Reign,all rivers shook during the West Zhou Dynasty...”.This the relatively detailed recorded earthquake in the geological history of China; the approximate location of this earthquake is determined and the damage intensity is recorded.The “Qishan Avalanche” recorded in the historical data corresponds to the collapse of the base rock of the mountain.Zhou Kexing et al.(2007) used the lichen dating method to determine the 382 peaks in the Qishan main peak area,successfully dating the north Jiankuoling and Jueshan landslides.The study indicates that the huge landslide in north Jiankuoling and Jueshan are caused by the 780 BC Qishan earthquake.
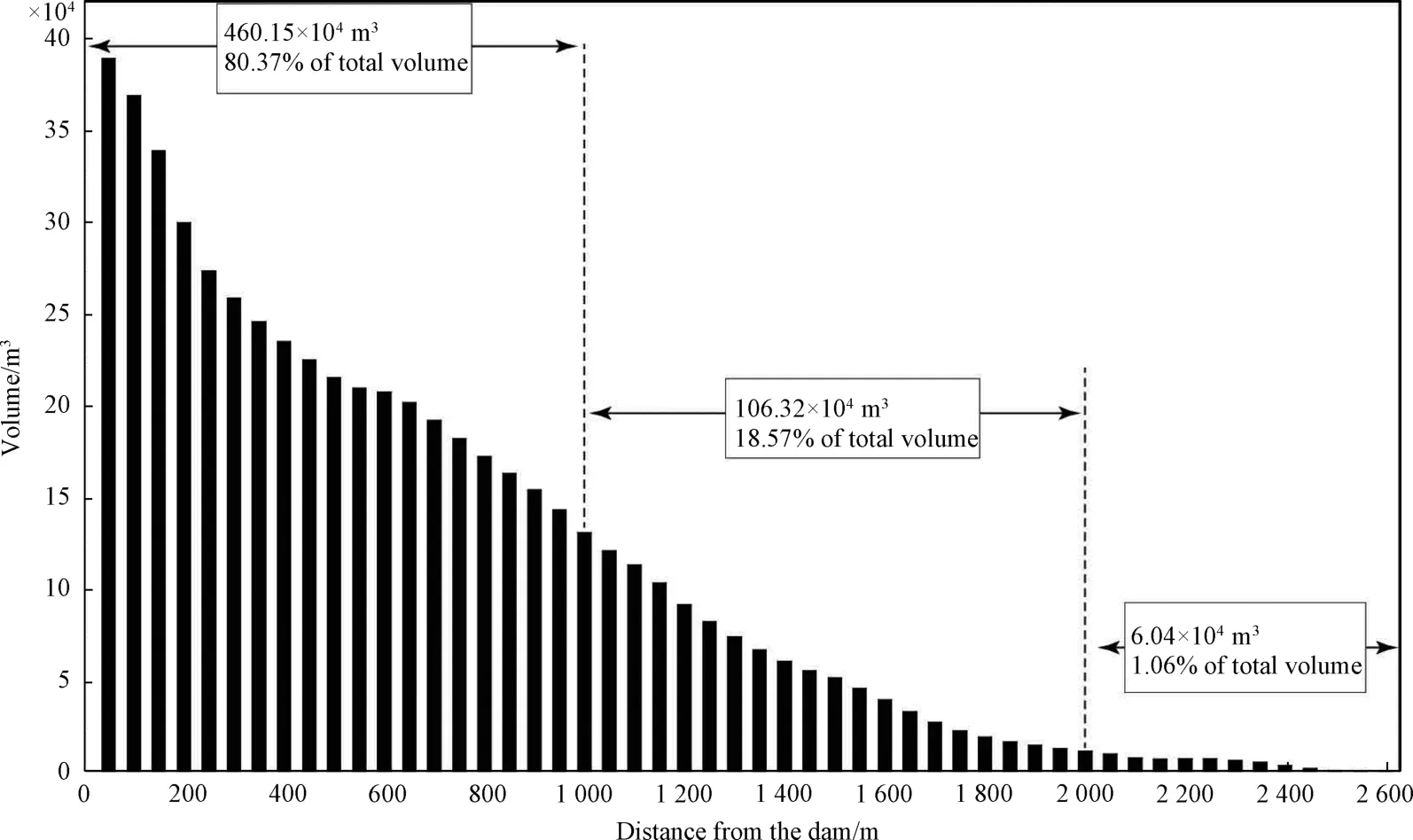
Figure 11 Volume statistics of each segment of the dammed lake sedimentary body (52 segments)
Regarding the “three rivers exhaust” recorded in the historical documents,according to the results of this study,it is likely that the 780 BC Qishan earthquake has triggered numerous landslides in the Loess Valley area.The landslide materials blocked the river valley and a dammed lake was formed as a result elongating the valley after the earthquake.The water of the Jinghe and Weihe Rivers have been significantly reduced.There are plentiful similar dammed lakes in the study area (Fig.1),some rivers have been abandoned,while others still exist.For example,Shilang Lake,a large-scale landslide dam,has already been reconstructed to a scenic spot.The local record concerning the Shilang Lake is related to Yan Ben,who was born in 1424 and died in 1479,indicating that Shilang Lake must have existed before the Huaxian earthquake of 1556.Therefore,we consider that Shilang Lake may have been induced by the Qishan earthquake,even though more information (i.e.Age of the sediments at the bottom of the lake deposit) are needed for determining the exact lake formation time.The volume of Qiuzigou Dammed Lake is approximately 5.73 × 104m3,with sediments originating from a volume of 4.57 km2watershed.The beginning time of sedimentation is estimated to be 2 890 ± 30 years ago,and the end of sedimentation is calculated to be 1975,with a sediment volume of 1.35 t/m3(Duan Juqing et al.,2009).Thus,the soil erosion modulus of this watershed is approximately 593 t/(km2·a-1),less than 1 000 t/(km2·a-1) (Qi Qing et al.,2009),indicating a slightly eroded level.The erosion rate of the enclosed watershed of the dammed lake is 0.44 mm/a,and the accumulation rate of the dammed lake is 15.05 mm/a.In addition,the deposition rate of the dammed lake is relatively high,which is an important reason for the disappearance of the dammed lake.The formation rate of Qiuzigou Dammed Lake is relatively high,and the dam height of the landslide body is approximately 50 m higher than that of the original river valley surface,thereby resulting in an abandonment time of approximately 3 000 years for the dammed lake.For some landslide bodies with small dam bodies,the formed dammed lake may be abandoned under the conditions of surface action within hundreds of years after the earthquake.Therefore,the formation and confirmation of some earthquake-landslide-induced dammed lakes still require detailed remote sensing interpretation for landslides and geological engineering investigations in the field.Determining the spatial distribution of a large number of abandoned dammed lakes induced by dense landslides,dating the age of some parts of the deposits at the bottom of lakes,and further establishing the relationship between dammed lakes and strong historical earthquakes are significant steps to provide valuable information for the quantitative assessment of the earthquake range and parameters.Numerous strong historical earthquakes have triggered dense landslides in the Loess Plateau.Most previous studies have focused on the records of earthquake-induced landslides in order to demonstrate the strength of these historically documented earthquakes.However,the temporal and spatial distribution of strong earthquakes and quantitative analyses still need to be studied.This study takes advantage of the simple and convenient low-altitude UAV method for data collection,utilizes the recovery method for presliding morphology restoration,and calculates the pre-and post-sliding volumes to obtain the volume deficit.The combination of these processes can give us each individual landslide volume and the scale of the barrier lake,thus providing robust information for the revision and reevaluation of the parameters of historical earthquakes.Since the formation age of historical earthquake landslides is often difficult to be determined,the present study attempts to use the age at the bottom of the dammed lake to represent the age shortly after the formation of the landslide,for the purpose of establishing the causal relationship between strong historical earthquakes and dense landslides in time and space,thus providing more approaches for the follow-up research.For this study,the follow-up will include the analysis of the spatial distribution of strong and extreme earthquakes from the perspective of age series and the quantitative evaluation of the scale of more typical landslide bodies.
4 CONCLUSION
Utilizing low-altitude UAV photogrammetry,this study successfully obtains the 0.5m DEM data of the Qiuzigou dammed lake and the corresponding landslides.Furthermore,by combining the information provided by the four boreholes that penetrate the river valley,we calculate the volume of both landslide body and the dammed lake deposits.Major conclusions are obtained as follows:①The volumes of the landslide bodies on the right and left banks of Qiuzigou are 235 × 104m3and 229 × 104m3,respectively.The accumulation of the two landslides constitutes the scale of the dam body of the barrier lake.②The total sediment volume of the dammed lake is 573 × 104m3.③The14C age at the bottom of borehole 2 is 2 890 ± 30 BP,which coincides with the Qishan earthquake in 780 BC,indicating that the Qiuzigou landslide is triggered by the Qishan earthquake.④The erosion rate of the enclosed watershed where the dammed lake is located is 0.44 mm/a.The accumulation rate of the dammed lake is estimated to be 15.05 mm/a.Furthermore,the soil erosion modulus of the watershed is 593 t/(km2·a-1),corresponding to slight erosion.Finally,these results are expected to broaden our understanding of the secondary disaster scale and source parameters of strong historical earthquakes.
 Earthquake Research Advances2020年4期
Earthquake Research Advances2020年4期
- Earthquake Research Advances的其它文章
- The Guest Editors of This special issue are:
- The Volume Calculation Method of Rock Collapses and Loess Landslides Triggered by the 1556 AD Huaxian M8 Earthquake in Shaanxi Province,China
- Impact of the Rainfall Intensity and Seepage on Slope Stability in Loess Plateau1
- Relationship between the Landslides Triggered by the Tongwei M7 Earthquake in 1718 AD and the Disappearance of Yongning Ancient Town
- Interpretation of the Spatial Distribution Characteristics of the Co-seismic Landslides Induced by the 1920 Haiyuan M8 Earthquake Using Remote Sensing Images1
- Early Identification of the Jiangdingya Landslide of Zhouqu Based on SBAS-InSAR Technology1
