OCX-32基因内含子变异对长顺绿壳蛋鸡蛋壳品质的影响
吴磊 谭光辉 李杰章 覃媛钰 张依裕 田琴
摘要:【目的】探討OCX-32基因对长顺绿壳蛋鸡蛋壳品质的遗传效应,为长顺绿壳蛋鸡的保种选育及开发利用提供参考依据。【方法】以长顺绿壳蛋鸡为材料,采用PCR产物直接测序法筛选OCX-32基因SNP多态位点,实时荧光定量PCR检测组织表达谱,运用SPSS 19.0广义线性模型(GLM)分析SNP位点基因型或双倍型与所测定性状指标的相关性。【结果】在长顺绿壳蛋鸡OCX-32基因中检测到3个SNPs位点,分别是位于内含子1上的g.22592323G>T及内含子3上的g.22597350T>C和g.22597555G>A。卡方(χ2)检测结果发现,g.22597350T>C位点的基因型分布显著偏离Hardy-Weinberg平衡(P<0.05,下同)。连锁不平衡分析结果显示,3个SNPs突变位点不存在强连锁不平衡,共发现4种单倍型和8种双倍型,单倍型H1和双倍型H1H2频率最高,分别为0.523和0.345。实时荧光定量PCR检测结果显示,OCX-32基因在长顺绿壳蛋鸡12个组织中存在不同程度的表达,表达量排序为肾脏>心脏>子宫>腹脂>小肠>脾脏>肝脏>腺胃>胸肌>胰腺>肺脏>肌胃。关联分析结果显示,g.22597350T>C位点CC基因型在蛋壳强度和蛋壳重2个品质指标上显著高于CT基因型和TT基因型;双倍型H4H4个体的蛋壳强度显著高于其他7种双倍型个体,蛋壳重显著高于H2H4个体。【结论】OCX-32基因内含子变异能影响长顺绿壳蛋鸡蛋壳品质,检测到的3个SNPs位点可作为鸡蛋壳品质选择的遗传分子标记,其中突变位点g.22597350T>C的CC基因型和双倍型H4H4是影响蛋壳强度和蛋壳重的关键基因型和双倍型,有利改善蛋壳品质。
关键词: 长顺绿壳蛋鸡;OCX-32基因;SNP;内含子;荧光定量PCR;蛋壳品质
中图分类号: S831.91 文献标志码: A 文章编号:2095-1191(2020)08-1872-08
Effects of OCX-32 gene intron variation on eggshell quality
of Changshun green-eggshell laying hens
WU Lei, TAN Guang-hui, LI Jie-zhang, QIN Yuan-yu, ZHANG Yi-yu*, TIAN Qin
(College of Animal Science, Guizhou University/Key Laboratory of Genetics, Breeding and Reproduction of Plateau Mountain Animals, Ministry of Education/Key Laboratory of Animal Genetics, Breeding and Reproduction
of Guizhou Province, Guiyang 550025, China)
Abstract:【Objective】To explore the genetic effects of OCX-32 gene on eggshell quality of Changshun green-shell laying hens,and to provide data support for breeding,development and utilization of Changshun green-eggshell laying hens. 【Method】Using Changshun green-eggshell laying hens as material,the SNP polymorphic site of OCX-32 gene was screened by direct sequencing of PCR products,and the tissue expression profile was detected by real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR. SPSS19.0 generalized linear model(GLM) was used to analyze the correlation between SNP locus genotype or diplotype and the tested traits. 【Result】Three SNPs loci were detected in OCX-32 gene of Changshun green-eggshell laying hens,which were located in g.22592323G>T mutation in intron 1,g.22597350T>C mutation in intron 3 and g.22597555G>A mutation in intron 3,respectively. Chi-square(χ2) test showed that the genotype distribution of g.22597350T>C mutation site significantly deviated from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium(P<0.05, the same below). The results of linkage disequilibrium analysis showed that there was no strong linkage disequilibrium at the three SNPs mutation sites. Four haplotypes and eight diplotypes were found. Haplotype H1 and diplotype H1H2 had the highest frequencies of 0.523 and 0.345,respectively. The results of real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR showed that OCX-32 gene was expressed in different degrees in 12 tissues of Changshun green-eggshell laying hens,and the order of expression was kidney>heart>uterus>abdominal fat>small intestine>spleen>liver>glandular stomach>chest muscle>pancreas>lung>mu-scle stomach. The results of association analysis showed that the eggshell strength and eggshell weight of CC genotype at g.22597350T>C were significantly higher than those of CT and TT genotypes,and the eggshell strength of diploid H4H4 was significantly higher than that of the other seven diplotypes,and the eggshell weight of diploid H4H4 was significantly higher than that of H2H4. 【Conclusion】The intron variation of OCX-32 gene can affect the eggshell quality of Changshun green-eggshell laying hens. The three SNPs loci detected can be used as genetic markers for eggshell quality selection. The CC genotype and diplotype H4H4 of the variation site g.22597350T>C are the key genotypes and diplotypes affecting eggshell strength and eggshell weight,which are more beneficial to improve eggshell quality.
Key words: Changshun green-eggshell laying hens; OCX-32 gene; SNP; intron; fluorescence quantitative PCR;eggshell quality
Foundation item: Guizhou Science and Technology Cooperation Planning Project(Qiankehe LH〔2016〕7454)
0 引言
【研究意义】鸡蛋由59%蛋清、31%蛋黄和10%蛋壳构成(Mann and Mann,2015)。蛋壳是卵生动物的卵外壳,是抵御外界物理损伤和微生物侵染的重要屏障,构成蛋壳主要有两部分:一是由蛋白纤维所构成的基质,二是在蛋白质基质上堆积钙质的结晶物(Eddin et al.,2019)。蛋壳品质是影响家禽生产力的重要性状,直接影响蛋的保存、运输和孵化,禽类蛋壳由蛋壳膜、钙化层和角质层组成,其生物学功能是保护胚胎发育时免受物理冲击而导致损伤,同时通过遍布整个钙化层的孔隙进行气体交换(Solomon,2010)。当前,蛋鸡养殖集约化水平越来越高,蛋壳品质呈现的问题也越来越严重。蛋壳品质受遗传、营养和饲养环境等多种因素影响,常规的育种手段已难以获得较高的遗传进展,而从分子遗传角度探明鸡蛋壳品质形成的作用机制是提高蛋壳质量的根本途径。【前人研究进展】蛋壳基质蛋白是禽类蛋壳中重要的有机成分,可能是影响蛋壳品质关键因素之一(Brionne et al.,2014)。众多蛋壳基质蛋白中,以Ovocalyxin-32(OCX-32)和OC-116蛋白含量最高,推测这2个蛋白基因是影响蛋壳性能的关键控制基因(Rodriguez-Navarro et al.,2015)。OCX-32基因由输卵管末端的上皮细胞所分泌,在输卵管的峡部和子宫区域高水平表达,最终沉积到蛋壳中,其表达量随蛋壳形成时间延长而递增,且具有终止蛋壳钙化的功能(Gautron et al.,2001,2011;Miksik et al.,2007)。鸡OCX-32基因定位于9号染色体上,包含5个内含子和6个外显子,编码275个氨基酸残基,分子量为32 kD,蛋壳形成末期在子宫液中高水平表达,是鸡蛋防御外界微生物侵袭的第一道屏障(Kawasaki and Weiss,2010;Hincke et al.,2012)。肖俊峰等(2012)报道,OCX-32基因表达量与蛋壳质量呈反比。刘亚平和马美湖(2015)研究表明,OCX-32基因在子宫部和输卵管峡部中的表达量最高。张丽萍(2016)研究发现,OCX-32基因第4内含子的变异位点G6566A与灵昆鸡蛋壳蛋白高度呈显著相关,推测OCX-32基因内含子变异与灵昆鸡的蛋壳品质密切相关。夏佳豪(2018)研究发现,OCX-32基因的第4内含子G6612A和第6外显子G7158A变异位点分别与30周龄蛋壳比例、蛋壳厚度、蛋白高度和蛋白比例,以及50周龄蛋壳厚度和蛋白高度显著相关,得出OCX-32基因SNP位点对汶上芦花鸡的蛋品质性状有显著影响。【本研究切入点】目前,国内外有关OCX-32基因在雞蛋壳品质方面研究相对较少,有待进一步证实OCX-32基因与蛋壳性状的相关性。【拟解决的关键问题】以产蛋高峰期的长顺绿壳蛋鸡为研究对象,采用PCR产物直接测序法筛选其SNP位点,以实时荧光定量PCR检测组织表达谱,分析其遗传特异性,并计算单倍型、双倍型与蛋壳品质的关联性,探讨OCX-32基因突变与鸡蛋壳品质的关系,为长顺绿壳蛋鸡的保种选育和开发利用提供参考依据。
1 材料与方法
1. 1 试验材料
随机选择饲养于贵州大学动物科学学院实验农场的同日出雏、健康无病、同等管理条件下的45周龄长顺绿壳蛋鸡200羽,逐一记录产蛋信息,根据《家禽生产学》(杨宁,2010)中蛋的构造和品质测定方法测定蛋形指数、蛋壳重、蛋壳强度、蛋重和蛋壳厚度等5个指标。每羽鸡翅静脉采血0.2~0.5 mL, -20 ℃保存备用。屠宰10羽,无菌采集子宫、心脏和肝脏等12个组织,-80 ℃保存备用。
1. 2 基因组DNA和总RNA提取及cDNA合成
按照血液/组织/细胞基因组提取试剂盒(DP304)操作说明提取血液DNA,以1.2%琼脂糖凝胶电泳和NANODROP 2000 DNA浓度测定仪(美国Thermo Scientific公司)联合评估提取质量,稀释成100 ng/μL后保存备用。采用常规TRIzol提取方法对每个个体的各组织样品进行总RNA提取,检测其浓度后稀释成100 ng/μL。按照2×T5 Fast qPCR Mix(SYBR Green I) Master Mix操作说明反转录合成cDNA。
1. 3 引物设计
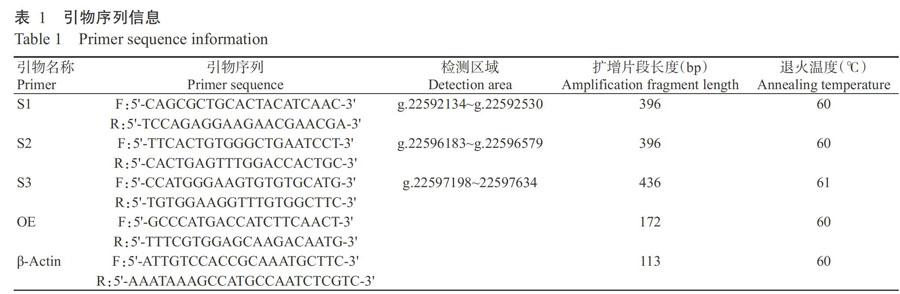
根据鸡OCX-32基因序列(GenBank登录号NC-006096),利用Primer 3.0设计3对多态引物S1(外显子1和内含子1)、S2(外显子2和内含子2)和S3(外显子3和内含子3),以及1对表达引物OE和1对内参引物β-Actin,引物序列信息见表1。
1. 4 长顺绿壳蛋鸡OCX-32基因表达检测
采用常规PCR检测长顺绿壳蛋鸡OCX-32基因和β-Actin基因表达引物的特异性,反应体系10.0 μL:RNase-Free Water 3.5 μL,2×Taq PCR Master Mix 5.0 μL,10 pmol/μL上、下游引物各0.5 μL,500 ng/μL cDNA模板0.5 μL。扩增程序:95 ℃预变性5 min;95 ℃ 30 s,60 ℃ 30 s,72 ℃ 45 s,进行35个循环;72 ℃延伸5 min。PCR产物采用1.3%琼脂糖凝胶电泳进行检测。
以β-Actin基因作内参对照,实时荧光定量PCR检测长顺绿壳蛋鸡OCX-32基因在各组织中的表达情况。实时荧光定量PCR反应体系10.0 μL:2×Ts Fast qPCR Mix 5.0 μL,500 ng/μL cDNA模板0.5 μL,10 pmol/μL上、下游引物各0.5 μL,ddH2O补足至10.0 μL。每个样品设3个重复。扩增程序:95 ℃预变性10 min;95 ℃ 15 s,60 ℃ 45 s,进行39个循环。
1. 5 长顺绿壳蛋鸡OCX-32基因多态性检测
对长顺绿壳蛋鸡OCX-32基因多态引物进行PCR扩增,反应体系20.0 μL:RNase-Free Water 7.0 μL,2×Taq PCR Master Mix 10.0 μL,10.0 pmol/μL上、下游引物各1.0 μL,100 ng/μL DNA 1.0 μL。扩增程序:94 ℃预变性6 min;94 ℃ 45 s,退火(表1)45 s,72 ℃ 50 s,进行35个循环;72 ℃延伸6 min。电泳检测后选取条带明亮的PCR产物送至昆泰锐(武汉)生物技术有限责任公司进行测序。
1. 6 统计分析
采用2-△△Ct法计算OCX-32基因在长顺绿壳蛋鸡各组织中的相对表达量。运用SHEsis(http://analysis.bio-x.cn/)计算SNP位点的等位基因频率、基因型频率、基因型分布卡方值(χ2)、单倍型频率及连锁不平衡的D'和γ2;参照Nei和Roychoudhury(1974)、Botstein等(1980)的方法计算有效等位基因数(Ne)、杂合度(He)和多态信息含量(PIC);运用SPSS 19.0中的广义线性模型(GLM)分析SNP位点基因型或双倍型与所测性状指标的相关性,模型为Y=μ+G+e,其中Y为性状观测值,μ为群体均值,G为基因型效应或双倍型效应,e为随机残差;采用最小显著性差异法(LSD)进行多重比较。
2 结果与分析
2. 1 长顺绿壳蛋鸡OCX-32基因SNP位点鉴定结果
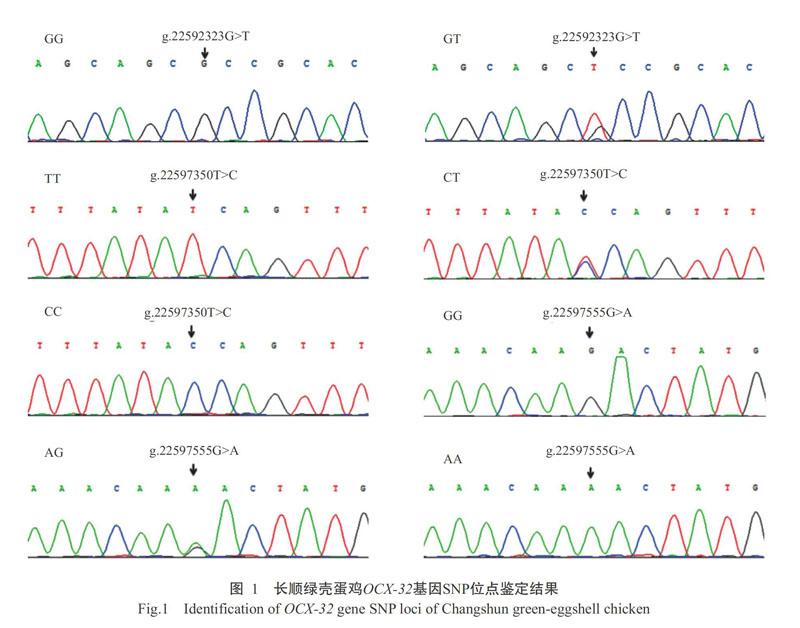
通过生物软件进行序列比对,结合测序峰图筛选SNP位点,结果在长顺绿壳蛋鸡OCX-32基因中共检测到3个新的SNPs位点:位于内含子1上的g.22592323G>T突变能产生2种基因型GG和GT;位于内含子3上的g.22597350T>C突变和g.22597555G>A突变则均产生3种基因型,序列峰见图1。
2. 2 长顺绿壳蛋鸡OCX-32基因SNP位点遗传特性
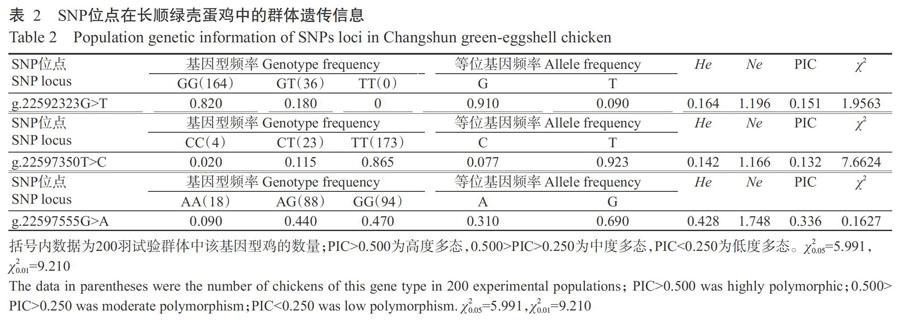
对长顺绿壳蛋鸡OCX-32基因3个SNPs位点进行遗传特性分析,结果见表2。由表2可知,长顺绿壳蛋鸡OCX-32基因g.22592323G>T位点的G等位基因和GG基因型分别为优势等位基因和优势基因型,对应的频率为0.910和0.820,呈低度多态性;g.22597350T>C位点的T等位基因和TT基因型分别为优势等位基因和优势基因型,对应的频率为0.923和0.865,呈低度多态性;g.22597555G>A位点的G等位基因和GG基因型分别为优势等位基因和优势基因型,对应的频率为0.690和0.470,呈中度多态性。χ2检测结果表明,g.22597350T>C位点的基因型分布显著偏离Hardy-Weinberg平衡(P<0.05,下同),而g.22592323G>T和g.22597555G>A位点尚未偏离Hardy-Weinberg平衡(P>0.05,下同)。
2. 3 长顺绿壳蛋鸡OCX-32基因SNP位点的连锁不平衡、单倍型及双倍型分析结果
对长顺绿壳蛋鸡OCX-32基因3个SNPs位点(g.22592323G>T、g.22597350T>C和g.22597555G>A)进行连锁不平衡分析,结果(表3)显示3个SNPs位点间的D'均小于0.800,γ2小于0.330。根据Ardlie等(2002)、Slatkin(2008)的報道,当|D'|>0.800和γ2>0.330时认为SNP位点间存在强连锁不平衡,说明本研究发现的3个SNPs位点间不存在强连锁不平衡。
对长顺绿壳蛋鸡OCX-32基因3个SNPs位点进行单倍型和双倍型分析,结果(表4)显示,在长顺绿壳蛋鸡OCX-32基因中,g.22592323G>T、g.22597350T>C和g.22597555G>A位点存在4种单倍型[H1(GTG)、H2(GTA)、H3(TTG)和H4(GCG)],频率分别为0.523、0.310、0.090和0.077;共检测到8种双倍型,其中H1H2(GGTTAG)频率最高,为0.345,其次是H1H1(GGTTGG),频率为0.250,而H4H4(GGCCGG)频率最低,为0.020。
2. 4 长顺绿壳蛋鸡OCX-32基因实时荧光定量PCR检测结果
OCX-32基因在长顺绿壳蛋鸡组织中的相对表达量测定结果(图2)显示,OCX-32基因在长顺绿壳蛋鸡12个组织中均有不同程度的表达。其中,在肾脏、心脏和子宫呈高度特异表达,显著高于在其他组织的相对表达量;在腹脂、小肠、肝脏和脾脏呈中度表达,显著高于在腺胃、胸肌、胰腺、肌胃和肺脏中的相对表达量。OCX-32基因在长顺绿壳蛋鸡各组织中的相对表达量排序依次为肾脏>心脏>子宫>腹脂>小肠>脾脏>肝脏>腺胃>胸肌>胰腺>肺脏>肌胃。
2. 5 OCX-32基因SNP位点与长顺绿壳蛋鸡蛋壳品质的关联分析结果
长顺绿壳蛋鸡蛋壳品质测定结果见表5。对长顺绿壳蛋鸡OCX-32基因3个SNPs位点g.22592323G>T、g.22597350T>C和g.22597555G>A进行蛋壳品质的关联分析,结果见表6和表7。由表6可知,g.22597350T>C位点CC基因型在蛋壳强度和蛋壳重2个品质指标上显著高于CT基因型和TT基因型。由表7可知,3个SNPs位点联合产生的双倍型对蛋壳品质指标蛋壳强度和蛋壳重的影响达显著水平,其中双倍型H4H4个体的蛋壳强度显著高于其他7种双倍型个体,蛋壳重显著高于H2H4个体,其余双倍型个体的各指标间差异均未达显著水平。
夏佳豪. 2018. 汶上芦花鸡蛋品质及其候选基因遗传效应分析[D]. 泰安:山东农业大学. [Xia J H. 2018. Analyses on charicteristics of egg quality and genetic effects of its candidate genes in Wenshang barred chicken[D]. Taian:Shandong Agricultural University.]
肖俊峰,武书庚,张海军,岳洪源,齐广海. 2012. 四种壳基质蛋白研究进展[J]. 中国家禽,34(9):44-47. [Xiao J F,Wu S G,Zhang H J,Yue H Y,Qi G H. 2012. Search on four shell matrix proteins[J]. Chinese Poultry,34(9):44-47.]
杨宁. 2010. 家禽生产学[M]. 北京:中国农业出版社. [Yang N. 2010. Poultry production[M]. Beijing:China Agriculture Press.]
杨智青,陈应江,金崇富,丁海荣,时凯,陈长宽. 2013. 防护林散养草鸡不同产蛋期蛋形、蛋壳指数比较[J]. 畜牧兽医杂志,32(6):12-14. [Yang Z Q,Chen Y J,Jin C F,Ding H R,Shi K,Chen C K. 2013. Comparative research on egg shape and eggshell index of different laying period in shelterbelt[J]. Journal of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine,32(6):12-14.]
葉幼荣,孙杰,张璐,赵宗胜. 2015. 蛋鸡不同产蛋期生殖器官中OC17,OC116和OCX32 mRNA相对定量研究[J]. 中国兽医学报,35(9):1518-1525. [Ye Y R,Sun J,Zhang L,Zhao Z S. 2015. Relative quantification of OC17,OC116 and OCX32 mRNA in reproductive organs of hens in different laying periods[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science,35(9):1518-1525.]
张丽萍,曾涛,卢立志,刘均,周树和,林兴钦,田勇. 2015. 灵昆鸡视黄醇结合蛋白(CRBP4)和蛋壳基质蛋白(OCX-32)基因多态性与产蛋性状的相关性研究[J]. 农业生物技术学报,23(10):1343-1349. [Zhang L P,Zeng T,Lu L Z,Liu J,Zhou S H,Lin X Q,Tian Y. 2015. Correlation analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms of Cellular retionol-binding protein 4(CRBP4) and Ovocalyxin-32(OCX-32) genes with egg production traits in Lingkun chicken(Gallus gallus)[J]. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology,23(10):1343-1349.]
张丽萍. 2016. 灵昆鸡CRBP4、OCX-32、VLDLR和CTSD基因与产蛋性状的关联分析[D]. 金华:浙江师范大学. [Zhang L P. 2016. Correlation analysis between CRBP4,OCX-32,VLDLR and CTSD genes and egg production traits in Lingkun chicken[D]. Jinhua:Zhejiang Normal University.]
张跃博,蒲蕾,张金山,颜华,王立刚,侯欣华,刘欣,高红梅,王立贤,张龙超. 2018. 杜洛克猪HLCS基因组织表达分析及其编码区多态性与剩余采食量的关联[J]. 畜牧兽医学报,49(6):1108-1115. [Zhang Y B,Pu L,Zhang J S,Yan H,Wang L G,Hou X H,Liu X,Gao H M,Wang L X,Zhang L C. 2018. Tissue expression profiles of HLCS gene and its association with residual feed intake in Duroc[J]. Acta Veterinaria Et Zootechnica Sinica, 49(6):1108-1115.]
Ardlie K G,Kruglyak L,Seielstad M. 2002. Patterns of linka-ge disequilibrium in the human genome[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics,3(4):299-309.
Botstein D,White R L,Skolnick M,Davis R W. 1980. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms[J]. American Journal of Human Genetics,32(3):314-331.
Brionne A,Nys Y,Hennequet-Antier C,Gautron J. 2014. Hen uterine gene expression profiling during eggshell formation reveals putative proteins involved in the supply of minerals or in the shell mineralization process[J]. BMC Genomics,15(1):220-223.
Dunn I C,Joseph N T,Bain M,Edmond A,Wilson P W,Milona P,Nys Y,Gautron J,Schmutz M,Preisinger R,Waddington D. 2008. Polymorphisms in eggshell organic matrix genes are associated with eggshell quality measurement in pedigree Rhode Island Red hens[J]. Animal Genetics,40(1):110-114.
Eddin A S,Ibrahim S A,Tahergorabi R. 2019. Egg quality and safety with an overview of edible coating application for egg preservation[J]. Food Chemistry,296(1):29-39.
Flint-Garcia S A,Thornsberry J M,Buckler E S. 2003. Structure of linkage disequilibrium in plants[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology,54:357-374.
Fulton J E,Soller M,Lund A R,Arango J,Lipkin E. 2012. Variation in the ovocalyxin-32 gene in commercial egg-laying chickens and its relationship with egg production and egg quality traits[J]. Animal Genetics,43(S1):102-113.
Gautron J,Hincke M T,Mann K,Panheleux M,Bain M,Mc-Kee M D,Solomon S E,Nys Y. 2001. Ovocalyxin-32,a novel chicken eggshell matrix protein. Isolatton,amino acid sequencing,cloning,and immunocytochemical loca-lization[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry,276(42):39243-39252.
Gautron J,Rehault-Godbert S,Nys Y,Mann P G,Righetti G. 2011. Use of high-throughput technology to identify new egg components[J]. Improving the Safety and Quality of Eggs and Egg Products,3(1):133-150.
Hincke M T,Nys Y,Gautron J,Mann K,Rodriguez-Navarro A B,McKee M D. 2012. The eggshell:Structure,composition and mineralization[J]. Frontiers in Biocience(Landmark Edition),17(1):1266-1280.
Kawasaki K,Weiss K M. 2010. Evolutionary genetics of vertebrate tissue mineralization:The origin and evolution of the secretory calcium-binding phosphoprotein family[J].Journal of Experimental Zoology. Part B:Molecular and Developmental Evolution, 306(3):295-316.
Mann K,Mann M. 2015. Proteomic analysis of quail calcified eggshell matrix:A comparison to chicken and turkey eggshell proteomes[J]. Proteome Science,13(1):22-25.
Miksik I,Eckhardt A,Sedláková P,Mikulikova K. 2007. Proteins of insoluble matrix of avian(Gallus gallus) eggshell[J]. Connect Tissue Research,48(1):1-8.
Nei M,Roychoudhury A. 1974. Sampling variances of heterozygosity and genetic distance[J]. Genetics,76(2):379-390.
Rodriguez-Navarro A B,Marie P,Nys Y,Hincke M T,Gautron J. 2015. Amorphous calcium carbonate controls avian eggshell mineralization:A new paradigm for understan-ding rapid eggshell calcification[J]. Journal of Structural Biology,190(3):291-303.
Slatkin M. 2008. Linkage disequilibrium-understanding the evolutionary past and mapping the medical future[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics,9(6):477-485.
Solomon S E. 2010. The eggshell:strength,structure and function[J]. British Poultry Science,51(1):52-59.
Takahashi H,Yang D,Sasaki O,Furukawa T,Nirasawa K. 2010. Mapping of quantitative trait loci affecting eggshell quality on chromosome 9 in an F2 intercross between two chicken lines divergently selected for eggshell strength[J]. Animal Genetics,40(5):779-782.
Tuiskula-Haavisto M,Honkatukia M,Dunn I C,Bain M M,de Koning D J,Preisinger R,Schmutz M,Arango J,Fischer D, Vilkki J. 2018. Validated quantitative trait loci for eggshell quality in experimental and commercial la-ying hens[J]. Animal Genetics,49(4):1247-1464.
van Mourik S,Alders B P G J,Helderman F,van de Ven L J F,Groot Koerkamp P W. 2016. Predicting hairline fractures in eggs of mature hens[J]. Poultry Science,96(6):1956-1962.
Xing J,Wellman-Labadie O,Gautron J,Hincke M T. 2007. Recombinant eggshell ovocalyxin-32:Expression,purification and biological activity of the glutathione S-transferase fusion protein[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. Part B:Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,147(2):172-177.
(責任编辑 罗 丽)
收稿日期:2019-09-11
基金项目:贵州省科技合作计划项目(黔科合LH字〔2016〕7454号)
作者简介:*为通讯作者,张依裕(1976-),副教授,主要从事动物遗传资源保护与利用研究工作,E-mail:zyy8yyc@163.com。吴磊(1993-),研究方向为畜牧养殖,E-mail:1475715385@qq.com

