Teicoplanin is a potential inhibitor of SARS CoV-2 replication enzymes: A docking study
Aatika Sadia,Muhammad Azam,Muhammad Asim Raza Basra
Institute of Chemistry,University of the Punjab,New Campus,Lahore-54590,Pakistan
ABSTRACT
KEYWORDS: Molecular docking; Oxicam; Antibiotics; Antiviral;SARS CoV-2
1.Introduction
The viruses of genus Betacoronavirus have been known to cause zoonotic respiratory infections such as Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome in human beings.A new and highly contagious respiratory infection Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19) erupted from novel SARS CoV-2 in December 2019 and became pandemic across the globe.SARS CoV-2 is a positive sense,single stranded RNA enveloped virus.Apart from spike,envelope,nucleocapsid,and membrane structural proteins,the nonstructural proteins (NSPs) of SARS CoV-2 mediate COVID-19 pathogenesis.NSP9-replicase and NSP3-ADP-ribose-phosphatase catalyze viral genome replication through restriction-transcriptioncomplex[1].NSP15-endoribonuclease triggers cytokine storm featuring CD4+-CD6+T-cells interleukins (IL-1β,IL-4,IL-10),monocyte chemoattractant protein-1,and interferon-γ[2].As NSP14-exonuclease proofreads the synthesized viral RNA during pathogenesis,the drugs that function through nucleotide analog therapy fail to alleviate COVID-19.Presently,binding of various drugs was studied against NSP9,NSP3,and NSP15 of SARS CoV-2,illuminating receptor analog mechanism as a promising solution.
2.Materials and methods
2.1.Selection and structural optimization of ligands
The commonly available non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs(NSAIDs) ampiroxicam (AMX),meloxicam (MEX),droxicam(DRX),isoxicam (ISX),lornoxicam (LOX),piroxicam (PIX) and tenoxicam (TNX) were selected due to their plausible inhibitory potential against intruding viroids in the host cells as reported previously[3]while the antibiotic drugs including teicoplanin (TPN),azithromycin (AZN),cefixime (CFM),antiviral drugs ribavirin(RBV),favipiravir (FVR),remdesivir (RVR),along with antimalarial drugs chloroquine (CQ) and hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) were selected for computational study due to promising results reported for COVID-19 treatment in the clinical trials of these drugs[4].The 3D structures of drugs to be used for docking were downloaded from PubChem and optimized structures were generated by using Avogadro software (Table 1).All these structures were subjected to optimization by Avogadro software for accurate docking[5].
2.2.Binding pockets determination
The NSPs including NSP9-replicase RNA binding protein,NSP3-ADP-ribose-phosphatase,and NSP15-endoribonuclease (PDB ids:6W4B,6W02,and 6VWW) were selected for docking and were obtained from RCSB PDB in the PDB formats.The structures were subjected to binding pocket determination by Deepsite-PlayMolecule[6].
2.3.Protein-inhibitor molecular docking
The molecular docking of selected proteins was performed by PatchDock Beta 1.3 a molecular docking algorithm that is based on shape complementarity principles[7].The outcomes were carefully selected according to the binding pockets of proteins.The docking scores,approximate interface area of protein-ligand complex,and atomic contact energy (ACE) values were recorded for each proposed inhibitor ligand.The docking mode was selected as enzyme-inhibition and the root mean square deviations for atomic positions were 1.5.The outcomes were visualized using UCSF Chimera 1.14[8].
3.Results
3.1.Ligand optimizations
Structures of all the drugs were optimized to minimum energy such that differential energy and constraints of the structures became zero(Figure 1A-O).
3.2.Binding pockets determination
The NSP9-replicase was found to contain potential binding pocket lined by amino acids Arg40A,Phe41A,Val42A,Lys59A,Thr68A,Glu71A,Pro72A,Cys74A,Tyr90A,Phe91A,Gly101A,Val103A,and Leu104A at its margins (Figure 2A-B).Amino acids Ser5A,Phe6A,Ser7A,Gly8A,Tyr9A,Tyr9B,Leu10B,Lys11B,Leu12B,Thr13B,Tyr17B,Ile18B,Lys19B,Val165B,Ser166B,and Phe168B resided around the margins of the binding pocket in NSP3-ADP-ribose-phosphatase (Figure 2C-D).The potential binding pocket for NSP15-endoribonuclease exhibited amino acids Thr48A,Thr49A,Leu50A,Met105A,Thr106A,Ile97A,Ser98A,Asp22B,Ile23B,His45B,Thr49B,Leu50B,Pro51B,Ser98B,Asp157B,Met105B,and Thr106A at its margins (Figure 2E-F).
3.3.Protein-inhibitor molecular docking
The docking results were selected based on the efficient interaction of drugs with the amino acids lining the binding pockets of the proteins.Although all the drugs showed interaction with NSP9-replicase of SARS CoV-2,TPN showed the most significant inhibition,with the highest dock score of 9 620 and the lowest ACE values of -547.52 Kcal/mol.The ligand completely obstructed the binding pocket and exhibited hydrogen bond of 0.4 Å relaxedconstraints with Thr36B (Figure 3A).Prominent docking scores of 6 252 and 5 472 were shown by RVR and AZN,respectively against NSP9-replicase.The order of docking score of selected medicinal compounds with inhibition against NSP9-replicase was as follows:TPN > RVR > AZN > HCQ > CQ > DRX > CFM > MEX > AMX >ISX > TNX > PIX > LOX > RBV > FVR (Table 2).

Table 1.Names of selected drugs and their IDs.
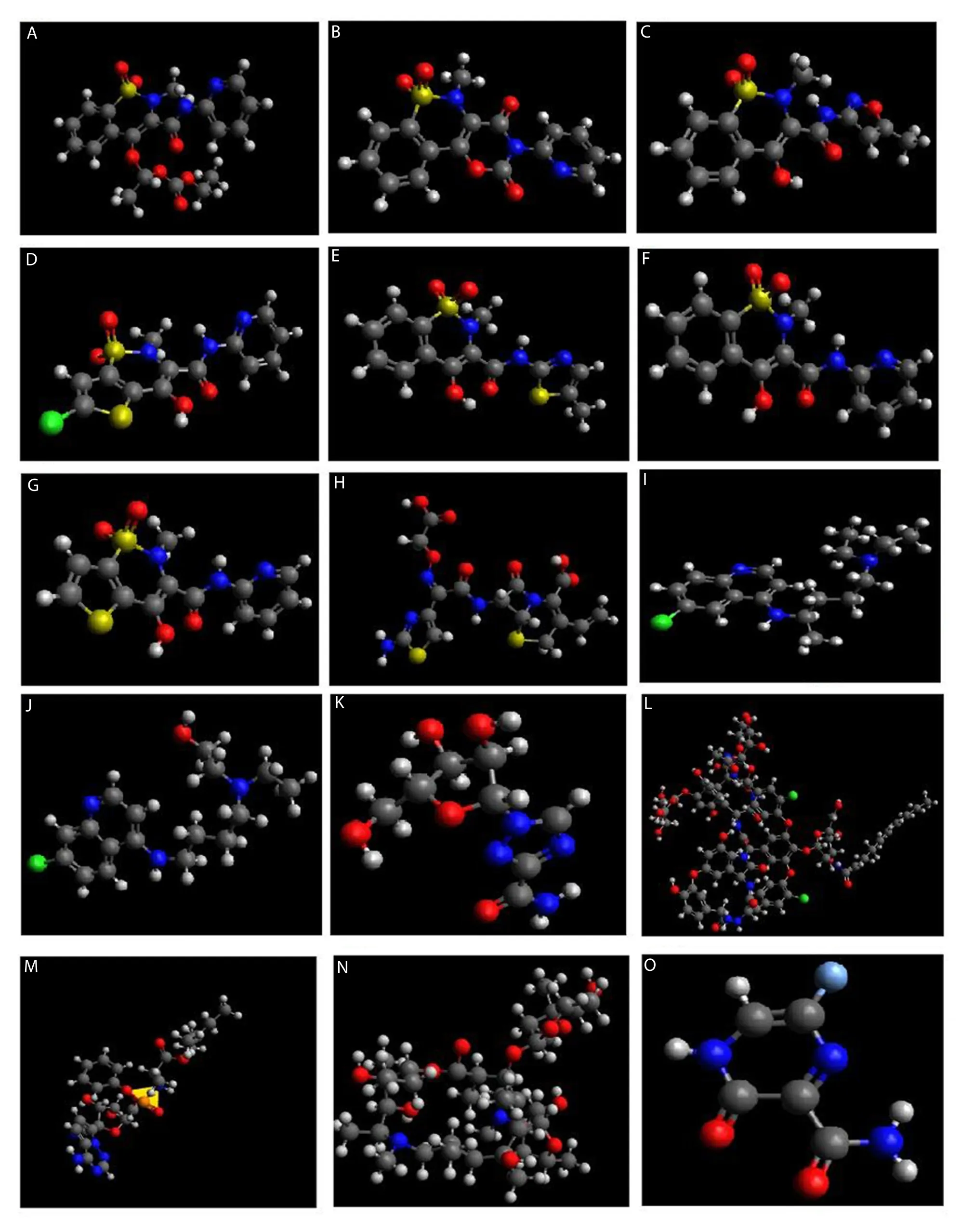
Figure 1.Optimized 3D structures of selected drugs.(A) Ampiroxicam,(B) droxicam,(C) isoxicam,(D) lornoxicam,(E) meloxicam,(F) piroxicam,(G)tenoxicam,(H) cefixime,(I) chloroquine,(J) hydroxychloroquine,(K) ribavirin,(L) teicoplanin,(M) remdesivir,(N) azithromycin and (O) favipiravir.
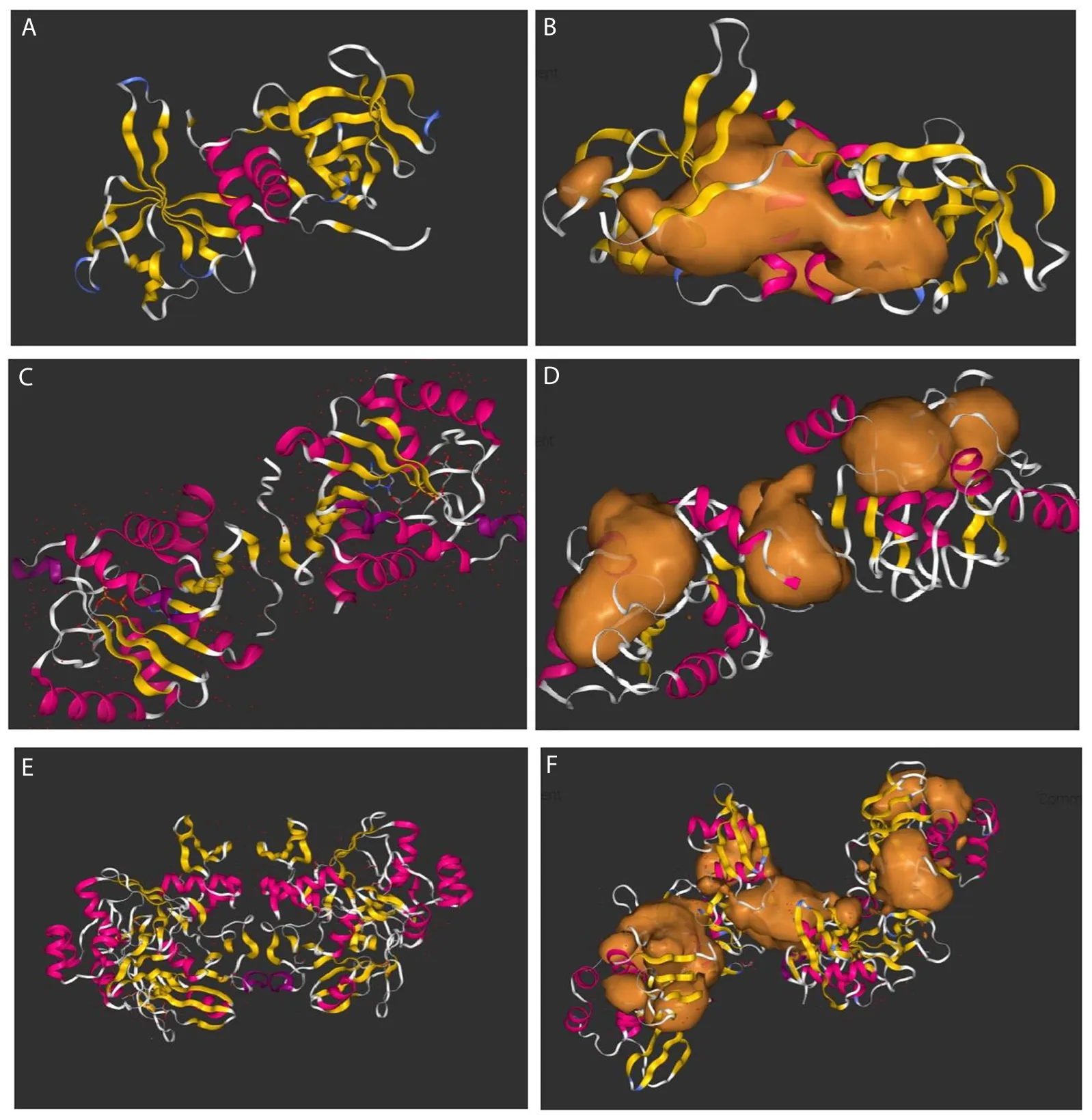
Figure 2.3D structures and binding pockets of SARS CoV-2 proteins.(A) 3D structure of NSP9 replicase,(B) Binding pockets of NSP9 replicase,(C) 3D structure of NSP3 ADP ribose phosphatase,(D) Binding pockets of Nsp3 ADP ribose phosphatase,(E) 3D structure of NSP15 endoribonuclease,and (F)Binding pockets NSP15 endoribonuclease.
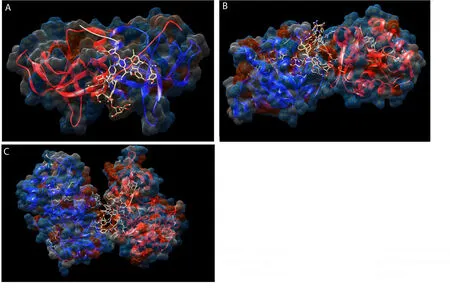
Figure 3.Docking studies of teicoplanin.(A) NSP9 replicase docked with teicoplanin,(B) NSP3 ADP ribose phosphatase docked with teicoplanin and(C) NSP15 endoribonuclease docked with teicoplanin.
NSP3-ADP-ribose-phosphatase of SARS CoV-2 also showed interactions with all selected drugs.TPN showed the highest binding potentials followed by AZN and RVR with docking scores of 9 846,5 604,and 5 548 and ACE values of -220.30,-132.28,and -116.49 Kcal/mol,respectively.However,the lowest ACE value of -291.10 was shown by AMX with a docking score of 4 640 (Table 2).The TPN showed hydrogen bonds of 0.4 Å relaxed constraints with Val147A,Thr149A,Asp 14A,Asn15A,Thr33B and covered the binding pocket completely for its inhibition (Figure 3B).The order of the docking scores of compounds with the inhibition against NSP3-ADP-ribose-phosphatase was as follows: TPN > AZN > RVR> AMX > MEX > CQ > HCQ > LOX > DRX >CFM > PIX > TNX> ISX > RBV > FVR (Table 2).
The NSP15-endoribonuclease of SARS CoV-2 also interacted with all selected drugs.TPN showed the highest docking score and lowest ACE value as 10 960 and -583.02 Kcal/mol,respectively.Amino acids Gly77A,Thr121A,and Lys110B on the surface of NSP15-endoribonuclease pocket exhibited hydrogen bonds of 0.4 Å relaxed constraints with TPN molecule such that its binding pocket was completely obstructed (Figure 3C).The order of docking score of selected medicinal compounds with inhibition against NPS15-endoribonuclease was as follows: TPN > AZN > RVR > AMX >CFM > CQ > MEX > ISX > LOX > DRX > HCQ > PIX > TNX >RBV > FVR (Table 2).
4.Discussion
Various drugs are under consideration for the treatment of COVID-19.The mild clinical features of COVID-19 include fever,sore throat,cough,and viremia.It may aggravate pneumonia and can be fatal in severe cases.NSAIDs are required to treat the fever and pleuritis,and at least one of the NSAIDs is included in the prescribed medicines to cure the infectious disease.PIX has been used to inhibit the viral pathogenesis of herpes[3],while MEX is known for its antiproliferative and cytotoxic activity[9].Likewise,MEX has been used in the treatment of COVID-19 along with HCQ and showed viral clearance.Hence these NSAIDs including AMX,MEX,DRX,ISX,LOX,PIX,and TNX might be considered for invitro and in-vivo evaluation and further clinical trials in COVID-19 treatment.The antimalarial drugs CQ and its less toxic derivative HCQ,antibiotics TPN,AZN and CFM,and antiviral RBV have been earlier reported for antiviral effects against SARS CoV and MERS CoV,while FVR has been reported to treat Ebola and influenza.The drugs RVR and TPN promisingly inhibit SARS CoV-2 in vitro while CQ,HCQ,AZN,RBV,and FVR have also been reported to show varying degrees of SARS CoV-2 inhibition.RVR and all these mentioned drugs showed viral clearance and potential in treatment of COVID-19[4].
In the computational drug discovery,the high docking scores and highly negative ACE values indicate the greater affinity of the ligand with protein and higher potential to inhibit the protein from its functioning.The inhibition of HCQ and CQ against NSP9-replicase supports the effectiveness of these drugs in treating the COVID-19.In the same way,CFM has also been recommended based on in-silico molecular docking against another SARS CoV-2enzyme protease[10].Our comparative findings suggest that the viral replication proteins of SARS CoV-2 are more efficiently inhibited by TPN as compared with other drugs,which is similar to previously reported therapeutic strategies.The half-life of TPN is much shorter(3-5 days) as compared with CQ and HCQ (45-55 and 22 days,respectively).The antibiotic AZN and antiviral RVR also show promising results.In addition to the inhibition of viral enzymes and NSPs,the suppression of proinflammatory cytokines is also required.Hence,the analgesics AMX and MEX should be considered for the treatment of COVID-19.

Table 2.Docking scores,area of interface,and atomic contact energy values of selected drugs.
Our study depicted complete blockade of the binding sites of NSP3,NSP9 and NSP15 of SARS CoV-2 by TPN,AZN and RVR through prominent receptor antagonism.Inhibiting replication of the viral genome and suppression of the cytokine storm may aid the COVID-19 patients to effectively combat the disease.In addition to their regular analgesic and antibiotic roles,these prescribed drugs could also be potent inhibitors of viral proteins of SARS CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Institute of Chemistry,University of the Punjab Lahore,Pakistan.
Authors’ contributions
AS is in charge of experimental studies,manuscript preparation;MA in charge of data analysis and interpretation; MARB in charge of concept,design,manuscript editing,and review.
 Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine2020年12期
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine2020年12期
- Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine的其它文章
- Ferulic acid alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced depression-like behavior by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis
- Role of higher levels of post-challenge antibodies in protective vaccination against Leishmania tropica infection of BALB/c mice
- Coconut oil nanoemulsion attenuates methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in Ehrlich ascites carcinoma-bearing mice
- Rotula aquatica Lour.inhibits growth and biofilm formation of clinically isolated uropathogenic Escherichia coli
- Potential bioactive phytochemicals,antioxidant properties and anticancer pathways of Nymphaea nouchali
