大连石城岛原驻老年居民PON1rs662基因多态性与高血压及其相关因素的关系研究
赫兰 唐晓慧 胡嘉慧 程栋 王兴宇 于勤


[摘要] 目的 探討大连石城岛原驻老年居民高血压的患病率及相关因素,血清对氧磷酶1(rs662)基因(PON1rs662)与高血压的关系。 方法 选取2016年6—8月石城岛654名65岁以上原驻居民对其进行高血压及相关因素流行病学调查,分别采用调整的世界卫生组织(WHO)-MONICA研究问卷进行问卷调查,进行生化及心脏超声相关检查;采用离心柱法提取脱氧核糖核酸(DNA),实时定量荧光聚合酶链反应(PCR)技术(TaqMan-PCR)对PON1rs662进行基因分型,确定所有研究对象PON1rs662基因型分布是否符合哈温伯格平衡定律,探讨PON1rs662基因与高血压的关系。 结果 调查对象总人群高血压患病率为73.1%,女性患病率为77.5%,男性患病率为68.3%;高血压与非高血压人群心率、体重指数(BMI)、腰围、尿酸(UA)、三酰甘油(TG)、左房前后径(LA)比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);研究对象PON1rs662基因型分布符合哈温伯格平衡(P > 0.05);等位基因模型和相加模型检测研究对象PON1rs662 SNP位点与高血压无相关性(P > 0.05)。 结论 大连石城岛原驻老年居民高血压患病率为73.1%;心率、BMI、腰围、UA、TG与岛上高血压患病率有关;PON1rs662基因与研究对象高血压患病率可能无相关性。
[关键词] 血清对氧磷酶1(rs662);高血压;海岛;老年;单核苷酸多态性
[中图分类号] R544.1 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-7210(2020)08(c)-0051-04
Study on the relationship between PON1rs662 gene polymorphism and hypertension and its related factors in Shicheng Island of Dalian
HE Lan1 TANG Xiaohui2 HU Jiahui2 CHENG Dong2 WANG Xingyu3 YU Qin2
1.Department of Ultrasound, Shanghai Eighth People′s Hospital, Shanghai 200233, China; 2.Department of Cardiology, Zhongshan Hospital Affiliated to Dalian University, Liaoning Province, Dalian 116001, China; 3.Beijing Hypertension Union Research Institute, Beijing 100039, China
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the prevalence and related factors of hypertension in the elderly in Shicheng Island of Dalian, and the relationship between serum P-oxophosphase 1(rs662) gene(PON1rs662) and hypertension. Methods The epidemiological survey on hypertension and related factors was conducted among 654 residents aged more than 65 from June to August 2016. The adjusted WHO-MONICA research questionnaire was used for questionnaire survey, biochemical and echocardiographic examinations were carried out. DNA was extracted by centrifugation column, and gene typing of PON1rs662 was carried out by TaqMan PCR. All the studies were determined whether the genotype distribution of PONIrs662 accord with Hardy-Weinberg Law, and the relationship between PON1rs662 gene and hypertension was investigated. Results The prevalence of hypertension was 73.1%, 77.5% in women and 68.3% in men. There were statistically significant differences in heart rate, body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, uric acid (UA), triglyceride (TG) and left atrial anteropostery (LA) between hypertensive and non-hypertensive subjects (P < 0.05). The genotype distribution of PON1rs662 was in line with Hardy-Weinberg Law (P > 0.05). Both the allele model and the additive moded showed no correlation between the PON1rs662 SNP and hypertension (P > 0.05). Conclusion The prevalence rate of hypertension in the old residents of Shicheng Island was 73.1%. Heart rate, BMI, waist circumference, UA and TG were associated with the prevalence of hypertension on the island. PON1rs662 gene may not be correlated with the prevalence of hypertension in these study objects.
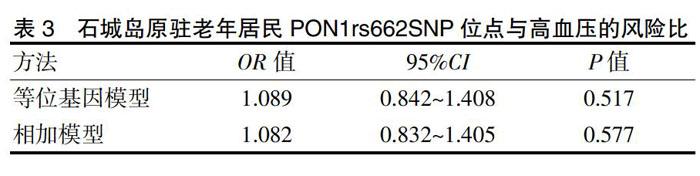
3.2 PON1rs662SNP分布情況及其与高血压的关系
PON基因多态性在不同民族、不同地区、不同国家背景下与多种代谢性疾病相关,有重要的研究意义,本研究选取人类基因组中PON1rs662位点在该岛上进行深入研究,PON1rs662位于人类7号染色体的长臂上[11],PON1rs662基因的多态性影响PON1的酶活性[17],PON1主要在肝细胞合成和分泌,是一种钙离子依赖血清脂酶。在人类血清中PON1与HDL-C结合保护LDL-C氧化修饰,减少LDL-C的氧化作用而保护血管[18]。PON1活性下降可加速动脉粥样硬化,增加高血压、糖尿病和冠心病等多种心血管疾病患病率[19]。由于SNP与疾病的关系在个体或人群之间关联不一致,而且疾病的发生是遗传和理化因素共同作用的结果,因此本研究选择北方海岛石城岛,该岛上出生并连续居住40年以上的原驻老年居民,从遗传学角度属于孤立人群,更有利于探讨PON1rs662与高血压及其相关危险因素的关系,本研究该岛上PON1rs662位点SNP分布情况,通过Allelic model和Additive model两个模型来分析PON1rs662与该岛高血压的关系,结果显示该岛上参与调查的老年人群中PON1rs662基因单核苷酸多态性与高血压差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),但这一结果并不能说明PON1rs662基因与该岛高血压无相关性,从人类遗传学角度来说,有可能PON1rs662等位基因和致病基因相距很近,存在连锁不平衡,也有可能因样本量不足,需要更多大样本的数据支持。
探讨高血压发病机制,有效规避遗传风险,做到高血压精准诊断与治疗有着十分重要的意义,该研究有可能为未来高血压的个体化、精准预防与治疗提供相关研究数据,在精准医学、精准健康时代的趋势下,做一些建设性的探索。
3.3 结论
大连石城岛65岁以上老年原驻居民高血压患病率为73.1%;该岛上高血压患病率可能与心率、BMI、腰围、UA及TG有关,或许是该岛上高血压相关危险因素;PON1rs662基因与研究对象高血压患病率可能无关。
3.4 研究不足
岛上原驻老年居民数量偏少,可能产生统计学偏倚,PON1rs662基因与高血压是真的不相关还是样本量不够,有待于更多的研究和证实。
[参考文献]
[1] Williams B,Mancia G,Spiering W,et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension [J]. Kardiologia Polska,2019,77(2):71-159.
[2] 潘锋.一级预防是我国心血管病防控的重点和难点—访中国科学院院士、中国医学科学院阜外医院顾东风教授[J].中国医药导报,2019,16(35):1-3.
[3] 李苏宁,陈祚,王增武,等.我国老年人高血压现状分析[J].中华高血压杂志,2019,27(2):140-148.
[4] Li Z,Guo X,Zheng L,et al. Grim status of hypertension in rural China:results from Northeast China Rural Cardiovascular Health Study 2013 [J]. J Am Soc Hypertens,2015,9(5):358-364.
[5] Wang L,Cheng F,Hu J,et al. Pathway-based gene-gene interaction network modelling to predict potential biomarkers of essential hypertension [J]. Bio Systems,2018,172:18-25.
[6] Turgut Cosan D,Colak E,Saydam F,et al. Association of paraoxonase 1 (PON1) gene polymorphisms and concentration with essential hypertension [J]. Clin Exp Hypertens,2016,38(7):602-607.
[7] Mei Z,Zhou S,Huang B,et al. Proteomic identification of candidate plasma biomarkers for preeclampsia in women with pregnancy-induced hypertension [J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol,2017,10(10):10383-10391.
[8] Bystrova AA,Ulitina AS,Kim MV,et al. Genetic Risk Factors of Macrovascular Complications in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes [J]. Kardiologiia,2017,57(2):17-22.
[9] Cheraghi M,Shahsavari G,Maleki A,et al. Paraoxonase 1 Activity,Lipid Profile and Atherogenic Indexes Status in Coronary Heart Disease [J]. Rep Biochem Mol Biol,2017, 6(1):1-7.
[10] 赵平,李冰,陈鑫,等.β受体阻滞剂治疗H型高血压患者的效果[J].河南医学研究,2018,27(2):256-257.
[11] Haberka M,Stolarz-Skrzypek K,Biedron M,et al. Obesity,Visceral Fat,and Hypertension-Related Complications [J]. Metab Syndr Relat Disord,2018,16(10):521-529.
[12] Zaremba YH,Rak NO,Zaremba OV,et al. Indscators of blood lipid profile,acute phase reactions and uric acid in patients with arterial hypertension combined with connective tissue dysplasia [J]. Wiad Lek,2018,71:356-360.
[13] 刘成国,阮连生,郭琼瑶,等.海岛地区居民心脑血管事件与代谢综合征的相关性研究[J].中国临床保健杂志,2015,18(1):68-69.
[14] Antit S,Zakhama L,Amri A,et al. Assessment of left atrial mechanical function by two-dimensional echocardiography in hypertensive patients [J]. Tunis Med,2019,97(7):882-890.
[15] Xu H,Qu Y. Correlation of PON1 polymorphisms with ankylosing spondylitis susceptibility:A case-control study in Chinese Han population [J]. Medicine,2017,96(42):e7416.
[16] 赵晶晶.对氧磷酶1(PON1)基因多态性与2型糖尿病易感性的meta分析[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2016:1-61.
[17] Macharia M,Kengne AP,Blackhurst DM,et al. Paraoxonase 1 Genetic Polymorphisms in a Mixed Ancestry African Population [J]. Mediators Inflamm,2014,2014:1-9.
[18] Luo JQ,Ren H,Liu MZ,et al. European versus Asian differences for the associations between paraoxonase-1 genetic polymorphisms and susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. J Cell Mol Med,2018,22(3):1720-1732.
[19] Luo JQ,Ren H,Liu MZ,et al. European versus Asian differences for the associations between paraoxonase-1 genetic polymorphisms and susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. J Cell Mol Med,2018,22(3):1720-1732.
(收稿日期:2019-12-30)
[基金項目] 国家自然科学基金资助项目(81770405)。
[作者简介] 赫兰(1985.3-),女,硕士;研究方向:高血压及其发病机制。
[通讯作者] 于勤(1966.12-),女,医学博士,主任医师,教授,博士生导师,大连大学附属中山医院循环三科主任,主要从事心肌病、心衰及高血压的基础与临床研究。

