多模式镇痛在全膝关节置换术患者中的应用研究
毕晔 赵秋华
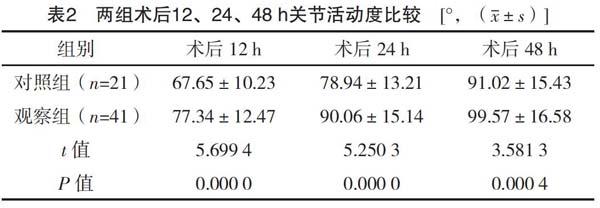
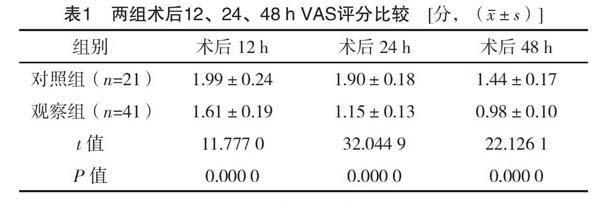
【摘要】 目的:探讨多模式镇痛在全膝关节置换术中的应用效果。方法:选取笔者所在医院2018年11月-2019年11月收治的62例人工全膝关节置换术患者作为研究对象,按照随机数字表法将其分为对照组(21例)和观察组(41例)。对照组采用静脉自控镇痛泵,观察组采用多模式镇痛。比较两组术后12、24、48 h VAS评分、关节活动度。結果:观察组术后12、24、48 h VAS评分均明显低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。观察组术后12、24、48 h 关节活动度明显大于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论:全膝关节置换术中采用多模式镇痛可有效缓解疼痛,促进膝关节恢复,从而有效提升患者生活质量,值得临床大力推广使用。
【关键词】 多模式镇痛 全膝关节置换术 VAS评分 临床效果
doi:10.14033/j.cnki.cfmr.2020.18.024 文献标识码 B 文章编号 1674-6805(2020)18-00-02
Study on the Application of Multimodal Analgesia in Total Knee Arthroplasty/BI Ye, ZHAO Qiuhua. //Chinese and Foreign Medical Research, 2020, 18(18): -57
[Abstract] Objective: To explore the effect of multimodal analgesia in total knee arthroplasty. Method: A total of 62 patients with artificial total knee arthroplasty who were admitted in our hospital from November 2018 to November 2019 were selected as the research object, and they were divided into the control group (21 cases) and the observation group (41 cases) according to the random number table method. The control group adopted intravenous controlled analgesia pump, and the observation group adopted multimodal analgesia. The VAS scores and joint mobility at 12, 24 and 48 h after surgery were compared between the two groups. Result: The VAS scores at 12, 24 and 48 h after surgery in the observation group were significantly lower than those in the control group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). The joint mobility at 12, 24 and 48 h after surgery in the observation group were significantly higher than those in the control group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion: Multimodal analgesia in total knee arthroplasty can effectively relieve pain, promote knee joint recovery and thus effectively improve patients quality of life, which is worthy of clinical application.
[Key words] Multimodal analgesia Total knee arthroplasty VAS score Clinical effect
First-authors address: Shijingshan Teaching Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100043, China
膝骨关节炎(KOA)是关节退行性疾病,多发于中老年人,关节软骨退化磨损丢失同时关节周缘及软骨下骨出现骨质增生,致病因素尚不明确[1]。近年来关节置换术技术快速发展,在治疗终末期KOA中得到认可,但围手术期疼痛控制仍是需要解决的关键问题。传统的单独药物镇痛易造成诸多不良反应,随着多模式镇痛方案的研究越来越受到重视,在减少副作用、改善术后早期疼痛中有重要作用,为了进一步研究多模式镇痛方案效果,本研究特选取笔者所在医院62例全膝关节置换术患者进行研究,具体报告如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取笔者所在医院2018年11月-2019年11月收治的62例人工全膝关节置换术患者作为研究对象。纳入标准:符合膝关节炎症,精神正常、表达清晰、临床资料完整。排除标准:血压控制不稳定、合并其他部位骨折、病情危重、过敏体质患者。按照随机数字表法将其分为对照组(21例)和观察组(41例)。对照组男11例,女10例;年龄62~78岁,平均(66.05±10.02)岁;体重(63.54±10.49)kg。观察组男23例,女18例;年龄60~79岁,平均(65.11±11.24)岁;体重(64.25±11.02)kg。两组患者基础资料比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),有可比性。本次研究获得医院伦理委员会批准,患者及家属知情同意并签署知情同意书。

