磁共振T2-mapping与DTI序列对膝关节软骨慢性损伤的应用研究
张新慧 于静红


[摘要] 目的 探討磁共振不同序列在膝关节骨性关节炎(KOA)关节软骨慢性损伤损伤程度评估中的应用价值。方法 收集2017年12月~2018年12月在内蒙古医科大学第二附属医院行膝关节核磁共振成像(MRI)检查的骨关节炎(OA)患者35例,作为病变组;另选取健康成人志愿者35名,作为正常组。两组同时行膝关节MRI常规序列及功能成像序列[T2弛豫时间图(T2-mapping)、扩散张量成像(DTI)]扫描,分别测量两组股骨内、外侧髁软骨,胫骨内、外侧平台软骨,髌骨软骨这5个感兴趣区T2-mapping值及髌骨软骨表观弥散系数(ADC)值、部分各向异性系数(FA)值。由两名医师(副主任医师)根据Recht MRI分级标准对病变组膝关节各个感兴趣区软骨进行分级(分为Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ级),同时对所测量值进行病变组组间比较及与正常组之间的统计学分析。 结果 病变组股骨内、外侧髁软骨,胫骨内、外侧平台软骨,髌骨软骨关节面T2-mapping值,髌骨软骨关节面ADC值均较正常组增高,髌骨软骨关节面FA值较正常组降低,差异均有高度统计学意义(均P < 0.01)。Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ级组膝关节股骨内、外侧髁软骨,胫骨内、外侧平台软骨,髌骨软骨关节面软骨T2-mapping值和膝关节髌骨软骨关节面ADC值均较正常组明显增高,且Ⅳ级组高于Ⅲ、Ⅱ、Ⅰ级组,Ⅲ级组高于Ⅱ、Ⅰ级组,Ⅱ级组高于Ⅰ级组,差异均有高度统计学意义(均P < 0.01)。Ⅰ级组膝关节髌骨软骨关节面FA值与正常组比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ级组膝关节髌骨软骨关节面FA值均较正常组降低,且Ⅳ级组低于Ⅲ、Ⅱ、Ⅰ级组,Ⅲ级组低于Ⅱ、Ⅰ级组,Ⅱ级组低于Ⅰ级组,差异均有高度统计学意义(均P < 0.01)。股骨内、外侧髁软骨,胫骨内、外侧平台软骨,髌骨软骨关节面T2-mapping值和髌骨软骨关节面ADC值均与Recht分级间呈明显正相关(r > 0,均P < 0.01),髌骨软骨关节面FA值与Recht分级间呈负相关(r < 0,P < 0.01)。病变组ADC值在髌骨软骨区曲线下面积较同一部位的T2-mapping值及FA值大。 结论 T2-mapping、DTI成像技术可以对KOA患者关节软骨损伤程度进行定量评估。
[关键词] 核磁共振成像;T2弛豫时间图;扩散张量成像;膝关节软骨
[中图分类号] R445.2 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-7210(2020)05(a)-0093-05
Study on the application of magnetic resonance T2-mapping and DTI sequence in chronic injury of knee articularcartilage
ZHANG Xinhui1 YU Jinghong2▲
1.Department of Medical Imaging, the First Affiliated Hospital of Hebei North University, Hebei Province, Zhangjiakou, 075000, China; 2.Department of Radiology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Hohhot 010030, China
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the application value of different magnetic resonance sequences in the assessment of chronic injury severity of articular cartilage in knee osteoarthritis (KOA). Methods A total of 35 patients with osteoarthritis (OA) who underwent knee magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University from December 2017 to December 2018 were selected as the pathological group and another 35 healthy adult volunteers were selected as the normal group. The two groups were simultaneously scanned with the conventional and functional MRI sequences of the knee joint (T2 relaxation time diagram [T2-mapping], diffusion tensor imaging [DTI]). T2-mapping values, apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value and fractional anisotropic (FA) value of the five areas of interest of the medial and lateral condylar cartilage of the femur, the medial and lateral tibial plateau cartilage, and patellar cartilage in the two groups were measured respectively. By two physicians (associate chief physician) according to the Recht MRI classification standard of the lesion group of knee joint cartilage in various areas of interest (divided intoⅠ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ and Ⅳ level). At the same time, the measured values were compared between the groups of the pathological group and were statistically analyzed between the pathological group and the normal group. Results The T2-mapping values of the medial and lateral condylar cartilage of the femur, the medial and lateral tibial plateau cartilage, the articular surface of the patella cartilage, the ADC values of the articular surface of the patella cartilage in the pathological group were all higher than those of the normal group, and the FA values of the articular surface of the patella cartilage were lower than those of the normal group, with highly statistically significant differences (all P < 0.01). The T2-mapping values of knee joint of the medial and lateral condylar cartilage of the femur, the medial and lateral tibial plateau cartilage, the articular surface of the patella cartilage and the ADC values of of knee joint of the articular surface of the patella cartilage in theⅠ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ level groups were significantly higher than those in the normal group, and Ⅳ level group was higher than Ⅲ, Ⅱ, Ⅰ level groups, Ⅲ level group was higher than Ⅱ, Ⅰ level group, Ⅱ level group was higher than Ⅰ level group, the differences were highly statistically significant (all P < 0.01). There was no statistically significant difference between the FA value of articular surface of patellar cartilage of the knee in theⅠ level group and that in the normal group (P > 0.05). The FA value of articular surface of patellar cartilage in the Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ level groups was lower than that in the normal group, and Ⅳ level group was lower than Ⅲ, Ⅱ, Ⅰ level groups, Ⅲ level group was lower than Ⅱ, Ⅰlevel group, Ⅱ level group was lower than Ⅰ level group, the differences were highly statistically significant (all P < 0.01). The T2-mapping values of the medial and lateral condylar cartilage of the femur, the medial and lateral tibial plateau cartilage, the articular surface of the patella cartilage, the ADC values of the articular surface of the patella cartilage were significantly positively correlated with the Recht classification (r > 0, all P < 0.01), and the FA values of the articular surface of the patella cartilage were negatively correlated with the Recht classification (r < 0, P < 0.01). The ADC value of the pathological group under the curve of the patellar cartilage area was larger than the T2-mapping value and the FA value of the same site. Conclusion T2-mapping and DTI imaging techniques can quantitatively assess the degree of articular cartilage injury in KOA patients.
[Key words] Magnetic resonance imaging; T2 relaxation time diagram; Diffusion tensor imaging; Knee cartilage
膝关节骨性关节炎(knee osteoarthritis,KOA)是临床常见慢性骨关节病,晚期致残率极高。核磁共振成像(MRI)生理成像序列如T2弛豫时间图(T2-mapping)、扩散张量成像(diffusion tensor imaging,DTI),弥散加权成像(diffusion weighted imaging,DWI)等能够对软骨损伤早期尚未出现形态学改变前进行诊断。本文通过对正常志愿者及KOA患者膝关节软骨T2-mapping值、表观弥散系数(apparent diffusion coefficient,ADC)值及部分各向异性系数(fractional anisotropic,FA)值进行测量与分析,探讨T2-mapping、DTI序列对膝关节慢性软骨损伤的定量诊断价值。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
收集2017年12月~2018年12月在内蒙古医科大学第二附属医院(以下简称“我院”)影像科行膝关节MRI检查的骨关节炎(OA)患者35例作为病变组,无外伤及膝关节不适史的健康成人志愿者35名为正常组,两组一般临床资料比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),具有可比性。见表1。本研究已得到我院医学伦理委员会的批准,所有受试者均已知情同意。
1.2 纳入及排除标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①1个月内膝关节反复疼痛;②X线片(站立位或负重位)示关节间隙变窄、关节面硬化和(或)囊性变、关节缘骨赘形成、软骨下骨硬化;③关节液清亮、赤稠,白细胞计数<2000个/mL;④中老年患者(≥40岁);⑤晨僵≥30 min;⑥活动时有骨摩擦音(感)。符合以上①+②条或①+③+⑤+⑥条或①+④+⑤+⑥条者。
1.2.2排除标准 ①有膝关节外伤史、药物治疗史;②有免疫性疾病,例如类风湿关节炎、强直性关节炎等关节肿痛者;③MRI检查禁忌及不能配合完成检查者、扫描图像未满足诊断标准者。
1.3扫描方法
1.3.1受试者准备 检查采用GE 1.5T磁共振仪MR-360(GE Medical System,USA),使用八通道膝关节扫描线圈。受试者采取仰卧位,足先进,膝关节伸直,且膝关节长轴与扫描床长轴平行。
1.3.2扫描参数 对病变组及正常组行FSE-fs-T2、T2-mapping及DTI序列扫描。①FSE-fs-T2扫描参数为:TR=4500 ms,TE=66 ms,层厚4.0 mm,FOV 20 mm×20 mm,矩阵320×320,NEX=4;②T2-mapping成像扫描参数为:TR=1500 ms,TE= 12.1 ms/24.3 ms/36.4 ms/45.5 ms/60.7 ms/72.8 ms/85 ms/97.1 ms,层厚4.0 mm,层间距2 mm,FOV 20 mm×20 mm,矩阵256×224,NEX=1。③DTI成像采用轴位扫描,扫描参数为:TR=6000 ms,TE=91.1 ms,层厚3.0 mm,层间距2 mm,FOV 20 mm×20 mm,矩阵96×96,NEX=6,b=600。
1.4图像观察与后处理
将扫描完成后的原始图像数据传至AW 4.6工作站,利用Functool 9.4.05软件进行重建得到T2-mapping、DTI伪彩图。在伪彩图上分别画出股骨内、外侧髁软骨,胫骨内、外侧平台软骨,髌骨软骨5个感兴趣区;在ADC伪彩图上画出髌骨软骨。感兴趣区包括软骨全层,尽量避开软骨下骨、软骨缺损和关节腔积液,并对其进行三等分并测量,计算其平均值,记录其平均T2-mapping、ADC及FA值。
1.5膝关节软骨MRI分级标准
根据Recht[1]MRI分级标准,0级:正常关节软骨,软骨弥漫性均匀变薄,但表面光滑,仍认为是正常关节软骨。Ⅰ級:软骨分层结构消失,软骨内出现局灶性低信号区,软骨表面光滑。Ⅱ级:软骨表面轮廓轻至中度不规则,软骨缺损深度未及全层厚度的50%。Ⅲ级:软骨表面轮廓重度不规则,软骨缺损深度达全层厚度的50%以上,但未完全剥脱。Ⅳ级:软骨全层缺损、剥脱,软骨下骨质暴露伴或不伴软骨下骨质信号改变。由两位副主任医师分别阅片,如结果不一致,进行协商达成一致意见。
1.6 统计学方法
利用SPSS 21.0软件对数据进行统计学分析,对MRI不同分级的所有数据进行Levene方差齐性检验。计量资料符合正态分布采用均数±标准差(x±s)表示,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,组间两两比较采用LSD法。计数资料采用百分率表示,组间比较采用χ2检验。利用ROC曲线分析ADC、FA及T2-mapping值鉴别病变组髌骨软骨关节面曲线下面积并比较其大小。Recht分级及膝关节软骨退变分期为分类变量,采用Spearman检验分析膝关节软骨各感兴趣区T2-mapping、ADC及FA值与Recht分级相关性。以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2结果
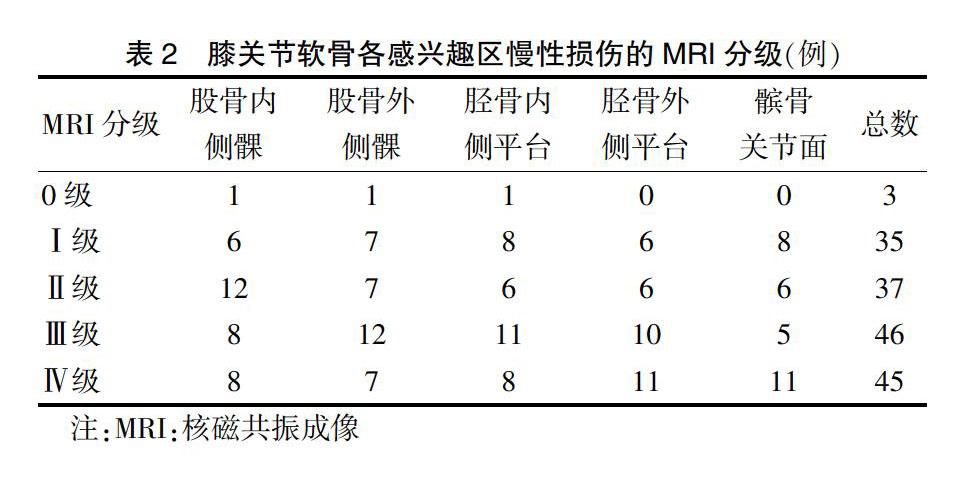
病变组35例(36个膝关节)行磁共振检查,图像质量良好。股骨内、外侧髁软骨,胫骨内、外侧平台软骨,髌骨软骨关节面中0级3个(1.8%),Ⅰ级损伤35个(21.1%),Ⅱ级损伤37个(22.2%),Ⅲ级损伤46个(27.7%),Ⅳ级损伤45个(27.2%)。见表2。
2.1 不同分组膝关节软骨各感兴趣区T2-mapping值测量结果比较
Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ级组在膝关节股骨内、外侧髁软骨,胫骨内、外侧平台软骨,髌骨软骨关节面软骨T2-mapping值均较正常组明显增高,且Ⅳ级组高于Ⅲ、Ⅱ、Ⅰ级组,Ⅲ级组高于Ⅱ、Ⅰ级组,Ⅱ级组高于Ⅰ级组,差异均有高度统计学意义(均P < 0.01)。见表3。
2.2 不同分组膝关节髌骨软骨关节面ADC及FA值测量结果比较
Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ级组膝关节髌骨软骨关节面ADC值均较正常组明显增高,且Ⅳ级组高于Ⅲ、Ⅱ、Ⅰ级组,Ⅲ级组高于Ⅱ、Ⅰ级组,Ⅱ级组高于Ⅰ级组,差异均有高度统计学意义(均P < 0.01);Ⅰ级组与正常组膝关节髌骨软骨关节面FA值比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ级组膝关节髌骨软骨关节面FA值均较正常组降低,且Ⅳ级组低于Ⅲ、Ⅱ、Ⅰ级组,Ⅲ级组低于Ⅱ、Ⅰ级组,Ⅱ级组低于Ⅰ级组,差异均有高度统计学意义(均P < 0.01)。见表4。
2.3膝关节各感兴趣区与Recht分级相关性
股骨内、外侧髁软骨,胫骨内、外侧平台软骨,髌骨软骨关节面T2-mapping值均与Recht分级呈明显正相关(r = 0.852、0.809、0.830、0.920、0.838,均P < 0.01);髌骨软骨关节面ADC值与Recht分级呈正相关(r = 0.591,P < 0.01);髌骨软骨关节面FA值与Recht分级呈负相关(r = -0.608,P < 0.01)。
2.4 两组膝关节各感兴趣区T2-mapping值及髌骨软骨关节面ADC、FA值结果比较
病变组股骨内、外侧髁软骨,胫骨内、外侧平台软骨,髌骨软骨关节面T2-mapping值,髌骨软骨关节面ADC值均较正常组增高,髌骨软骨关节面FA值较正常组降低,差异均有高度统计学意义(均P < 0.01)。见表5。
2.5 ADC值、FA值及T2-mapping值评估病变组髌骨软骨退变的ROC曲线下面积比较
ADC值曲线下面积为0.958,较同一节段的T2-mapping值(0.953)、FA值(0.914)大。见图1。
3 讨论
T2-mapping是一种定量MRI技术,是国内外应用最广泛的MR生理成像技术。近年来国内一些研究表明T2-mapping成像技术能够诊断早期OA[2-3],随着软骨损伤程度的加重,T2-mapping值逐渐增高,可以很好地区分早晚期OA[4-9]。这与本研究结果相同,这是由于退变早期,软骨内自由水含量显著增加且PG含量减低,而T2-mapping值与水含量呈正相关,与PG含量呈负相关,故而T2-mapping值可以反映早期关节软骨的损伤[10-14]。Soellner等[15]研究表明随着软骨损伤等级的增加,T2-mapping值增加,与分级标准之间存在显著正相关,与本研究中股骨内、外侧髁软骨,胫骨内、外侧平台软骨,髌骨软骨关节面T2-mapping值均与Recht分级呈明显正相关的结果相同,即T2-mapping值对定量分析膝关节软骨退变具有重要意义。
蛋白多糖主要影响关节软骨ADC值,而FA值能够间接反映胶原纤维网络的完整性。赵丹丹等[16]对髌骨软骨退变不同年龄组的研究表明,随着软骨的退变着年龄的增长,髌骨软骨的FA值逐渐下降,而ADC值逐渐增加。Raya等[17]研究表明OA组中髌骨软骨的FA值在Ⅰ~Ⅲ级中差异无统计学意义,这與本研究结果相似,即说明FA值可以检测软骨损伤但不能区分早期软骨损伤。有学者[18-20]通过对OA患者的1年随访测试发现,ADC值可以发现OA早期改变,这与本研究成果相同,这是由于OA的最早征兆即PG的丧失和胶原网络的破坏,故DTI可以鉴别早期关节软骨的退变。
本研究通过对病变组及正常组髌骨软骨的T2-mapping、ADC、FA值进行比较,发现ADC值诊断膝关节软骨退变的能力更强,即敏感度、特异度相较其他两个检查参数更高,为KOA的诊断提供了参考。
总而言之,本研究中样本量相对较少,还需要继续扩大样本量并进行深入研究,以期得出更准确的数据。
[参考文献]
[1] Recht MP,Kramer J,Marcelis S,et al, Abnormalities of articular cartilage in the knee:analysis of available MR techniques [J]. Radiology,1993,187(2):473-478.
[2] 于秀英,何勇,赵蕾,等.MRI T2-Mapping成像对膝关节髌软骨早期退变的诊断价值[J].中国中西医结合影像学杂志,2019,17(1):10-12.
[3] 孙兆男,王旭超,徐敏,等.磁共振T2 mapping成像评价膝关节骨关节炎软骨损伤的应用价值[J].磁共振成像,2019,10(9):680-684.
[4] 樊子健,吴丽萍,任有忠,等.3.0 T磁共振T2-Mapping、3D-FSE-Cube与常规序列对膝关节软骨损伤分级对比分析[J].磁共振成像,2017,8(9):675-680.
[5] 杨彦伟.MRI与CT诊断膝关节半月板和关节软骨损伤的临床价值对比研究[J].内蒙古医学杂志,2018,50(2):188-189.
[6] 武淑锋.膝半月板和关节软骨损伤CT与MRI诊断价值对比[J].影像研究与医学应用,2018,2(10):82-83.
[7] 徐国辉.CT与MRI诊断膝半月板和关节软骨损伤临床价值对比[J].影像研究与医学应用,2018,2(9):132-133.
[8] 李晓芬,张宁,徐荣春,等.3.0T磁共振T2-mapping成像对早期膝关节软骨损伤的应用价值[J].江西医药,2016, 51(3):212-216.
[9] 田明波,刑林卿,李守峰,等.CT与MRI在不同分期膝半月板和关节软骨损伤患者中的诊断对比[J].中国CT和MRI杂志,2019,17(1):133-136.
[10] Guermazi A,Alizai H,Crema MD,et al. Compositional MRI techniques for evaluation of cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis [J]. Osteoarthritis Cartilage,2015,23(10):1639-1653.
[11] Wei B,Du X,Liu J,et al. Associations between the properties of the cartilage matrix and findings from quantitative MRI in human osteoarthritic cartilage of the knee [J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol,2015,8(4):3928-3936.
[12] Jungmann PM,Kraus MS,Alizai H,et al. Metabolic Risk Factors are associated with Cartilage Degradation assessed by T2 Relaxation Time at the Knee[J]. Arthritis Care Res(Hoboken),2013,65(12):1942-1950.
[13] Wise BL,Niu J,Guermazi A,et al. Magnetic resonance imaging lesions are more severe and cartilage T2 relaxation time measurements are higher in isolated lateral compartment radio graphic knee osteoarthritis than in isolated medial compartment disease-data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative [J]. Osteoarthritis Cartilage,2017, 25(1):85-93.
[14] 赵双全.膝关节正常软骨及骨性关节炎软骨病变的MRI形态及T1、T2、T2* Mapping临床研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2019.
[15] Soellner ST,Goldmann A,Muelheims D,et al. Intraoperative validation of quantitative T2 mapping in patients with articular cartilage lesions of the knee[J]. Osteoarthritis Cartilage,2017,25(11):1841-1849.
[16] 趙丹丹,李红,秦灏,等.DTI在正常成人髌骨软骨的初步应用及临床意义[J].磁共振成像,2016,7(2):131-135.
[17] Raya JG,Arnoldi AP,Weber DL,et al. Ultra-high field diffusion tensor imaging of articular cartilage correlated with histology and scanning electron microscopy[J]. MAGMA,2011,24(4):247-258.
[18] Raya JG. Techniques and Applications of in vivo Diffusion Imaging of Articular Cartilage[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging,2015,41(6):1487-1504.
[19] 李明楷,石磊,王可欣,等.磁共振弥散张量成像在评估骨关节炎髌软骨退变中的应用[J].疑难病杂志,2018, 17(9):918-921.
[20] Ukai T,Sato M,Yamashita T,et al. Diffusion tensor imaging can detect the earlystages of cartilage damage:a comparison study[J]. BMC Musculoskelet Disord,2015, 16:35.
(收稿日期:2019-10-26 本文编辑:顾家毓)

