Splenic Trauma 脾外伤
Key Facts
Definition:Damage to the splenic parenchyma or splenic vessels secondary to blunt or penetrating trauma.
Spleen is most commonly injured organ following blunt trauma.Spleen injury accounts for about 40% of patients with blunt organ injury.Nonoperative management possible in about 60% of patients.Failure of nonoperative management increases with grade of injury.The only finding at CT may be perisplenic blood.
Imaging Findings
Types of injury:(1)Laceration:Linear or curved area of low attenuation relative to spleen; (2)Intrasplenic hematoma:Rounded inhomogeneous area of low attenuation; (3)Subcapsular hematoma:Crescentic low attenuation area compressing the parenchyma; (4)Fracture:Multiple crossing lacerations or fragmentation; (5)Hilar vascular injury:Devascularized splenic segment or devascularized whole spleen.CT findings:(1)In addition to the above findings,CT may show the following of which both increase the likelihood of intervention.(2)Active bleeding;(3)Expanding hematoma on a follow-up scan.
Imaging recommendations:Splenic injury is evaluated during routine CT for trauma,using an injection rate of at least 2.5 ml/s for 135-180 ml of contrast,and using a 75 s delay after beginning injection until starting the scan at the dome of the diaphragm.
Delayed scanning may be useful if there is active arterial hemorrhage.Follow-up scan may be useful if patient is suspected of having continued bleeding from expanding hematoma or rupture of the spleen.Differential diagnosis:None.
Staging or Grading Criteria
Subcapsular hematoma:(1)Grade Ⅰ:<10% surface area; (2)Grade Ⅱ:10%-50%,<5cm diameter; (3)Grade Ⅲ:>50% or expanding intraparenchymal hematoma,>5 cm or expanding.
Laceration:(1)Grade Ⅰ:<1 cm in length; (2)Grade Ⅱ:1-3 cm; (3)GradeⅢ:>3 cm.Devascularization:(4)Grade Ⅳ:>25% of splenic area; (5)GradeⅤ:Total spleen.
Shattered spleen (fragmentation,multiple fractures):Grade Ⅴ.
医学词汇注释与简要讲解
splenic parenchyma 脾实质
blunt trauma 钝伤
penetrating trauma 穿通伤
laceration 裂伤
intrasplenic hematoma 脾内血肿
subcapsular hematoma 包膜下血肿
fracture 脾断裂
hilar vascular injury 脾门血管损伤
【prefix】de-解、除、去、脱
devascularized 无血供的,去血管化
decalicification 脱钙
decompression 减压
dome of the diaphragm 膈顶
shattered spleen 脾碎裂
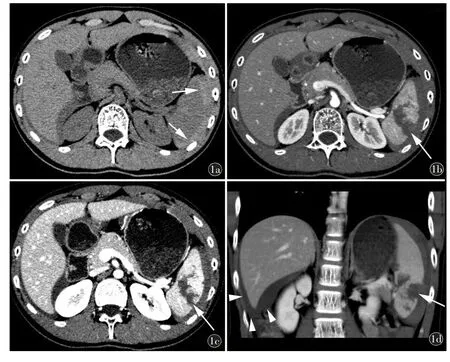
Fig 1 a)Subcapsular hematoma(blood) is surrounding lateral surface of spleen (arrows) and shows higher attenuation on nonenhanced CT.On enhanced CT of arterial phase (b)and venous phase (c),a through and through laceration is present(arrow).d)Coronal CT reconstruction shows a fracture of the spleen(arrow)and ascites(arrow heads) around liver.There is fragmentation and the fracture extends to the splenic hilum.
Clinical Issues
Presentation:Acute injury may lead to hypotension and a drop in hematocrit;and delayed rupture will also present in this way.
Treatment:Surgery is required if the patient becomes hemodynamically unstable after initial stabilization.Predictors of failure of nonoperative management:(1)Onset of homodynamic instability.(2)Injury grade Ⅳor Ⅴ.(3)Large associated hemoperitoneum.(4)Active arterial extravasation seen on CT.
Complications following nonoperative management:(1)“Delayed rupture”weeks to years after initial injury; seen in <1% of patients if initial CT is normal.(2)Pseudoaneurysm.(3)Pseudocyst; if >5 cm there is 25% risk of rupture.(4)Abscess which may be delayed months or years.
手术治疗的指征包括:
(1)血流动力学不稳定;
(2)4 级 或5 级损伤;
(3)大量腹腔积血;
(4)动脉出血表现。
未手术者的并发症包括:
(1)延迟脾破裂;
(2)假性动脉瘤;
(3)假性囊肿;
(4)脾脓肿。

