上消化道黏膜病变病理诊断结果分析
陶源 徐俊林 张艳


摘要:目的 探讨上消化道黏膜病变的病理类型和临床特点的关系,为临床诊治该病提供参考依据。方法 回顾性分析2014年1月~2018年12月我院收集的9659例上消化道黏膜活檢病理诊断结果,观察胃炎、息肉、溃疡和肿瘤病变与年龄、性别、幽门螺杆菌(Hp)感染情况的关系。结果 ①胃炎:不同年龄段慢性炎症、萎缩、肠化、上皮内瘤变人数比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。女性慢性炎症轻度和中度人数高于男性,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);不同性别萎缩、肠化、上皮内瘤变人数比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);慢性炎症、萎缩、肠化、上皮内瘤变不同严重程度Hp(+)人数高于Hp(-),差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。②息肉:不同年龄段胃息肉、贲门息肉、食道息肉病变人数比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。女性胃息肉、食道息肉人数高于男性,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);不同性别贲门息肉、十二指肠息肉人数比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。胃息肉、贲门息肉不同类型Hp(+)人数高于Hp(-),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);食道息肉、十二指肠息肉HP感染人数比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。③溃疡和肿瘤病变:不同年龄段胃溃疡、胃癌、食管癌人数比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);不同年龄段贲门溃疡人数比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。男性胃溃疡、食道溃疡、贲门溃疡、胃癌、食管癌人数高于女性,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。胃溃疡、食道溃疡、贲门溃疡、胃癌、食管癌Hp(+)人数高于Hp(-),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 轻度慢性胃炎好发于青中年性,息肉、溃疡、肿瘤病变好发于中老年人,轻度慢性胃炎、息肉病变好发于女性,溃疡和肿瘤病变好发于男性,胃炎相关病变、息肉、溃疡、肿瘤与Hp感染密切相关。
关键词:上消化道黏膜病变;慢性胃炎;幽门螺杆菌
中图分类号:R57 文献标识码:A DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2020.02.036
文章编号:1006-1959(2020)02-0125-05
Abstract:Objective To explore the relationship between pathological types and clinical characteristics of upper gastrointestinal mucosal lesions, and to provide reference basis for clinical diagnosis and treatment of the disease. Methods A retrospective analysis of 9659 cases of upper gastrointestinal mucosal biopsy collected in our hospital from January 2014 to December 2018 was performed to observe the gastroenteritis, polyps, ulcers, tumor lesions, age, gender, and Helicobacter pylori (Hp) infection relationship. Results ①Gastritis:There were significant differences in the number of chronic inflammation, atrophy, intestinalization, and intraepithelial neoplasia at different ages (P<0.05). The number of women with mild and moderate chronic inflammation was higher than that of men,the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05); there was no significant difference in the number of atrophy, intestinalization, and intraepithelial neoplasia between different genders (P>0.05);Chronic inflammation, atrophy, intestinalization, and intraepithelial neoplasia were more severe in Hp (+) than Hp(-),the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). ②Polyps:There were statistically significant differences in the number of lesions of gastric polyps, cardia polyps, and esophageal polyps at different ages(P<0.05). The number of women with gastric polyps and esophagus polyps was higher than that of men,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). There was no significant difference in the number of different genders of cardia polyps and duodenal polyps (P>0.05). The number of different types of Hp(+) in gastric polyps and cardia polyps was higher than Hp (-),the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). There was no significant difference in HP infection among esophageal polyps and duodenal polyps(P>0.05). ③Ulcers and tumor lesions:There was a statistically significant difference in the number of gastric ulcers, gastric cancer, and esophageal cancer at different ages(P<0.05); there was no statistically significant difference in the number of cardiac ulcers at different ages (P>0.05). The number of gastric ulcer, esophageal ulcer, cardia ulcer, gastric cancer, and esophageal cancer was higher in men than in women,the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Gastric ulcer, esophageal ulcer, cardiac ulcer, gastric cancer, and esophageal cancer Hp (+) were higher than Hp (-), the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion Mild chronic gastritis is more common in young and middle-aged people, polyps, ulcers, and tumor lesions are more common in middle-aged and elderly people. Mild chronic gastritis and polyp lesions are more common in women, and ulcers and tumors are more common in men.Polyps, ulcers, tumors are closely related to Hp infection.
Key words:Upper gastrointestinal mucosal lesions;Chronic gastritis;Helicobacter pylori
上消化道黏膜病變(gastric mucosa pathological changes)通常表现为黏膜肿胀、糜烂、隆起等,常见于消化道炎症、息肉、黏膜肿瘤、癌前病变、早期癌等[1]。目前通过电子胃镜黏膜活检组织的病理诊断是金标准,电子胃镜结合上消化道黏膜活体组织检查可进一步提高上消化道疾病的准确性,对胃癌和疑难、罕见的上消化道疾病的早发现、早诊断、早治疗起着重要作用。本研究结合2014年1月~2018年12月北京市昌平区中医医院9659例上消化道黏膜活检病理资料,探讨上消化道黏膜病变的病理类型与年龄、性别、幽门螺杆菌(Hp)感染的关系,现报道如下。
1资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 回顾性分析2014年1月~2018年12月北京市昌平区中医医院9659例上消化道黏膜活检病理诊断结果,其中男性4359例,女性5300例,年龄14~90岁,平均年龄(50.12±13.52)岁;青年(<45岁)3143例,中年(45~59岁)3949例,老年(≥60岁)2567例。慢性炎症共9610例,其中轻度3609例、中度4881例、重度1120例;萎缩共108例,其中轻度107例、中度1例;肠化1728例,其中轻度718例、中度920例、重度90例;上皮内瘤变共377例,其中轻度341例、中度27例、重度9例;胃息肉共800例,其中增生性息肉478例、炎性息肉316例、腺瘤性息肉6例;贲门息肉38例,其中炎性息肉23例、增生性息肉15例;食道息肉17例,其中炎性息肉9例、增生性息肉8例;十二指肠息肉7例,其中炎性息肉5例、增生性息肉2例;溃疡和肿瘤病变共424,胃溃疡282例、食道溃疡24例、贲门溃疡18例、胃癌53例、食管癌47例。
1.2 方法 活检标本均为胃镜钳夹组织,采用自动脱水机(脱水机LEICA ASP 200S)脱水(甲醛固定,酒精梯度脱水,二甲苯透明,浸蜡)及石蜡包埋后(包埋机LEICA EG 1150H),进行人工切片(4 μm)(切片机LEICA RM2235),最后进行苏木素-伊红染色。
1.3统计学方法 应用Excel 2007建立数据库,使用SPSS 25.0统计软件对进行数据处理。计量资料以(x±s)表示;计数资料以(n)表示,对于无序分类资料采用?字2检验,对于有序分类资料采用非参数检验-秩和检验,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2结果
2.1胃炎病变分级与年龄、性别、Hp感染的关系
2.1.1胃炎与年龄的关系 轻度慢性炎症好发于<45岁和45~59岁年龄段,中度、重度均以45~59岁年龄段最多;萎缩轻度以45~59岁年龄段居多;肠化均以45~59岁和≥60岁年龄段居多;上皮内瘤变轻度、中度以45~59岁和≥60岁年龄段为多,重度则以≥60年龄段为多。不同年龄段慢性炎症、萎缩、肠化、上皮内瘤变人数比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表1。
2.1.2胃炎与性别的关系 女性慢性炎症轻度和中度人数高于男性,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);不同性别萎缩、肠化、上皮内瘤变人数比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),见表2。
2.1.3胃炎与Hp感染的关系 慢性炎症、萎缩、肠化、上皮内瘤变不同严重程度Hp(+)人数高于Hp(-),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表3。
2.2息肉与年龄、性别、Hp感染的关系
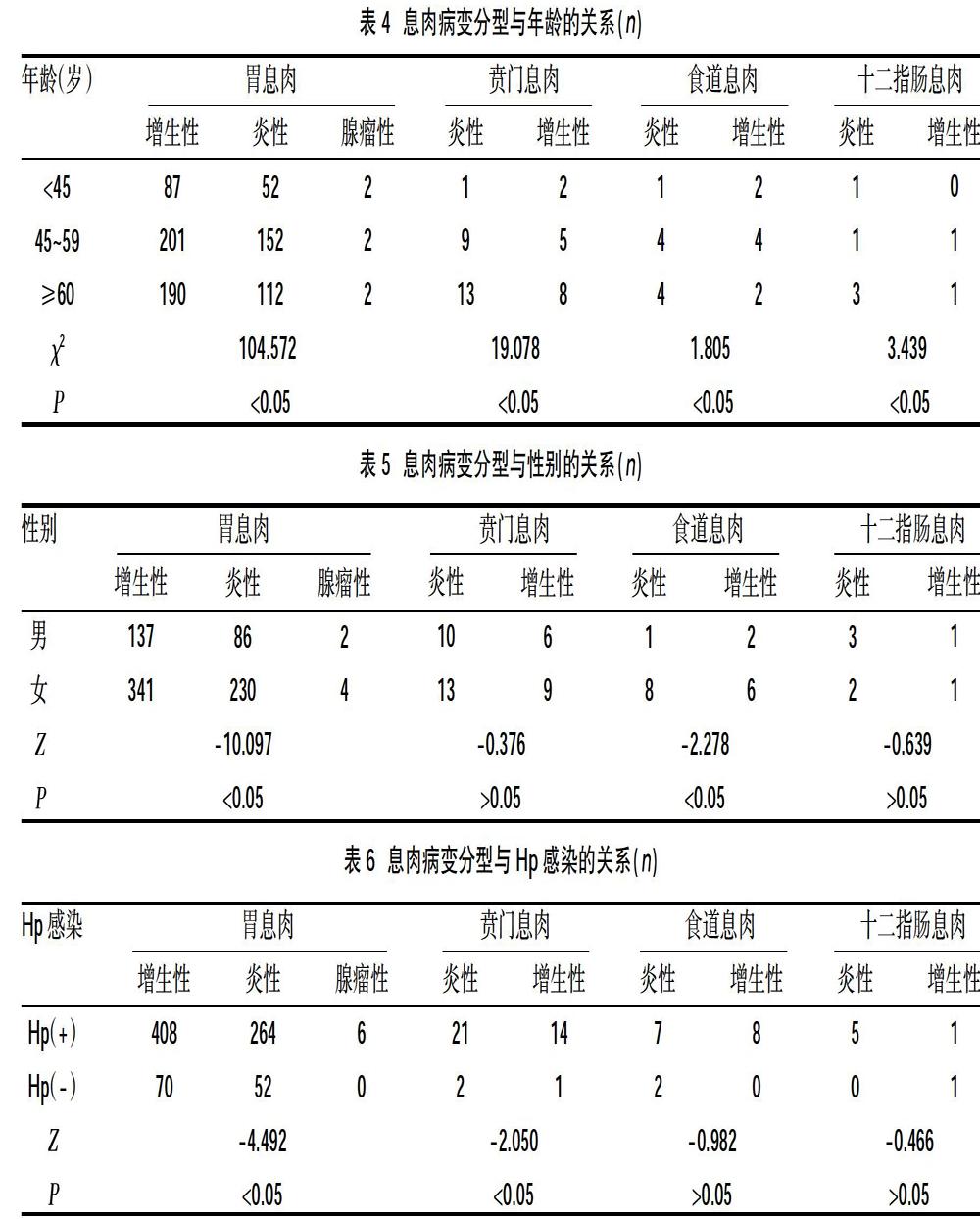
2.2.1息肉与年龄的关系 胃息肉中增生性和炎性好发于45~59岁和≥60岁年龄段;贲门息肉中炎性和增生性均以≥60岁年龄段最多,其次为45~59岁年龄段;食道息肉和十二指肠息肉均以炎性为多,好发于≥60岁年龄段。不同年龄段胃息肉、贲门息肉、食道息肉病变人数比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表4。
2.2.2息肉与性别的关系 女性胃息肉、食道息肉人数高于男性,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);不同性别贲门息肉、十二指肠息肉人数比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),见表5。
2.2.3息肉与Hp感染的关系 胃息肉、贲门息肉不同类型Hp(+)人数高于Hp(-),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);食道息肉、十二指肠息肉Hp感染人数比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),见表6。
2.3溃疡和肿瘤病变与年龄、性别、Hp感染的关系
2.3.1溃疡和肿瘤病变与年龄的关系 胃溃疡以45~59岁年龄段为最多,其次为≥60岁年龄段;食道溃疡、贲门溃疡好发于45~59年龄段;胃癌和食管癌好发于≥60岁年龄段。不同年龄段胃溃疡、胃癌、食管癌人数比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);不同年龄段贲门溃疡人数比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),见表7。
2.3.2溃疡和肿瘤病变与性别的关系 男性胃溃疡、食道溃疡、贲门溃疡、胃癌、食管癌人数高于女性,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表8。
2.3.3溃疡和肿瘤病变与Hp感染的关系 胃溃疡、食道溃疡、贲门溃疡、胃癌、食管癌Hp(+)人数高于Hp(-),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表9。
3讨论
慢性胃炎是由多种原因引起的胃黏膜的慢性炎性反应,是消化系统常见病之一。该病易反复发作,严重影响患者的生活质量。慢性萎缩性胃炎伴肠上皮化生、上皮内瘤变者发生胃癌的危险度增加,临床上需引起重视[2]。

