MAIN TOPICS,ABSTRACTS & KEY WORDS
Effectofpretensiononfatiguelifeofstainlesssteelresistancespotweldedjoint
Zhu Guoren1,Pang Lilin1,Zhu Kaixun1,Yang Ming1,Wang Hongxiao2
(1. Jilin University, Changchun 130022, China; 2. CRRC Changchun Railway Vehicles Co., Ltd., Changchun 130062, China).p1-4
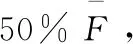
Keywords:resistantspotweldedjoint,residualstress,pretensionload,fatiguelife
Developmentofhighspeeddriverforelectronbeamscanningcoil
Yang Bo, Xu Haiying, Sang Xinghua
(AVIC Manufacturing Technology Institute, Beijing 100024, China).p5-10
AbstractIn order to meet the need of high speed deflection scanning of electron beam, a high speed driver for electron beam scanning coil was developed. Specifically, the driver input stage circuit was designed by means of voltage reduction, compensation and differential input to improve the response and processing speed of the circuit to high-speed signals. The current closed-loop regulating circuit was designed by emitter following to improve the closed-loop regulating speed and stability of the circuit. The circuit simulation analysis and parameter optimization were done by Cadence simulation. According to the above results, a high-speed driver for electron beam scanning coil was developed and tested. The results showed that the output current could respond to any input signal in a high-speed closed-loop manner when the inductive load was drove. The operating frequency could reach 100 kHz and the maximum driving current was ± 2 A.
Keywords:electronbeam,scanningcoildriver,high-speedcurrentclosed-loopregulation,Cadencecircuitsimulation
OptimizationofcompositionsofFeNiCrBClasercladdinglayerforminesupportbasedonThermo-Calc
Yao Zhichao, Li Zhengqiu, Gao Xiangzhou, Ma Chunchun
(BGRIMM Technology Group, Beijing 100029, China)p.11-16,36
AbstractAiming at the problem of poor corrosion resistance and easy cracking of the FeNiCrBC cladding layer for mine supports, the content of Ni and Nb elements in the cladding layer was adjusted to increase the content of retained austenite in the cladding layer and reduce the phenomenon of intergranular chromium depletion, so as to arrive the purpose of decreasing crack sensitivity and improving corrosion resistance. In this study, the influence of contents of Ni and Nb elements on the microstructure and precipitated phase in FeNiCrBC cladding layer was investigated through the thermodynamics software Thermo-Calc. The chemical compositions of cladding layer were optimized based on the research results. The result showed that the percentage of σ phase decreased with the Ni content increasing from 1% to 8%. The proportion of retained austenite in FeNiCrBC cladding layer reached the maximum when the Ni content was 4%. With the addition amount of Ni element increasing from 0.3% to 2.0%, the Cr content in martensite first increased and then tended to be steady, and it in carbide and boride decreased gradually, while the amount of Nb in such two compounds increased. After the elements Ni and Nb were adjusted to 4% and 1% respectively, the corrosion resistance of FeNiCrBC cladding layer got improved apparently, and also the cracking susceptibility decreased obviously.
Keywords:Thermo-Calc,claddinglayer,precipitatedphases,corrosionresistance,crackingsusceptibility
Weldingdeformationcontrolofaluminumalloyconnectionframework
Gao Yanfang, Liao Chuanqing, Wan Jun, Gao Jiashuang, Yu Bin, Xia Wenjia
(Shanghai Aerospace Equipments Manufacturing Co., Ltd., Shanghai 200245, China).p17-20,55
AbstractTaking aluminum alloy connection framework as the product object, whose welding deformation control was researched. Welding deformation and weld quality of connection framework were controlled by methods of optimization of matching welding components, prediction of welding deformation, optimal design of welding fixture, reservation of welding allowance in parts and process control of post weld heat treatment. Finally, the difference of diagonal length of the upper framework and the bottom framework was no more than 3 mm, and the flatness of mounting surface of upper framework and bottom framework did not exceed 1.3 mm. Weld quality of connection framework fulfilled the requirement of level II in QJ 2698A—2011 standard.
Keywords:aluminumalloy,weldingfixture,weldingdeformation,connectionframework,SYSWELD
MicrostructuretransformationandmechanicalpropertiesofEH40shipbuildingplatesteelforhighheatinputweldingapplication
Liu Hongbo1, Li Jianxin2, Lin Zhangguo1, Qi Jianjun1, Tian Zhiqiang1, Liu Chong1
(1. Research Institute of HBIS Group, Shijiazhuang 050000, Hebei, China; 2. HBIS Company Limited, Shijiazhuang 050000, Hebei, China).p21-27
AbstractHBIS group developed EH40 shipbuilding plate steel for high heat input welding application by oxide metallurgy technology. The continuous cooling transformation behavior and microstructure transformation under different cooling rates of welding heat affected zone (HAZ) in EH40 shipbuilding plate steel were studied by DIL805L quenching and phase transformation dilatometer in combination with thermal simulation technology. In addition, thermal simulation experiments were conducted on a Gleeble-3800 thermal simulation testing machine, and then the mechanical properties of HAZ were tested. Simulated HAZ continuous cooling transformation (SHCCT) curves showed that ferrite and pearlite formed when the cooling rate was less than 0.1℃/s. As the cooling rate increased to 0.2 ℃/s, bainite began to precipitate. When the cooling rate was 2~3 ℃/s, ferrite/pearlite and granular bainite transformation occurred. When the cooling rate was 5~10 ℃/s, ferrite/granular bainite transformation occurred. Moreover, with the increase of cooling rate, the proportion of granular bainite increased gradually. Lath bainite formed when the cooling rate increased to 15 ℃/s. When the cooling rate increased to 30~100 ℃/s, martensite began to generate and the proportion of martensite became increased. Furthermore, the results of welding thermal simulation and impact test showed that the average impact absorbed energy in HAZ of EH40 shipbuilding plate steel was 205 J at -40 ℃ after a simulated welding thermal cycle of 200 kJ/cm heat input, which was much higher than the national standard value of 41 J. The scanning electron microscope and energy dispersive spectrometer were adopted to analyze particles precipitated in HAZ of EH40 shipbuilding plate steel, the results illustrated that (Ti, Mn, Si, Mg)Ox-MnS particles were nucleation sites to promote the formation of acicular ferrite in HAZ, which could effectively improve the low temperature toughness of HAZ.
Keywords:highheatinputwelding,EH40shipbuildingplatesteel,heataffectedzone,continuouscooling,microstructuretransformation
Lowtemperaturelead-freesolderingof6063aluminumalloy
Yang Fang, Li Tianli, He Xin, Han Jichao, He Jinchuan
(Liaoning Technical University, Fuxin 123000, Liaoning, China).p28-31
AbstractA new low temperature lead-free solder was prepared by adding mass fraction 1%, 2%, 3% and 4% Bi with 1% Ga to Sn-9Zn binary alloy, by which the hot dip galvanized 6063 aluminum alloy was soldered. Laser confocal microscope, scanning electron microscope, X-ray diffractometer and Vickers were carried out on the soldered joint to observe microstructure, analyze phase, element distribution and microhardness, respectively. Effects of Bi and Ga element on the interface microstructure and formation mechanism of the soldered joint were studied through comparing with three kinds of traditional lead-containing soldered joints. The results showed that the galvanizing was good at the temperature of 450 ℃ for 10 s, the zinc liquid and 6063 aluminum alloy diffused with each other. The addition of Bi and Ga elements improved the wettability of the solder. Al0.71Zn0.29 compound particles existed in the soldered joint of Sn-9Zn-xBi-Ga/galvanized layer/6063 aluminum alloy. The maximum microhardness of Sn87Zn9Bi3Ga soldered joint was 38.4 HV0.2 and the soldered joint had the closest metallurgical bond, which was suitable for low temperature soldering of 6063 aluminum alloy.
Keywords:soldering,lead-freesolder,hotdipgalvanizing,wettability,microhardness
Applicationstatusofexternalmagneticfieldanddeepcryogenictreatmentinaluminumalloywelding
Gao Wenguo, Gao Shan, Hu Jiangang
(Taiyuan University of Science and Technology, Taiyuan 030000, China).p32-36
AbstractResearch progress of external magnetic field and deep cryogenic treatment in aluminum alloy welding was systematically reviewed in the article. Influence of external magnetic field and deep cryogenic treatment on arc physics and macroscopic effects in the aluminum alloy welding process was emphatically analyzed, as well as its relationship with welding process. Moreover, research results of microstructure were reviewed and analyzed from different scales, such as microstructure, mechanical properties and formation mechanism. The results showed that the addition of external magnetic field changed the shape of welding arc, the mode of droplet transition and the flow of molten metal in the molten pool, and good microstructure and shape of weld could be obtained under the appropriate magnetic field parameters. After deep cryogenic treatment, the grain of aluminum alloy rotated and refined, which ultimately made the performance of deep cryogenic treatment part more excellent. This article provided some guidance for the research and application of external magnetic field and deep cryogenic treatment in aluminum alloy welding.
Keywords:externalmagneticfield,deepcryogenictreatment,aluminumalloywelding,weldedjoint,microstructure
Researchingstatusofdissimilarmetalweldingoftitaniumandaluminum
Yu Deshui, Zhang Yan, Zhou Jianping, Bi Yuanbo, Bao Yang
(Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China).p37-45
AbstractControl methods of brittle Ti-Al intermetallic compounds in welding process of titanium/aluminum dissimilar metals were reviewed. Research status of fusion welding (laser welding, electron beam welding), brazing, welding-brazing, diffusion welding, friction stir welding and explosion welding were introduced, and the existing problems and development trend were discussed. The results showed that brittle Ti-Al intermetallic compounds were easily formed in titanium/aluminum welded joints, which resulted in a decrease in the strength of titanium/aluminum joint. In the process of laser welding and electron beam welding, the content of Ti-Al intermetallic compounds could be reduced by means of heat source migration. By adopting welding-brazing process and reasonable interlayer, not only the content of Ti-Al intermetallics was reduced, but also intermetallics with better plasticity were formed. The formation of brittle Ti-Al intermetallic compounds could be effectively reduced by diffusion welding process, adding intermediate layer, aluminizing on titanium surface and reasonable control of technological parameters, but tensile strength of the joint was not high. The titanium/aluminum joints with good performance were obtained by adding interlayer in friction stir welding to suppress the formation of brittle Ti-Al intermetallic compounds in titanium/aluminum joints, but which was affected by the shape of weldment. Metal particles in the interface were refined to improve strength of titanium/aluminum joint by explosive welding technology.
Keywords:titaniumalloy,aluminumalloy,joint,Ti-Alintermetalliccompounds
Effectofaddedtemperatureandcontentofthixotropicagentonprintingpropertiesofsolderpaste
Wu Xin, Lu Mengdi, Qin Junhu, He Huan, Wang Yannan, Xiong Xiaojiao
(Tin Products Manufacturing Co., Ltd. of YTCL, Kunming 650217, China).p46-49
AbstractThixotropic agent in solder paste can adjust the viscosity, thixotropic index and anti-collapse performance of solder paste to improve the printing performance of solder paste. Effects of added temperature of thixotropic and contents of thixotropic at the same temperature on the printing properties of solder paste were studied. The results showed that in preparing soldering flux and under the condition of thixotropic agent completely melting synthesis, thixotropic agent was added near the melting point and the content was 6%~8%, the corresponding solder paste printing performance was the best.
Keywords:solderpaste,thixotropicagent,printingproperties
Discussiononkeyfactorsofpressurevesselweldingintelligence
Shou Mingyao1, Yu Huanwei2, Zhu Yuan1, Yu Xiang2
(1. Shaoxing Administration for Market Regulation, Shaoxing 312000,Zhejiang, China; 2. Shaoxing Special Equipment Testing Institute, Shaoxing 312000, Zhejiang, China).p50-55
AbstractTaking pressure vessel manufacturing enterprises in Shaoxing as an example, the welding status of enterprises was investigated and studied. The results showed that traditional manufacturing mode was still the main mode in the current pressure vessel welding manufacturing industry, where manual visual monitoring of welding process was needed basically and the degree of welding intelligence was seriously insufficient. Welding factors of pressure vessels were analyzed by principal component analysis (PCA) and two independent principal component indexes were obtained which mainly corresponded to welder factor and welding hardware equipment factor. Key factors of pressure vessel welding intelligence upgrading were illustrated by combining with the actual investigation of enterprises and then approaches to realize pressure vessel welding intelligence were discussed, which could provide a decision basis for the related industrial upgrading.
Keywords:weldingintelligence,principalcomponentanalysis,pressurevessel,intelligentmanufacturing
FailuremechanismofCAFreliabilityaffectedbysolderingprocess
Cao Xiujuan, Zheng Jiahua, Zhang Long, Mei Cong, Liu Lu
(Dongguan Kaifa Technology Company, Dongguan 523951, Guangdong, China).p56-60
AbstractStarting from printed circuit board (PCB) welding process and based on the growth mechanism of conductive anodic filament (CAF), ANASYS simulation was used to analyze the influence mechanism of thermal stress on the stress and strain of PCB dielectric layer in different welding conditions, which better explained the reason why the probability of cracks was greater in the core plate area of longitudinal structure in the actual failure products. At the same time, through the experimental analysis, the influence of soldering heat on the dielectric layer between plated through hole and anti-CAF performance. The results showed that thermal stress could lead to the increase of white fiber diameter and crack length, which provided a channel for CAF to reduce anti-CAF performance of PCB. For plates with different curing systems, the defect characteristics of materials after being soldered were also different. Finally, based on CAF experimental data and Bell Labs model to analyze the CAF life, the method to determine the safe hole wall spacing in the product design process was obtained, which provided design for manufacture and design for reliability reference for product design.
Keywords:platedthroughhole,solderingheat,conductiveanodicfilament,reliability

