数字化导航模板在脊柱畸形矫正术中的应用效果
叶书熙 陈荣春 游辉 郭朝阳
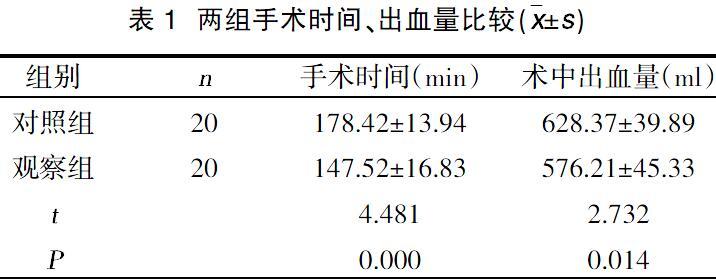

摘要:目的 研究數字化导航模板在脊柱畸形矫正术中的临床应用。方法 选择2016年5月~2018年5月在我院拟行手术治疗的脊柱畸形患者40例,随机分为观察组与对照组,各20例。对照组用椎弓根钉内固定法进行矫形,观察组先进行个性化数字导航模板设计,完成术前规划及虚拟手术,再采用椎弓根钉内固定法矫形。比较两组手术时间、术中出血量、Cobb角矫正率及术后并发症发生率。结果 观察组Cobb角矫正率为84.20%,高于对照组的70.07%,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);观察组手术时间、术中出血量少于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);观察组术后并发症发生率低于对照组(0 vs 50.00%),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 数字化导航模板应用于脊柱畸形矫正术中效果确切,可有效提高Cobb角的矫正率,减少手术时间以及术中出血量,降低并发症的发生。
关键词:数字化导航模板;脊柱畸形;并发症
中图分类号:R687.3 文献标识码:A DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2019.20.027
文章编号:1006-1959(2019)20-0098-03
Application Effect of Digital Navigation Template in Correction of Spinal Deformity
YE Shu-xi,CHEN Rong-chun,YOU Hui,GUO Chao-yang
Abstract:Objective To study the clinical application of digital navigation templates in the correction of spinal deformity. Methods 40 patients with spinal deformity who underwent surgery in our hospital from May 2016 to May 2018 were randomly divided into observation group and control group, 20 cases each. The control group was orthopedic with pedicle screw fixation. The observation group first designed the personalized digital navigation template, completed preoperative planning and virtual surgery, and then used pedicle screw fixation to correct the shape. The operation time, intraoperative blood loss, Cobb angle correction rate and postoperative complication rate were compared between the two groups. Results The Cobb angle correction rate was 84.20% in the observation group, which was higher than that in the control group 70.07%,the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). The operation time and intraoperative blood loss were lower in the observation group than in the control group,the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05).The incidence of postoperative complications in the observation group was lower than that in the control group (0 vs 50.00%),the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion The digital navigation template is effective in the correction of spinal deformity, which can effectively improve the correction rate of Cobb angle, reduce the operation time and intraoperative blood loss, and reduce the occurrence of complications.
Key words:Digital navigation template;Spinal deformity;Complications

