多疗程DC-CIK免疫疗法治疗晚期肺癌的临床疗效
周立莉 周冬霞 徐寿华 吴金芸 蔡茂怀
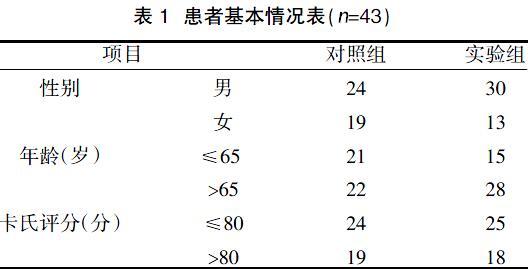
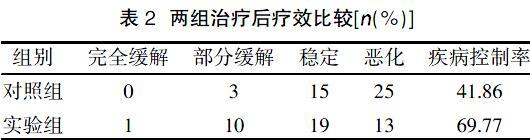
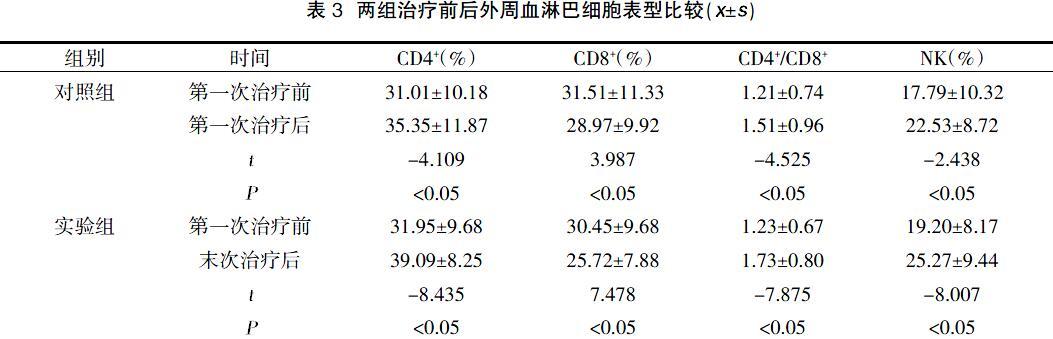
摘要:目的 觀察多疗程DC-CIK治疗晚期肺癌的临床疗效。方法 选取2014年12月~2018年12月我院收治的化疗后肺癌患者86例,采用随机数字表法分为对照组和实验组,各43例。对照组行1个疗程DC-CIK治疗,实验组行3个疗程以上的DC-CIK治疗。比较两组治疗后疗效、淋巴细胞水平、细胞因子水平、肿瘤标志物表达以及不良反应发生情况。结果 实验组疾病控制率(69.77%)高于对照组(41.86%)。治疗后两组CD4+、CD4+/CD8+、NK表达均较治疗前升高,且实验组高于对照组(P<0.05);治疗后两组CD8+表达均较治疗前下降,且实验组低于对照组(P<0.05);两组治疗前后IL-4、IL-6、IL-10无明显变化(P>0.05);治疗后两组IL-2、TNF-α、IFN-γ均较治疗前升高,且随着治疗次数增加,IL-2、TNF-α、IFN-γ逐渐升高(P<0.05);治疗后两组AFP、NSE、CYfra21-1均较治疗前下降(P<0.05);两组第一次治疗后CEA升高(P<0.05);实验组末次治疗后,CEA下降(P<0.05);两组均未出现不良反应。结论 多疗程DC-CIK免疫疗法治疗晚期肺癌临床疗效确切,能有效清除肿瘤细胞,且安全无副作用。
关键词:DC-CIK;肺癌;免疫疗法;多疗程
中图分类号:R734.2 文献标识码:A DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2019.20.002
文章编号:1006-1959(2019)20-0005-04
Clinical Efficacy of Multiple Courses of DC-CIK Immunotherapy in the Treatment
of Advanced Lung Cancer
ZHOU Li-li1,ZHOU Dong-xia1,XU Shou-hua1,WU Jin-yun2,CAI Mao-huai1
Abstract:Objective To observe the clinical efficacy of multi-course DC-CIK in the treatment of advanced lung cancer. Methods 86 patients with lung cancer after chemotherapy from December 2014 to December 2018 were enrolled. The patients were divided into the control group and the experimental group by random number table, 43 cases each. The control group received one course of DC-CIK treatment, and the experimental group received three courses of DC-CIK treatment. The therapeutic effects, lymphocyte levels, cytokine levels, tumor marker expression, and adverse reactions were compared between the two groups.Results The disease control rate (69.77%) in the experimental group was higher than that in the control group (41.86%). The expressions of CD4+,CD4+/CD8+ and NK in the two groups were higher than those before treatment, and the experimental group was higher than the control group (P<0.05).The expression of CD8+ in the two groups decreased after treatment, and the experimental group was lower than the control group (P<0.05). There was no significant change in IL-4, IL-6 and IL-10 before and after treatment (P>0.05). The latter two groups of IL-2, TNF-α, IFN-γ were higher than before treatment, and with the increase of treatment times, IL-2, TNF-α, IFN-γ increased gradually(P<0.05).After treatment, AFP, NSE and CYfra21-1 were lower than those before treatment(P<0.05); CEA increased after the first treatment in both groups (P<0.05); CEA decreased after the last treatment in the experimental group(P<0.05); no adverse reactions occurred in either group.Conclusion Multi-course DC-CIK immunotherapy is effective in the treatment of advanced lung cancer. It can effectively remove tumor cells and has no side effects.
本研究86例患者中,有5例治疗前白细胞低于正常值,给予200 mg GM-CSF刺激,72 h后检测血常规,待白细胞正常,采血行DC-CIK治疗。本研究结果显示,实验组疾病控制率(69.77%)高于对照组(41.86%)。第一次治疗后两组CEA较治疗前升高,在末次治疗后实验组CEA与第一次治疗前相比出现下降。治疗后两组AFP、NSE、CYfra21-1均较治疗前下降,表明DC-CIK治疗可以降低肺癌患者的肿瘤标志物,对肿瘤的持续杀伤具有很好的作用。研究发现,实验组CEA出现升高又降低的情况,可能是由于DC-CIK在杀伤肿瘤时,肿瘤凋亡释放出大量肿瘤相关蛋白,使肿瘤标志物升高,随后随着杀伤的不断进行,这些物质作为代谢物被清除体内,肿瘤标志物随之下降。
免疫功能方面,本研究结果显示,治疗后两组CD4+、CD4+/CD8+、NK表达均较治疗前升高,且实验组高于对照组,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05);治疗后两组CD8+表达均较治疗前下降,且实验组低于对照组,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。细胞因子IL-4、IL-6、IL-10治疗前后无明显变化,IL-2、TNF-α、IFN-γ也随疗程持续升高,表明DC-CIK通过增加CD4+、CD4+/CD8+、NK的表达调节机体免疫功能。IL-2主要由活化T细胞产生,对机体的免疫应答和抗病毒感染等有重要作用。TNF-α具有特异性杀伤肿瘤细胞表面不损伤正常细胞的功能。IFN-γ由活化T细胞、自然杀伤细胞及NKT细胞产生,具有抗病毒、免疫调节剂、抗肿瘤的特性。当NKT细胞的表达持续升高时, IL-2、TNF-α、IFN-γ也随之升高。有研究表明 IL-2、TNF-α和IFN-γ 能增强 NK细胞及 T 细胞的活性,既能抑制肿瘤细胞增殖又能直接杀伤肿瘤细胞,并且能减少肿瘤的复发和转移[13,16-18,]。多疗程的治疗就相当于形成了一个正反馈调节,不断的提升免疫力,杀伤肿瘤细胞,调节肿瘤患者的免疫功能,并且多疗程DC-CIK改善程度更大。两组在治疗过程中均未发现有不良反应,说明DC-CIK治疗安全性较高。
综上所述,多疗程的DC-CIK治疗可提升肺癌患者的免疫功能、杀伤肿瘤细胞,对后续进行放化疗、肿瘤靶向治疗等具有很好的辅助作用。
参考文献:
[1]Bray F,Ferlay J,Soerjomataram I,et al.Global cancer statistics 2018:GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2018,68(6):394-424.
[2]Heather Wakelee.50 Years of Progress in the Systemic Therapy of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer[J].Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book,2014:177-89.
[3]Hirsch FR,Scagliotti GV,Mulshine JL,et al.Lung cancer:current therapies and new targeted treatments[J].Lancet,2017,389(10066):299-311.
[4]吳军,杨小平.分子靶向药物治疗非小细胞肺癌的研究进展[J].医学理论与实践,2019, 32(10):1489-1490.
[5]Ren PT,Zhang Y.Comparative investigation of the effects of specific antigen?sensitized DC-CIK and DC-CTL cells against B16 melanoma tumor cells[J].Mol Med Rep,2017,15(4):1533-1538.
[6]人体细胞治疗研究和制剂质量控制技术指导原则(国家食药监督局文件), http://samr.cfda.gov.cn/WS01/CL0237/15709.html
[7]Gao D,Li C,Xie X,et al.Autologous tumor lysate-pulsed dendritic cell immunotherapy with cytokine-induced killer cells improves survival in gastric and colorectal cancer patients[J].PLoS One,2014,9(4):e93886.
[8]韦庄怡,任小朋,王博.DC-CIK自体回输对化疗后胃癌患者T淋巴细胞亚群及NK细胞的影响[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2019,18(11):1179-1182.
[9]单海霞,黄广清.DC-CIK联合化疗治疗进展期胃癌45例的临床疗效评价[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,2014,23(12):1416-1419.
[10]王金烁,谢泽新,李慧杰.DC-CIK联合化疗治疗晚期胃癌的近期疗效[J].实用肿瘤杂志,2016,31(1):38-42.
[11]吴有军,曹志宇,张庆军.DC-CIK对结直肠癌根治术后肝转移患者疗效和循环肿瘤细胞的影响[J].中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志,2018,25(1):89-93.
[12]Mai HX,Mei GH,Zhao FL,et al.Retrospective analysis on the efficacy of sunitinib/sorafenib in combination with dendritic cells-cytokine-induced killer in metastasis renal cell carcinoma after radical nephrectomy[J].Cancer Res Ther,2018,14(Supplement):S427-S432.
[13]Qin W,Xiong Y,Chen J,et al.DC-CIK cells derived from ovarian cancer patient menstrual blood activate the TNFR1-ASK1-AIP1 pathway to kill autologous ovarian cancer stem cells[J].Cell Mol Med,2018,22(7):3364-3376.
[14]Hu J,Hu J,Liu X,et al.Effect and safety of cytokine-induced killer (CIK) cell immunotherapy in patients with breast cancer[J]. Medicine,2017,96(42):e8310.
[15]Xiao X,Ye X,Xu C,et al.Successful alternative treatment for relapsed adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia with dendritic cells-cytokine-induced killer cells combined with a rituximab-based regimen[J].Onco Targets Ther,2018,29(11):7555-7558.
[16]Dhupkar P,Gordon N.Interleukin-2:Old and New Approaches to Enhance Immune-Therapeutic Efficacy[J].Adv Exp Med Biol,2017(995):33-51.
[17]Gong W,Hoffmann JM,Stock S,et al.Comparison of IL-2 vs IL-7/IL-15 for the generation of NY-ESO-1-specific T cells[J].Cancer Immunol Immunother,2019,68(7):1195-1209.
[18]Wang L,Wang Y,Song Z,et al.Interferon Cytokine Res[J]. Deficiency of interferon-gamma or its receptor promotes colorectal cancer development,2015,35(4):273-280.
收稿日期:2019-7-2;修回日期:2019-7-13
編辑/肖婷婷

