利用TCGA数据集分析LncRNA LINC00319在肺腺癌中的表达及临床意义
陈少婷 曹鹏驹 杨阳
[摘要] 目的 研究長链非编码RNA(lncRNA)LINC00319在肺腺癌及其癌旁组织中的表达及临床意义。 方法 从癌症基因组图谱(TCGA)数据库下载516例肺腺癌组织(肿瘤组)与59例癌旁组织(癌旁对照组)RNAseq数据及对应的肺腺癌患者临床数据,对数据中LINC00319基因表达进行分析处理。分析比较其表达与肺腺癌临床病理特征的相关性及对预后的影响。通过COX风险比例模型评估肺腺癌患者预后的独立危险因素。采用基因集富集分析(GSEA)方法预测LINC00319功能富集的分子通路。 结果 LINC00319在肿瘤组中的表达水平显著高于癌旁对照组(P < 0.05),其表达水平与性别、年龄、N分期无关(P > 0.05),与吸烟、T分期、M分期以及Stage分期显著相关(P < 0.05),生存分析显示肺腺癌患者中高LINC00319表达水平预示预后差(P < 0.05)。多因素COX风险比例模型结果显示,高表达水平、Ⅲ+Ⅳ及T3+T4是肺腺癌患者预后差的独立危险因素(P < 0.05)。在GSEA分析中,发现LINC00319功能主要富集在细胞黏附、细胞因子相互作用、血管内皮生长因子信号通路、细胞凋亡等通路中。 结论 LINC00319可能通过多种途径促进肺腺癌的发生、发展,进而影响肺腺癌患者的预后生存,因此,LINC00319可作为肺腺癌患者的预后标志物或潜在治疗靶点。
[关键词] 肺腺癌;癌症基因组图谱;长链非编码RNA;LINC00319
[中图分类号] R734.2 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-7210(2019)08(b)-0122-05
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the expression and clinical significance of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) LINC00319 in lung adenocarcinoma and its adjacent tissues. Methods The RNAseq data of 516 cases of lung adenocarcinoma tissues (tumor group) and 59 cases of paracancer tissues (para-cancer control group) and the corresponding clinical data of lung adenocarcinoma patients were downloaded from the cancer genome atlas (TCGA) database, and the expression of LINC00319 gene in the data set was analyzed and processed. The correlation between its expression and the clinicopathological features of lung adenocarcinoma and its effect on prognosis were analyzed and compared. Independent risk factors for prognosis of patients with lung adenocarcinoma were assessed by COX risk ratio model. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) was used to predict the functional enrichment of LINC00319 molecular pathways. Results The expression level of LINC00319 in tumor group was significantly higher than that in the para-carcinoma control group (P < 0.05). The expression level had no correlation with gender, age and N-staging (P > 0.05), and significantly correlated with smoking, T-staging, M-staging and Stage grading (P < 0.05). Survival analysis showed that high LINC00319 expression predicted worse prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma patients (P < 0.05). The results of multiariable COX risk scale model showed that, high expression level, stage Ⅲ+Ⅳ and T3+T4 were independent risk factors for poor prognosis of patients with lung adenocarcinoma (P < 0.05). In GSEA analysis, it was found that LINC00319 mainly enriched in cell adhesion, cytokine interaction, vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway, apoptosis and other pathways. Conclusion LINC00319 may promote the occurrence and development of lung adenocarcinoma through various ways, thereby affecting the prognosis and survival of lung adenocarcinoma patients. Therefore, LINC00319 can be used as a prognostic marker or potential therapeutic target for lung adenocarcinoma patients.
[Key words] Lung adenoarinoma; Cancer genome atlas; Long noncoding RNA; LINC00319
肺癌是目前全球最常见的恶性肿瘤之一。男性肺癌新发病例及死亡率居所有恶性肿瘤第1位。女性肺癌新发病例居第3位,死亡率居第2位[1]。肺腺癌是具有腺样分化或黏液分泌的恶性上皮肿瘤,目前已成为最常见的肺癌病理类型[2-3]。
长链非编码RNA(lncRNA)是一类大于200个核苷酸的非编码RNA链的总称[4]。LncRNA通过调节靶基因转录因子、调控翻译和剪切等机制,在细胞的生长发育,迁移、侵袭,凋亡中发挥作用[5-6]。在肿瘤中,lncRNA以内源性RNA身份竞争miRNA的结合位点,起着癌基因或抑癌基因的作用[7]。越来越多的研究[8-9]发现lncRNA在多种肿瘤中发挥作用。He等[10]发现lncRNA AFAP1-AS1可以上调AFAP1促进肺腺癌细胞的迁移。Zhao等[11]发现lncRNA NSCLCAT1增加细胞的侵袭和迁移。
本研究通过癌症基因组图谱公共数据集(the cancer genome stlas,TCGA),研究LINC00319在肺腺癌中的表达及其相关病理特征的关系,为研究其在肿瘤发生发展中的作用机制提供参考。
1 材料与方法
1.1 组织样本数据下载及预处理
利用TCGA(https://cancergenome.nih.gov/)搜索并下载肺腺癌表达谱数据,排除缺失临床参数和生存资料的病例后,获得516例肺腺癌组织(肿瘤组)与59例癌旁组织(癌旁对照组)的RNAseq数据及对应的肺腺癌患者临床数据。预处理肺腺癌数据集lncRNA表达的RNAseqV2数据。
1.2 LINC00319表达与临床病理特征和预后的关系
对数据集中LINC00319的表达进行由高到低排序,采用四分位法,选取75%为截断值,将样本分为高表达组(LINC00319≥6.1286)和低表达组(LINC00319<6.1286)。根据病床病理特征对数据进行分析比较。随后利用Kaplan-Meier Plotter数据中的肺癌数据集进行在线分析(http://kmplot.com/analysis/)。
1.3 基因集富集分析(gene set enrichment analysis,GSEA)
通过对LINC00319的表达值进行K(K = 2)均值聚类,根据聚类结果将样本分为低表达组和高表达组。利用GSEA的R语言版本进行富集分析,分析的通路来自于MsigDB数据库中的c2.cp.kegg.v6.2.symbols.gmt数据集。采取的是GSEA中的加权富集分析方法,通过对样本标扰动的方式进行随机计算,随机次数设置为1000次,计算P值。
1.4 统计学方法
采用SPSS 22.0软件进行统计学分析,使用GraphPad Prism v6进行图片绘制。LINC00319在肺腺癌及相应癌旁组织中的表达水平比较采用非参数秩和检验,卡方检验用于评估其表达水平与临床参数之间的关系。Kaplan-Meier曲线及Log Rank检验对不同LINC00319表达水平肺腺癌患者进行分析。COX风险比例模型用于评估肺癌患者的独立危险预后因数。以P < 0.05为有统计学意义。
2 结果
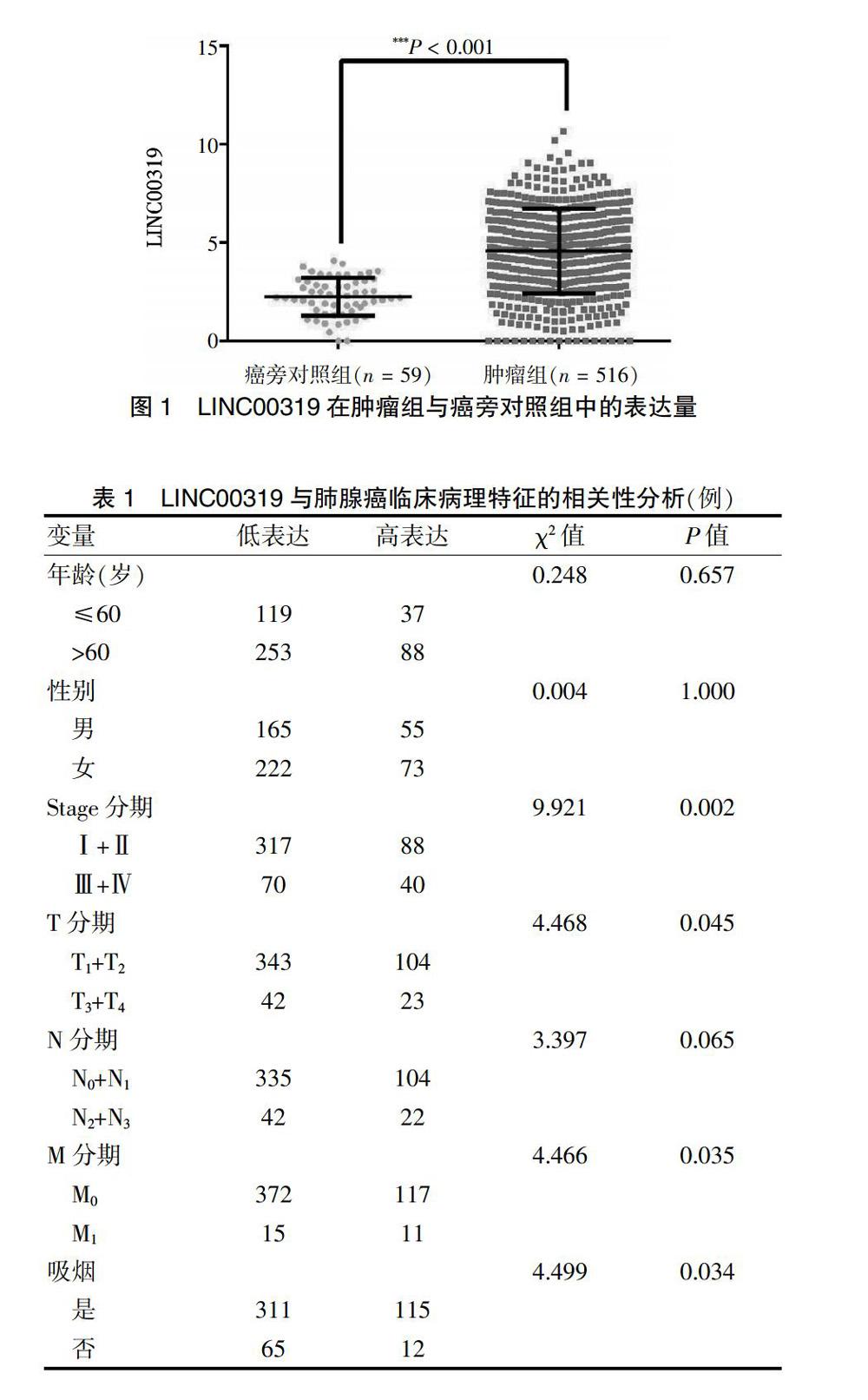
2.1 LINC00319在肿瘤组与癌旁对照组中的表达量及其与肺腺癌临床病理特征的相关性
与癌旁对照组比较,LINC00319表達水平在肿瘤组中明显升高(P < 0.001)。见图1。相关性分析结果显示,其表达水平与性别(P = 0.065)、年龄(P = 1.000)、N分期(P = 0.065)无关,与吸烟(P = 0.045),T分期(P = 0.045)、M分期(P = 0.040)以及Stage分期(P = 0.002)有关。见表1。
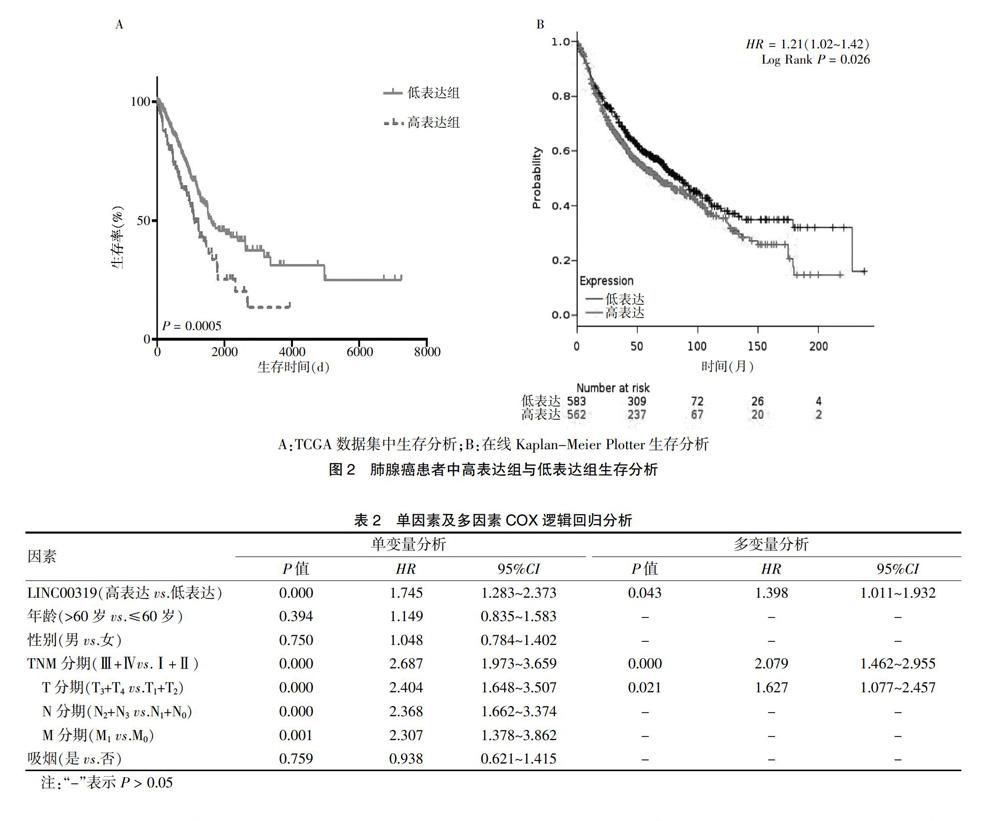
2.2 LINC00319表达与肺腺癌患者预后关系
本研究利用TCGA进行生存预后分析,结果显示:LINC00319表达水平与肺腺癌患者预后有显著相关性(P = 0.005),表达越高,预后越差(图2A)。同时,利用在线Kaplan-Meier曲线进行分析,其结果(P = 0.026)与TCGA分析一致(图2B)。多因素COX风险比例模型结果显示,高LINC00319表达水平(P = 0.043),Ⅲ+Ⅳ(P = 0.000)及T3+T4(P = 0.021)是肺腺癌患者预后差的独立危险因素。见表2。
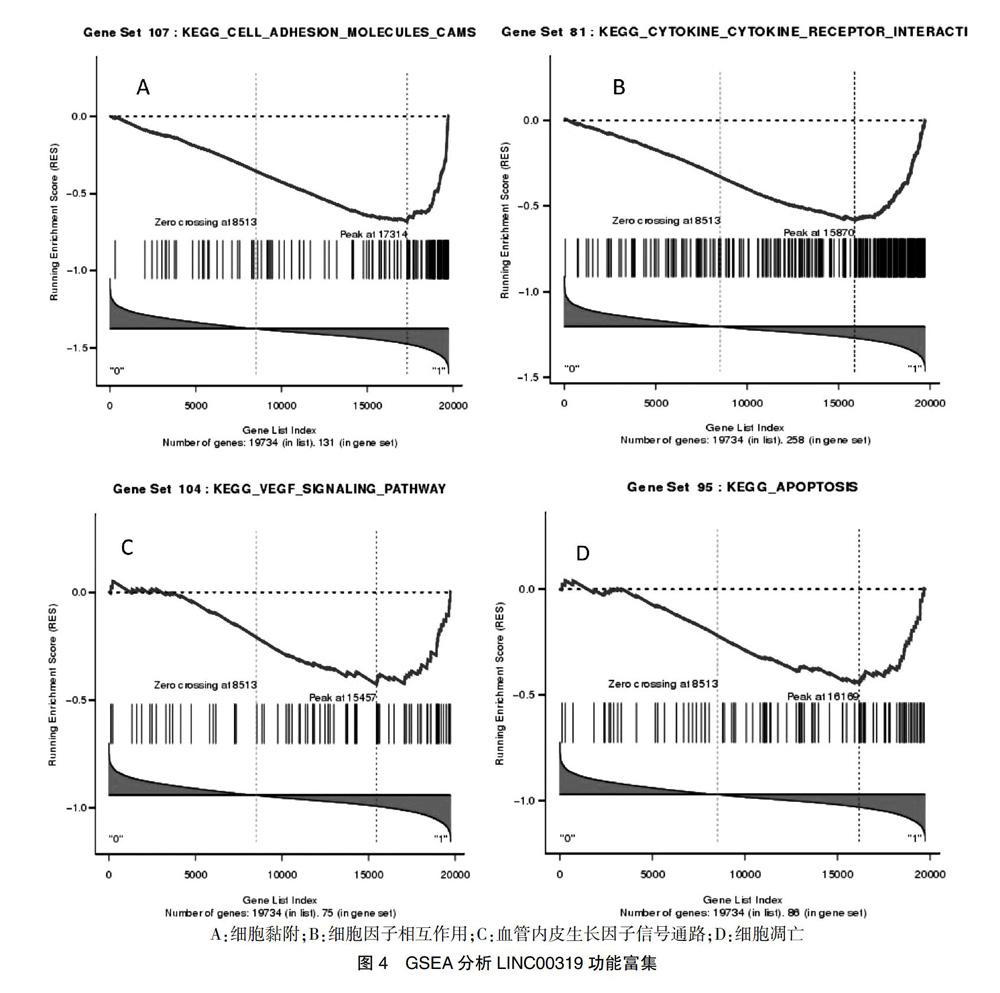
2.3 LINC00319功能基因集富集
GSEA分析结果显示:LINC00319功能富集在细胞黏附(FDR = 0,见图4A)、细胞因子相互作用(FDR = 0,见图4B)、VEGF信号通路(FDR = 0.04,见图4C)、细胞凋亡(FDR = 0.04,见图4D)等通路中。
3 讨论
肺癌是目前全球最常见的恶性肿瘤之一,肺腺癌作为肺癌最常见的病理类型,其发病机制需引起我们的关注。LncRNA表达与肺癌的发生发展存在密切关系。Wang等[12]发现LINC00968能够抑制体外非小细胞肺癌的生长、迁移和侵袭。Hu等[13]认为lncRNA可用于预测铂类治疗在肺癌患者中的反应和毒性。李雪萍等[14]研究发现过表达LOC90024可促进A549的生长、迁移和侵袭,提示其可能在肺癌中起癌基因的作用。Lu等[15]认为高表达LncRNA MEG3抑制非小细胞肺癌细胞增殖,引起细胞周期阻滞,抑制肿瘤生长。
LINC00319位于基因组21q22.3上,含有5个外显子。Zhou等[16]发现LINC00319通过直接结合并下调miR-32来促进肺癌细胞的细胞增殖和侵袭。Du等[17]研究表明LINC00319通过抑制miR-423-5p上调NACC1表达来促进卵巢癌的进展。Song等[18]发现LINC00319在鼻咽癌中显著增加,其过表达提示鼻咽癌患者预后不良。Li等[19]发现LINC00319通过miR-1207-5p介导的细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶3的调节在皮肤鳞状细胞癌中发挥致癌作用。Zhang等[20]发现LINC00319通过调节miR-450b-5p/EZH2信号途径促进肺腺癌进展。目前,LINC00319在肺腺癌中的表达、对预后的影响等在我国未见相关报道。
本研究通過生物信息学分析,发现LINC00319在肺腺癌中的表达明显高于对照组,其表达与性别、年龄、N分期无关,与吸烟、T分期、M分期以及stage分期均存在关系,预后分析结果表明,其表达与肺腺癌患者预后存在显著相关性,表达越高,预后越差。多因素COX逻辑回归分析显示,高LINC00319表达水平,Ⅲ/Ⅳ及T3/T4是肺腺癌患者预后差的独立危险因素。在GSEA分析中,发现LINC00319功能富集在细胞黏附、细胞因子相互作用、VEGF信号通路、细胞凋亡等通路中,而这些通路均与肿瘤的转移、侵袭密切相关。
综上所述,LINC00319可能通过多种途径促进肺腺癌的发生、发展,进而影响肺腺癌患者的预后生存,因此,LINC00319可作为诊断肺腺癌的标志物或者潜在治疗靶点。在未来工作中,我们将进一步收集临床标本进行分析,为肺腺癌发生发展分子机制的研究探讨奠定基础。
[参考文献]
[1] Torre LA,Bray F,Siegel RL,et al. Global cancer statistics,2012 [J]. CA Cancer J Clin,2015,65(2):87-108.
[2] Siegel RL,Miller KD,Jemal A. Cancer statistics,2016 [J]. CA Cancer J Clin,2016,66(1):7-30.
[3] Chen WQ,Zheng RS,Baade PD,et al. Cancer statistics in China 2015 [J]. CA Cancer J Clin,2016,66(2):115-132.
[4] Ponting CP,Oliver PL,Reik W. Evolution and Functions of Long Noncoding RNAs [J]. Cell,2009,136(4):629-641.
[5] Mercer TR,Dinger ME,Mattick JS. Long non-coding RNAs:insights into functions [J]. Nat Rev Genet,2009,10(3):155-159.
[6] Fatica A,Bozzoni I. Long non-coding RNAs:new players in cell differentiation and development [J]. Nat Rev Genet,2013,15(1):7-21.
[7] Jiang T,Guo J,Hu Z,et al. Identification of Potential Prostate Cancer-Related Pseudogenes Based on Competitive Endogenous RNA Network Hypothesis [J]. Med Sci Monit,2018,20(24):4213-4239.
[8] Seiler J. The lncRNA VELUCT strongly regulates viability of lung cancer cells despite its extremely low abundance [J]. Nucleic Acids Res,2017,45(9):5458-5469.
[9] Wang C,Gu Y,Zhang E,et al. A cancer-testis non-coding RNA LIN28B-AS1 activates driver gene LIN28B by interacting with IGF2BP1 in lung adenocarcinoma [J]. Oncogene,2019,38(10):1611-1624.
[10] He J,Wu K,Guo CL. Long non-coding RNA AFAP1-AS1 plays an oncogenic role in promoting cell migration NSCLC [J]. Cell Mol Life Sci,2018,75(24):4667-4681.
[11] Zhao W,Zhang LN,Wang XL,et al. Long noncoding RNA NSCLCAT1 increases non-small cell lung cancer cell invasion and migration through the Hippo signaling pathway by interacting with CDH1 [J]. FASEB J,2019, 33(1):1151-1166.
[12] Wang Y,Zhou J,Xu YJ,et al. Long non-coding RNA LINC00968 acts as oncogene in NSCLC by activating the Wnt signaling pathway [J]. Cell Physiol,2018,233(4):3397-3406.
[13] Hu L,Chen SH,Lv QL. Clinical Significance of Long Non-Coding RNA CASC8 rs10505477 Polymorphism in Lung Cancer Susceptibility,Platinum-Based Chemotherapy Response,and Toxicity [J]. Environ Res Public Health,2016,13(6):545-557.
[14] 李雪萍,梁鑫,刘政,等.LncRNA LOC90024对肺癌细胞生长、迁移和侵袭的影响[J].西安交通大学学报:医学版,2019,40(1):43-48.
[15] Lu KH,LI W,Liu XH,et al. Long non-coding RNA MEG3 inhibits NSCLC cells prolifcration and induces apoptosis by af fecting p53 expression [J]. BMC Cancer,2013,13(1):461-472.
[16] Zhou B,Yuan W,Li XL,et al. Intergenic Noncoding RNA 319 (linc00319) Promotes Cell Proliferation and Invasion in Lung Cancer Cells by Directly Downregulating the Tumor Suppressor MiR-32 [J]. Oncol Res,2017.
[17] Du W,Feng Z,Sun Q. LncRNA LINC00319 accelerates ovarian cancer progression through miR-423-5p/NACC1 pathway [J]. Bioch em Biophys Res Commun,2018,507(14):198-202.
[18] Song P,Yin SC. Long non-coding RNA 319 facilitates nasopharyngeal carcinoma carcinogenesis through regulation of miR-1207-5p/KLF12 axis [J]. Gene,2019,5(680):51-58.
[19] Li F,Liao J,Duan X. Upregulation of LINC00319 indicates a poor prognosis and promotes cell proliferation and invasion in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Cell Biochem,2018,119(12):10 393-10 405.
[20] Zhang ZW,Chen JJ,Xia SH,et al. Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 319 aggravates lung adenocarcinoma carcinogenesis by modulating miR-450b-5p/EZH2 [J]. Gene,2018,15(650):60-67.
(收稿日期:2019-03-27 本文編辑:封 华)

