阿托伐他汀对合并睡眠呼吸暂停综合征冠心病患者PCI术后血清炎症细胞因子水平的影响
赵芳
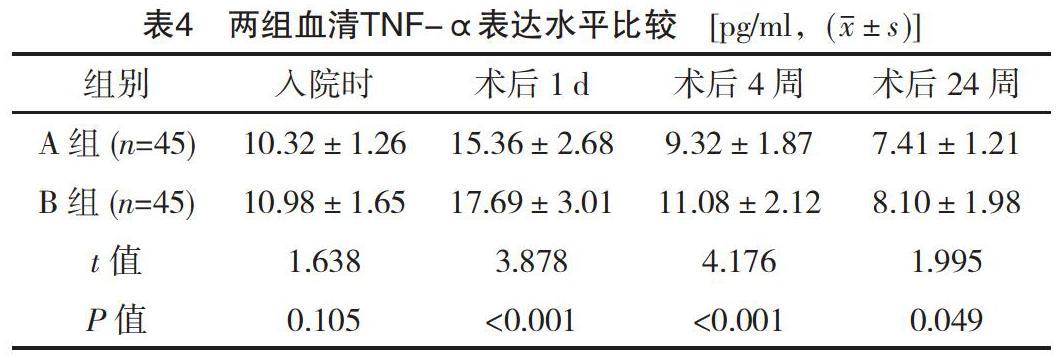


【摘要】 目的:探讨不同阿托伐他汀治疗方案对合并睡眠呼吸暂停综合征(SAS)冠心病患者经皮冠状动脉介入治疗(PCI)术后血清炎症细胞因子水平的影响。方法:选取2016年1月-2017年12月笔者所在医院收治的90例冠心病合并SAS患者作为研究对象,将其随机分为A组和B组,每组45例。A组患者在PCI术前1周接受阿托伐他汀80 mg/d治疗,术后将剂量调整至40 mg/d,4周后调至20 mg/d,持续治疗20周。B组患者PCI术前不给予阿托伐他汀治疗,术后给予阿托伐他汀40 mg/d治疗,4周后将剂量调整至20 mg/d,持续治疗20周。比较两组PCI术后LVEDD、LVEF和IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α表达水平。结果:PCI术后3 d,两组LVEF和LVEDD比较,差异无統计学意义(P>0.05);A组术后24周LVEF明显高于B组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),而两组LVEDD比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。A组患者在PCI术后1 d、4、24周时,血清IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α表达水平均低于B组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论:冠心病合并SAS患者在PCI治疗前加载负荷剂量的阿托伐他汀,有助于改善心脏功能和机体免疫炎症水平。
【关键词】 阿托伐他汀; 睡眠呼吸暂停综合征; 冠心病; 经皮冠状动脉介入治疗
doi:10.14033/j.cnki.cfmr.2019.21.016 文献标识码 B 文章编号 1674-6805(2019)21-00-03
Effect of Atorvastatin on Serum Inflammatory Cytokines Levels in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease Complicated with Sleep Apnea Syndrome after PCI/ZHAO Fang.//Chinese and Foreign Medical Research,2019,17(21):-42
【Abstract】 Objective:To investigate the effects of different Atorvastatin regimens on serum inflammatory cytokines in patients with coronary heart disease complicated with sleep apnea syndrome(SAS) after percutaneous coronary intervention(PCI).Method:From January 2016 to December 2017,90 patients with coronary heart disease combined with SAS admitted in our hospital were selected as research objects.They were randomly divided into group A and group B,with 45 cases in each group.Patients in group A received Atorvastatin 80 mg/d one week before PCI,and the dose was adjusted to 40 mg/d after PCI,then to 20 mg/d
after 4 weeks of continuous treatment for 20 weeks.Patients in group B were not treated with Atorvastatin before PCI,and were treated with atorvastatin 40 mg/d
after PCI.After 4 weeks,the dose was adjusted to 20 mg/d for 20 weeks.The expressions levels of LVEDD,LVEF,IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α were compared between the two groups after PCI.Result:3 days after PCI,there were no significant differences in LVEF and LVEDD between the two groups(P>0.05).The LVEF in group A was significantly higher than that in group B at 24 weeks after operation,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05),but there was no significant difference in the comparison of LVEDD between the two groups(P>0.05).The levels of serum IL-1β,IL-6 and TNF-α in group A were lower than those in group B at the 1day,4 and 24 weeks after PCI,the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05).Conclusion:Loading dose of Atorvastatin before PCI in patients with coronary heart disease complicated with SAS can improve cardiac function and immune inflammation.
参考文献
[1]秦宇君,王健,柳景华.冠心病经皮冠状动脉介入治疗后非罪犯血管病变进展的机制研究[J].心肺血管病杂志,2017,36(8):701-703.
[2]张榕,赵雪婷,马涵英.阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征与冠心病[J].中国全科医学,2015,18(29):3528-3532.
[3]严爱芬,吴伟萍,陈捷,等.老年冠心病合并阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停综合征患者ghrelin/obestatin比值的变化及意义[J].中华全科医学,2017,15(2):302-303.
[4]卿思敏,陈日垦,刘恒,等.NoSAS评分与四种量表评估阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征的应用价值比较[J].中华结核和呼吸杂志,2018,41(3):213-219.
[5]王霁翔,高静,任珉,等.早期保护性肺通气和主动脉内球囊反搏联合急诊经皮冠状动脉介入治疗急性心肌梗死合并心源性休克的疗效[J].中华老年医学杂志,2017,36(7):724-729.
[6]孟哲,李凌.不同剂量阿托伐他汀对合并SAS的冠心病患者PCI术后的影响[J].实用医学杂志,2018,34(2):269-272.
[7]李志,王伟群,张明亮,等.冠心病患者血清炎性细胞因子的表达及意义[J].中国老年学杂志,2018,38(7):1559-1560.
[8]高荣华,张韶辉.冠心病患者冠状动脉病变与免疫细胞的相关研究[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2017,9(6):727-729.
[9]唐国栋,郑耐心,张慧平,等.瑞舒伐他汀短期强化治疗对急性冠状动脉综合征患者经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术后心功能、心肌损伤及血清炎症因子影响研究[J].临床军医杂志,2017,45(5):534-536.
[10]李奎,余丹.睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征对冠心病患者行经皮冠状动脉介入治疗的疗效影响[J].岭南心血管病杂志,2016,22(1):34-37.
[11]谢进,胡沛,唐冰,等.阿托伐他汀对冠心病患者脂蛋白(a)及CETP水平的影响[J].现代生物医学进展,2017,17(14):94-97.
[12]徐健强,赵国军,王燕,等.阿托伐他汀的抗炎作用及其机制的研究进展[J].中国动脈硬化杂志,2016,24(4):419-423.
(收稿日期:2019-05-21) (本文编辑:桑茹南)

