常规疗法与布地奈德雾化吸入法治疗小儿肺炎的效果对比
刘春花 万致婷
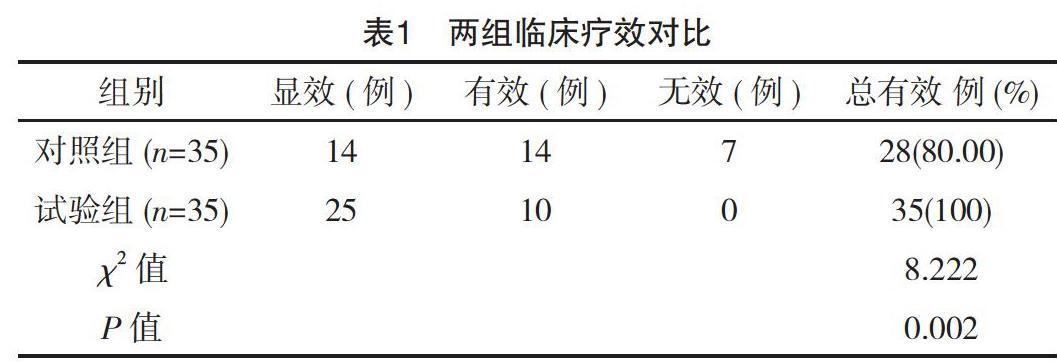

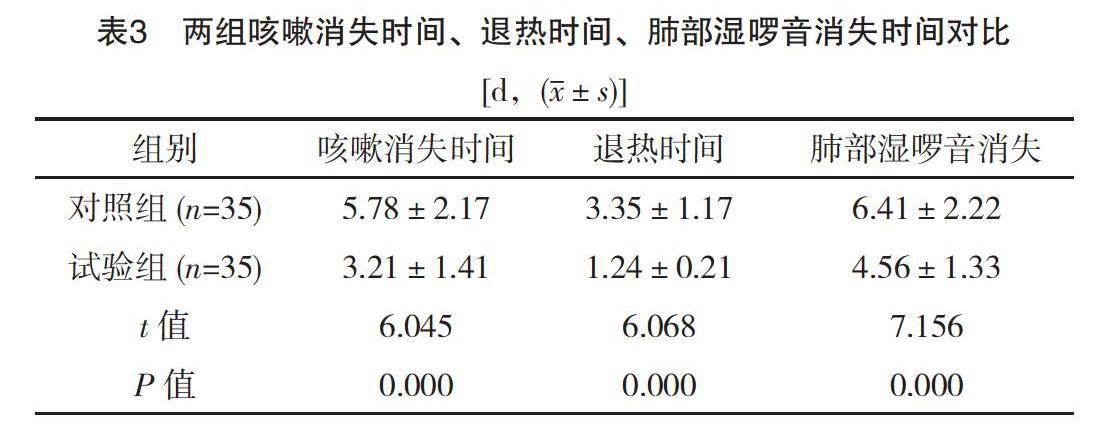
【摘要】 目的:探讨常规疗法与布地奈德雾化吸入法治疗小儿肺炎的效果。方法:将笔者所在医院2016年1月-2018年12月的70例小儿肺炎患儿进行随机分组,对照组给予常规疗法,试验组开展布地奈德雾化吸入法。比较两组疗效、肺炎症状消失时间、治疗前后炎症指标及肺功能水平、不良反应发生率。结果:试验组总有效率高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。治疗前,两组炎症指标及肺功能水平比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。治疗后,试验组炎症指标及肺功能水平均优于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。试验组咳嗽消失时间、退热时间、肺部湿啰音消失时间均短于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。试验组不良反应发生率(2.85%)低于对照组(20.00%),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。
結论:对小儿肺炎患儿实施布地奈德雾化吸入法效果确切,可缩短临床症状消失时间和改善肺功能,控制炎症。
【关键词】 常规疗法; 布地奈德雾化吸入法; 小儿肺炎; 疗效
doi:10.14033/j.cnki.cfmr.2019.21.008 文献标识码 B 文章编号 1674-6805(2019)21-00-03
Comparative Analysis of the Efficacy of Conventional Therapy and Budesonide Inhalation in the Treatment of Pediatric Pneumonia/LIU Chunhua,WAN Zhiting.//Chinese and Foreign Medical Research,2019,17(21):-23
【Abstract】 Objective:To study the efficacy of conventional therapy with Budesonide Inhalation in the treatment of pediatric pneumonia.Method:70 children with pediatric pneumonia from January 2016 to December 2018 were randomly divided into two groups.The control group was given conventional therapy.The experimental group was given Budesonide Inhalation.The curative effect,and the time of disappearance of pneumonia symptoms,the level of inflammation index and lung function before and after treatment,and the incidence of adverse reactions of two groups were compared.Result:The total effective rate of the experimental group was higher than that of the control group,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).Before treatment,the levels of inflammatory index and lung function were compared between the two groups,the differences were not statistically significant(P>0.05).The levels of inflammatory index and lung function in the experimental group were better than those of the control group after treatment,the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05).The time of disappearance of cough,antifebrile time,and the disappearance time of moist rales in the lungs in the experimental group were shorter than those of the control group,the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05).The incidence of adverse reactions in the experimental group(2.85%) was lower than that of the control group(20.00%),and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).Conclusion:The effect of Budesonide Inhalation in children with pediatric pneumonia is accurate,shortening the time of disappearance of clinical symptoms and improving lung function and controlling inflammation.

