布地奈德联合螺内酯对支气管肺发育不良早产儿血液中IL-1β、TNF-α变化的影响
叶旭强 戴怡蘅 刘卫东?曾立军 麦丽珊 张李霞
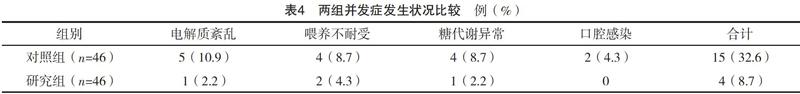
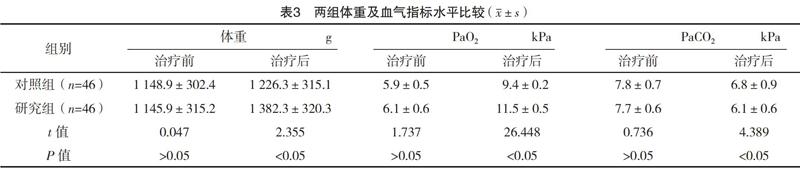
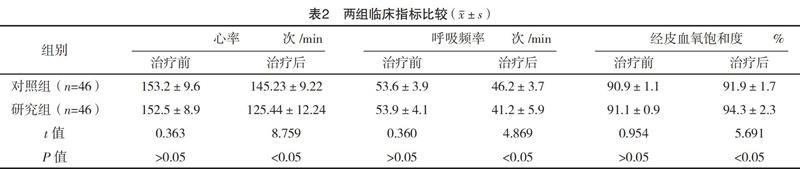
【摘要】 目的:探讨布地奈德联合螺内酯对支气管肺发育不良(BPD)早产儿血液中IL-1β、TNF-α变化的影响。方法:选取2012年11月-2017年11月在本院出生的早产儿92例,患儿均有BPD症状。按照随机数字表法将其分为对照组与研究组,各46例。对照组给予螺内酯治疗,研究组应用布地奈德联合螺内酯治疗。对比两组炎性因子水平(IL-1β、TNF-α、IL-8)、临床指标、体重、血气分析指标、并发症。结果:治疗后,研究组IL-1β、TNF-α、IL-8水平均低于对照组(P<0.05);治疗后,研究组心率、呼吸频率、经皮血氧饱和度、体重、血气分析指标均优于对照组(P<0.05);研究组并发症发生率为8.7%,低于对照组的32.6%,差异有统计学意义(字2=8.026,P<0.05)。结论:应用布地奈德联合螺内酯治疗早产儿BPD,可以显著改善患儿血液中IL-1β、TNF-α、IL-8等炎性因子水平,调节血气指标,安全有效,值得推广。
【关键词】 布地奈德; 螺内酯; 支气管肺发育不良; 早产儿; IL-1β; TNF-α
Effect of Budesonide Combined with Spironolactone on Changes of IL-1β and TNF-α in Blood of Premature Infants with Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia/YE Xuqiang,DAI Yiheng,LIU Weidong,et al.//Medical Innovation of China,2019,16(19):0-057
【Abstract】 Objective:To investigate the effect of Budesonide combined with Spironolactone on the changes of IL-1β and TNF-α in blood of premature infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia(BPD).Method:92 cases of premature infants born in our hospital from November 2012 to November 2017 were selected,all of them had BPD symptoms.According to the random number table method,they were divided into control group and study group,46 cases in each group.The control group was treated with Spironolactone,while study group was treated with Budesonide combined with Spironolactone.The levels of inflammatory factors(IL-1β,TNF-α,IL-8),clinical indicators,body weight,blood gas analysis indicators and complications were compared between two groups.Result:After treatment,the levels of IL-1β,TNF-α,IL-8 in study group were lower than those of control group(P<0.05).After treatment,the indexes of heart rate,respiratory rate,percutaneous oxygen saturation,body weight and blood gas analysis in study group were better than those of control group(P<0.05).The incidence of complications was 8.7% in study group,which was lower than 32.6% of control group(字2=8.026,P<0.05).Conclusion:The application of Budesonide combined with Spironolactone in treatment of BPD in premature infants can significantly improve the levels of IL-1β,TNF-α,IL-8 and other inflammatory factors in the blood of the infants,regulate blood gas indicators,which is safe and effective,and is worthy of promotion.
【Key words】 Budesonide; Spironolactone; Bronchopulmonary dysplasia; Premature infants; IL-1β; TNF-αFirst-authors address:Foshan Maternal and Child Health Hospital,Foshan 528000,China
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2019.19.014
支氣管肺发育不良(BPD)常见于早产儿,临床特征表现为对氧气的长时间依赖,属慢性呼吸系统的常见病,严重呼吸窘迫综合征为其原发疾病,影响患儿机体发育[1]。随着现代医疗技术水的提高,早产儿的存活率也有所提升,因此随之出现的BPD、神经系统发育异常等早产儿病变也出现了较高的发生率。由于早产,患儿机体肺未完全发育,肺泡数量少,伴随机体不断发育,肺泡数量也持续增多,由于感染、机械通气、炎性反应等诸多不利因素的作用,患儿极易出现肺泡停滞发育的状况,影响患儿身体发育[2]。当前阶段,针对早产儿BPD的防治,尚无系统规范化治疗方案,主要措施有氧疗、支气管扩张剂、抗生素、肺泡表面活性剂、一氧化氮、糖皮质激素、维生素A、利尿剂等治疗[3],其中糖皮质激素的预防及治疗作用被证实是有效的,布地奈德为吸入性糖皮质激素,疗效类似于其他类糖皮质激素,具有防治BPD的功效[4]。本研究对BPD早产儿进行布地奈德联合螺内酯治疗,将布地奈德联合螺内酯治疗对血液中IL-1β、TNF-α变化的影响以及相关不良反应发生状况进行探讨,现报道如下。

