九香虫防卫素基因CcDef1的克隆及特征分析
喻廷君 杜娟 李尚伟



摘 要:九香虫Coridius chinensis是一种重要的资源昆虫,防卫素是抗菌肽家族中一个重要的成员。本文从九香虫中克隆了一种防卫素基因CcDef1,其cDNA的长度为395 bp,包含一个300 bp的开放阅读框,编码99个氨基酸。CcDef1的前体由信号肽、前体肽和成熟肽组成,成熟CcDef1形成包含1个α-螺旋、2个β-折叠片和3个二硫键的三维结构。CcDef1蛋白的相对分子量为4589.37 Da,总净电荷量为+1,理论等电点为7.84。同源性和聚类分析显示,CcDef1与红尾碧蝽Palomena prasina防卫素的亲缘关系最近。该研究为进一步明确CcDef1基因的功能及开发新型抗菌药物奠定基础。
关键词:九香虫;抗菌肽;昆虫防卫素;基因克隆
中图分类号:R282
文献标识码:A
文章编号:1008-0457(2019)03-0006-06 国际DOI编码:10.15958/j.cnki.sdnyswxb.2019.03.002
Abstract:Coridius chinensis is an important resource insect and defensin is an important member of the antimicrobial peptides family. In this study,a defensin gene,designated as CcDef1,was cloned from C. chinensis. The CcDef1 cDNA is 395 bp in length,containing a 300 bp open reading frame (ORF) that encodes 99 amino acids. The precursor of CcDef1 is composed of a signal peptide,a propeptide and a mature peptide. The mature CcDef1 forms a three-demensional structure consisted of 1 α-helix,2 β-pleated sheets and 3 disulfide bonds. The molecular weight of CcDef1 protein is 4589.37 Da,the total net charge is +1,and the theoretical isoelectric point is 7.84. CcDef1 protein is involved in the immune protection process of organisms. Homology and cluster analyses showed that CcDef1 possesses the closest relationship with that of Palomena prasina and Halyomorpha halys. The study laid the foundation for futher clarifying the function of CcDef1 gene and developing new antibacterial drugs.
Key words:Coridius chinensis; antimicrobial peptide; insect defensins; gene cloning
青霉素的發现及提纯是人类历史上最伟大的发现之一,它揭开了人们将抗生素应用于临床的序幕。抗生素在挽救生命的同时,致使一些病原菌对其产生抗性,如耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌、新德里金属β-内酰胺酶-1等。耐药性细菌的产生加快了人们寻求新型抗菌药物的步伐,抗菌肽(antimicrobial peptides,AMPs)以最有可能替代抗生素成为新型的抗菌药物出现在人们的视线中[1],其已经成为医药领域的研究热点。抗菌肽是一类由外界病原菌诱导宿主生物而产生的具有免疫作用的短肽,具有分子量小、热稳定性强、水溶性好、强碱性、广谱抗菌和不破坏正常细胞等特点,在免疫反应过程中发挥重要的作用。先前的研究表明,抗菌肽具有抑制细菌、原生生物、真菌、病毒和癌细胞生长等生物活性[2-8]。防卫素(defensins)是抗菌肽中的一员,可大致分为α-防卫素、β-防卫素、θ-防卫素、植物防卫素和昆虫防卫素。
昆虫防卫素(insect defensins)是昆虫产生的一种为了应对创伤或病原菌感染的小分子阳离子短肽,由33~46个氨基酸组成,在位置Cys1-Cys4、Cys2-Cys5和Cys3-Cys6形成3个分子内二硫键[9]。昆虫防卫素最先在褐尾麻蝇(Sarcophaga peregrina)[10]和新陆原伏蝇(Phormia terranovae)[11]中发现,它们对革兰氏阳性菌都具有抗菌活性。此后,陆续有新型昆虫防卫素被发现,如来自白星花金龟(Protaetia brevitarsis)的Psdefensin,对革兰氏阳性菌和革兰氏阴性菌具有抗菌活性[12];在丝光绿蝇(Lucilia sericata)体内发现的LSer-Def3和Lser-Def6,二者对革兰氏阳性菌有控制作用[13];从版纳绳蚋(Simulium bannaense)分离纯化的SibaDef能抑制革兰氏阳性菌的生长 [14];一种来自棉铃虫(Heliothis virescens)幼虫抗真菌的防卫素[15];来自桔小实蝇(Bactrocera dorsalis)的BdPho[16];从黑水虻(Hermetia illucens)幼虫中分离的DLP4对耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌具有抗性[17]以及来自铜绿蝇(Lucilia cuprina)的lucifensin和lucifensin II[18]等。
九香虫(Coridius chinensis)是一种半翅目(Hemiptera)兜蝽科(Dinidoridae)昆虫[19],其发育类型为渐变态发育,其生活史包括卵、若虫和成虫三种形态,在自然条件下一年只产生一代[20]。九香虫具有理气止痛、温中助阳的功效,它已经被中国药典(2014版)收录,而且居住在中国贵州省剑河县和道真县的人们具有食用九香虫的习惯。由此可见,九香虫在药用和食用领域具有巨大的开发利用价值。先前的研究报道了一些半翅目昆虫防卫素,如使用大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli)和藤黄微球菌(Micrococcus luteus)的混合菌液诱导始红蝽(Pyrrhocoris apterus)产生1种由43个氨基酸组成的防卫素,对革兰氏阳性菌具有抗菌活性[21];Chernysh等[22]在红尾碧蝽(Palomena prasina)体内发现1种具有43个氨基酸的防卫素含有6个半胱氨酸;Lopez等[23]从长红猎蝽(Rhodnius prolixus)分离出由43个氨基酸组成的defensin A。先前的研究表明九香虫体内可能含有多种抗菌肽[24-25],表明其体内含有抗菌肽。目前关于九香虫防卫素的报道较少。因此,在本文中,我们从九香虫中克隆获得一种防卫素基因,命名为CcDef1,并对其生物学特征进行分析,为进一步研究该基因的功能及开发新型抗菌药物奠定基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1 供试昆虫
九香虫采集于中国贵州省凯里市碧波镇的一个农场,人工饲养于贵州大学昆虫研究所,温度为(25 ±1)℃,80%的相对湿度,光周期为14 L:10 D。
1.2 RNA的提取及cDNA的合成
使用HP Total RNA Kit(Omega Bio-Tek,GA,USA)提取九香虫成虫总RNA,根据试剂盒说明书进行操作。RNA的质量和浓度分别使用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳和NanoDrop 2000紫外分光光度计(Thermo Fisher,MA,USA)进行检测。以获得的九香虫RNA为模板,用RevertAid First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Thermo Fisher,MA,USA)反转录合成cDNA,以此作为基因克隆的模板。
1.3 九香虫防卫素基因克隆
从九香虫全长转录组数据中筛选出防卫素基因序列,根据此序列用Primer Premier 6.0设计PCR引物(CcDef1-F:ATCTTACCACTAACCTCTACTACAC; CcDef1-R:TAATTTAAGCAGCAAGCGATGG),并送至生工生物工程(上海)有限公司进行合成。通过T100 Thermal Cycler(Bio-Rad,CA,USA)进行聚合酶链式反应(PCR)实验,反应体系为25 μL:12.5 μL 2× TsingKe Master Mix(北京擎科生物科技有限公司),8.5 μL灭菌超纯水,2 μL cDNA模板,上、下游引物(10 μM)各1 μL。反应条件: 94°C 预变性3 min;94°C变性30 s,52°C退火30 s,72°C延伸30 s,进行30个循环; 72°C延伸10 min。PCR产物经1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测后,用Gel Extraction Kit(Omega Bio-Tek,GA,USA)对目的基因进行回收纯化。然后,将纯化产物连接到pMD18-T载体上,转化E.coli JM109感受态细胞,菌落PCR筛选重组子。经PCR验证的阳性克隆最后送至生物工程(上海)股份有限公司进行测序。使用DNAMAN 9.0软件,将测序结果与转录组数据进行对比。
1.4 生物信息学分析
利用NCBI的ORF Finder(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/orffinder/)預测该基因的开放阅读框,用ProP 1.0 Server(http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/ProP/)分析信号肽和前体肽。用ProtParam tool(https://web.expasy.org/protparam/)预测理化性质,用DISULFIND(http://disulfind.dsi.unifi.it/index.php)预测二硫键,用ProtScale(https://web.expasy.org/protscale/)分析亲/疏水性。糖基化位点预测采用NetNGlyc 1.0 Server (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/NetNGlyc/)和NetOGlyc 4.0 Server (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/NetOGlyc/)进行分析,磷酸化位点预测采用NetPhos 3.1 Server (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/NetPhos/)在线软件进行分析。CcDef1的二级结构使用SOPMA(https://npsa-prabi.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=npsa_sopma.html)进行预测;亚细胞定位使用Target P 1.1 Server(http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TargetP/)进行预测;功能预测使用InterProScan(http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/search/sequence-search)进行分析。用SWISS MODEL(https://www.swissmodel.expasy.org/)的同源建模方法预测成熟CcDef1的三维结构,并使用PyMOL 1.4绘制其分子结构图。将该防卫素在抗菌肽数据库APD(http://aps.unmc.edu/AP/)中进行相似性搜索和特性分析。用Clustal Omega (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/)和GeneDoc 2.7将CcDef1氨基酸序列与其他12种昆虫防卫素氨基酸序列进行对齐分析;使用MEGA-X进行聚类分析。用于多序列对齐和聚类分析的防卫素来源物种及GenBank登录号列于表1中。
2 结果与分析
2.1 PCR扩增CcDef1基因
九香虫总RNA的电泳检测结果显示,28S 和 18S 这两条带清晰且明亮,没有出现拖尾和弥散带的现象(图1-A),表明所提 RNA 的完整度好。紫外分光光度计检测显示总RNA的 A260/A280 值为 1.93,表明RNA的纯度较好。RT-PCR电泳结果显示,在约400 bp位置出现一条明亮的扩增带,与预期大小一致(图1-B)。
A:九香虫总RNA;B:CcDef1基因扩增。M:DL2000 DNA marker;1:CcDef1基因
2.2 CcDef1的cDNA
九香虫防卫素基因CcDef1的PCR产物经测序得到该基因的cDNA序列 (GenBank登录号:MK304482)。该cDNA长395 bp,包含一个长度为300 核苷酸(nt)的开放阅读框,编码99个氨基酸;5’端有29 nt的非编码区(UTR),3’端有66 nt的UTR。该防卫素CcDef1的N端具有一段由17个氨基酸组成的信号肽和长度为39个氨基酸的前体肽(图2)。
2.3 CcDef1的特征分析
九香虫防卫素CcDef1的分子式为C189H308N60O57S8,相对分子量为4589.37 Da,理论等电点为7.84,包含2个带负电荷氨基酸残基(D,E)和3个带正电荷氨基酸残基(R,K)。该防卫素在N16处有一个N-糖基化位点,无O-糖基化位点,具有3个磷酸化位点(S63,T66,T82)。在CcDef1的氨基酸序列中,含有6个半胱氨酸,在59Cys1-90Cys4,76Cys2-95Cys5,和80Cys3-97Cys6形成3个二硫键(图3)。对成熟CcDef1的亲/疏水性预测结果显示,疏水氨基酸的比例大于亲水氨基酸的比例,表明成熟CcDef1为疏水蛋白。跨膜结构域的预测结果显示,CcDef1拥有1个跨膜结构域,位置在L4~Y21。
2.4 同源性比较和聚类分析
将CcDef1氨基酸序列在NCBI中进行Blast比对,结果显示该防卫素与红尾碧蝽(P.prasina)、茶翅蝽(H.halys)及褐飞虱(N.lugens)的防卫素分别具有76.76%、65.31%和63.16%的相似性。多序列对齐结果显示,成熟CcDef1含有6个稳定表达的半胱氨酸和2个连续而且稳定表达的甘氨酸(图4)。在抗菌肽数据库APD中的预测显示,CcDef1与厩螫蝇(Stomoxys calcitrans,AP01366)的Smd2、 丝光绿蝇(Lucilia sericata,AP01532)的Lucifensin、温带臭虫(Cimex lectularius,AP02651)的CL-defensin和銅绿蝇(Lucilia cuprina,AP02240)的lucifensin II 的相似性分别为66.66%、61.36%、59.09 %和59.09% 。
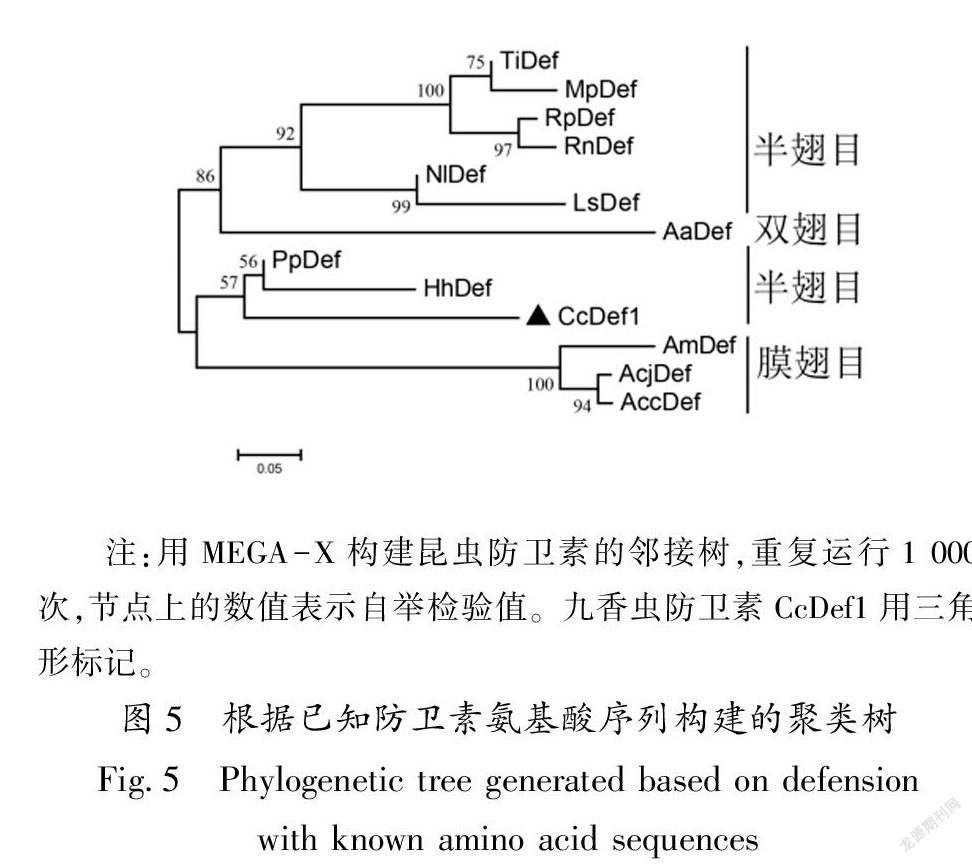
聚类分析显示,红尾碧蝽和茶翅蝽的防卫素与CcDef1聚在一起,然后与膜翅目昆虫防卫素聚为一支;双翅目昆虫防卫素与其他半翅目昆虫防卫素聚为另一支(图5)。同源性比较和聚类分析的结果表明,CcDef1与红尾碧蝽防卫素的亲缘关系最近,其次是茶翅蝽。
3 结论与讨论
昆虫是地球上数量最多的动物群体,它们的踪迹几乎遍布世界的每一角落,对环境具有极强的适应能力。昆虫资源的开发利用一直是人们关注的焦点,发现新的昆虫抗菌肽能为人们抵抗病原菌的感染及癌症治疗提供新的方法。目前,生物信息学已经应用于多个领域,包括基因结构分析、蛋白质结构分析及蛋白质功能分析[26-28]等。使用多参数综合预测的方法对未知基因进行预测,可以显著地提高预测结果的可靠性。在本文中,我们采用综合分析方法对九香虫防卫素基因CcDef1进行了特征分析。
昆虫防卫素是一种阳离子短肽,其成熟蛋白形成3个二硫键[9],CcDef1蛋白的总静电荷数为+1,在位置59Cys1-90Cys4,76Cys2-95Cys5和80Cys3-97Cys6形成3个二硫键。在无脊椎动物防卫素氨基酸序列中,半胱氨酸的排列模式为Cys-X5~16-Cys-X3-Cys-X9~10-Cys-X4~7-Cys-X1-Cys [29],CcDef1蛋白的半胱氨酸的排列模式为Cys-X16-Cys-X3-Cys-X9-Cys-X4-Cys-X1-Cys,符合无脊椎动物防卫素的半胱氨酸排列模式。三维结构预测显示,CcDef1蛋白含有1个CS-αβ结构域,这是昆虫防卫素具有抗菌活性的一个重要结构基础[30],参与生物体的免疫防护过程。 CcDef1蛋白是分泌通道蛋白,分布在细胞外和细胞质的概率较高,因此可以推测CcDef1与其他昆虫防卫素一样,在脂肪体中合成,经过一系列修饰后分泌到血淋巴中发挥生物学效应[31]。CcDef1与红尾碧蝽和茶翅蝽防卫素的亲缘关系较近,可以判断其为昆虫防卫素家族中的一员。
本研究成功克隆了九香虫防卫素CcDef1基因,并对其特征进行分析,为今后进一步研究该基因的功能及开发新型抗菌药物奠定基础。
参 考 文 献:
[1] Hassan M,Kjos M,Nes I F,et al.Natural antimicrobial peptides from bacteria:characteristics and potential applications to fight against antibiotic resistance[J].Journal of applied microbiology,2012,113(4):723-736.
[2] Luna-Ramirez K,Tonk M,Rahnamaeian M,et al.Bioactivity of Natural and Engineered Antimicrobial Peptides from Venom of the Scorpions Urodacus yaschenkoi and U.manicatus[J].Toxins,2017,9(1):22.
[3] Farkas A,Maróti G,Kereszt A,et al.Comparative analysis of the bacterial membrane disruption effect of two natural plant antimicrobial peptides[J].Frontiers in microbiology,2017,8:51.
[4] Rahman M S,Choi Y H,Choi Y S,et al.Glycin-rich antimicrobial peptide YD1 from B.amyloliquefaciens,induced morphological alteration in and showed affinity for plasmid DNA of E.coli[J].AMB Express,2017,7(1):8.
[5] Rogozhin E A,Ryazantsev D Y,Grishin E V,et al.Defense peptides from barnyard grass (Echinochloa crusgalli L.) seeds[J].Peptides,2012,38(1):33-40.
[6] Cai S,Qiao X,Feng L,et al.Python Cathelicidin CATHPb1 Protects against Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcal Infections by Antimicrobial-Immunomodulatory Duality[J].Journal of medicinal chemistry,2018,61(5):2075-2086.
[7] Gui L,Zhang P,Zhang Q,et al.Two hepcidins from spotted scat (Scatophagus argus) possess antibacterial and antiviral functions in vitro[J].Fish & shellfish immunology,2016,50:191-199.
[8] Peng X,Zhou C,Hou X,et al.Molecular characterization and bioactivity evaluation of two novel bombinin peptides from the skin secretion of Oriental fire-bellied toad,Bombina orientalis[J].Amino acids,2018,50(2):241-253.
[9] Cézard C, Silva-Pires V, MulliéC, et al. Antibacterial peptides:a review [A]. Méndez-Vilas A. Science against microbial pathogens:communicating current research and technological advances[C]. Badajoz:FORMATEX, 2011:926-937.
[10] Matsuyama K,Natori S.Purification of three antibacterial proteins from the culture medium of NIH-Sape-4,an embryonic cell line of Sarcophaga peregrina[J].Journal of Biological Chemistry,1988,263(32):17112-17116.
[11] Lambert J,Keppi E,Dimarcq J L,et al.Insect immunity:isolation from immune blood of the dipteran Phormia terranovae of two insect antibacterial peptides with sequence homology to rabbit lung macrophage bactericidal peptides[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,1989,86(1):262-266.
[12] Lee J,Bang K,Hwang S,et al.cDNA cloning and molecular characterization of a defensin-like antimicrobial peptide from larvae of Protaetia brevitarsis seulensis (Kolbe)[J].Molecular biology reports,2016,43(5):371-379.
[13] Pppel A K,Vogel H,Wiesner J,et al.Antimicrobial peptides expressed in medicinal maggots of the blow fly Lucilia sericata show combinatorial activity against bacteria[J].Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy,2015,59(5):2508-2514.
[14] Wei L,Mu L,Wang Y,et al.Purification and characterization of a novel defensin from the salivary glands of the black fly,Simulium bannaense[J].Parasites & vectors,2015,8(1):71.
[15] Lamberty M,Ades S,Uttenweiler-Joseph S,et al.Insect immunity isolation from the lepidopteran Heliothis virescens of a novel insect defensin with potent antifungal activity[J].Journal of Biological Chemistry,1999,274(14):9320-9326.
[16] Liu S H,Li H F,Yang Y,et al.Antimicrobial peptide gene BdPho responds to peptidoglycan infection and mating stimulation in oriental fruit fly,Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel)[J].AMB Express,2018,8(1):5.
[17] Park S I,Kim J W,Yoe S M.Purification and characterization of a novel antibacterial peptide from black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae[J]. Developmental & Comparative Immunology,2015,52(1):98-106.
[18] er ^ovsk V,Bm R.Lucifensins,the insect defensins of biomedical importance:the story behind maggot therapy[J].Pharmaceuticals,2014,7(3):251-264.
[19] 蔣 超,黄璐琦,袁 媛,等.《中国药典》动物药材基原物种中文名和拉丁学名引证规范[J].中国科学:生命科学,2018,48(7):772-782.
[20] 魏 超,舒国周,罗会嵩,等.九香虫的形态特征和生物学特性[J].山地农业生物学报,2015,34(4):26-30.
[21] Cociancich S,Dupont A,Hegy G,et al.Novel inducible antibacterial peptides from a hemipteran insect,the sap-sucking bug Pyrrhocoris apterus[J].Biochemical Journal,1994,300(2):567-575.
[22] Chernysh S,Cociancich S,Briand J P,et al.The inducible antibacterial peptides of the Hemipteran insect Palomena prasina:Identification of a unique family of prolinerich peptides and of a novel insect defensin[J].Journal of Insect Physiology,1996,42(1):81-89.
[23] Lopez L,Morales G,Ursic R,et al.Isolation and characterization of a novel insect defensin from Rhodnius prolixus,a vector of Chagas disease[J].Insect biochemistry and molecular biology,2003,33(4):439-447.
[24] 赵柏松,杜 娟,王金固,等.九香虫血淋巴的抗菌活性初步研究[J].贵州农业科学,2011,39(6):85-89.
[25] 李尚伟,赵柏松,杜 娟.九香虫抗菌肽CcAMP1的分离纯化和抗菌活性检测[J].昆虫学报,2015,58(06):610-616.
[26] 张雪钰.桃PpRBD1基因特征及功能分析[D].秦皇岛:河北科技师范学院,2018.
[27] 于畅.西瓜噬酸菌hrcQ、abmR和abmK基因功能分析[D].北京:中国农业科学院,2018.
[28] 纪丹丹,陈福禄,肖龙等.大豆Nup98蛋白结构及功能预测分析[J].分子植物育种,2017,15(12):4813-4824.
[29] Seufi A M,Hafez E E,Galal F H.Identification,phylogenetic analysis and expression profile of an anionic insect defensin gene,with antibacterial activity,from bacterial-challenged cotton leafworm,Spodoptera littoralis[J].BMC molecular biology,2011,12:47.
[30] Cornet B,Bonmatin J M,Hetru C,et al.Refined three-dimensional solution structure of insect defensin A[J].Structure,1995,3(5):435-448.
[31] Hoffmann J A,Hetru C.Insect defensins:inducible antibacterial peptides [J].Immunology today,1992,13(10):411-415.

