替普酶溶栓后早期行PCI治疗STEMI的有效性研究
杨宪刚
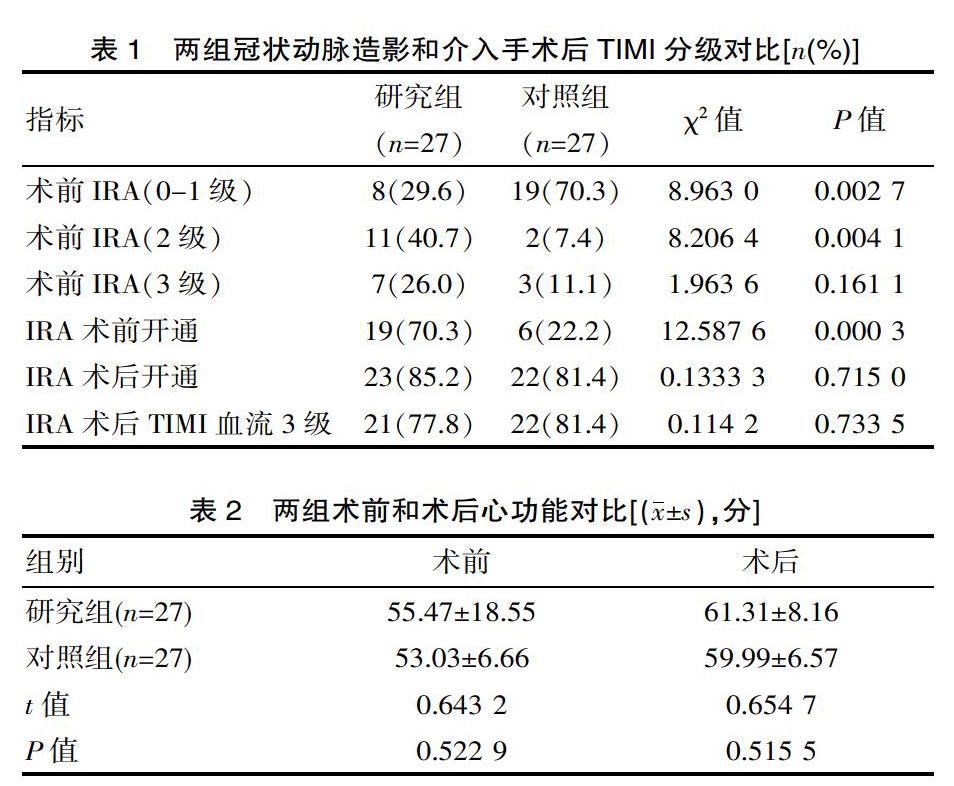
[摘要] 目的 探討瑞替普酶溶栓后早期行经皮冠状动脉介入术治疗ST段抬高型心肌梗死患者的临床价值。 方法 方便选取该院于2016年2月—2017年8月期间所收治的ST段抬高型心肌梗死患者54例纳入该次研究中,根据当时患者入院情况将其分为研究组和对照组,每组各为27例。研究组行易化PCI手术治疗,对照组行直接PCI术治疗,对比两组冠状动脉造影和介入手术后TIMI分级情况、术前、术后心功能对比以及随访情况。结果 ①研究组冠状动脉造影时的TIMI血流2-3级明显高于对照组,组间对比有统计学意义(P<0.05),但介入干预后两组最终TIMI血流2、3级患者对比差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);②术前研究组心功能(55.47±18.55)分和对照组(53.03±6.66)分差异无统计学意义(t=0.643 2 P>0.05),术后研究组(61.31±8.16)分和对照组(59.99±6.57)分对比差异无统计学意义(t=0.654 7 P>0.05);③研究组27例中出现心脏不良反应共6例,对照组出现8例不良反应,组间对比差异无统计学意义(χ2=0.385 7 P>0.05)。结论 易化PCI手术的应用对ST段抬高型心肌梗死的治疗更加有利。
[关键词] 易化PCI手术;直接PCI手术;ST段抬高型心肌梗死;瑞替普酶
[中图分类号] R5 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1674-0742(2019)05(c)-0081-03
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the clinical value of early percutaneous coronary intervention for patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction after thrombolytic therapy with reteplase. Methods A total of 54 patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction who were admitted to our hospital from February 2016 to August 2017 were convenient selected and included in the study. According to the admission of the patients at the time, they were divided into study group and control group, 27 cases each. The study group underwent PCI and the control group underwent direct PCI. The TIMI grading, preoperative and postoperative cardiac function comparison and follow-up were compared between the two groups. Results 1.The TIMI blood flow of the study group was significantly higher than that of the control group at 2-3 grades. The comparison between the two groups was statistically significant (P<0.05), but the final TIMI blood flow of patients with grade 2 and 3 after interventional intervention. There was no difference in contrast (P>0.05). 2.There was no statistically significant difference between the preoperative group (55.47±18.55)points and the control group (53.03±6.66)points (t=0.643 2, P>0.05). There was no significant difference between the scores of (61.31±8.16)points and the control group (59.99±6.57)points (t=0.654 7, P>0.05). 3.There were 6 cases of adverse cardiac reactions in 27 cases in the study group and 8 cases of adverse reactions in the control group. There was no statistically significant difference between the groups (χ2=0.385 7, P>0.05). Conclusion The application of facilitating PCI is more beneficial for the treatment of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.
[Key words] Facilitative PCI surgery; Direct PCI surgery; ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; Reteplase

