早期颅骨修补联合脑室-腹腔分流术治疗重度脑外伤术后并脑积水的效果分析
林宇国 杨金星 沈卫民
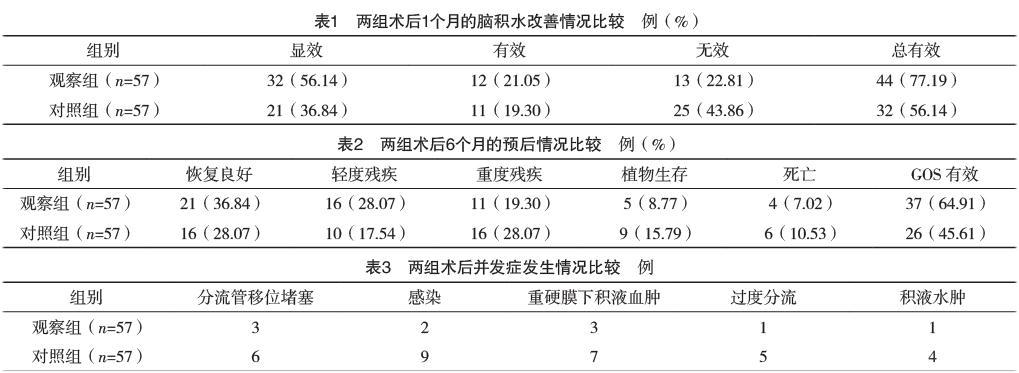
【摘要】 目的:探讨早期颅骨修补联合脑室-腹腔分流术治疗重度脑外伤术后并脑积水的临床效果。方法:选取2015年2月-2017年10月本院收治的重度脑外伤术后并脑积水患者114例作为研究对象,按照随机数字表法将其分为观察组(n=57)和对照组(n=57)。观察组采用早期颅骨修补联合脑室-腹腔(ventriculo-peritoneal,V-P)分流术,患者先行开颅血肿清除去骨瓣减压术后2个月内,再行V-P分流联合颅骨修补术治疗。对照组先行V-P分流术,3~6个月后根据患者恢复情况再行颅骨修补术。观察比较两组术后1个月的脑积水改善、術后6个月的预后及并发症发生情况。结果:术后1个月,观察组的脑积水改善总有效率明显高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(字2=5.684,P=0.017)。术后6个月,观察组的格拉斯哥预后评分(GOS)有效率明显高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(字2=4.293,P=0.038)。观察组术后并发症发生率为17.54%(10/57),明显低于对照组的54.39%(31/57),差异有统计学意义(字2=16.797,P=0.001)。结论:早期颅骨修补联合脑室-腹腔分流术治疗重度脑外伤术后并脑积水效果显著,安全性高,值得临床推广应用。
【关键词】 早期颅骨修补联合脑室-腹腔分流术; 重度脑外伤; 脑积水
【Abstract】 Objective:To investigate the clinical effect of early skull repair combined with ventriculo-peritoneal shunt in the treatment of hydrocephalus after severe traumatic brain injury.Method:A total of 114 patients with hydrocephalus after severe traumatic brain injury admitted in our hospital from February 2015 to October 2017 were selected as the study objects.According to the random number table method,they were divided into observation group(n=57)and control group(n=57).The observation group was treated with early early skull repair combined with ventriculo-peritoneal(V-P)shunt.The patients were treated with craniotomy hematoma clearance and decompression of bone flaps removal after operation within 2 months,V-P shunt and skull repair were performed.The control group was treated with V-P shunt,the skull repair was performed after 3-6 months according to the recovery of the patients. The improvement of hydrocephalus after operation 1 month,prognosis after operation 6 months and complications between the two groups were observed and compared.Result:After operation 1 month,the total effective rate of hydrocephalus improvement in the observation group was significantly higher than that in the control group,the difference was statistically significant(字2=5.684,P=0.017).After operation 6 months,the Glasgow prognosis score(GOS)effective rate of the observation group was significantly higher than that of the control group,the difference was statistically significant(字2=4.293,P=0.038).The incidence of postoperative complications in the observation group was 17.54%(10/57),which was significantly lower than 54.39%(31/57)in the control group,the difference was statistically significant(字2=16.797,P=0.001).Conclusion:Early skull repair combined with ventriculo-peritoneal shunt is effective and safe in the treatment of hydrocephalus after severe traumatic brain injury.It is worthy of clinical application.

