加巴喷丁在全膝关节置换术后镇痛效果中的前瞻性研究
王帆 贺智榆 陈孝均
【摘要】 目的:研究加巴喷丁在全膝关节置换术后疼痛管理中的镇痛效果。方法:采用随机双盲安慰剂对照的方法,将2016年10月-2018年2月西南医科大学附属中医医院骨伤科拟行初次膝关节置换的患者80例纳入研究,按照随机量表法将患者分为两组(加巴喷丁组40例和安慰剂组40例),每个加巴喷丁组的患者术后定期加服加巴喷丁胶囊,安慰剂组术后服用乳糖胶囊安慰剂,比较两组的镇痛效果。結果:加巴喷丁胶囊作为多模式多环节疼痛管理中的辅助镇痛药物能有效地改善术后48 h内的疼痛,同时明显改善患膝术后早期(7 d)的功能恢复,且未出现明显药物不良反应。但在6个月的随访中发现两组患者的膝关节功能恢复差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论:加巴喷丁胶囊辅助镇痛作用确切,可有效地缓解全膝关节置换术患者术后的疼痛,促进全膝关节置换术患者早期进行关节活动,缩短住院时间,且不会增加药物不良反应,是较为理想的镇痛药物。
【关键词】 加巴喷丁胶囊; 全膝关节置换术; 镇痛
【Abstract】 Objective:To investigate the analgesic effect of Gabapentin in the evaluation of pain management after total knee arthroplasty(TKA).Method:Randomized,double-blind,placebo controlled from October 2016 and February 2018,80 patients underwent unilateral TKA were randomly divided into two groups,40 cases each in each group.After surgery,Gabapentin group took Gabapentin Capsules regularly and placebo group took Lactose Placebo Capsules,the analgesic effects of two groups were compared.Result:Gabapentin Capsule,as an assistant analgesic drug in multi-mode and multi-link pain management,can effectively improve the pain in 48 h after surgery.At the same time,it significantly improved the functional recovery in the early(7 d)after knee surgery,and there was no obvious drug adverse reaction.However,there was no statistical significant difference in the recovery of knee joint function between two groups at the six-month follow-up(P>0.05).Conclusion:Gabapentin Capsule has a definite analgesic effect. It can effectively relieve pain after total knee arthroplasty,promote early joint activity,shorten hospitalization time,and do not increase adverse drug reactions.It is an ideal analgesic drug.
【Key words】 Gabapentin Capsule; Total knee arthroplasty; Analgesia
First-authors address:Naxi District Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Luzhou City,Luzhou 646300,China
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2019.03.005
由于严重的膝关节退变病例越来越多,全膝关节置换术(total knee arthroplasty,TKA)在目前的医疗前景中被使用得越来越广泛[1-2]。虽然膝关节退变的早期疼痛使用非甾体类抗炎药镇痛可以取得良好的效果,但是并不能根治[3]。在病情发展到一定程度的时候均会出现剧烈的疼痛并且严重影响生活质量,这时候TKA对减轻患者痛苦、提高患者生存质量显得尤为重要[4]。但TKA术后的急性疼痛在临床上处理起来非常困难,疼痛会直接影响患者的手术效果。良好的术后镇痛能有效地促进患者的早期功能锻炼,降低术后并发症(如深静脉血栓)和平均住院时间4~5 d[5]。目前TKA的镇痛方式有连续股神经阻滞(continuous femoral nerve block,CFNB)镇痛、口服非甾体类止痛药、患者静脉自控镇痛(patient controlled intravenous analgesia,PCIA)等[6]。但目前单一模式的镇痛由于其有限的镇痛效果和相对较大的副作用已经使用得越来越少[7]。多模式镇痛可以在多个阶段(术前、术中、术后),通过多种途径(外周局部、脊髓水平、脊髓上水平),联合应用多种药物[阿片类药物、非甾体抗炎药(NSAIDs)、局麻药]来达到最有效的平衡镇痛[8]。由于各种条件限制,临床上多在TKA术后使用阿片类药物与NSAIDs合用起到协同镇痛、增强镇痛效果[9]。加巴喷丁胶囊作为一种新型抗癫痫药,临床中广泛用于治疗癫痫、抗惊厥和神经性疼痛,对其可缓解神经性疼痛的作用已得到越来越多临床医师的关注和重视[10-11]。但加巴喷丁胶囊用于TKA术后镇痛在国内外报告并不多见[12]。加巴喷丁胶囊口服吸收,药物利用率高,达到最大药物浓度时间短,半衰期长。其主要副作用包括恶心、眩晕、步态不稳、疲劳感等[13]。为了进一步评价加巴喷丁胶囊在TKA术后是否有比较理想的镇痛效果,笔者设计了本次临床研究,以验证该药在TKA术后的镇痛效果,同时为临床工作提供一定的用药参考。现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 采用随机双盲安慰剂对照的方法,将2016年10月-2018年2月西南医科大学附属中医医院骨伤科拟行初次膝关节置换的患者80例纳入研究,按照随机量表法将患者分为两组(加巴喷丁组40例和安慰剂组40例)。由SAS统计软件自动生成随机化方案,药物分配根据随机化数字量表排序,分配结果保密。研究中的观察者、受试者以及统计方均不知兩组的代号与各代号对应的意义。纳入标准:年龄18~75岁;拟行初次TKA的手术患者;患者自愿参加,并签署知情同意书。排除标准:有心脑血管疾病、肝、肾疾病以及神经、精神病史者;有慢性疼痛综合征者;有酒精、药物滥用史者;语言交流困难者;对局麻药过敏者。退出标准:因各种原因未能完成手术者;患者因故自愿退出者。
1.2 手术技术 取膝前正中切口,沿股四头肌内侧髌旁支持带进入。沿髌骨内侧髌腱内缘向下延长至胫骨的前内侧面。前内侧关节囊和胫侧副韧带剥离至膝关节后内侧,松解髌骨股骨外侧。切除前交叉韧带、内外侧半月板前角。股骨远端外翻6°截骨,股骨后髁外旋3°截骨。胫骨侧髓外定位方式截骨,平衡软组织,安放试模测得稳定后置入假体。脉冲冲洗后逐层缝合软组织及皮肤。
1.3 镇痛方法
1.3.1 术前 两组均在术前2 d口服选择性环氧化酶-2(COX-2)抑制剂塞来昔布胶囊(生产企业:辉瑞药业,国药准字J20140072,规格:0.2 g×6粒/盒),200 mg/次,2次/d;氨酚曲马多片[生产企业:哈尔滨三联药业,国药准字H20150014,规格:盐酸曲马多37.5 mg:对乙酰氨基酚325 mg×10片/(板·盒)],325 mg/次,3次/d。
1.3.2 术中 两组患者术中假体植入后均予鸡尾酒式镇痛混合剂,罗哌卡因[生产企业:成都天台山,国药准字H20052666,规格:75 mg/(10 mL·支)]275 mg,甲基强的松龙(生产企业:辉瑞药业,国药准字H20080284,规格:40 mg/瓶)40 mg,加入0.9%氯化钠注射液100 mL,局部软组织内注射。
1.3.3 术后 两组均常规口服塞来昔布胶囊(200 mg/次,2次/d)和氨酚曲马多片(325 mg/次,3次/d)。加巴喷丁组于术后12 h起至术后第7天加用加巴喷丁胶囊[生产企业:江苏恩华药业,国药准字H20051068,规格:0.3 g×2×12粒/(板·盒)]100 mg/次,3次/d,口服,安慰剂组加用乳糖胶囊,100 mg/次,3次/d。术后镇痛效果不佳者需适当追加阿片类药物氨酚曲马多片镇痛。
1.4 观察指标与评定标准
1.4.1 术后镇痛评定 采用视觉模拟疼痛评分(VAS)来评估疼痛水平,术后12 h、24 h、48 h、7 d分别记录VAS评分。记录术后1 d、3 d、7 d和6个月膝关节活动度(ROM)。记录使用加巴喷丁胶囊后的各种不良反应。
1.4.2 补救性镇痛药物的使用 患者术后在标准镇痛的情况下(塞来昔布胶囊,200 mg/次,2次/d;氨酚曲马多片,325 mg/次,3次/d,加巴喷丁组加服加巴喷丁胶囊,100 mg/次,3次/d,安慰剂组加用乳糖胶囊,100 mg/次,3次/d)。观察记录两组患者是否追加镇痛药。
1.4.3 次要观察指标 患者的年龄、性别比例、体质指数、患膝术前活动度等。要求患者术后6个月来院随访时行登楼实验,术前和术后6个月随访时的Keen Society Score(KSS)评分,评价患者患膝恢复情况。
1.4.4 安全性观察指标 主要包括:临床观察两组不良反应详细记录、及时处理。观察塞来昔布胶囊和阿片类药物的不良反应。
1.5 统计学处理 采用SPSS 21.0软件对所得数据进行统计分析,正态分布计量资料用(x±s)表示,比较采用t检验;计数资料以率(%)表示,比较采用重复测量资料采用方差分析。检验水准α=0.05,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
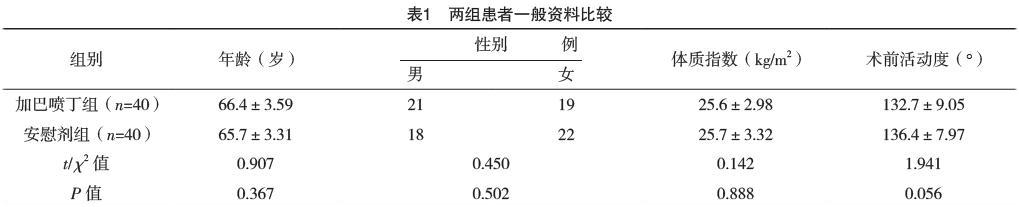
2.1 两组患者一般资料比较 两组年龄、性别、体质指数、术前活动度比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05),见表1。
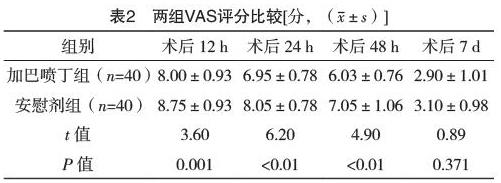
2.2 两组VAS评分比较 术后12、24、48 h加巴喷丁组VAS评分均较安慰剂组低,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05);术后7 d两组VAS评分比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表2。
2.3 两组追加使用镇痛剂情况 加巴喷丁组的阿片类药物追加使用量较安慰剂组的用量明显降低,12 h加巴喷丁组6例,安慰剂组15例(字2=4.588,P=0.032);24 h加巴喷丁组4例,安慰剂组11例(字2=4.013,P=0.045);36 h加巴喷丁组3例,安慰剂组7例(字2=4.528,P=0.33);48 h加巴喷丁组1例,安慰剂组4例(字2=4.073,P=0.044)。
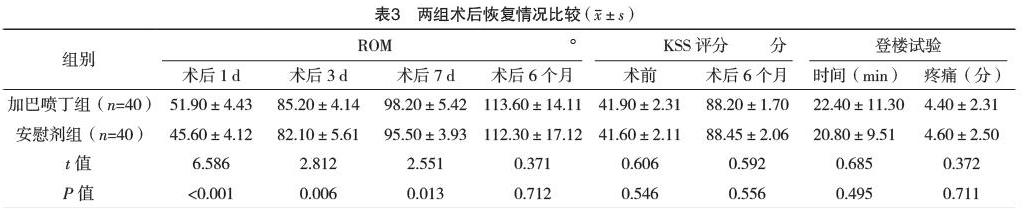
2.4 两组术后恢复情况比较 加巴喷丁组术后1、3、7 d膝关节活动度明显优于安慰剂组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。两组登楼实验比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。两组术前、术后6个月KSS膝关节功能评分比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表3。
2.5 两组术后镇痛副作用情况比较 两组术后均未出现严重不良反应。加巴喷丁组尿潴留1例,安慰剂组2例。加巴喷丁组2例发生恶心呕吐,安慰剂组3例。两组均有1例出现皮肤瘙痒症状。两组术后均未出现腹痛、腹胀等胃肠道副反应。两组不良反应发生情况比较,差异无统计学意义(字2=1.421,P=0.212>0.05)。
3 讨论
骨科手术术后的疼痛一直是医生们处理的一项难题[14-17],其中TKA患者术后的急性疼痛更是大家研究和讨论的一个热点。TKA患者平均住院时间短,早期的急性炎症反应重,导致术后的疼痛更加明显,所以TKA患者术后的短期镇痛更具临床价值[18]。美国在2002年将加巴喷丁列为神经病理性疼痛的一线药物,其对神经病理性疼痛明确的镇痛效果是本研究的基础[19]。虽然加巴喷丁镇痛的具体机制描述尚不明确,但是其在中枢镇痛的作用效果明显,并且在抑制损伤后的外周神经异位放电上有明确的作用[20]。
本研究結果显示,TKA术后12、24、48 h的短期镇痛中,加巴喷丁组的镇痛效果明显优于安慰剂组(P<0.05),说明加巴喷丁胶囊能有效地提高TKA患者术后的短期镇痛效果。笔者亦发现加巴喷丁组患者TKA术后阿片类药物的使用量较安慰剂组有明显减少(P<0.05),并且巴喷丁组在早期膝关节活动度上也有更好的表现(P<0.05)。由此可见,早期使用加巴喷丁胶囊能加速患者的康复。
本研究表明加巴喷丁胶囊在TKA术后的急性镇痛上疗效明显,能有效地帮助患者对抗早期急性疼痛,在术后恢复和进行康复锻炼上有重要的意义。但是在术后6月的随访中发现,两组KSS评分与登楼实验比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。说明早期镇痛对患者在晚期的功能康复上两组并没有表现出明显的差异[21]。研究表明,在围手术期(术前与术后服用加巴喷丁胶囊,200 mg/次,3次/d)除了能明显减少术后阿片类药物的使用,还能降低患者的疼痛评分,缩短患者的住院时间[22]。
有研究表明术前、术后的焦虑与抑郁也会显著增加患者的术后疼痛,对术后的康复效果有重要的影响[23]。有学者选取高焦虑评分的女性患者作为研究对象,发现在接受大手术前使用1 200 mg加巴喷丁胶囊可以明显改善患者的焦虑情况和降低患者的术后疼痛[24]。有学者在围手术期使用加巴喷丁胶囊600 mg,即可改善患者焦虑情况,在患者的术后康复上起到明显的作用。有研究发现加巴喷丁胶囊在替代卡马西平进行三叉神经痛的效果更好,且在副作用和安全性等方面表现优异[25-27]。本研究结果显示,两组均发生各种副作用,但差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),可见加巴喷丁胶囊在早期镇痛的安全性上得到了肯定。Clarke等[28]在加巴喷丁的动物试验中发现其早期的镇痛效果虽然明显,但是长期试验中大鼠出现的耐药情况愈发明显。
综上所述,加巴喷丁胶囊在TKA术后的短期镇痛中效果明显,能够明显减轻患者术后的急性期疼痛,改善患者术后的康复情况,减少患者住院时间,是临床上值得推广的一种镇痛方式。加巴喷丁胶囊长期的镇痛效果有待进一步研究。
参考文献
[1] Bastick A N,Damen J,Agricola R,et al.Characteristics associated with joint replacement in early symptomatic knee or hip osteoarthritis:6-year results from a nationwide prospective cohort study(CHECK)[J].Br J Gen Pract,2017,67(663):e724-e731.
[2] Lange T,Schmitt J,Kopkow C,et al.What Do Patients Expect From Total Knee Arthroplasty?A Delphi Consensus Study on Patient Treatment Goals[J].Journal of Arthroplasty,2017,32(7):2093-2099.
[3] Kelley T C,Adams M J,Mulliken B D,et al.Efficacy of multimodal perioperative analgesia protocol with periarticular medication injection in total knee arthroplasty:a randomized,double-blinded study[J].Journal of Arthroplasty,2013,28(8):1274-1277.
[4] Han C,Li X D,Jiang H Q,et al.The use of gabapentin in the management of postoperative pain after total knee arthroplasty:A PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J].Medicine,2016,95(23):1-7.
[5] Mao Y,Wu L,Ding W.The efficacy of preoperative administration of gabapentin/pregabalin in improving pain after total hip arthroplasty:a meta-analysis[J].Bmc Musculoskeletal Disorders,2016,17(1):373.
[6] Kukreja P,Feinstein J,Kalagara H K,et al.A Summary of the Anatomy and Current Regional Anesthesia Practices for Postoperative Pain Management in Total Knee Arthroplasty[J].Cureus,2018,10(6):e2755.
[7] Shi Z B,Dang X Q.Efficacy of multimodal perioperative analgesia protocol with periarticular medication injection and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use in total knee arthroplasty[J].Niger J Clin Pract,2018,21(9):1221-1227.
[8] Lim Y C,Quek H Y K,Phoo W H J,et al.A randomised,controlled trial comparing adductor canal block and femoral nerve block for knee arthroplasty[J].Singapore Med J,2018[Epub ahead of print].
[9] van Haagen M H M,Verburg H,Hesseling B,et al.Optimizing the dose of local infiltration analgesia and gabapentin for total knee arthroplasty,a randomized single blind trial in 128 patients[J].Knee,2018,25(1):153-160.
[10] Marmura M J,Kumpinsky A S.Refining the Benefit/Risk Profile of Anti-Epileptic Drugs in Headache Disorders[J].Cns Drugs,2018,32(8):735-746.
[11] Dosenovic S,Jelicic K A,Miljanovic M,et al.Interventions for Neuropathic Pain:An Overview of Systematic Reviews[J].Anesthesia & Analgesia,2017,125(2):643-652.
[12] Clarke H A,Katz J,Mccartney C J L,et al.Perioperative gabapentin reduces 24 h opioid consumption and improves in-hospital rehabilitation but not post-discharge outcomes after total knee arthroplasty with peripheral nerve block[J].British Journal of Anaesthesia,2014,113(5):855-864.
[13] Enke O,New H A,New C H,et al.Anticonvulsants in the treatment of low back pain and lumbar radicular pain:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J].CMAJ,2018,190(26):E786-E793.
[14] Saraev A V,Kornilov N N,Kulyaba T A.Efficiency of the multimodal approach to analgesia in total knee arthroplasty[J].Khirurgiia(Mosk),2018(6):83-90.
[15] Berninger M T,Friederichs J,Leidinger W,et al.Effect of local infiltration analgesia,peripheral nerve blocks,general and spinal anesthesia on early functional recovery and pain control in total knee arthroplasty[J].Bmc Musculoskeletal Disorders,2018,19(1):232.
[16] Han C,Li X D,Jiang H Q,et al.The use of gabapentin in the management of postoperative pain after total hip arthroplasty:a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials[J].J Orthop Surg Res,2016,11(1):79.
[17] Paul J E,Nanthaaree M,Buckley N,et al.Randomized controlled trial of gabapentin as an adjunct to perioperative analgesia in total hip arthroplasty patients[J].Can J Anaesth,2015,62(5):476-484.
[18] Zhai L,Song Z,Liu K.The Effect of Gabapentin on Acute Postoperative Pain in Patients Undergoing Total Knee Arthroplasty:A Meta-Analysis[J].Medicine,2016,95(20):e3673.
[19] Matsuda K M,Sharma D,Schonfeld A R,et al.Gabapentin and pregabalin for the treatment of chronic pruritus[J].J Am Acad Dermatol,2016,75(3):619-625.
[20] Zeng M,Dong J,Lin N,et al.Preoperative Gabapentin Administration Improves Acute Postoperative Analgesia in Patients Undergoing Craniotomy:A Randomized Controlled Trial[J].J Neurosurg Anesthesiol,2018[Epub ahead of print].
[21] Kj?r K P,Lunn T H,Husted H,et al.The influence of pre- and perioperative administration of gabapentin on pain 3-4 years after total knee arthroplasty[J].Scand J Pain,2018,18(2):237-245.
[22] Paul J E,Nanthaaree M,Buckley N,et al.Randomized controlled trial of gabapentin as an adjunct to perioperative analgesia in total hip arthroplasty patients[J].Can J Anaesth,2015,62(5):476-484.
[23] Pinto P R,Mcintyre T,Ferrero R,et al.Predictors of Acute Postsurgical Pain and Anxiety Following Primary Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty[J].Journal of Pain,2013,14(5):502-515.
[24] Theunissen M,Peters M L,Bruce J,et al.Preoperative Anxiety and Catastrophizing:A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of the Association With Chronic Postsurgical Pain[J].Clin J Pain,2012,28(9):819.
[25] Zakrzewska J M,Wu N,Lee J Y K,et al.Characterizing Treatment Utilization Patterns for Trigeminal Neuralgia in the United States[J].Clin J Pain,2018,34(8):691-699.
[26] Stefano G D,Truini A,Cruccu G.Current and Innovative Pharmacological Options to Treat Typical and Atypical Trigeminal Neuralgia[J].Drugs,2018[Epub ahead of print].
[27] Husted H,Lunn T H,Troelsen A,et al.Why still in hospital after fast-track hip and knee arthroplasty?[J].Acta Orthopaedica,2011,82(6):679-684.
[28] Clarke H,Kirkham K R,Orser B A,et al.Gabapentin reduces preoperative anxiety and pain catastrophizing in highly anxious patients prior to major surgery:a blinded randomized placebo-controlled trial[J].Can J Anaesth,2013,60(5):432-443.
(收稿日期:2018-09-12) (本文編辑:程旭然)

