尿微量白蛋白与尿糖联合检测糖尿病患者肾损伤的诊断价值分析
董庆泽 牛铁明
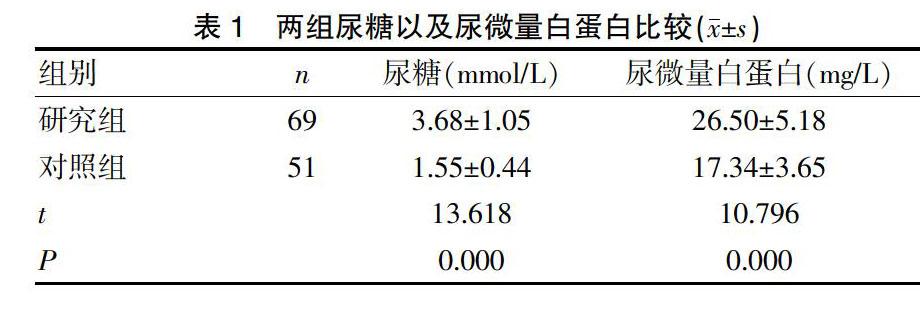
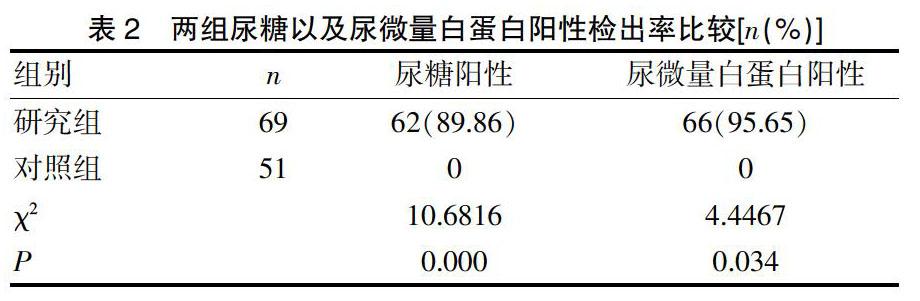
[摘要] 目的 探讨尿微量白蛋白与尿糖联合检测分析糖尿病患者肾损伤的诊断价值。 方法 2016年3月~2017年3月期间收集糖尿病肾损伤患者共69例为研究组,同期选择健康体检人群51例为对照组。对两组全部采用尿微量白蛋白与尿糖联合检测,分析研究两组阳性检出率以及尿糖尿微量白蛋白水平情况。 结果 研究组患者的尿糖水平为(3.68±1.05)mmol/L、尿微量白蛋白水平为(26.50±5.18)mg/L,明显高于对照组的(1.55±0.44)mmol/L、(17.34±3.65)mg/L,组间差异显著(P<0.05)。同时研究组患者的尿糖阳性以及尿微量白蛋白阳性检出率显著高于对照组,组间差异显著(P<0.05)。 结论 与健康人群相比,糖尿病肾损伤患者尿微量白蛋白和尿糖检测指标明显增高,采用尿微量白蛋白与尿糖联合检测可以提高糖尿病患者的检出率,值得在临床中推广应用。
[关键词] 糖尿病;肾损伤;尿微量白蛋白;尿糖
[中图分类号] R587 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2019)07-0039-03
[Abstract] Objective To explore the diagnostic value of urine microalbumin combined with urine glucose in detecting renal damage in diabetic patients. Methods A total of 69 patients with diabetic kidney injury were collected from March 2016 to March 2017 as the study group, and 51 healthy controls were selected as the control group. The combination of urinary microalbumin and urine glucose was used in both groups to analyze the positive detection rate and urine glucose and urine microalbumin levels in the two groups. Results The urine glucose level of the study group was (3.68±1.05) mmol/L, and the urine microalbumin level was(26.50±5.18) mg/L, which were significantly higher than those of the control group [(1.55±0.44) mmol/L, and (17.34±3.65) mg/L], and the differences between the groups were significant (P<0.05). The positive rate of urine glucose and the positive rate of microalbuminuria in the study group were significantly higher than those in the control group, and the difference between the groups was significant (P<0.05). Conclusion Compared with healthy people, the levels of urinary microalbumin and urine glucose in patients with diabetic kidney injury are significantly increased. The combination of urine microalbumin and urine glucose can improve the detection rate of diabetic patients, which is worthy of popularization in clinical practice.
[Key words] Diabetes; Kidney damage; Urine microalbumin; Urine glucose
人体内分泌胰岛素无法正常发挥作用或机体分泌胰岛素功能异常等均有可能导致糖尿病发生[1]。目前我国糖尿病患者以中老年患者居多,属于临床中极为常见的一种代谢紊乱性疾病,典型的症状为患者血糖明显升高。据有关调查数据显示,在糖尿病患者中,2型糖尿病者所占的比例高达90%以上[2]。待病情进展后,糖代谢紊乱可严重影响机体中脂质以及蛋白质的代谢,并能对多脏器结构造成损伤,从而引发诸多的并发症,糖尿病肾损伤便是其中一种。针对肾损伤患者而言,若血糖一直处于较高状态,极有可能对其他脏器产生一定损伤,使患者功能性紊乱,最终导致衰竭情况发生[3]。因此,对患者做好相关疾病的诊断和检查就显得极为重要[4]。本次研究对69例糖尿病肾损伤患者以及健康人群同时采用尿微量白蛋白与尿糖联合检测,现将结果报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1一般资料
收集2016年3月~2017年3月期間糖尿病肾损伤患者69例为研究组,同期选择健康体检人群51例为对照组。对两组人群全部采用尿微量白蛋白与尿糖联合检测,研究组男38例,女31例,年龄56~78岁,平均(65.3±4.8)岁;对照组男28例,女23例,年龄60~80岁,平均(66.5±5.0)岁;本次研究中所有患者均签署知情同意书,同时经我院伦理会审核批准,研究相关程序满足伦理学标准。两组研究对象性别、年龄等一般资料比较,无统计学差异(P>0.05),具有可比性。

