Inhibitory Effect of Photodynamic Therapy on Keloids
Chuan-hua YOU,Yi-he Wang ,Xue-fei LU
1Department of plastic and aesthetic surgery
2Department of anesthesiology,The first affiliated hospital of hainan medical college,Hainan Haikou 570102,china.
ABSTRACT Objective To investigate the inhibitory effect of photodynamic on keloid by observing the changes of various indicators of keloid under the action of different concentration of photosensitizer aminoketovaleric acid combined with laser.Methods Fifteen healthy nude mice were randomly divided into experimental group 1,experimental group 2 and control group .Keloid tissue was implanted into the back to form stable pathological scars.10% aminoketovaleric acid solution,20% aminoketovaleric acid solution,saline solution were applied to the back of the nude mice within 4,8 and 12 weeks,respectively,for half an hour,635 nm CW laser irradiation,and scar tissue was cut at 6,10 and 14 weeks for detection.Scar related indicators.Results Scar index,number of fibroblasts,number of TGF-beta 1 protein and alpha-SMA in the experimental group were lower than those in the control group,and more than 2 indexes in the experimental group were lower than those in the experimental group 1.There was significant difference among the groups.Conclusion 20% aminoketovaleric acid can produce cytotoxic effect,induce apoptosis of fibroblasts,regulate and reduce epithelial-mesenchymal transition of scar,and inhibit keloid.
KEY WORDS photodynamic,aminoketovaleric acid,keloid,cytotoxicity,epithelial-mesenchymal transition
Keloid is a common benign fibroplasia disease of skin tissue in clinic.It is a disease characterized by fibroblast proliferation and accumulation of extracellular matrix[1].At present,there are many kinds of clinical treatments such as surgical excision,drug injection,laser,radiotherapy,physiotherapy and so on,but the recurrence rate is high and the overall effect is unsatisfactory[2].We still need to find a treatment with exact curative effect,low adverse reaction rate and recurrence rate.We used aminolevulinic acid-photodynamic therapy (ALA-PDT)to study keloid model and achieved some results.
EXPERIMENT SUBJECTS AND MATERIALS
Experiment Animal
Fifteen healthy adult nude mice.
Reagents and Instruments
Photosensitizer:Aminovalerate Hydrochloride for External Use (5-ALA,trade name Aila,produced by Shanghai Fudan Zhangjiang Biomedical Co.,Ltd.,Chinese medicine approval No.H20070027)
Laser Equipment:Photodynamic Therapeutic Instrument(Produced by Wuhan Yage Photoelectric Technology Co.,Ltd.,Model LED-EB)
EXPERIMENT METHODOLOGY
Construction of Animal Keloid Model
Source of keloids:The keloids formed within 1 to 2 years after trauma,without any intervention treatment.They were resected by operation and confirmed by pathological examination.The patients were informed and had given consent.Construction of keloid model:Under disinfection environment,normal tissue of keloid epidermis and basal part was removed,and then cut with 1.0 cm inner diameter ring drill and scalpel to form cylindrical keloid particles with diameter of 1.0 cm and height of 0.5 cm.Two incisions of about 1.5 cm long were made at the middle line of the interval between the two sides of the back of nude mice.The incisions reached the surface of the dorsal musculofascial of the mice.The peri-wound was slightly separated.The keloid particles were buried under the skin and sutured by 2-3 stitches.Four keloids were implanted in the dorsal side of each nude mouse,and stable pathological scars were formed after 15 to 20 weeks [3].
Grouping of Experiment Animal
Fifteen nude mice were numbered from 1 to 15 in turn and were randomly divided into three groups:experimental group 1,experimental group 2 and control group.There were 60 keloids in total,20 keloids in each group on 5 mice.
Experiment Methodology
The experiment was carried out at the 4th,8th and 12th week,respectively.The keloids of nude mice were treated with 10% aminolevulinic acid solution for 30 minutes in experimental group 1,20% aminolevulinic acid solution for 30 minutes in experimental group 2,and normal saline cotton tablets in control group.Then,the continuous wave laser with 635 nm output wavelength was used to irradiate the keloids of nude mice for 20 minutes with power density of 100J/cm2 and laser spot diameter of 1cm.
Collection of Sample
Fifteen nude mice in three groups were selected at 6th,10th and 14th weeks.One keloid on the same part of the back and the surrounding normal skin were removed from each mouse.The depth of incision was from the epidermis to the surface of myofascial fascia.After incision,the back wounds of nude mice were sutured and disinfected.
Examination of Indicators
Appearance and the Microscopic &Scar Index
The surrounding fat and muscle tissues were removed from the incised keloids,which were then cut into two parts from the epidermis to the basement from the median.One part was fixed with 4% neutral formaldehyde solution,embedded in paraffin and sliced at 5 μm thickness.After HE staining,it was detected under low power light microscopy.The thickness from the highest point of the protrusion to the surface of the myofascial was measured as H1,and the thickness from surface of normal tissue skin to the myofascial as H2.The scar index HI (HI=H1/H2)was then calculated.
Fibroblast Number (NA)
Masson staining slices were examined under low power light microscopy.Five visual fields were randomly selected for each slice.The number of blue-stained collagen fibers was counted by image analysis system,and the results were averaged.
Number of Transfer Growth Factor-β1 (TGF-β1)
Method 1:Immunohistochemical staining and 200-fold light microscopy of homogenate centrifugal supernatant were performed on keloid tissues at 6th,10th and 14th week respectively.TGF-β1 was brown or yellowish brown granules.The staining results were observed in 5 visual fields.The integrated optical density (IOD)of TGF-β1 was measured by Image-Pro Plus 6.0 image analysis software[4].
Western blot test
Quantitative scar specimens were grinded and digested with trypsinase and centrifuged.lysate was added into cell precipitation to extract protein.They were photographed for retention after mixing,filming,transforming,closing and developing.The data were collected by image analysis software Image J and analyzed by Graph pad 6.0.
Statistical Methods
The experimental results were expressed as mean± standard deviation(±s),analyzed by SPSS 17.0 statistical software,and analyzed by t-test and repeated measurements of variance between groups.P <0.05 indicatedd significant difference.
RESULTS
Appearance and the Microscopic
There was no significant difference in the appearance of three groups at 6th week.From Week 9 to Week 10,the scar atrophy of the experimental group 2 was significantly better than that of the control group,and also better than that of the experimental group 1.Hardness and congestion were improved.Under electron microscopy,the nuclear membrane of the experimental group atrophied,a large number of vacuoles were found in the plasma,the number of mitochondria decreased and the volume increased,while the nuclear membrane of the control group was smooth,and the mitochondria were abundant.
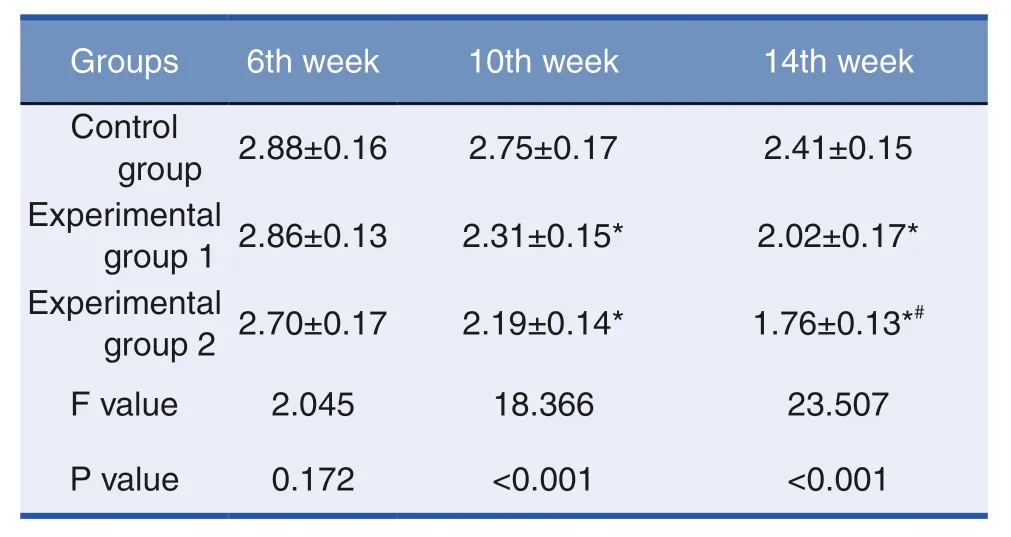
Table 1:Scar Index (n=15)
Scar Index and Fibroblast Number
The data of each group showed that after one treatment with ALAL-PDT,the scar index (Table 1)and the fibroblast number (Table 2)decreased,but not significantly.After two or three treatments,the scar index and the fibroblast number in the experimental groups were significantly lower than those in the control group,and there were also differences between the experimental group 1 and 2.There were significant differences among the groups (P <0.05).
TGF-β1 IOD Value
The expression of TGF-β1 was positive in all three groups.The number,intensity and density of positive staining granules in the control group were significantly higher than those in the experimental groups (Table 3)(P <0.01),indicating that TGF-β1 in the experimental groups decreased significantly after treatment.
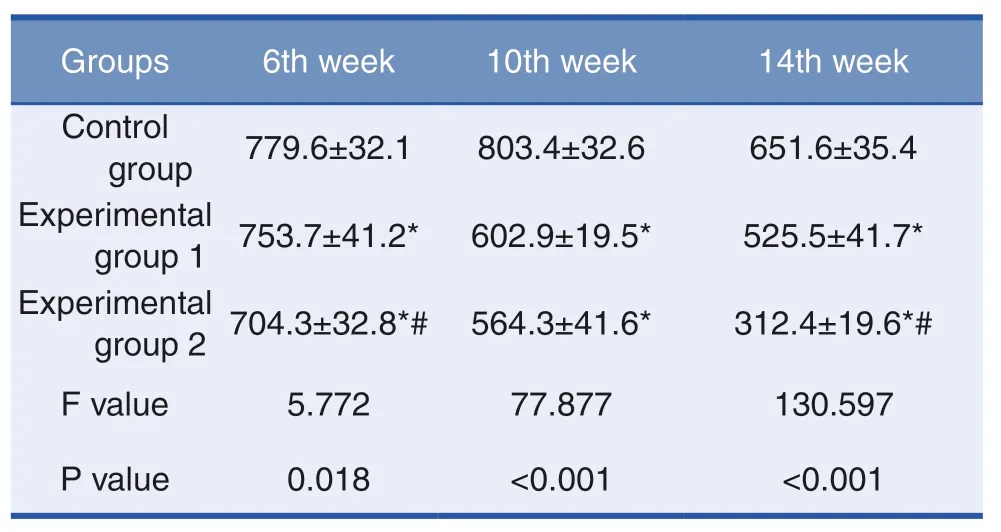
Table 2:Fibroblast Number in Scar Tissues (n=15)
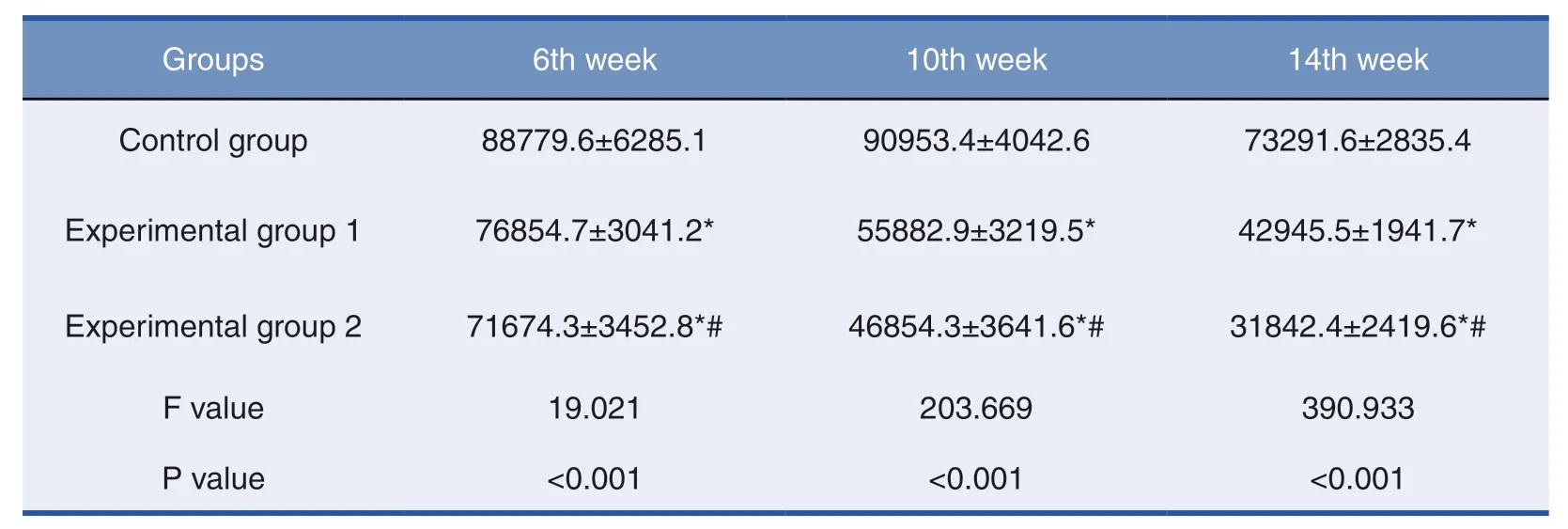
Table 3:TGF-β1 IOD Value of Scar Tissues (n=15)
Western blot Test
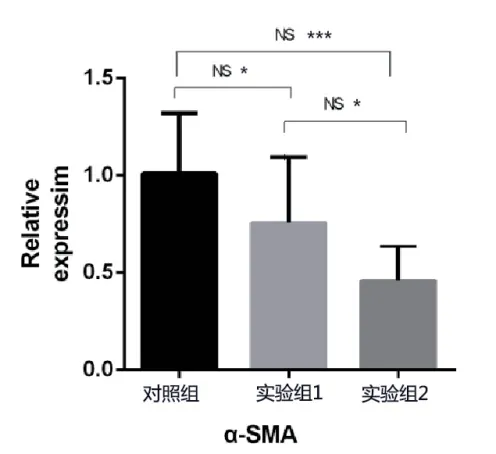
After detection,α-SMA was expressed in all three groups,in which control group was relatively higher and experimental group 2 was the lowest.There were differences among all three groups and such difference was significant between experimental group 2 and control group.
DISCUSSIONS
Keloids are mainly characterized by fibroblast disorder and excessive proliferation of collagen fibers[5].They show decompensated and uncontrolled growth.Ordinary surgical excision often results in new damage,and the repair mechanism starts.Under certain conditions,fibroblasts proliferate and regenerate into keloids in a new round.How to control the biosynthesis and proliferation of fibroblasts and induce the apoptosis of fibroblasts is the key to the inhibition of keloid growth.
Hypertrophic scars and keloids implanted into nude mice can maintain their original histological structure within about 20 weeks[6].It is therefore feasible to establish a keloid model in nude mice.The possible mechanism of the effect of PDT on keloids can be inferred through the analysis of relevant scar indicators after PDT treatment.
The cell metabolism of scar tissue is more vigorous than that of other tissues,and the absorption of photosensitizer is also higher than that of other tissues.This specific effect makes scar as a target cell of photosensitizer.After 30 minutes of external application of ALA,part of the transdermal absorption was converted into protoporphyrin IX (PpIX)in target cells,which was stimulated by 635 nm laser irradiation.PpIX undergoes type I and II photodynamic reactions,from singlet system to triplet state,and then to hydroxyl radical and singlet oxygen(1O2).These two products cause chain reaction and oxidation of free radicals[7].Fibroblasts in keloids play a dominant role in the absorption of photosensitizers in keloids.Injury directly induces apoptosis of fibroblasts,causes the atrophy of keloids,and achieves the goal of treatment.
In our study,two weeks after treatment,the thickness of scar began to decrease,the number of microvessels and fibroblasts decreased,and collagen fibers arranged in a regular and orderly manner under the microscope,indicating that early scar hyperplasia has been inhibited,which may be caused by the toxic reaction of oxidative damage.However,the degree of scar retraction in the treatment group was still much faster than that in the control group in the later stage of treatment,suggesting that oxidative reaction may not be the only reason to induce apoptosis.Skin dermal histopathology is classified as epithelial tissue,keloid as mesenchymal tissue,and the process of scar hyperplasia involves the transformation from epithelial tissue to mesenchymal tissue.Studies have shown that TGF-β1 can promote epithelial-mesenchymal transformation (EMT)[8]of keloid epidermal cells,while α-SMA is a specific expression protein of fibroblasts during epithelial-mesenchymal transformation and also an important molecular protein for the role of TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway [9].In this experiment,TGF-β1 and α-SMA in the experimental groups were significantly lower than those in the control group.By regulating the upstream signal,the secretion of cytokines and chemokines in epithelial tissue was reduced,and the expression of mesenchymal tissue-specific proteins such as α-SMA and vimentin was induced to decrease,thus inhibiting the process of EMT and preventing scarring.According to this analysis,ALA-PDT can destroy the process of fibroblast synthesis,inhibit formation and proliferation of fibroblast,as well as the production of collagen and other extracellular matrix,and ultimately inhibit scar proliferation.
In the experimental comparisons,we found that PDT+20% ALA had the best inhibitory effect on scar proliferation,which was consistent with other scholars’researches [10].However,from the appearance of the back of nude mice,even at the 16th week,there were still obvious scar bulges.PDT decreased the overall volume of keloid slowly,which may be due to the uptake and storage of more photosensitizers by fibroblasts in the superficial part of the skin.PDT treatment can play a better cytotoxic role,while deep tissue has relatively poor effect due to its limited ability of drug penetration and absorption as well as laser penetration.It also suggests that for larger keloids,the combination of PDT after surgical removal of the core may be more effective.
In conclusion,this experimental study showed that the number of fibroblasts in keloid was decreased and the scar proliferation was inhibited by ALA-PDT,especially at the concentration of 20% ALA.Its mechanism may be as follows:(1)collagen decomposition caused by laser energy;(2)photosensitizer decomposition to form singlet oxygen cytotoxicity,which induces apoptosis of fibroblasts;(3)reducing the content of TGF-β1 and α-SMA,regulating and reducing epithelial-mesenchymal transformation of keloid epidermal cells,and reducing fibroblast synthesis and extracellular matrix deposition,but further experimental studies were needed.
Fund program
Foundation project:Scientific Research Projects of HeaIth FamiIy PIanning Industry in Hainan Province(No.16A200116)
 Chinese Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery2019年2期
Chinese Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery2019年2期
- Chinese Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery的其它文章
- Experience of VSD in the treatment of foot tophi rupture with severe infection wounds
- Clinical Observation of Anesthesia Effect of 2% Lidocaine by Air Pressure Injection in Facial Skin Aesthetic Treatment
- Implantation Instrument on the Expression of Collagen-I and Cell Proliferation Markers in Pathological Scar
- Experimental Effect of Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Stress Urinary Incontinence Rats Model and Efficient Tracking in vivo with MRI
- The common complications associated with osteotomy genioplasty:A literature review and meta-analysis
- Advances in Evaluation of Facial Asymmetry
