Analysis of the action mechanism of Fang Ji Huang Qi decoction in treating rheumatoid arthritis by network pharmacology
Yang Hu, Dan Chen
1Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital, National Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Tianjin, China,
2Department of Pharmacology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin, China.
Background
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease. In China, the incidence rate of RA is increasing every year,causing great pain to patients and affecting their normal life. The cause of this disease is still unclear. Currently,the conventional clinical treatments mostly involve the use of western medicine, including anti-inflammatory drugs, hormones, anti-rheumatic drugs, and biological agents. However, the clinical treatments are not stable.and the difference between them is large, and some drugs with obvious curative effect are expensive [1]. With developments in the field of medicine, the treatment of RA has entered a stage of diversified comprehensive treatment. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) as a supplemental and alternative drug might play a key role in treating RA [2].
Fang Ji Huang Qi decoction (FHD) has been documented in Jin Gui Yao Lue, which was written by Zhong Jing Zhang at the beginning of the third century A.D., and has been recorded in the thesis of Jing Shi Bing.It consists of Fang Ji (Radix Stephaniae Tetrandrae),Huang Qi (Radix A stragali), BaiZhu (Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae), and Gan Cao (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch) in the ratio of 4:5:3:2 [3]. FHD has the effects of replenishing Qi and strengthening the spleen.Its action benefits from reducing water and phlegm, and is widely used clinically to treat rheumatic diseases,chronic glomerulonephritis, and cancerous ascites [4, 5].It is now believed that the key to the onset of RA is abnormal immunity. In Chinese medicine, RA belongs to the category "Bi Zheng". The main cause is lack of vital-Qi, caused by wind, moisture, cold, and heat [6].Several clinical studies have shown that FHD has an important role in the treatment of RA. Chen Yue et al.reported that the combination of FHD and Lei Gong Teng Tablets can significantly reduce morning stiffness, joint swelling, and joint pain in patients with RA, as well as reduce the levels of erythrocyte sedimentation rate,C-reactive protein, and rheumatoid factor [6]. Chen GX found that the effect of FHD combined with Du Huo Ji Sheng decoction on RA was higher than that of the control (methotrexate group), and it improved the main symptoms, and incidence of adverse reactions [7].
However, owing to the diversity of TCM ingredients and the complexity of interaction in human body, it is difficult to explore the potential molecular mechanism of action of the compounds, and the TCM network pharmacology provides novel ideas and perspectives for the study of complex Chinese medicine systems [8].Network pharmacology combines the concepts of systems biology and multi-directional pharmacology. It explores the relationship between drugs and diseases from a holistic perspective, emphasizing the holistic and systematic interaction between drugs, targets, and diseases, explaining the multi-component and multi-target relationship of TCM. The integrated and systematic characteristics of its research strategy coincide with the theory of TCM in diagnosis and treatment of diseases from the perspective of holistic concept and syndrome differentiation [9, 10]. In the present study, network pharmacology method was used to (1) analyze and predict the mechanism of action of FHD, (2) analyze the drug ingredients, action targets, and their relationship with RA from the perspective of compound formula, and(3) explain the mechanism of action of FHD to treat the above diseases at the molecular level, as a supplement to previous clinical studies, to provide a theoretical basis for rational and effective use of the compound formula in the future.
Materials and methods
Screening the active ingredients and targets of FHD
In this study, through the Chinese herbal medicine ingredient database TCMSP (http://lsp.nwu.edu.cn/tcmspsearch.php), all the chemical constituents of Fang Ji(Radix Stephaniae Tetrandrae), Huang Qi (Radix Astragali), BaiZhu (Rhizoma A tractylodis Macrocephalae), and Gan Cao (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch) were retrieved, and a total of 472 compounds were collected. Among them, 50 were from Fang Ji (Radix Stephaniae Tetrandrae), 87 from Huang Qi (Radix Astragali), 55 from Bai Zhu (Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae), and 280 from Gan Cao (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch). Due to limitations and high cost of biological experiments, the use of computer simulation tools to identify the pharmacokinetics of drugs(absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion) has become one of the important methods in drug research[11]. In this study, 472 compounds were screened by oral bioavailability (OB) and drug-likeness (DL), and compounds with OB ≥ 30% and DL ≥ 0.18 were selected for follow-up studies. The target protein of each active ingredient was subsequently obtained from the TCMSP database. The gene name of each target protein was obtained from the UniProtKB web platform(http://www.uniprot.org) and the Genecards(http://lsp.nwu.edu.cn/tcmspsearch.php) database.
Screening the targets of RA
Using "rheumatoid arthritis" as the key word, the current internationally recognized disease target search database CTD (http://ctdbase.org/) was used to search and screen known disease targets.
Constructing active ingredient-target network
Cytoscape is an open source bioinformatics software platform, whose core architecture is the network. Each node is a gene, protein, or molecule, and the junction between nodes represents the interaction between these biomolecules [12]. The chemical compositions of the pre-organized Fang Ji (Radix Stephaniae Tetrandrae),Huang Qi (Radix A stragali), BaiZhu (Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae), and Gan Cao (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch) and the corresponding targets were imported into Cytoscape 3.5.1 (http://www.cytoscape.org/)software to construct the compound-target network.Subsequently, the network analyzer plug-in network characteristic analysis was used to identify important ingredients and targets in the decoction, and simultaneously, track the literature to analyze the interaction.
Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network construction
To illustrate the role of FHD in the treatment of RA,target protein at the system level, the gene for drug component, and disease intersection target were uploaded to the online STRING 10.5 (https://string-db.org/)database to obtain protein interaction information. The STRING database is a database that stores known and predicted protein interactions, including direct and indirect interactions between proteins. It has a score for each protein interaction. The higher the score, the more mutual the interaction between proteins and the higher the confidence level [13]. Therefore, the high-confidence protein interaction data with a score of > 0.9 were selected and imported into Cytoscape 3.5.1 software to construct the PPI network. Further, the key genes based on the degree of value were screened.
Genetic ontology (GO) Kyot o gene and genome encyclopedia (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses
To illustrate the role of TCM compounds in the treatment of diseases, target protein genes and signaling pathways were analyzed. The DAVID 6.7 data platform(https://david.ncifcrf.gov/) was used for the GO and KEGG enrichment analyses of proteins in the PPI network. The DAVID database integrates multiple categories of database resources and uses the improved Fisher's exact test algorithm to perform enrichment analysis on gene sets, providing P-value and false discovery rate (FDR) that enrich the results of the analysis [14]. In this study, three modules, viz., biological process, molecular function, and cellular component in GO, were used to functionally annotate the genes.
Results
Component-target network construction and analysis of FHD
In this study, a total of 472 compounds were obtained from the TCMSP database. After screening by OB and DL values, 105 active ingredients were retained,including 4 from Fang Ji (Radix Stephaniae Tetrandrae),20 from Huang Qi (Radix Astragali), 7 from Bai Zhu(Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae), and 93 from Gan Cao (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch). There were 98 components for RA targets. Table 1 provides the information of top 10 active ingredients. As shown in Figure 1, the compound-target network included a total of 173 nodes and 614 edges. The red diamond node represents the Mlo ID of the drug component, and the blue circular node represents the target. The edge represents the interaction between the nodes. In this network, the average number of targets per compound was 8.18, and each target interacted with an average of 6.27 compounds. Therefore, one compound interacted with multiple targets during the treatment of RA.Simultaneously, different compounds act together on the same target, which embodies the mechanism of interaction between multi-component and multi-target of FHD, and also meets the characteristics of multi-component and multi-target synergy of TCM compounds. Using the degree value, the representative components in the network and nodes of the target were effectively screened to obtain nodes with high correlation.With respect to compounds, there were approximately nine compounds with targets > 9, of which the representative component nodes were quercetin(MOL000098), kaempferol (MOL000422), 7-O-methylisomucronulatol (MOL000378), and 7-methoxy-2-methyl isoflavone (MOL003896); among them, quercetin and kaempferol have significant anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects.
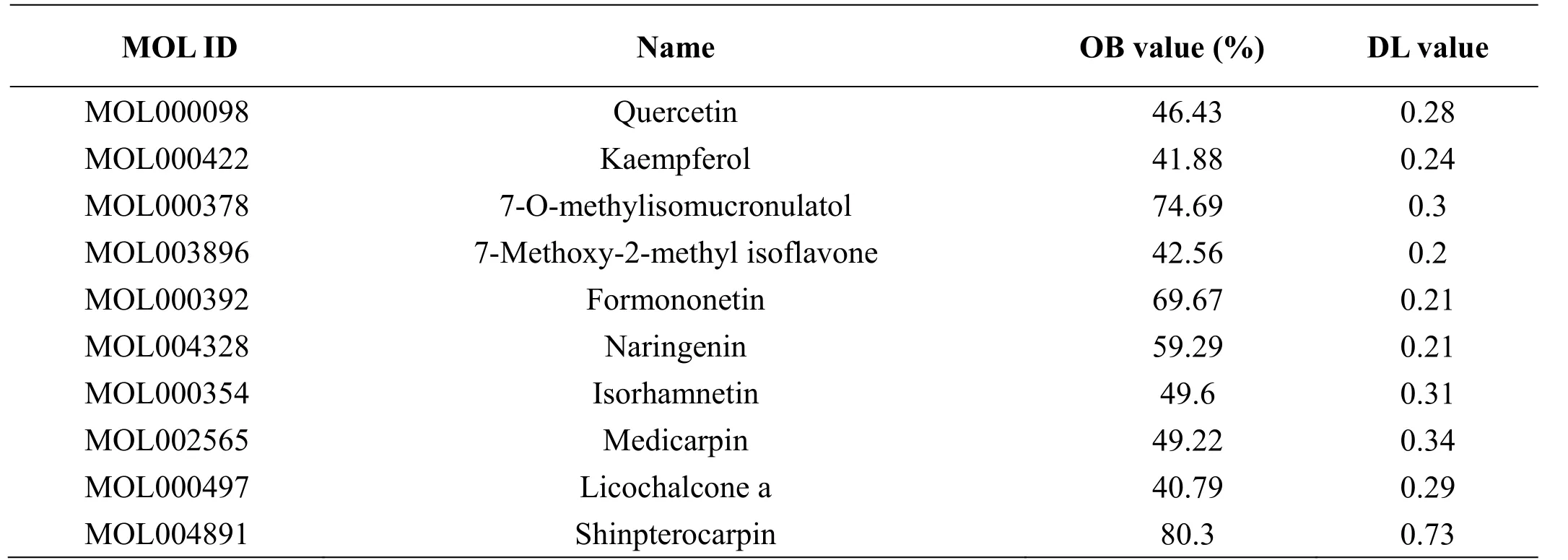
Table 1 Active ingredients information statistics
With respect to targets, the targets with higher degree of value included prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 (PTGS2)and nitric oxide synthase 2, which combined with 94 and 69 proteins, respectively. These targets play an important role in the inflammatory response and in the immune regulation process.
After data mining and molecular docking, the drug targets were input into the STRING database for analysis,and the protein interaction data were imported into Cytoscape for further analysis. As shown in Figure 2, the PPI network had a total of 75 nodes, and the interactions between the nodes were as many as 1357. The nodes represent proteins and each edge represents the interaction between proteins. According to the network topology, there were 37 key nodes with degree value higher than the mean (36.2). Among them, the highest value was for tumor protein 53, which can interact with 67 proteins, followed by JUN and interleukin 6 (IL-6),which can interact with 66 and 63 proteins, respectively.
GO enrichment and KEGG analysis
The GO and KEGG enrichment analyses were performed on 75 targets in the above PPI networks using the DAVID data analysis platform. In the GO analysis, a total of 260 entries (FDR < 0.05) were determined according to the false discovery rate (FDR), of which 246 were the most biologically functional items. Table 2 lists the top 10 biofunctional items of the crossover target genes, mainly related to the regulation of apoptosis, regulation of programmed cell death, positive regulation of molecular function, ans so on. In the KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of 75 targets in the PPI network, we obtained a total of 55 pathways. A total of 19 FDR < 0.05, including pathways in cancer (hsa05200), Toll-like receptor (TLRs)signaling pathway (hsa04620), and NOD-like receptor(NLR) signaling pathway (hsa04621). Figure 3 lists the top 10 KEGG pathways based on FDR values. The results indicate that the active ingredients of FHD might be used to treat RA, and they act on these signaling pathways.
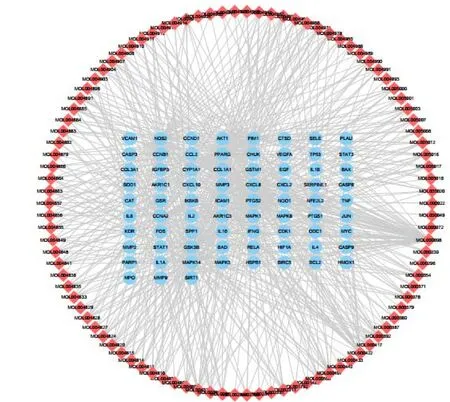
Figure 1 Component-target network
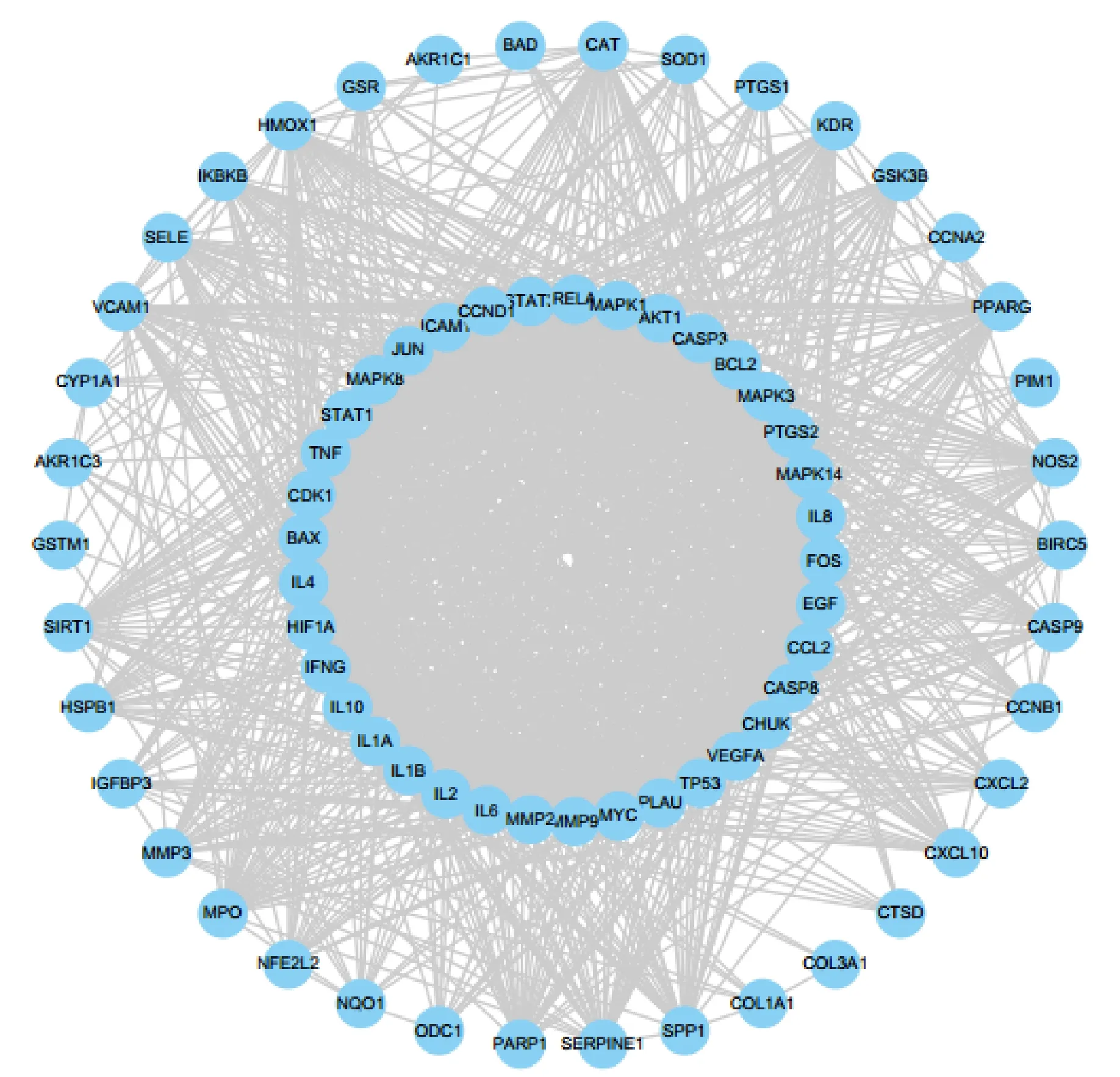
Figure 2 Protein-protein interaction network of Fang Ji Huang Qi decoction in the treatment of RA
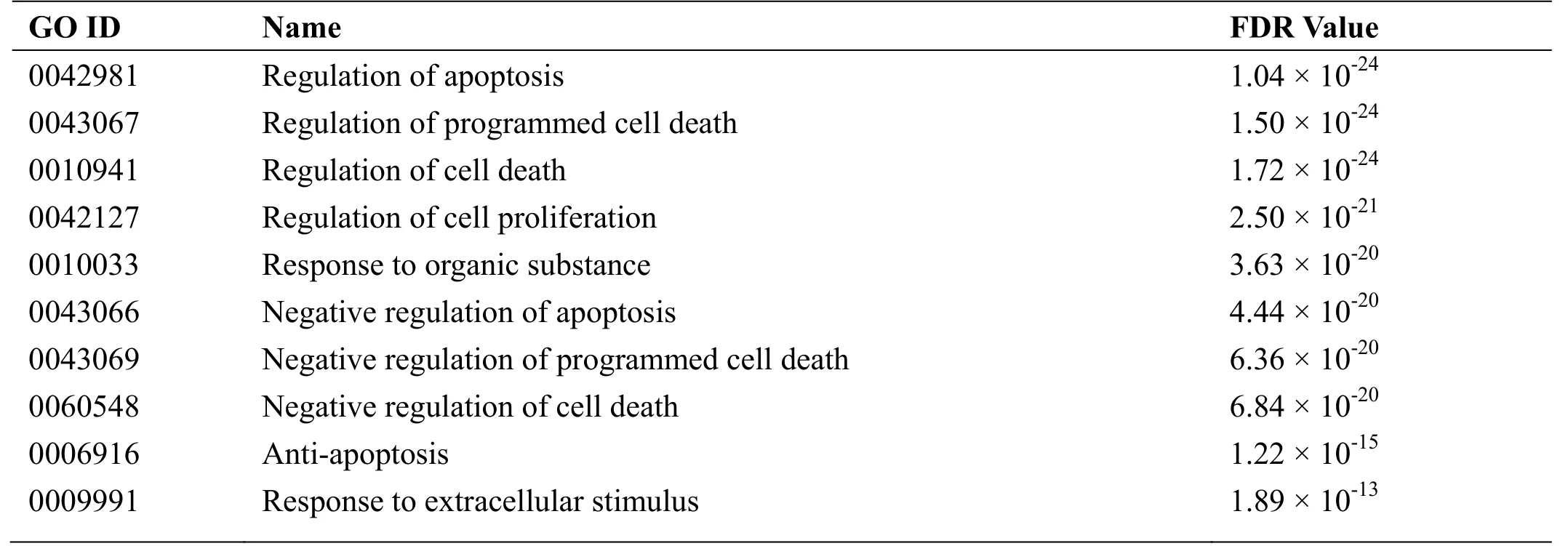
Table 2 List of GO enrichment results to genes in PPI network
Signal pathway of FHD in treating RA
Based on the above analysis, the key components and functional targets of FHD for the treatment of diseases were extracted. These targets were combined with the signal pathways they were used to map the main signal pathways for the prevention of diseases by FHD (Figure 4). As shown in figure 4, TLRs recognize pathogen associated molecular patterns, such as gram negative bacilli endotoxin lipopolysaccharide, gram-positive bacteria of the skin chitosan, and lipid teichoic acid, and activate monocyte/macrophages, neutrophils, and lymphocytes. The release of a large number of inflammatory mediators causes inflammation. Studies have shown that nuclear transcription factor-κB (NF-κB)is the central link of the immune response regulated by TLRs, and several immune molecules rely on the activation of the TLR-induced NF-κB pathway [15].Therefore, the inhibition of TLRs signaling pathway and NF-κB pathway play an important role in the inhibition of inflammatory response. In addition, NOD (the intracellular sensors of PAMPs) -like signaling pathway also plays a key role in the development of RA. The MAPK signaling pathway is a key pathway in several complex pathway networks of NLRs signaling pathways[16]. In addition, a prominent feature of RA is the proliferation of synovial cells caused by the production of a large number of high-level cytokines. The receptors for cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-α and IL-1 are enzyme-coupled receptors. When these receptors bind to the ligand, the Ras (rat sarcoma) protein is activated; this in turn activates MAPK to cause a series of inflammatory reactions [17].
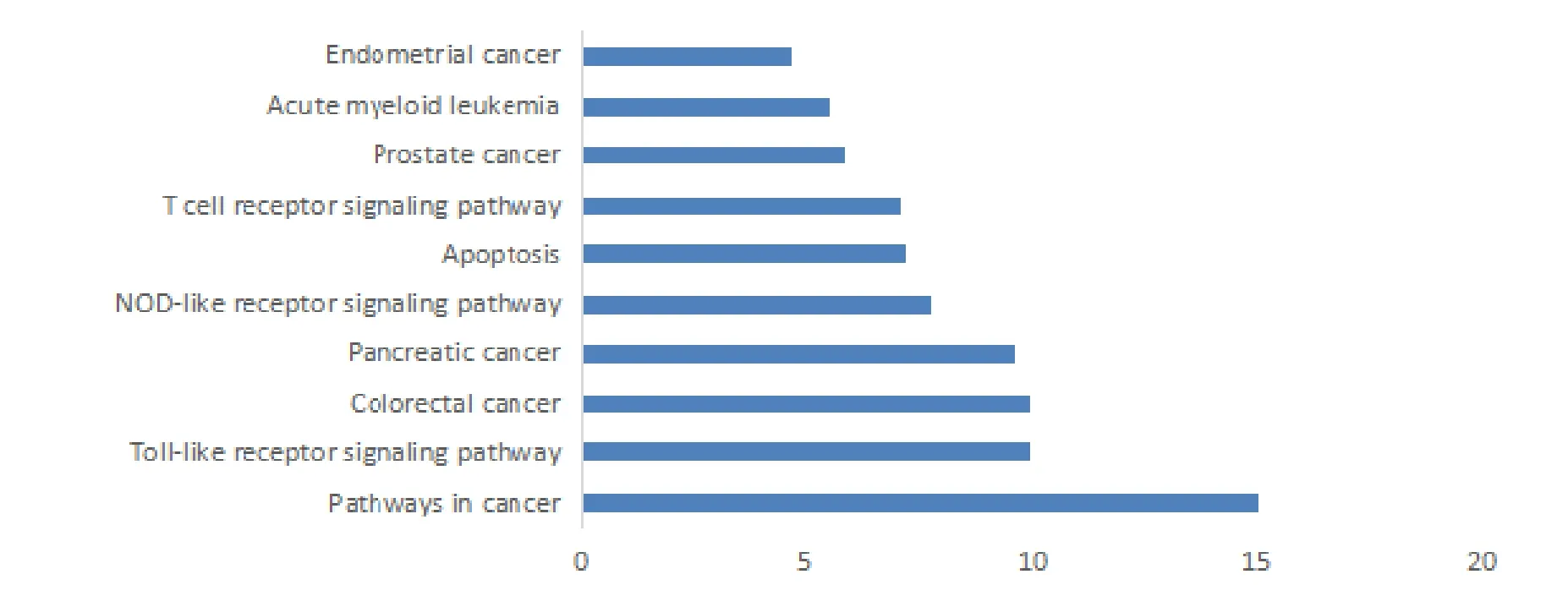
Figure 3 List of pathway enrichment results to genes in protein-protein interaction network
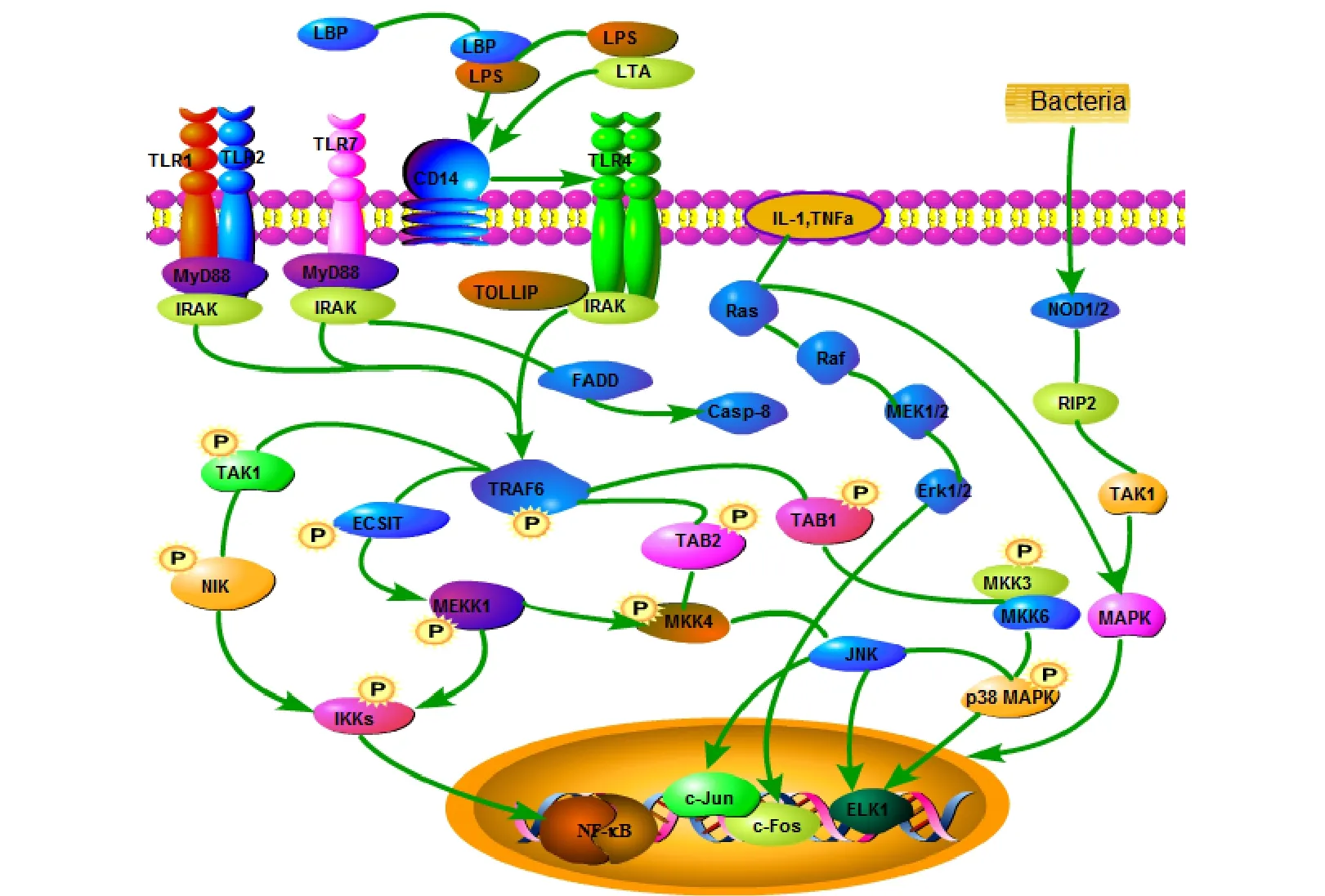
Figure 4 Signal pathways involved in Fang Ji Huang Qi decoction in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Discussion
FHD is a famous ancient prescription for treating rheumatism and Qi deficiency. It is widely used in the treatment of RA and chronic nephritis in clinical practice.With the continuous development of modern medicine,the applications of FHD are also increasing. To study the mechanism of action of FHD, this study relied on the TCMSP to study the active constituents of FHD. The CTD database queried the target of RA and constructed a compound-target network. The direct interaction between the compound and the target was analyzed, which provided a reference for the treatment mechanism of multi-component, multi-target, and multi-channel.
The key compounds in the compound-target network of FHD are quercetin and kaempferol in Gan Cao(Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch), and their degree value was much higher than that of other compounds. It is speculated that Gan Cao (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch)might play a major role in the decoction. Studies have shown that quercetin has anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor,immunomodulatory, vasodilating, and antihypertensive effects [18-20]. Xiao Peng et al. found that quercetin regulates the expression of B-cell lymphoma/leukemia-2 protein and B-cell lymphoma/leukemia-2-associated X protein to affect the apoptosis of human RA fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Subsequently, when the concentration of dermatan increased, the bcl-2/bax value decreased correspondingly, and the apoptosis rate of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in human RA increased [21].Monica Comalada et al. suggest that quercetin can exhibit its anti-inflammatory effect via the inhibition of the NF-κB pathway [22]. Kaempferol is mainly derived from the roots of the Shan Nai (Kaempferia galangal), and it is widely found in various fruits, vegetables, and beverages.It has been extracted from tea, broccoli, witch hazel,propolis, grapefruit, and other green plants [23, 24]. The signaling pathways such as MAPK, protein kinase,phosphatidylinositol3-kinase and Janus kinase/signal transducer, and activator of transcription are involved in the regulation of inflammatory mediators [25]. Activation of these signaling pathways enhances the expression of NF-κB and activator protein-1, thereby promoting inflammation. It was found that kaempferol can significantly inhibit the MAPK pathway in human monocyte-derived THP-1 macrophages induced by LPS,and reduce the production of macrophage-derived chemokine and interferon-induced protein-10 and enhance the production of IL-8 and other inflammatory factors, thereby effectively inhibiting the occurrence of inflammation [26].
The key targets in the compound-target network of FHD are PTGS2 and nitric oxide synthase 2. These targets are involved in various aspects of disease regulation such as inflammation control and endocrine therapy of tumors. PTGS is a key rate-limiting enzyme involved in the synthesis of prostaglandins from arachidonic acid. There are two isomerases-PTGS1 and PTGS2. PTGS2 plays an important role in the development of RA [27]. Studies have shown that the expression of cyclooxygenase is significantly increased in the synovial tissue of patients, accompanied by the induction of prostaglandin E2 and inflammatory factors are synthesized in large quantities. This causes the infiltration of inflammatory cells, abnormal proliferation of synovial tissue, and formation of neovascularization,resulting in swelling and degeneration of joints [28].Therefore, by inhibiting the expression of PTGS2 in synovial cells, the synthesis of prostaglandin E2 can be reduced, consequently reducing the inflammatory response of RA and improving the disease [29]. Therefore,FHD or the combination of the above components for some key targets, plays an important role in the regulation of inflammatory response.
In the present study, to illustrate the role of FHD target in gene function and signaling pathway, GO function enrichment and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses were performed on genes appearing in the PPI network.The GO function enrichment analysis found that the gene function in the treatment of RA by FHD is mainly reflected in the regulation of apoptosis, regulation of programmed cell death, and positive regulation of molecular function. pathways in cancer, NLRs signaling pathway, and TLR signaling pathway were involved in the action mechanism of FHD. Human TLRs are a class of cell surface signal transduction receptors, which play an important role in the anti-infective immunity of plants,animals, and insects [30]. NLRs are newly discovered cytoplasmic recognition receptors in the NLRs signaling pathways. NLRs and TLRs specifically identify"non-self-components" such as pathogenic microorganisms, non-microorganisms, and some dangerous signals at different sites, and interact with each other (the TLRs exhibits detonating effect) to jointly regulate the body's immune response [31]. Therefore, it is speculated that the active ingredients of FHD can be used to treat RA by acting on these signaling pathways.Besides, it is well known that inflammation is closely related to the development of cancer. The abnormal changes in the TLRs signaling pathways are also closely related to the development of tumors [30]. Therefore, the curative effects of FHD on cancer were also observed,suggesting its potential applications in the treatment of cancer.
As TCM is characterized by multi-component,multi-target, multi-level, and network-based therapeutic effects, traditional pharmacy, pharmacology, and molecular biology research is not enough to explain its complex mechanism and material basis. Based on the big data platform of network pharmacology research (a database involving multiple drug components, disease targets, protein interactions, and signal pathways), the overall analysis of the material basis and mechanism of action is not only comprehensive, but also conducive for refining its main therapeutic efficacy-related targets,components, pathways, and a comprehensive view of the problem. However, there were some limitations to this study. For example, although there are some clinical studies on the anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of the compounds analyzed, these mechanisms need to be further verified.
1. Bao CD. Current status and prospects of rheumatoid arthritis treatment. Shanghai Med J 2003, 26:449-451.
2. Li LL. Research progress on anti-rheumatic arthritis of active ingredients in natural medicine. Zhongnan Pharm 2011, 9: 130-134.
3. Wang XL. Progress in studies on the pharmacological effects and chemical components of each single flavor of fanghengqi decoction. Chin Herb Med 2016, 47: 3527-3534.
4. Zhang FX, Zhu YC, Cai YY. Advances in the application of jing fang fang ji huang qi decoction.J Guangxi Univ TCM 2013, 16: 82-84.
5. Wang WS. A preliminary study on the treatment of cancerous ascites with jia wei fang ji huang qi decoction. Chin Med Sichuan 2007, 25: 59.
6. Chen Y. Observation on the curative effect of fang ji huang qi decoction and Lei Gong Teng(Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. f.) tablet in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Sichuan Chin Med 2008, 26: 72-73.
7. Chen GX. Observation on the therapeutic effect of 32 cases of rheumatoid arthritis treated by fang ji huang qi decoction and du huo decoction. Chin Med Herald 2012, 18: 58-59.
8. Wu JR. Analysis of the mechanism of action of "flos lonicerae - forsythia" based on network pharmacology. Chin J Exp formulat 2017, 7:179-183.
9. Hopkins AL. Network pharmacology: the next paradigm in drug discovery. Nat Chem Biol 2008. 4:682-690.
10. Zhang YQ, Li S. Advances in the study of network pharmacology and TCM. Chin J Pharm Toxicol 2015, 29: 883-892.
11. Zeng L, Yang K. Exploring the pharmacological mechanism of Yanghe Decoction on HER2-positive breast cancer by a network pharmacology approach.J Ethnopharmacol 2017, 199: 68-85.
12. Missiuro PV, Liu K, Zou L, et al. Information flow analysis of interactome networks. PLoS Comput Biol 2009, 5: e1000350.
13. Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S, et al.STRING v10: protein-protein interaction networks,integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res 2015, 43: D447-452.
14. Huang DW, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 2009.4: 44-57.
15. Carmody R.J, Chen YH. Nuclear factor-kappaB:activation and regulation during toll-like receptor signaling. Cell Mol Immunol 2007, 4: 31-41.
16. Shaw PJ, LamkanfiM, Kanneganti TD. Kanneganti,NOD-like receptor (NLR) signaling beyond the inflammasome. Eur J Immunol 2010, 40: 624-627.
17. Chen XJ. Research progress in the influence of TCM on rheumatoid arthritis signaling pathway. Chin J TCM 2016, 7: 1735-1739.
18. Ke CH. Advances in the mechanism of quercetin against breast cancer. Chin J Hosp Pharm 2016, 36:1420-1425.
19. Hou GJ. A study on the antihypertensive effect and mechanism of quercetin on renal hypertension rats. J integr Chin West Med Cardiovasc Cerebrovasc Dis 2016, 2: 137-139.
20. Huang JQ. Effects of quercetin on the treatment and renal function of gout rats. Tianjin Pharm 2016, 44:188-192.
21. Xiao P. Quercetin regulates the expression of b-cell lymphoma/leukemia-2, b-cell lymphoma/leukemia-2 related X protein and its effect on the apoptosis of human rheumatoid arthritis fibroid synovial cells.Chin J Exp Surg 2016, 22: 2378-2380.
22. Comalada M, Camuesco D, Sierra SM, et al. In vivo quercitrin anti-inflammatory effect involves release of quercetin, which inhibits inflammation through down-regulation of the NF-kappaB pathway. Eur J Immunol 2005, 35: 584-592.
23. Zhang YW. Advances in the study of the biological functions of phenols. Life Sci 2017, 4: 400-405.
24. Chen YH, Zhou KY, Yuan HX. Advances in the study of the efficacy of monet. Guangdong Med 2010, 21: 1064-1066.
25. Fan G, Jiang X, Wu X et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of tanshinone IIA in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages via miRNAs and TLR4-NF-kappaB pathway. Inflammation 2016, 39:375-384.
26. Huang CH, Jan RL, Kuo CH et al. Natural flavone kaempferol suppresses chemokines expression in human monocyte THP-1 cells through MAPK pathways. J Food Sci 2010, 75: 254-259.
27. Jing WX. Correlation between vascular endothelial growth factor and rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Chin Med Clin J 2014, 21: 15-18.
28. Yao HP. Expression of synovial fibroblast cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase in rheumatoid arthritis. Chin J Lab Med 2002, 25: 24-27.
29. Zhang YH. Effects of shikonin on the expression of COX-2 in synovial fibroblasts of rheumatoid arthritis. J Harbin Med Univ 2012, 46: 261-265.
30. Yang W. Research progress on TLRs signaling pathway and tumor development. J Clin Surg 2008,16: 566-568.
31. Ma LX. Research progress in Nod-like receptors and Toll receptor-mediated inflammation. Int J Immunol 2009, 5: 345-349.
 Traditional Medicine Research2018年6期
Traditional Medicine Research2018年6期
- Traditional Medicine Research的其它文章
- The role of Si-Jun-Zi decoction in the management of gastric precancerous lesions and its mechanism
- Recent advances in network pharmacology applications in Chinese herbal medicine
- A network pharmacology approach to investigate the mechanisms of Si-Jun-Zi decoction in the treatment of gastric precancerous lesions
- Network pharmacology-based approach to investigate the mechanisms of Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang Powder in the treatment of malignant tumors
- Camel milk could be helpful in the treatment of asthma
