A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of Yiyiren Decoction in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Hai-Yu Wang, Chen-Hui Song, Fang-Kai Li, Xiao-Ping Liu , Wei Zhen, Yu-Ting Zhang, Yue-Lan Zhu, Xiu-Juan Hou*
1Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China. 2Dongfang Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine,Beijing, China.
Abstract Objective: To systematically evaluate the efficacy and safety of Yiyiren Decoction combined with western medicine and western medicine alone in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Methods: Databases of CNKI, VIP, Wanfang Data,PubMed, Medline, Cochrane Library, and Embase were retrieved by computers. The references of the included studies,relevant dissertations, and conference proceedings were manually retrieved. The search intervals were from the database inception until July 2017. The retrieval and screening of studies were carried out respectively by 2 researchers, and the quality and data were evaluated and extracted according to Jadad quality scale. Meta-analysis was performed with RevMan5.3 software. Results: (1) A total of 7 randomized controlled trials and 485 patients were enrolled, among which 262 cases were in experimental group and 223 cases were in control group. The point of 2 studies was 3, other studies were 1-2. The studies included indicated that the group baselines were comparable. (2)The total effective rate of Yiyiren Decoction with western medicine group was higher than that of western medicine group (RR = 0.85, 95%CI [0.78, 0.92].Improved Conditions of tender joint count (MD = -2.79, 95%CI [-3.47, -2.12]); erythrocyte sedimentation rate (MD =-9.5, 95%CI [15.67, -3.33]); and C-reactive protein (MD = -3.36, 95%CI [-5.45, -1.27]) were superior to control group.There was no significant difference on the side effects of drugs and the rheumatoid factor between the two groups.Conclusion: Yiyiren Decoction with western medicine had advantages in alleviating clinical symptoms and laboratory index of rheumatoid arthritis patients. While, the quality of included studies was low and possible publication bias was present, further multi-center double-blind randomized control trials with larger sample are needed.
Keywords: Rheumatoid arthritis, Yiyiren Decoction, Meta-analysis
Background
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is one of the most common inflammatory arthritis [1], the longer sick period, the higher the disability rate, which often brings an economist burden and mental stress to the patients and families. Therefore, it will have great significance to choose the realizable and effective treatment for patients with RA to improve the quality of life, and reduce economic as well as psychological burden. The disease has no way to cure currently, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, diseases modifying anti-rheumatic drugs, glucocorticoids, biological agents and other commonly used clinical drugs will cause varying degrees of adverse reactions [2], thus affecting the long-term treatment of this disease. Chinese medicine has a better advantage in the treatment of the disease.Yiyiren Decoction from theLeizhengzhicaiis a classic prescription in the treatment of RA induced by cold and dampness. At present, a number of studies have proved the effectiveness and safety of Yiyiren Decoction combined with western medicine in the treatment of RA[3]. Due to the small sample size, the clinical significance of guiding the clinical treatment is limited. In this study,the meta-analysis method was used to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Yiyiren Decoction combined with western medicine in the treatment of RA, and to provide some evidence for clinical diagnosis and treatment.
Materials and methods
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Study type.Randomized controlled trials (RCTs)published at home and abroad and language limited to Chinese and English.
Subjects of study.All included cases were in line with the diagnostic criteria for RA established in the United States in 1987. Chinese medical syndrome, age, and gender were not limited. Exclusion criteria: (1) Pregnant and lactating women. (2) People who were allergic to drugs. (3) Patients with severe liver and kidney function and hematopoietic system damage. (4) People with mental abnormalities. (5) Literature without the full text.
Intervention measures.Patients in experimental group were given Yiyiren Decoction combined with western medicine treatment. The control group was treated with western medicine alone. The western medicine used in two groups was exactly the same. Different western medicine or combined with other traditional Chinese medicine preparations and massage therapy were excluded.
Outcome indicators.The effective indicators: total effective rate; clinical quantitative indicators: morning stiffness time, tender joint count. The main laboratory indicators: erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR),C-reactive protein (CRP). Adverse reactions: blood toxicity, gastrointestinal reactions, liver and kidney injury,etc.
Search strategy
To retrieve literature published at home and abroad. The database of CNKI, VIP, Wanfang, PubMed, Medline,Cochrane library, and Embase were searched from database inception until 2017 July. At the same time,references of the literature were also retrieved. Search terms were used:#1 yiyirenDecoction, #2 Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), #3 “randomized controlled trials” OR“random” OR “control” OR “trials”, #4 #1 and #2 and #3.
Screening the data included
Two researchers independently completed the literature screening and data extraction. In case of disagreements,they discussed to come to an agreement. By reading the title and abstract of literature, the literature not meeting the inclusion criteria were initially screened. For the literature which may meet the inclusion criteria, it is needed to read the full text to decide whether or not to be included. If the opinion is inconsistent, it will be determined by the experienced third party in the team.
Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
The quality of included studies was evaluated by the revised Jadad quality scale [4] (low quality: 1-3 points,high quality: 4-7 points). Evaluation content: (1) the generation of random sequences; (2) allocation of hidden;(3) blind method; (4) quit/lost to follow-up. The methodological quality evaluation was performed by two reviewers independently. In case of disagreement, the third party would discuss and resolve it.
Statistical methods
Meta-analysis of the extracted outcome was performed using the Rev Man 5.3 software provided by the Cochrane Collaboration Network. Continuous variable was represented as mean difference (MD), the standard mean difference (SMD) was used when the measurement scale of the outcome indicator is different; the relative risk (RR) or odds ratio (OR) was used for the dichotomous data, with 95% confidence interval (CI). I2<50% suggested there was no statistical heterogeneity among the studies, and fixed effect model was adopted;and I2> 50% suggested the heterogeneity existed in the study, and random effects model was adopted;P< 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Characteristics of included studies
We screened 54 literature initially and 7 literature were included eventually [5-11]. The flowchart of literature screening process was shown in Figure 1, and the characteristics of the literature were shown in Table 1.
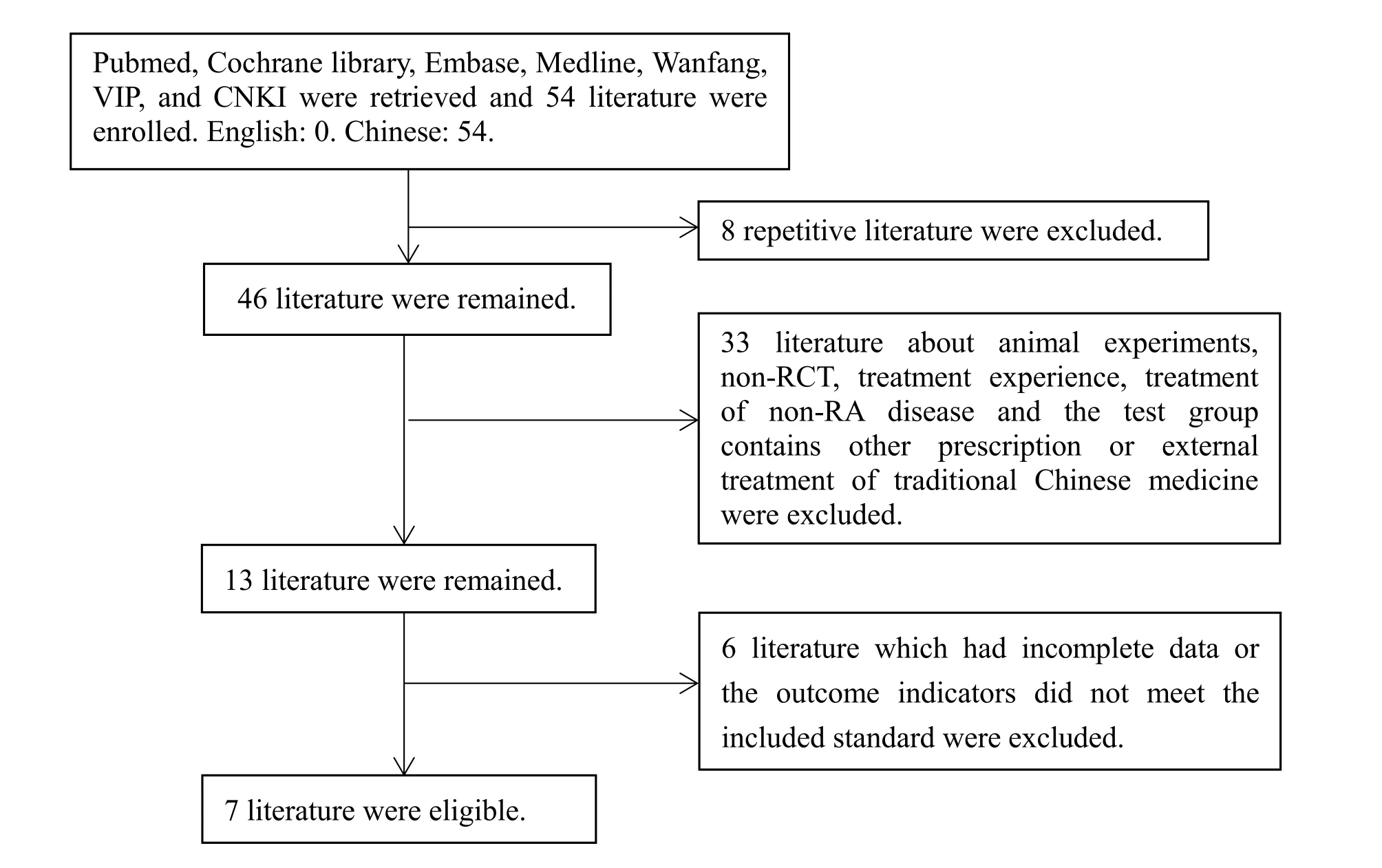
Figure 1 Flow chart of literature screening
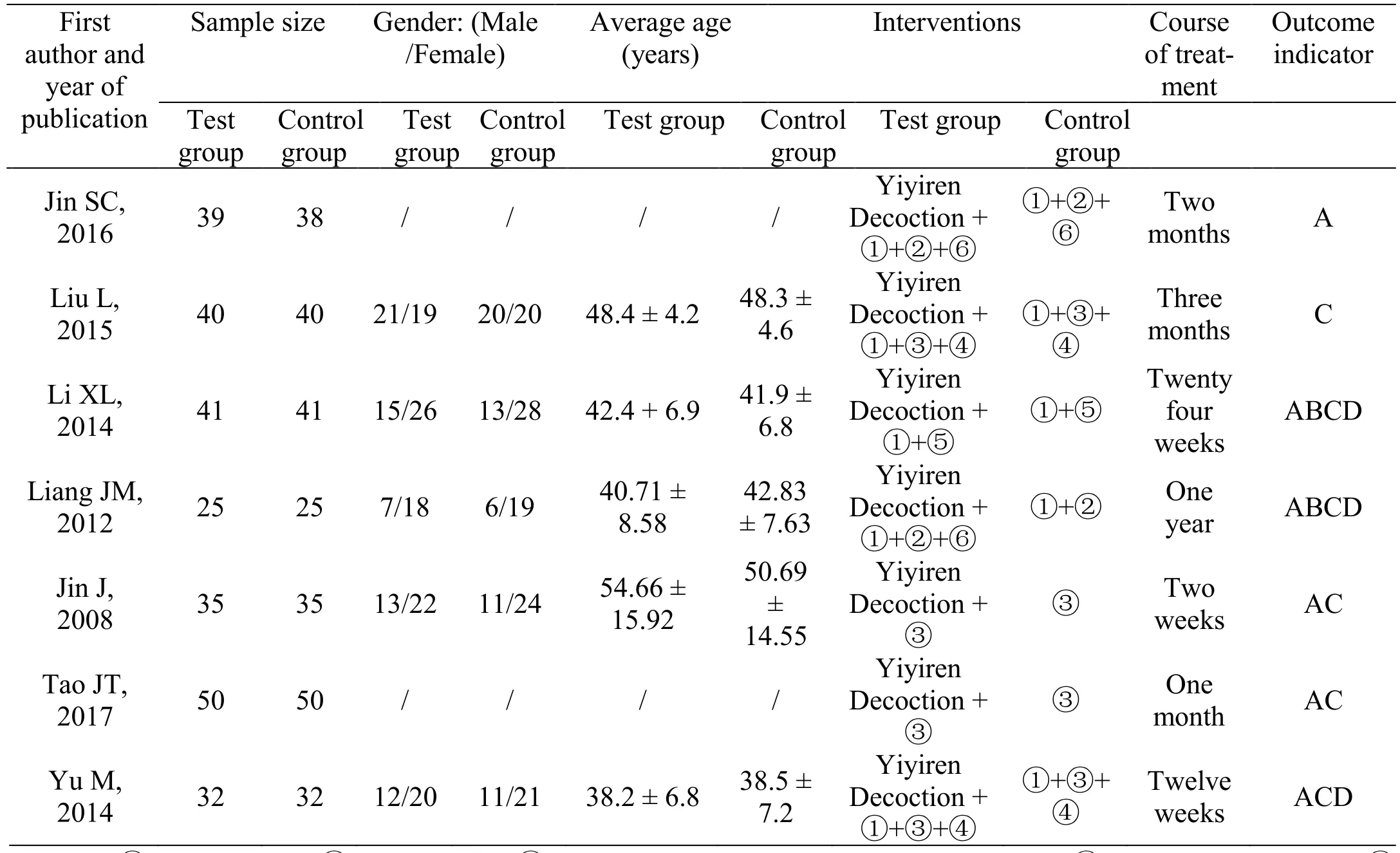
Table 1 Characteristics of inclusion literatures
Quality evaluation results
In this study, a total of 7 Chinese literature were included.The quality evaluation of all the literature was performed according to the Jadad quality scale. Among them, there were 2 literature with 3 points [7-8], and the remaining literature were 1-2 points [5-6, 9-11]. All of the included literature referred to randomization, of which four studies had shown the method of randomization [5, 7-8, 10].None of the seven studies referred to allocation concealment and blind method. Seven studies were randomized and indicated that the baseline between groups was comparable, without uncompleted report outcome, and selective report outcome. Specific design methods and quality evaluation were shown in Table 2.
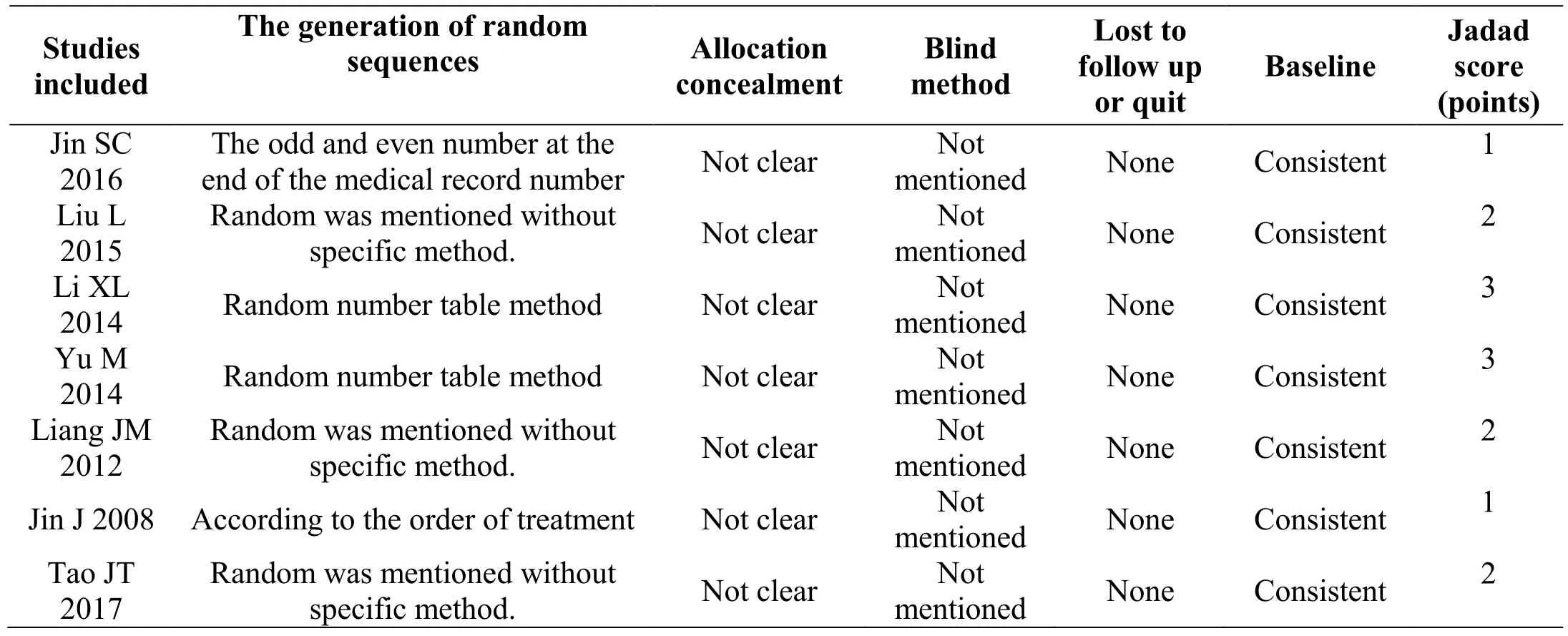
Table 2 Methodological evaluation of studies included
Meta-analysis of the results
Effective rate.Six studies including 405 patients were reported total effective rate [5, 7-11]. There was no heterogeneity among the studies (P= 0.91, I2= 0), and a fixed effect model was selected (Figure 2). Results of meta-analysis showed that the total effective rate of the experimental group was significantly higher than that of control group, the difference was statistically significant(RR = 0.85, 95%CI [0.78, 0.92],P< 0.001).
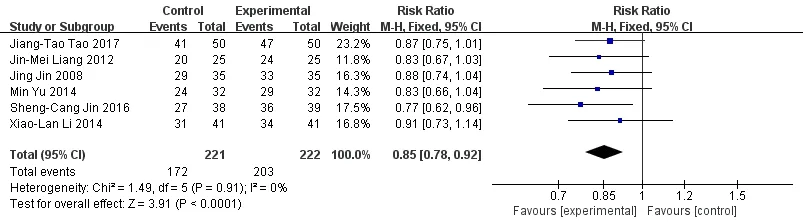
Figure 2 Meta-analysis forest map of two groups of total effective rate
Meta-analysis forest map of CRP in both groups.CRP was reported in 3 literature [7-9]. Meta-analysis showed that the experimental group was superior to the control group in the aspect of CRP, and the difference was statistically significant. (MD = -3.36, 95%CI [-5.45,-1.27],P= 0.202) (Figure 3).
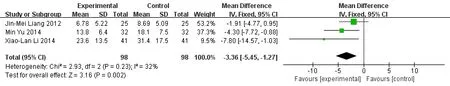
Figure 3 Meta-analysis forest map of CRP in both group
Meta-analysis forest map of two groups of ESR.ESR was reported in 3 literature [7-9]. Meta-analysis showed that the experimental group was superior to the control group in the ESR, and the difference was statistically significant. (MD = -9.5, 95%CI [15.67, -3.33],P= 0.003)(Figure 4).
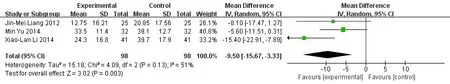
Figure 4 Meta-analysis forest map of two groups of ESR
Meta-analysis forest map of the joint tender count.The joint tender count was reported in 3 articles [6-8].Results of meta-analysis showed that the joint tender count of the experimental group was significantly less than that of the control group. (MD = -2.79, 95%CI [-3.47,-2.12],P< 0.001) (Figure 5).
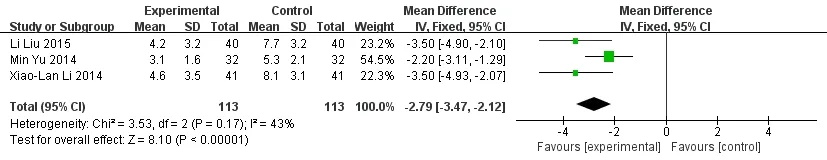
Figure 5 Meta-analysis forest map of the joint tender count
Meta-analysis forest map of rheumatoid factor in two groups.Rheumatoid factor (RF) was reported in 3 articles [7-8]. Results of meta-analysis showed that RF in the experimental group has no statistical significance compared with the control group (SMD = -0.17, 95%CI[-0.50, 0.16],P= 0.31) (Figure 6).

Figure 6 Meta-analysis forest map of rheumatoid factor in two groups
Meta-analysis forest map of the incidence of adversereactions in 2 groups.Adverse reactions were reported in 2 literature [7-8]. Meta-analysis showed that there was no significant difference between the experimental group and the control group (OR = 1.23, 95%CI [0. 05, 28.89],P= 0.90) (Figure 7).
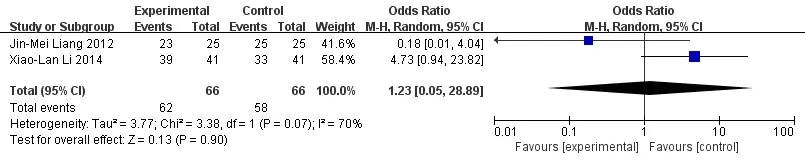
Figure 7 Meta-analysis forest map of the incidence of adverse reactions in 2 groups
Publication bias and sensitivity analysis
Inverted funnel plot of publishing bias.The funnel plot about the total effective rate of Yiyiren Decoction combined with western medicine group and western medicine group alone treating RA was made to perform publication bias analysis. The funnel plot of total effective rate is asymmetric, suggesting the possibility of publication bias existed, which indicates the low quality of studies included. This may be related to the fact that negative results were not included and positive results were easily published (Figure 8). Because the number of ESR, CRP, joint tenderness, and adverse drug reactions were less than 4, the funnel plot analysis of its publication bias was not performed.
Sensitivity analysis.The results of the meta-analysis of the total effective rate, CRP, joint tender count, adverse drug reaction, sensitivity analysis of effect model did not substantially change the results of meta-analysis. This indicated the results of the study were reliable. But the resultant effect of ESR and RF have changed, which indicated the instability existed in meta-analysis. The results of the specific sensitivity analysis were shown in Table 3.
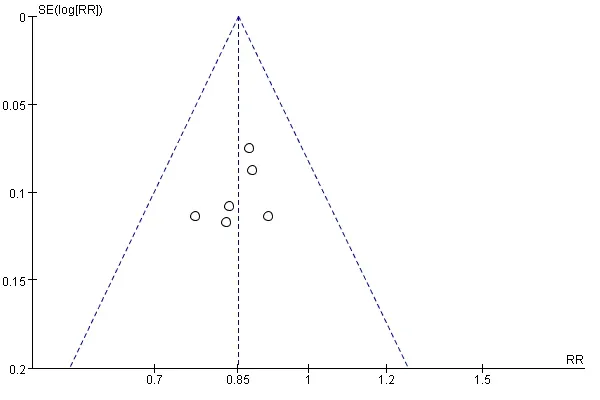
Figure 8 Inverted funnel plot of publishing bias analysis of the total effective rate
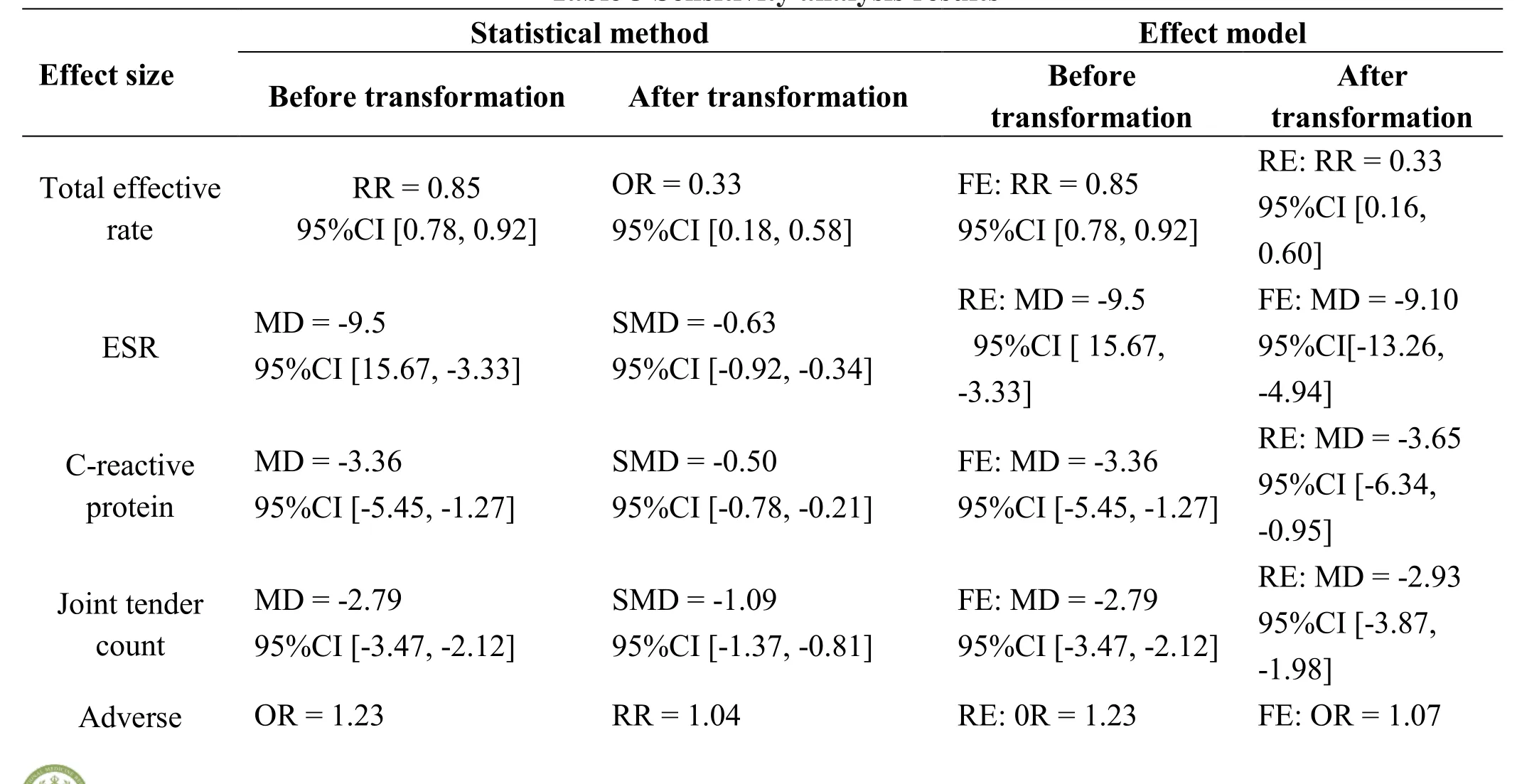
Table 3 Sensitivity analysis results

reactions 95%CI [0.05, 28.89] 95%CI [0.80,1.35] 95%CI [0.05, 28.89] 95%CI [0.95,1.20]Rheumatoid factor SMD = -0.17 95% CI [-0.50, 0.16]MD = -4.99 95%CI [-11.25, -1.26]RE: SMD = -0.17 95% CI [-0.50, 0.16]FE: SMD = -0.18 95%CI [-0.55,0.20]
Discussion
Methodological Quality of Literature
Seven studies included were in low quality according to the Jadad quality score. Only three literature referred to random and did not mention the specific method of randomization. All the literature did not mention the allocation concealment and blind method. Absence of blind method may be relevant to the usage of traditional Chinese medicine decoction, which was difficult to be blind in clinic. Most of the studies did not mention follow-up and loss to follow-up, which affected the quality of the literature. The study also found that the number of negative results of the literature was small, and a certain publication bias might exist.
Curative effect analysis
Yiyiren Decoction is from theLeizhengzhicai, in which Yiyiren (Coicis Semen) and Cangzhu (Atractylodes Rhizoma) can tonify spleen and dehumidify; Duhuo(Angelicae Pubescentis Radix), Qianghuo (Notopterygh Rhizoma Et Radix) and Fangfeng (Saposhnikoviae Rdix)can dispel wind and overcome dampness; Chuanwu(Aconiti Radix), Mahuang (Ephedrae Herba) and Guizhi(Cinnamomi Ramulus) can warm and activate meridian,dissipate cold and dispel dampness; Danggui (Angelicae Sinensis Radix) and Chuanxiong (Chuanxiong Rhizoma)can nourish the blood and promote blood circulation and promote the circulation of qi; Shengjiang (Zingiberis Rhizoma Recens), and Gancao (Glycyrrhizae Radix Et Rhizoma) can invigorate spleen and regulate the middle warmer, avoid evil and preserve substantial vital energy.All herbs combined can dissipate cold, dispel dampness and activate meridians to stop pain. It's reported that Yiyiren Decoction can significantly inhibit the ear inflammation caused by xylene, and significantly reduce the permeability of capillaries and the PGE2 content of inflammatory tissue, which has good anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. Yiyiren (Coicis Semen) is sweet,tasteless, and cold in nature, which can clear damp,promote diuresis, invigoratie the spleen, stop diarrhea,treat rheumatism, and expel pus. Studies indicated that Yiyiren’s active ingredient coixenolide can increase the proportion of Foxp3+, CD4+, CD25+, and Treg in collagen-induced arthritis mice, which may have an immunoregulation in RA [13]. This study evaluated the efficacy of Yiyiren Decoction combined with western medicine in the treatment of RA by the meta-analysis method of the Cochrane Handbook. The results showed that the total effective rate, CRP, ESR, joint tender count and morning stiffness time in Yiyiren Decoction combined with western medicine were better than those in western medicine group. In the aspect of RF and the incidence of adverse reactions, the difference was not statistically significant. Taking into account the limitation of the literature included, it needs to further develop a multi-center, random, double-blind, and large sample study to provide a higher level of evidence.
The limitations of this system evaluation
(1) Blind method in literature included was not adopted,which may have a psychological impact on patients and further affect the clinical efficacy. (2) The original data of many literature were incomplete and can’t be obtained after contacting the authors by E-mail, which affected the comprehensiveness of the data. (3) The confounding factors of different randomized controlled trials included would affect the authenticity and the reliability of the study.
The significance for future research
In recent years, studies concerning Chinese medicine in the treatment of RA are getting more and more, but the quality of methodological still needs to be improved.Evidence-based medicine requires a high-quality RCT study, but only two of the seven literature included in this study were rated as 3 points based on the Jadad quality scale, the others were 1 to 2 points, and the quality of the literature was low in general. Therefore, it is recommended that future relevant studies should clearly report the generation method of random sequences; the hiding measures of random allocation programs; blind method or placebo control should be used; the dispose of quit or loss to follow-up; the integrity of the test data should be made to avoid selective outcome report; and tracking drug adverse reactions. Ensure the authenticity and reliability of the research results as far as possible.
 TMR Modern Herbal Medicine2018年2期
TMR Modern Herbal Medicine2018年2期
- TMR Modern Herbal Medicine的其它文章
- Acupuncture for hyperlipidaemia in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Chinese medicine in the treatment of intracranial vascular stenosis in 1 case
- Clinical evaluation of Xiaoyao Jieyu prescription in the treatment of persistent postural-perceptual dizziness
- Shenxian Shengmai Oral Liquid for treatment of slow arrhythmia: a randomized controlled trial
- Metabolites identification and quantification of antcin H in mice tumors after oral administration of the anticancer mushroom Antrodia camphorata
- Progress of Alzheimer’s disease related glucose metabolism regulating hormones and a research perspective in nootropics of herbal medicine
