基于新型肌肉定量评估仪分析影响小腿三头肌硬度的因素
李亚鹏,冯亚男,朱 毅,张红庆,刘书芳,张志杰
1.广州体育学院运动康复教研室,广东广州市510500;2.河南省洛阳正骨医院,河南省骨科医院,河南洛阳市471002;3.海南省农垦总医院康复治疗中心,海南海口市570311
肌肉硬度是肌肉机械特性的重要参数之一[1],能够客观反映肌肉的功能状态[2]。通常肌肉在疲劳[3]、痉挛[4]和帕金森病[5]等病变状态下硬度显著增加。目前临床中对肌肉硬度的检查往往通过双手触诊来评估,但是双手触诊有很大的主观性,不能对肌肉机械特性进行量化评估[6]。因此,及时准确地测量肌肉硬度对早期病变的监测有重要意义。此外,肌肉的硬度受性别、年龄和负重程度等因素影响。
目前,临床上对肌肉硬度的评估有磁共振弹性成像(magnetic resonance elastography,MRE)和超声弹性成像(ultrasound elastography)。Domire等[7]用 MRE 分析年龄对骨骼肌剪切模量的影响,发现两者之间不相关。Chino等[8]对放松状态下腓肠肌肉硬度、Brandenburg等[9]对健康儿童被动拉伸下腓肠肌肉硬度进行测量并进行信度研究,结果发现超声弹性成像有很高的信度,而且没有性别差异。Eby等[10]发现,无论哪个年龄段,女性肌肉剪切模量总比男性高。Chino等[11]发现踝关节跖屈30°下,腓肠肌内侧头硬度无性别差异。目前,新型肌肉定量评估仪MyotonPRO也可以测量肌肉硬度,例如肱二头肌[12]、股四头肌[13]和小腿三头肌[14]等,有操作简单、无创、便携和快速检测等优点。
前期研究结果显示,影响肌肉硬度的因素无确切的结果。本研究旨在应用新型MyotonPRO探讨影响小腿三头肌硬度的因素。
1 对象与方法
1.1 对象
2016年8月于河南省洛阳正骨医院(河南省骨科医院)筛选40例健康实习生参加,其中男性20例,女性20例;平均(24.50±1.26)岁;身高(168.72±8.80)cm;体质量(61.05±9.70)kg;体质量指数(body mass index,BMI)(21.35±2.16)kg/m2;每周运动时间1~5.0 h,平均2.5 h。
纳入标准:①无小腿部肌肉拉伤史、创伤史;②无骨盆倾斜;③无扁平足和踝关节内、外翻;④无脑及脊髓神经病变等导致的颈肩部、小腿肌肉萎缩等疾病。
排除标准:①患有跟腱炎、足底筋膜炎;②测前有大量运动;③测量过程中不配合。
本研究经河南省洛阳正骨医院伦理委员会批准,所有受试者均签署知情同意书。
1.2 仪器及测量原理
MyotonPRO通过将探头把预压力(0.18 N)加于被测目标的表面,通过机械脉冲快速释放0.58 N(15 ms),再由加速度感应器记录肌肉的振荡(400 ms),然后通过对原始信号进行处理(10 ms)计算出参数(5 ms)。这些参数包括:①肌张力或肌肉压力的状况,自然阻尼振荡频率(Hz)(natural oscillation frequency,F)描述肌张力或肌肉压力;②生物力学特性,动态硬度(dynamic stiffness,S)、自然阻尼振荡的对数衰减量(logarithmic decrement of natural oscillation,D)描述肌肉弹性;③黏弹性,机械压力释放时间(ms)(mechanical stress relaxation time,R)、肌肉达到最大变形所需时间和肌肉内部机械压力释放时间的比率(ratio of deformation and relaxation time,C)又称为德博拉数。本研究只观察S。
1.3 腓肠肌内、外侧头硬度测量
测量前,告知受测人员测试程序,取得受测人员配合。令受试者俯卧于治疗床,下肢自然伸直,双脚悬于床外[15]。测量点位于腘窝横纹两侧至内、外踝距离的30%处,因为此处肌肉横截面积最大[16]。测量前令受试者先休息放松5 min,之后由测试人员用MyotonPRO测量利腿与非利腿腓肠肌内、外侧头的硬度。其中利腿按照在受试者面前放一个足球,受试者潜意识用哪条腿踢球来选取[17]。每个标记部位分别测量3次,取平均值。
1.4 统计学分析
本研究采用SPSS 16.0统计软件对所测量的数据进行统计学分析。所有计量资料均以(xˉ±s)表示。采用独立t检验分析性别对腓肠肌肉硬度的影响。采用相关性分析分析体质量对腓肠肌肉硬度的影响。采用配对t检验分析对比利腿和非利腿腓肠肌外侧头和内侧头硬度。显著性水平α=0.05。
2 结果
男性两侧腓肠肌内、外侧头硬度明显大于女性(P<0.01)。见表1。体质量与两侧腓肠肌内、外侧头硬度均呈正相关(P<0.05)。见表2。利腿与非利腿外侧头、内侧头硬度均无显著性差异(P>0.05)。见表3。
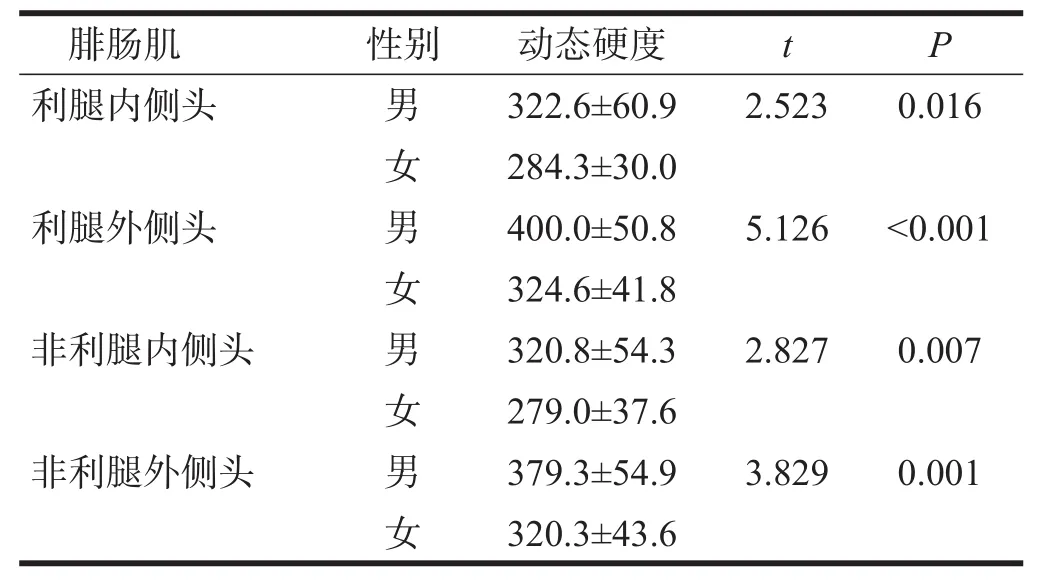
表1 不同性别受试者两侧腓肠肌内、外侧头硬度(N/m)

表2 体质量与两侧腓肠肌内、外侧头硬度的相关性分析

表3 利腿与非利腿内、外侧头硬度比较(N/m)
3 讨论
本研究发现,性别对腓肠肌肉内、外侧头硬度有影响,其中男性利腿外侧比女性大23.23%,内侧比女性大13.47%;非利腿外侧比女性大18.42%,内侧比女性大14.98%。Morse[18]对腓肠肌被动拉伸下的硬度进行分析,发现男性硬度比女性大,其原因可能是不同性别人群肌肉黏弹性不同。Dietsch等[19]用Myoton-3测量不同年龄、性别受试者的肌肉硬度,发现与性别显著性相关,并表明可能与组织成分和厚度有很大的关系。Wang等[20]对放松和收缩状态下肌肉硬度进行性别对比,结果表明女性比男性硬度低;可能与男性肌肉有更大的横截面积、质量,有更多的肌肉纤维横桥和肌联蛋白有关。因此,在评估患者肌肉硬度时,应注意性别差异引起的肌肉硬度的不同。
本研究还发现,腓肠肌内、外侧头硬度与体质量呈正相关,这与先前国外学者关于负重研究结果相一致。Blackburn等[21]进行等长、等张训练对腘绳肌硬度的影响,用肌电图评估腘绳肌肉硬度,结果发现硬度与等长训练明显相关(P=0.006),与等张训练不相关(P=0.089)。Green等[22]通过MRE对倒走离心训练后腓肠肌内侧头硬度进行测量,结果硬度增加17%。Murayama等[23]进行肘屈肌离心训练的研究,结果肌肉硬度在3 d后增加45%。同样Janecki等[24]用Myoton-3对肘屈肌离心训练后即时效应进行测量,结果硬度增加13%,并且保持5 d。负重对肌肉硬度的影响可能是因为过大的负重增加肌肉内的压力与张力,日久改变肌肉纤维不同类型的构成比例。不同的负重训练研究,可以科学地指导康复锻炼。
此外,本研究还发现利腿与非利腿的内、外侧头硬度均无显著性差异。表明在两侧对称性良好的前提下,进行临床评估时,可以用健侧与患侧对比,进行对照分析治疗前后的效果。
MyotonPRO是由爱莎尼亚Vain博士发明的,能够无创测量身体表面肌肉和其他生物软组织。Agyapong-Badu等[12]用MyotonPRO研究年龄对股直肌、肱二头肌张力的影响,结果发现随着年龄的增加,肌肉硬度和张力增加,黏弹性下降,与Eby等[10]的研究结果一致。很多国外学者基于MyotonPRO评估技术进行了大量的健康人群基础研究,如Mullix等[25]对股直肌、股二头肌肉,Agyapong-Badu等[26]对年轻、年老健康男性股直肌和肱二头肌测量信度进行研究,结果均为优秀。还有一些学者对肱二头肌[27]、股四头肌[13]对称性进行研究,结果发现老年男性肱二头肌对称性差,股四头肌对称性良好。李亚鹏等[28]研究斜方肌上束的信度与对称性,结果测试者间信度和重测信度为好和优秀,且双侧无显著性差异,左右对称。Nair等[29]对健康人腰部筋膜硬度进行测量,结果男性筋膜硬度比女性高,右侧筋膜硬度比左侧高。Brendle[30]对静态拉伸与动态拉伸进行对比分析,结果表明动态牵拉有助于田径运动员肌肉爆发力的增加,在热身后优选静态拉伸。Schneider等[31]在失重状态下对肌肉组织特性改变进行研究,结果在失重状态下肌肉硬度显著降低。
此外,MyotonPRO还可以实时监测治疗效果。Wang等[32]发现用贴扎技术治疗扁平足患者后,能够即时降低下肢肌肉的硬度。Gordon等[33]利用筋膜触发点释放法治疗慢性肩痛前后肌肉硬度进行评估,结果治疗区硬度明显降低。还有学者[34]进行针刺前后的肌肉特性观察。可见MyotonPRO可以精准、快速、无创实时监测肌肉的特性,为临床服务。
本研究在测量前休息放松5 min,主要目的是消除因行走等带来的肌肉紧张;测量部位的选取主要由于该处皮下组织薄,肌肉丰厚,利于肌肉硬度真实值的测量;每部位测量3次,取平均值,降低误差。另外本研究的受测者BMI为(21.35±2.16)kg/m2,属于正常值18.5~24.99 kg/m2,为中等体型。然而,本研究仍存在一定的误差,比如测前每个人运动量无法统一、测量定位误差、探针与测量部位表面夹角等都会影响数值的高低。本研究考虑到此些因素,并尽可能地排除干扰因素。
尽管MRE、超声弹性成像和MyotonPRO都可以用来测量肌肉硬度,但MyotonPRO相对于MRE、超声弹性成像操作更方便、测量结果更直观,能够无创、快速提供被测量肌肉特性参数。MyotonPRO测量不受体位和重力的影响,可以在航天医学中应用;测量结果数字化,精准,重测信度高,方便携带。然而,该测量仪器只能测浅表层肌肉,不能测深层肌肉;只能测单个肌肉不能测量肌肉群;厚度小于3 mm的肌肉不能测。
综上所述,性别和体质量对左右两侧腓肠肌肉硬度有很大的影响,且下肢左右两侧肌肉硬度对称。临床检查腓肠肌肉硬度过程中,要考虑到性别和体质量带来的个体差异,必要时可进行双侧对比来诊断。
]
[1]Chuang LL,Wu CY,Lin KC.Reliability,validity,and responsiveness of myotonometric measurement of muscle tone,elasticity,and stiffness in patients with stroke[J].Arch Phys Med Rehabil,2012,93(3):532-540.
[2]Yanagisawa O,Niitsu M,Kurihara T,et al.Evaluation of human muscle hardness after dynamic exercise with ultrasound real-time tissue elastography:a feasibility study[J].Clin Radiol,2011,66(9):815-819.
[3]Niitsu M,Michizaki A,Endo A,et al.Muscle hardness measurement by using ultrasound elastography:a feasibility study[J].Acta Radiol,2011,52(1):99-105.
[4]Leonard CT,Stephens JU,Stroppel SL.Assessing the spastic condition of individuals with upper motoneuron involvement:validity of the myotonometer[J].Arch Phys Med Rehabil,2001,82(10):1416-1420.
[5]Marusiak J,Jaskólska A,Budrewicz S,et al.Increased muscle belly and tendon stiffness in patients with Parkinson's disease,as measured by myotonometry[J].Mov Disord,2011,26(11):2119-2122.
[6]Ishikawa H,Muraki T,Morise S,et al.Changes in stiffness of the dorsal scapular muscles before and after computer work:a comparison between individuals with and without neck and shoulder complaints[J].Eur J Appl Physiol,2017,117(1):179-187.
[7]Domire ZJ,Mccullough MB,Chen Q,et al.Feasibility of using magnetic resonance elastography to study the effect of aging on shear modulus of skeletal muscle[J].J Appl Biomech,2009,25(1):93-97.
[8]Chino K,Akagi R,Dohi M,et al.Reliability and validity of quantifying absolute muscle hardness using ultrasound elastography[J].PLoS One,2012,7(9):e45764.
[9]Brandenburg JE,Eby SF,Song P,et al.Feasibility and reliability of quantifying passive muscle stiffness in young children by using shear wave ultrasound elastography[J].J Ultrasound Med,2015,34(4):663-670.
[10]Eby SF,Cloud BA,Brandenburg JE,et al.Shear wave elastography of passive skeletal muscle stiffness:Influences of sex and age throughout adulthood[J].Clin Biomech(Bristol,Avon),2014,30(1):22-27.
[11]Chino K,Takahashi H.Measurement of gastrocnemius muscle elasticity by shear wave elastography:association with passive ankle joint stiffness and sex differences[J].Eur J Appl Physiol,2016,116(4):823-830.
[12]Agyapong-Badu S,Warner M,Samuel D,et al.Measurement of ageing effects on muscle tone and mechanical properties of rectus femoris and biceps brachii in healthy males and females using a novel hand-held myometric device[J].Arch Gerontol Geriatr,2016,62:59-67.
[13]Aird L,Samuel D,Stokes M.Quadriceps muscle tone,elasticity and stiffness in older males:Reliability and symmetry using the MyotonPRO[J].Arch Gerontol Geriatr,2012,55(2):e31-e39.
[14]张志杰,王季,洪文侠,等.深层肌肉刺激对小腿三头肌张力影响的短期效果[J].中国康复医学杂志,2016,31(11):1253-1254.
[15]Taniguchi K,Shinohara M,Nozaki S,et al.Acute decrease in the stiffness of resting muscle belly due to static stretching[J].Scand J Med Sci Sports,2015,25(1):32-40.
[16]Kanehisa H,Ikegawa S,Tsunoda N,et al.Cross-sectional areas of fat and muscle in limbs during growth and middle age[J].Int J Sports Med,1994,15(7):420-425.
[17]Guette M,Gondin J,Martin A.Time-of-day effect on the torque and neuromuscular properties of dominantand non-dominant quadriceps femoris[J].Chronobiol Int,2005,22(3):541-558.
[18]Morse CI.Gender differences in the passive stiffness of the human gastrocnemius muscle during stretch[J].Eur J Appl Physiol,2011,111(9):2149-2154.
[19]Dietsch AM,Clark HM,Steiner JN,et al.Effects of age,sex,and body position on orofacial muscle tone in healthy adults[J].J Speech Lang Hear Res,2015,58(4):1145-1150.
[20]Wang D,De Vito G,Ditroilo M,et al.A comparison of muscle stiffness and musculoarticular stiffness of the knee joint in young athletic males and females[J].J Electromyogr Kinesiol,2015,25(3):495-500.
[21]Blackburn JT,Norcross MF.The effects of isometric and isotonic training on hamstring stiffness and anterior cruciate ligament loading mechanisms[J].J Electromyogr Kinesiol,2014,24(1):98-103.
[22]Green MA,Sinkus R,Gandevia SC,et al.Measuring changes in muscle stiffness after eccentric exercise using elastography[J].NMR Biomed,2012,25(6):852-858.
[23]Murayama M,Nosaka K,Yoneda T,et al.Changes in hardness of the human elbow flexor muscles after eccentric exercise[J].Eur JAppl Physiol,2000,82(5):361-367.
[24]Janecki D,Jarocka E,Jaskólska A,et al.Muscle passive stiffness increases less after the second bout of eccentric exercise compared to the first bout[J].J Sci Med Sport,2011,14(4):338-343.
[25]Mullix J,Warner M,Stokes M.Testing muscle tone and mechanical properties of rectus femoris and biceps femoris using a novel hand held MyotonPRO device:relative ratios and reliability[J].Working Papers in Health Sciences,2012,1:1-8.
[26]Agyapong-Badu S,Aird L,Bailey L,et al.Interrater reliability of muscle tone,stiffness and elasticity measurements of rectus femoris and biceps brachii in healthy young and older males[J].Working Papers in Health Sciences,2013,1:1-11.
[27]Bailey L.Parameters representing muscle tone,elasticity and stiffness of biceps brachii in healthy older males:symmetry and within-session reliability using the MyotonPRO[J].J Neurol Disord,2013,1(1):1-7.
[28]李亚鹏,冯亚男,刘春龙,等.一种新型弹性测试仪用于健康人群斜方肌弹性评估的信度研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2017,32(10):1183-1185.
[29]Nair K,Masi AT,Andonian BJ,et al.Stiffness of resting lumbar myofascia in healthy young subjects quantified using a handheld myotonometer and concurrently with surface electromyography monitoring[J].J Bodyw Mov Ther,2016,20(2):388-396.
[30]Brendle S.Acute effect of static and dynamic stretching on tone and elasticity of hamstring muscle and on vertical jump performance in track-and-field athletes[J].Acta Kinesiologiae Universitatis Tartuensis,2014,20(3):48-59.
[31]Schneider S,Peipsi A,Stokes M,et al.Feasibility of monitoring muscle health in microgravity environments using Myoton technology[J].Med Biol Eng Comput,2015,53(1):57-66.
[32]Wang JS,Um GM,Choi JH.Immediate effects of kinematic taping on lower extremity muscle tone and stiffness in flexible flat feet[J].J Phys Ther Sci,2016,28(4):1339-1342.
[33]Gordon CM,Andrasik F,Schleip R,et al.Myofascial triggerpoint release(MTR)for treating chronic shoulder pain:A novel approach[J].J Bodyw Mov Ther,2016,20(3):614-622.
[34]Ortega-Cebrian S,Luchini N,Whiteley R.Dry needling:effects on activation and passive mechanical properties of the quadriceps,pain and range during late stage rehabilitation of ACL reconstructed patients[J].Phys Ther Sport,2016,21:57-62.
——基于体育核心期刊论文(2010—2018年)的系统分析

