Extensions of Modules with ACC on d-annihilators
OUYANG LUN-QUN,ZHOU QIONG,LIU JIN-WANG AND XIANG YUE-MING
(1.School of Mathematics,Hunan University of Science and Technology,Xiangtan,Hunan,411201)
(2.Department of Mathematics and Applied Mathematics,Huaihua University,Huaihua,Hunan,418000)
Communicated by Du Xian-kun
1 Introduction
Throughout this paper all ringsRare associative with identity and all modulesMRare unitary rightR-modules.The set of all positive integers is denoted byN+.Letαbe an endomorphism andδanα-derivation of a ringR.We denote byR[x;α,δ]the Ore extension whose elements are the polynomials overR,the addition is defined as usual and the multiplication is subject to the relationxa=α(a)x+δ(a)for anya∈R.Clearly,polynomial ringsR[x],skew polynomial ringsR[x;α]and differential polynomial ringsR[x;δ]are specialOre extension rings.Given a rightR-moduleMR,we can makeM[x]into a rightR[x;α,δ]-module by allowing polynomials fromR[x;α,δ]to act on polynomials inM[x]in the obvious way,and apply the above twist whenever necessary.The verification that this defines a validR[x;α,δ]-module structure onM[x]is almost identical to the verification thatR[x;α,δ]is a ring and it is straightforward(see[1]).
For an elementa∈R,AnnM(a)={m∈MR|ma=0}denotes the annihilator ofainMR.Following Frohn[2],a moduleMRis said to satisfy acc ond-annihilators if for every sequence(an)nof elements ofR,the ascending chain AnnM(a1)⊆AnnM(a1a2)⊆···of submodules ofMRstabilizes.IfRRsatisfies acc ond-annihilators,then we say that the ringRis a ring satisfying acc ond-annihilators.Clearly,strongly Laskerian modules satisfy acc ond-annihilators,and ifMRsatisfies acc ond-annihilators,so is every submodule ofMR(see[2]).Visweswaran[3]showed that the zero-dimension rings with acc ond-annihilators are exactly the perfect rings.So in order to characterize the perfect ringsR,it is important to consider the modulesRRwith acc ond-annihilators.Hence find more examples of modules with acc ond-annihilators is meaningful in module theory.It is well known that,in the module theory literature,many surprising examples and counterexamples have been produced via the triangular matrix extensions.So in this paper we first investigate the relationship between the acc ond-annihilators property ofMRand that of the various triangular matrix extension modules overMR,and then obtain more examples of modules with acc ond-annihilators.
Polynomial extension of modules with acc ond-annihilators was studied by Frohn.He proved in[2]that ifRis reduced and satisfies acc ond-annihilators,then the polynomial ringR[X]for any setXof indeterminates also has acc ond-annihilators.We generalize this result.In Section 3,we consider the acc ond-annihilators property of the Ore extension modulesM[x]R[x;α,δ]over the Ore extension ringsR[x;α,δ].We show that ifMRis an(α,δ)-compatible reduced module,then the Ore extension moduleM[x]R[x;α,δ]satisfies acc ond-annihilators if and only ifMRsatisfies acc ond-annihilators.So the Frohn’s recent work(see[2],Corollary 2.4])is extended to a more generally setting.
2 Triangular Matrix Extension Modules
LetRbe a ring andMRa rightR-module.Let
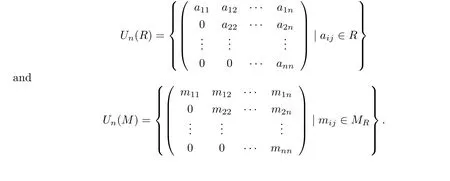
ThenUn(M)is a rightUn(R)-module under usual matrix operations.
Proposition 2.1Let R be a ring and MRa right R-module.Then the following statements are equivalent:
(1)MRsatisfies acc on d-annihilators;
(2)Un(M)Un(R)satisfies acc on d-annihilators.
Proof.(1)⇒(2).Suppose thatMRsatisfies acc ond-annihilators.We proceed by induction onnto show that the rightUn(R)-moduleUn(M)also satisfies acc ond-annihilators.Letn=2.Put

be a sequence of elements ofU2(R).SinceMRsatisfies acc ond-annihilators,there exists ak∈N+such that for any positive integerl>k,

Consider the sequence(ck+m)mof elements ofR.By the condition thatMRsatisfies acc ond-annihilators,we can find a positive integerp∈N+such that for anyq>p,
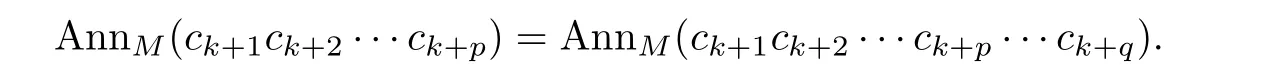
Now we show that for any positive integerv∈N+,
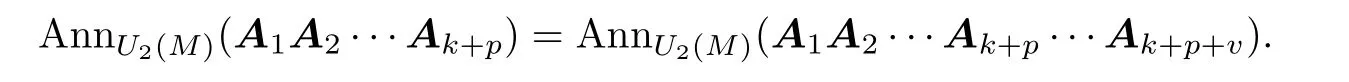
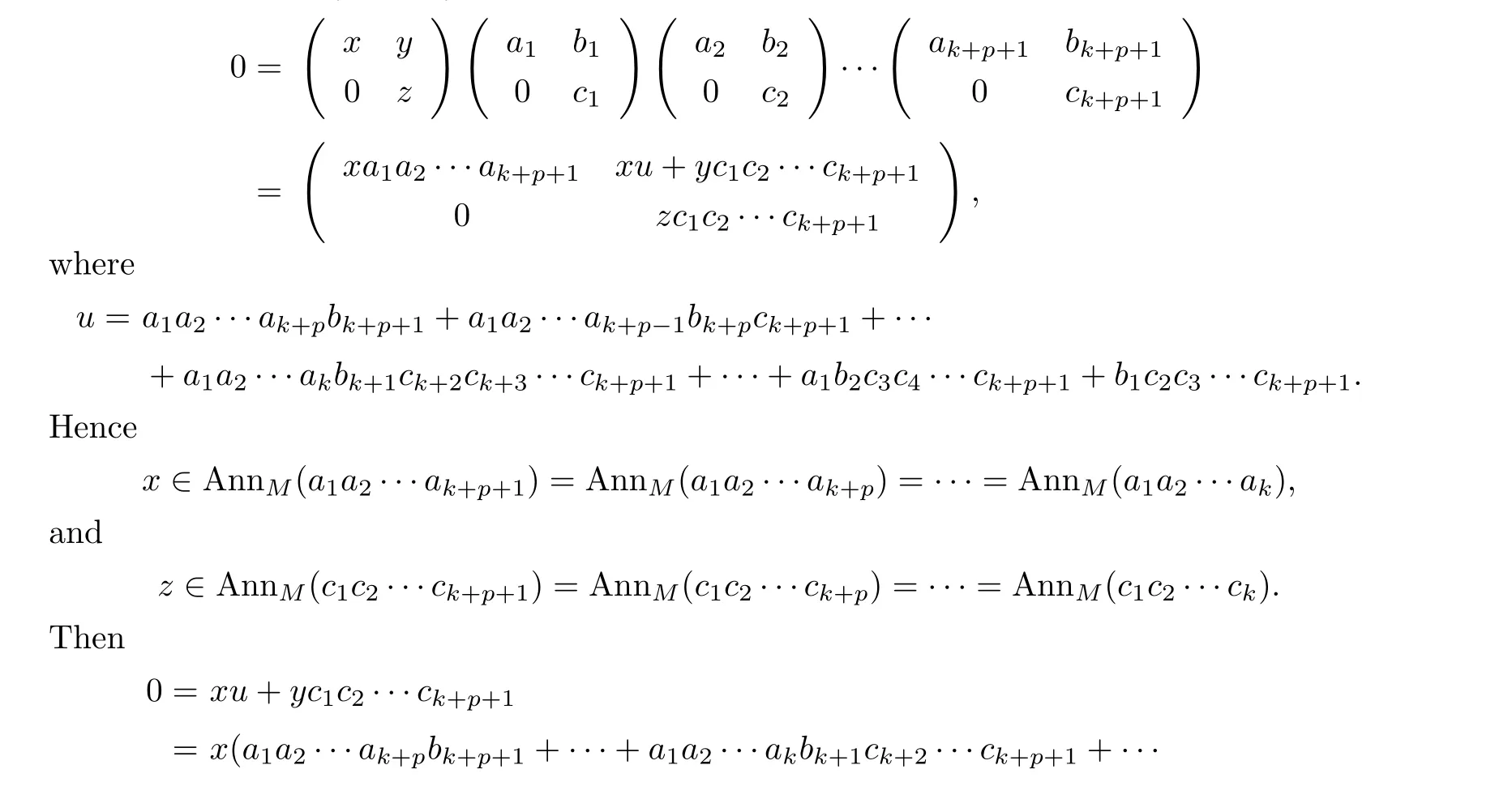
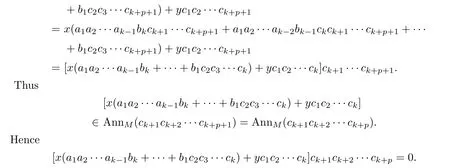
By a routine computations,we obtain
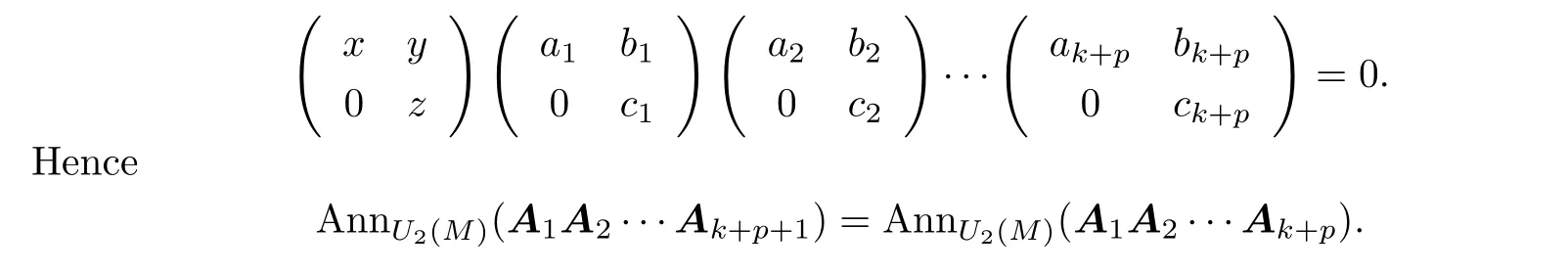
Similarly,we can show that for any positive integerv∈N+,
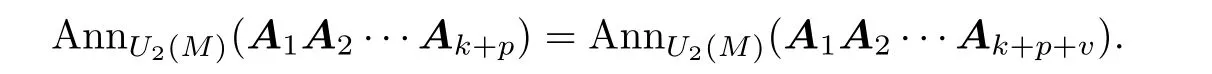
ThereforeU2(M)satisfies acc ond-annihilators.
Next we assume that the result is true forn−1,and let
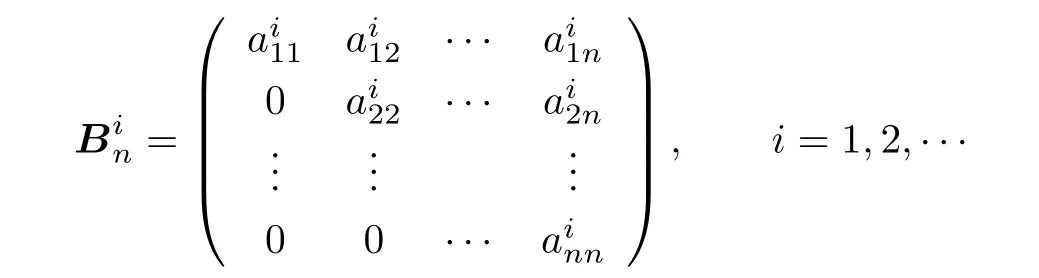
be a sequence of elements ofUn(R).In the following we show that
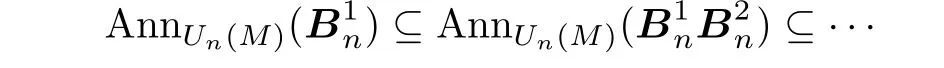
stabilizes.Put
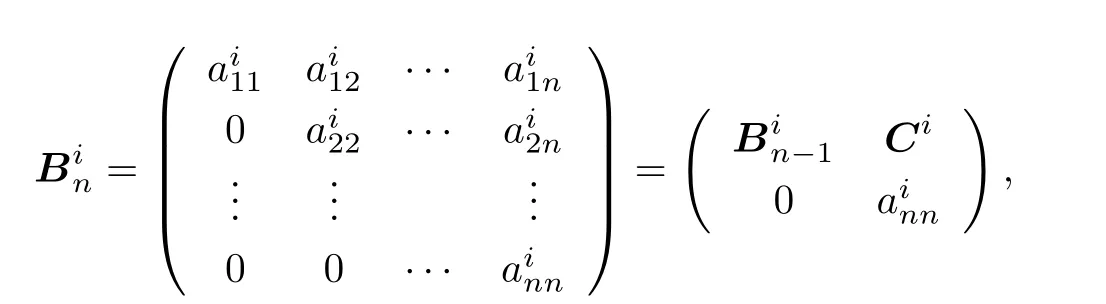
By the induction hypothesis,we can find a positive integerm∈N+such that for anys>m,
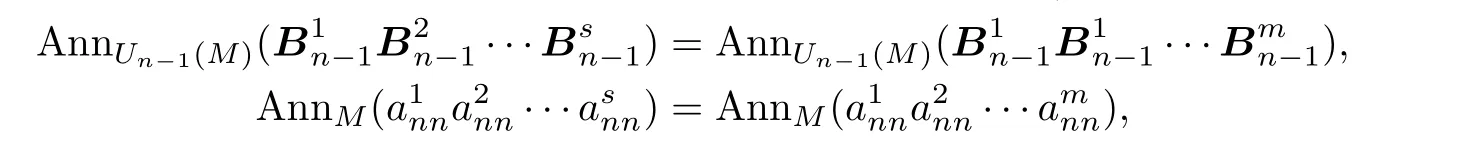
and a positive integeru∈N+such that for anyv>u,
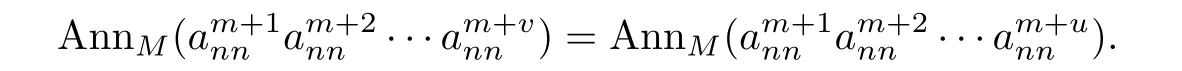
Then by using the same way as above,we can show that for any positive integerw∈N+,
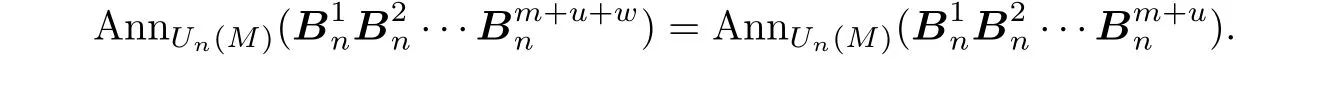
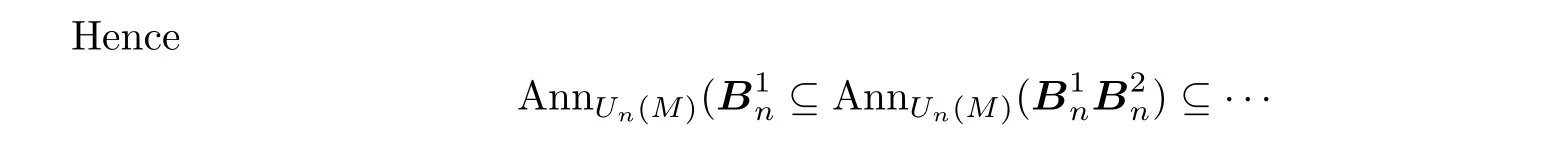
stabilizes.ThereforeUn(M)Un(R)satisfies acc ond-annihilators by induction.
(2)⇒(1).It is trivial.
The proof is completed.
LetLn(R)denote the lower triangular matrix ring overR,and let

ThenLn(M)is a rightLn(R)-module under usual matrix operations.
Corollary 2.1The following statements are equivalent:
(1)MRsatisfies acc on d-annihilators;
(2)Ln(M)Ln(R)satisfies acc on d-annihilators.
Proof.It is similar to the proof as given in the Proposition 2.1.
LetRbe a ring andMRa rightR-module.Let
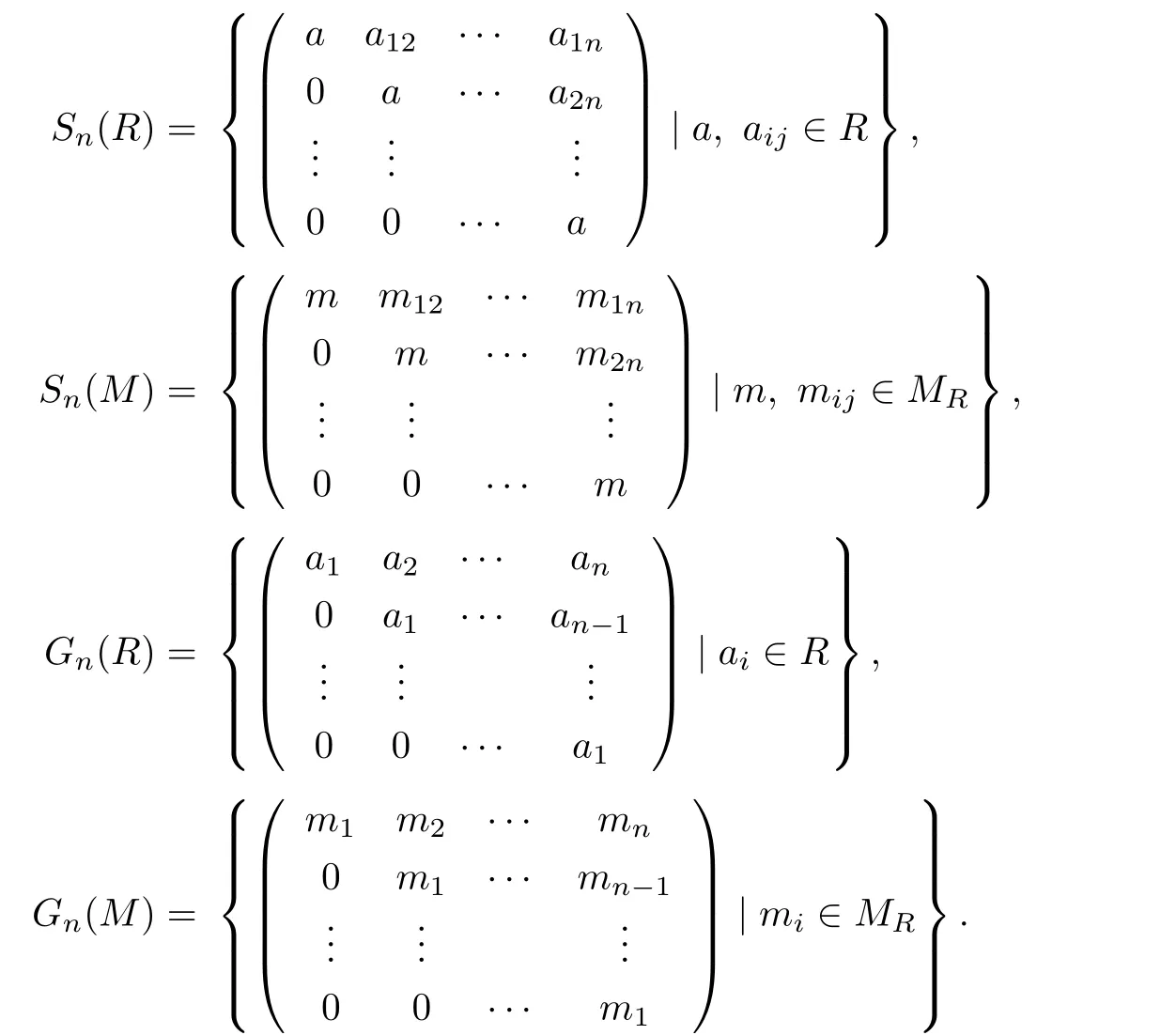
The following two corollaries give more examples of modules satisfying acc ond-annihilators.
Corollary 2.2The following statements are equivalent:
(1)The right R-module MRsatisfies acc on d-annihilators;
(2)The right Sn(R)-module Sn(M)satisfies acc on d-annihilators;
(3)The right Gn(R)-module Gn(M)satisfies acc on d-annihilators.
Proof.Employing the same method in the proof of Proposition 2.1,we complete the proof.
Corollary 2.3The following statements are equivalent:
(1)R satisfies acc on d-annihilators;
(2)Un(R)satisfies acc on d-annihilators;
(3)Ln(R)satisfies acc on d-annihilators;
(4)Sn(R)satisfies acc on d-annihilators;
(5)Gn(R)satisfies acc on d-annihilators;
(7)R[x]/(xn)satisfies acc on d-annihilators.
Proof.The equivalence(1)⇔(2)follows by Proposition 2.1.The equivalence(1)⇔(3)follows by Corollary 2.1.The equivalence(1)⇔(4),(1)⇔(5)and(1)⇔(6)follow by Corollary 2.2.The equivalence(1)⇔(7)follows by Corollary 2.2 and the fact thatR[x]/(xn)∼=Gn(R).
LetRbe a ring andMRa rightR-module.Let
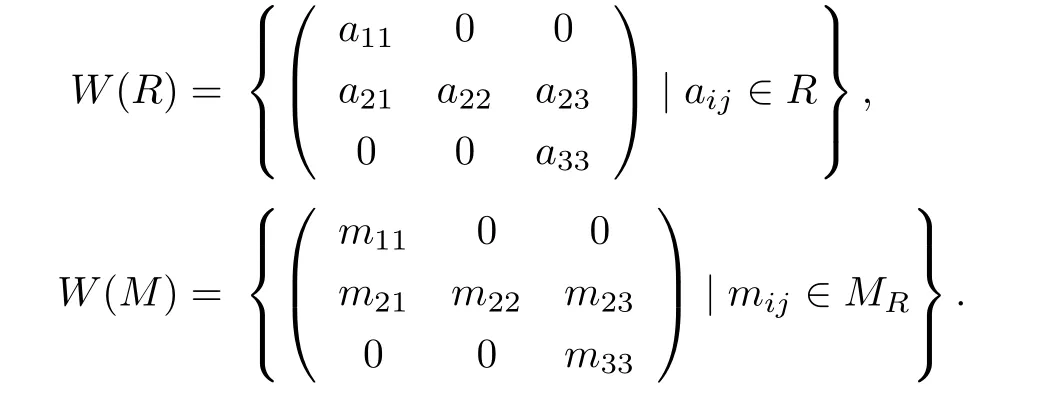
ThenW(M)is a rightW(R)-module under usual matrix operations.In fact,W(M)possesses the similar form of both the lower triangular matrix module and the upper triangular matrix module.A natural problem asks if the acc ond-annihilators property of such a module coincides with that ofMR.This inspire us to consider the acc ond-annihilators property ofW(M)W(R).
Proposition 2.2Let R be a ring and MRa right R-module.Then the following statements are equivalent:
在高中机器人编程学习课堂上,高中生不仅要学习基于硬件的编程,更是要注重基于任务的编程学习,基于任务的编程学习主要是以执行任务为学习中心,并且要以完成任务为学习目的,所以学生在判断应该选用那个传感器进行接受信息,应该选用哪个传感器来进行命令的下达,都要以任务本身为依据,要给于任务来开展机器人的编程。所以在进行基于任务的编程学习,要注意以下几点内容:
(1)MRsatisfies acc on d-annihilators;
(2)W(M)W(R)satisfies acc on d-annihilators.
Proof.It suffices to show that(1)⇒(2).Let
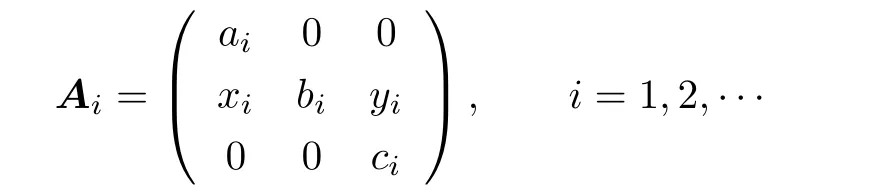
be a sequence of elements ofW(R).SinceMRsatisfies acc ond-annihilators,there exists somek∈N+such that for all positive integerl>k,
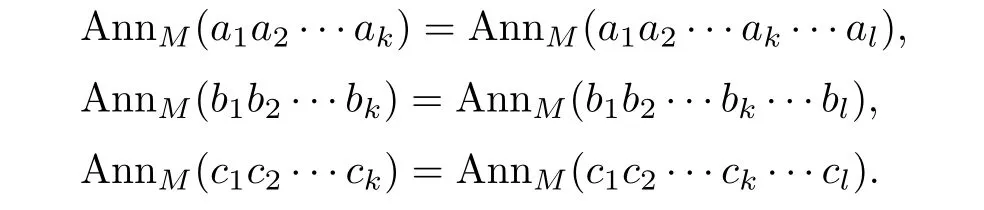
Consider the sequences(ak+n)n,(bk+n)nand(ck+n)nof elements ofR,there exists ap∈N+such that for allq>p,
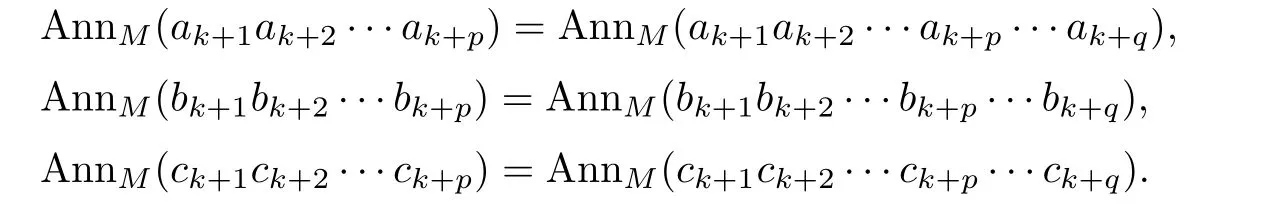
Now we show that for any positive integerv∈N+,
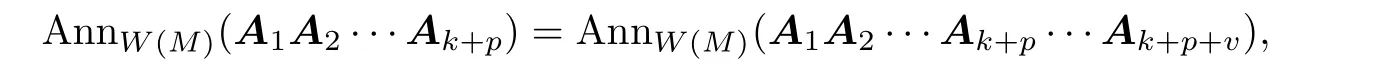
which implies that AnnW(M)(A1)⊆AnnW(M)(A1A2)⊆···stabilizes.First,we show that
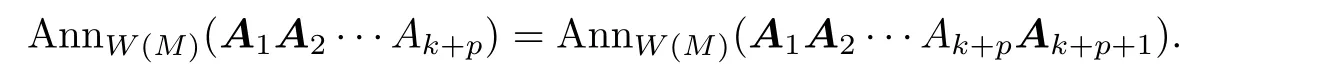
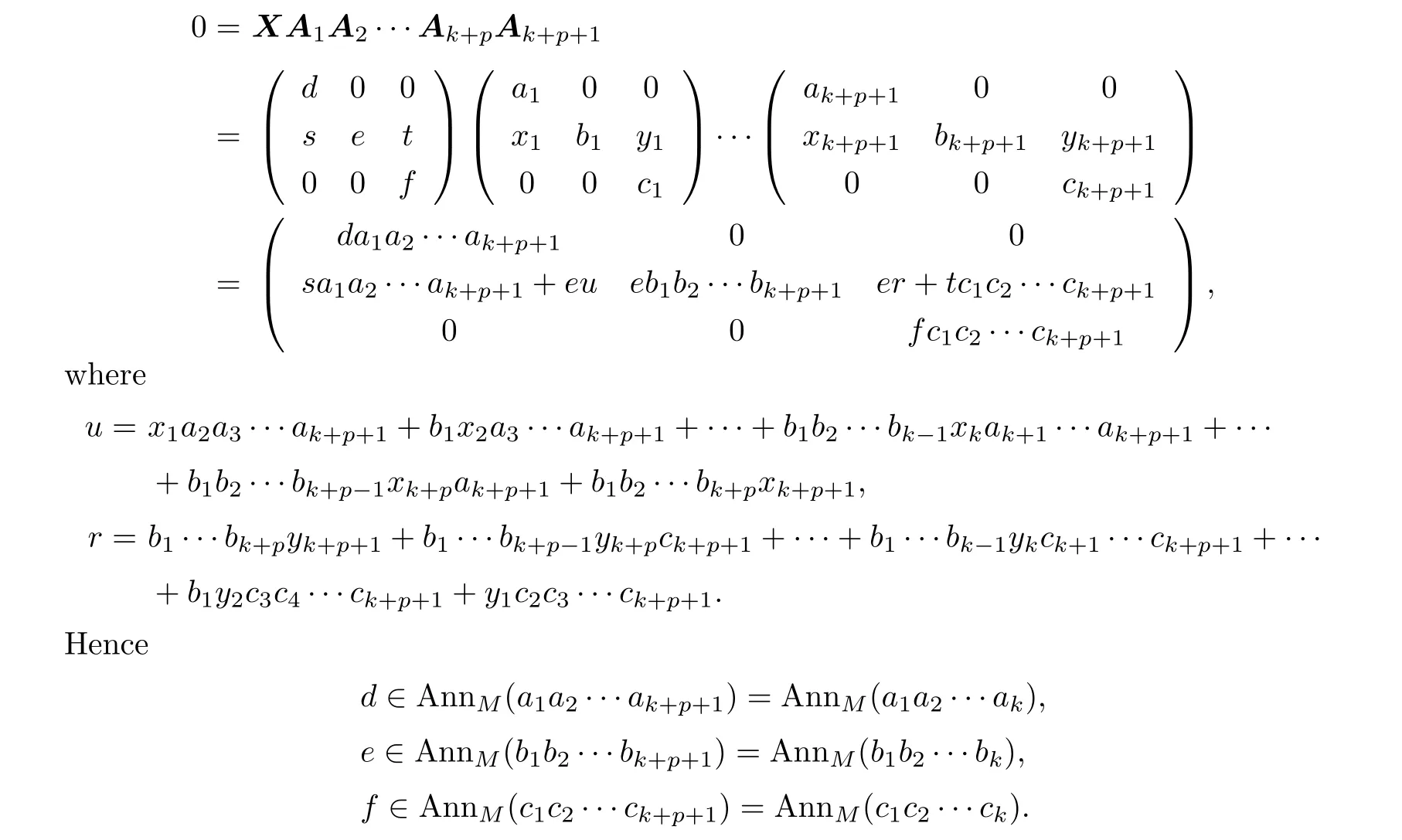
By using the same way as the proof of Proposition 2.1,we also have

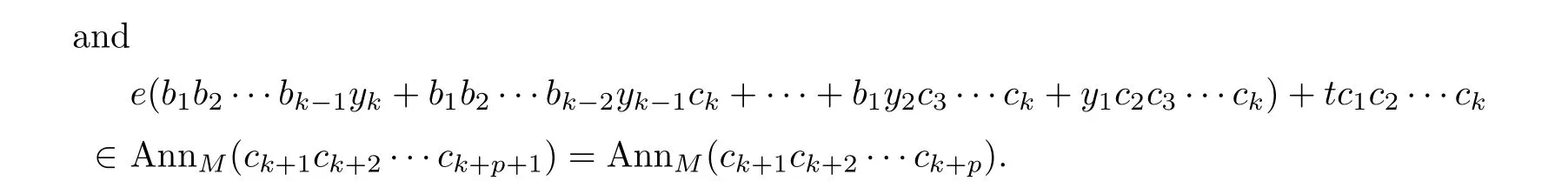
Then by a routine computations,we can show that
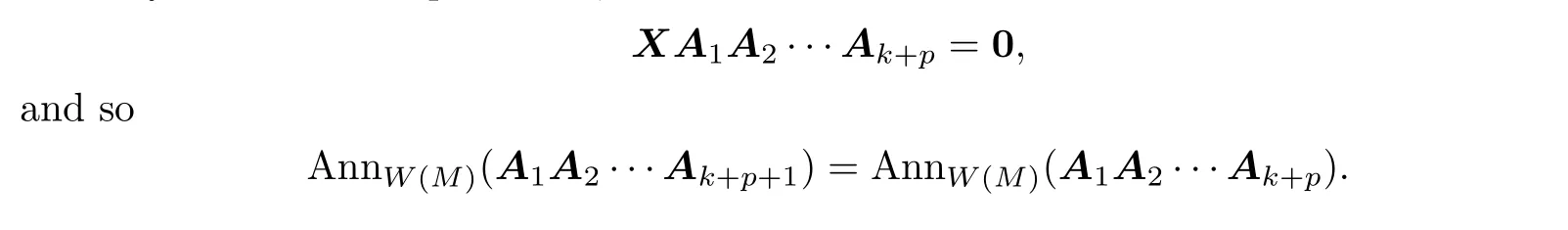
Similarly,we can show that
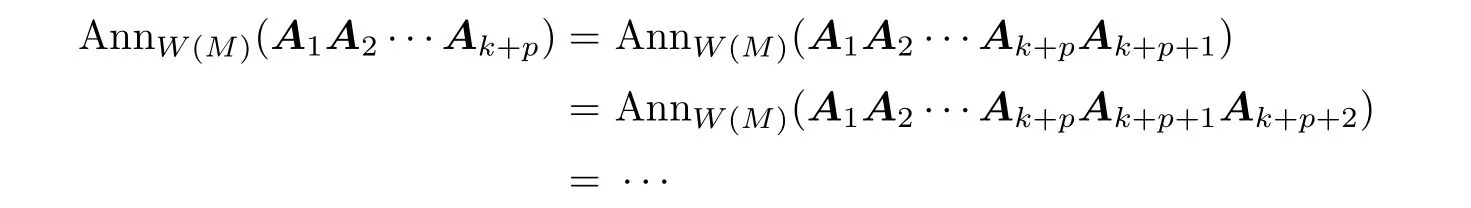
ThereforeW(M)satisfies acc ond-annihilators.
LetRbe a ring andMRa rightR-module.Then under usual matrix operations,we

Proposition 2.3Let R be a ring and MRa right R-module.Then the following statements are equivalent:
(1)The right R-module MRsatisfies acc on d-annihilators;
(2)The right W1(R)-module W1(M)satisfies acc on d-annihilators;
(3)The right W2(R)-module W2(M)satisfies acc on d-annihilators;
(4)The right W3(R)-module W3(M)satisfies acc on d-annihilators;
(5)The right W4(R)-module W4(M)satisfies acc on d-annihilators.
Proof.By analogy with the proof of Proposition 2.2,we complete the proof.
Corollary 2.4Let R be a ring.Then the following statements are equivalent:
(1)R satisfies acc on d-annihilators;
(2)W(R)satisfies acc on d-annihilators;
(3)W1(R)satisfies acc on d-annihilators;
(4)W2(R)satisfies acc on d-annihilators;
(5)W3(R)satisfies acc on d-annihilators;
(6)W4(R)satisfies acc on d-annihilators.

are all rings satisfying acc ond-annihilators.
Following Hamimouet al.[4],a ringRis right strongly Hopfian if the chain of right annihilators AnnR(a)⊆AnnR(a2)⊆···stabilizes for eacha∈R.Based on Corollaries 2.3 and 2.4,we can derive the following:
Corollary 2.5Let R be a ring.If R satisfies acc on d-annihilators,then the following hold:
(1)Un(R)is a right strongly Hopfian ring;
(2)Ln(R)is a right strongly Hopfian ring;
(3)W(R)is a right strongly Hopfian ring;
(4)Wi(R)(i=1,2,3,4)is a right strongly Hopfian ring;
(5)Sn(R)is a right strongly Hopfian ring;
(6)Gn(R)is a right strongly Hopfian ring;
(7)The trivial extension R▷◁R of R by R is a right strongly Hopfian ring;
(8)R[x]/(xn)is a right strongly Hopfian ring.
3 Ore Extension Modules
In the Ore extensionR[x;α,δ],we have
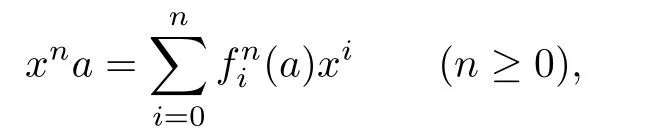
The following definition appears in[1].
Definition 3.1Given a module MR,an endomorphism α:R−→R and an α-derivation δ:R−→R,we say that MRis α-compatible if for each m∈MRand r∈R,one has mr=0⇔mα(r)=0.Moreover,we say that MRis δ-compatible if for each m∈MRand r∈R,one has mr=0⇒mδ(r)=0.If MRis both α-compatible and δ-compatible,we say that MRis(α,δ)-compatible.
Note that ifMRisα-compatible(resp.δ-compatible),thenMRisαi-compatible(resp.δi-compatible)for alli≥1.It is clear that ifMRisα-compatible(resp.δ-compatible),then so is any submodule ofMR.The following definition appears in[6].
Definition 3.2Let MRbe a right R-module.We say that MRis reduced,if,for any m∈MRand any a∈R,ma=0implies mR∩Ma=0.
Clearly,ifMRis reduced,then for allm∈MRanda∈R,ma=0 impliesmRa=0 andma2=0 impliesma=0.
As a immediate consequence of Definitions 3.1 and 3.2,we obtain the following lemma.
Lemma 3.1Let MRbe an(α,δ)-compatible reduced module.Then the following hold:
(1)ma=0if and only if mαn(a)=0,where n is a positive integer;
(2)mab=0implies mfji(a)fts(b)=0;
(3)mab=0implies mba=0and mRaRb=0.
The next lemma is known and very useful,we leave the proof for the reader.
Lemma 3.2Let MRbe a reduced module and X={a1,a2,···,an}⊆R be a finite subset of R.Then for any m∈MR,mX=0if and only if m(Ra1R+Ra2R+···+RanR)=0,where Ra1R+Ra2R+···+RanR denotes the ideal of R generated by a1,a2,···,an.
Lemma 3.3Let R be a ring and MRa reduced module satisfying acc on d-annihilators.Then for every sequence(An)nof finitely generated ideals of R,the ascending chainAnnM(A1)⊆AnnM(A1A2)⊆···stabilizes.
Proof.SinceMRis reduced,for anym∈MRand anya,b∈R,by Lemma 3.1,mab=0 impliesmba=0 andmRaRb=MRbRa=0.Then similar to the proof of Theorem 2.3(b)in[2],we complete the proof.
Proposition 3.1Let α be an endomorphism and δ an α-derivation of a ring R.If MR is an(α,δ)-compatible reduced module,then the following statements are equivalent:
(1)MRsatisfies acc on d-annihilators;
(2)The right R[x;α,δ]-module M[x]satisfies acc on d-annihilators.
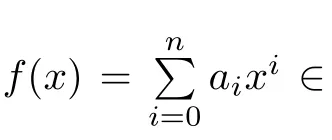
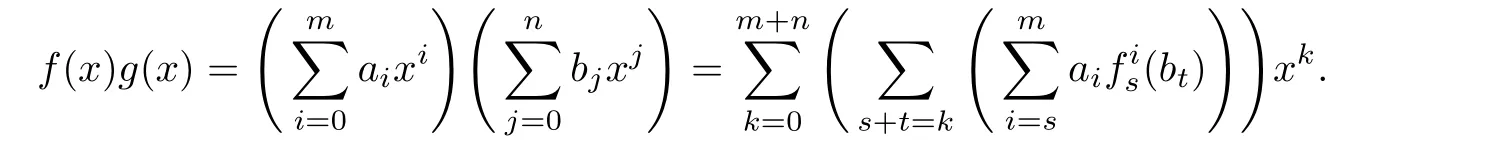
Ifr∈AnnM(AfAg),then
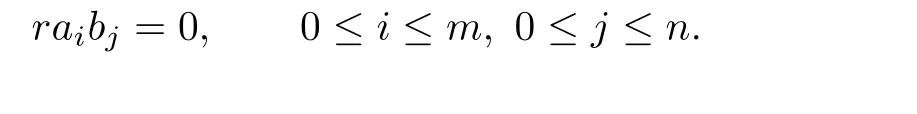
SinceMRis(α,δ)-compatible,by Lemma 3.1,we have
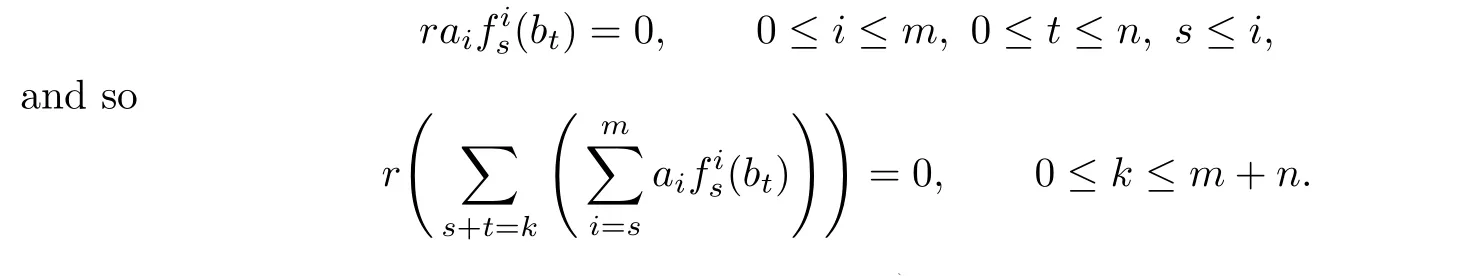
Hence by Lemma 3.2,we obtainr∈AnnM(Afg)and so AnnM(AfAg)⊆AnnM(Afg).We now turn our attention to proving AnnM(AfAg)⊇AnnM(Afg).Letr∈AnnM(Afg).Then we have the following system of equations:
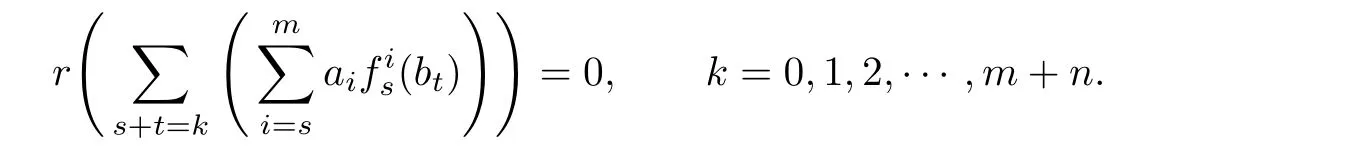
Fork=m+n,we have
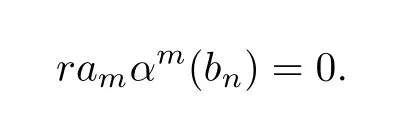
Then by Lemma 3.1,we obtain
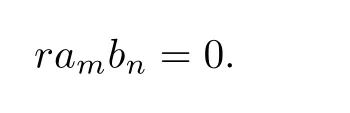
Fork=m+n−1,we have
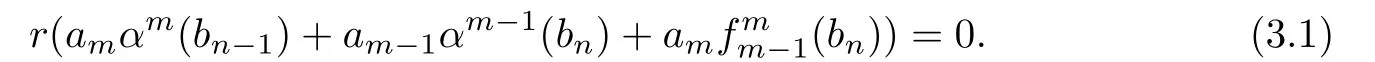
Multiplying(3.1)on the right side byam,then by Lemma 3.1,we obtain
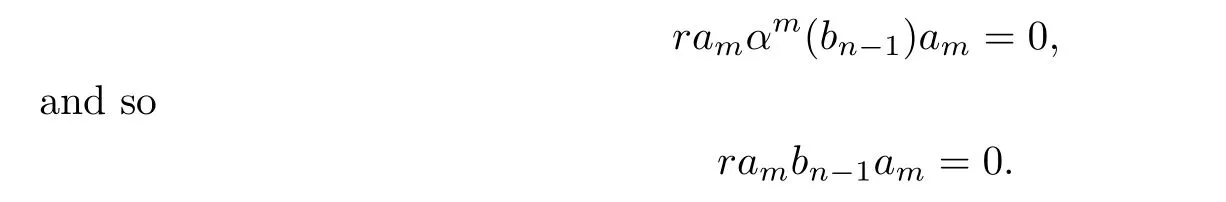
SinceMRis reduced,we have
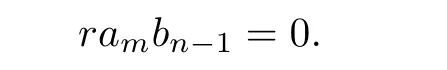
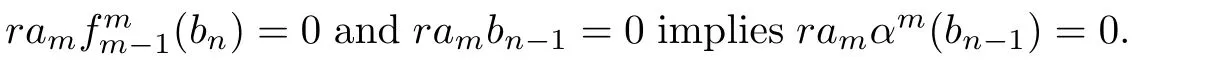
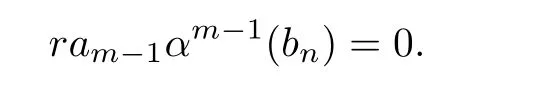
Then by Lemma 3.1,we have
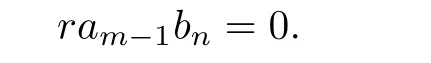
Fork=m+n−2,we have
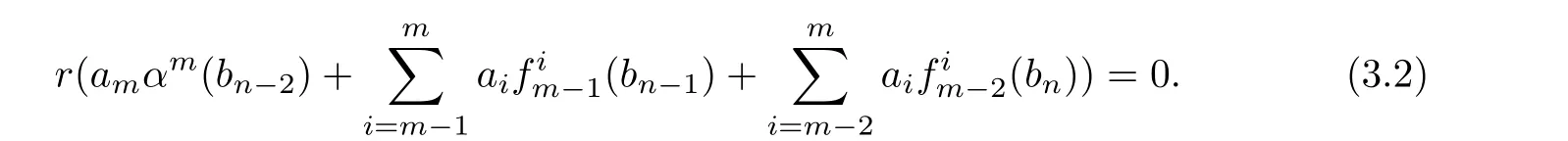
Multiplying(3.2)on the right side byamand using Lemma 3.1,we obtain
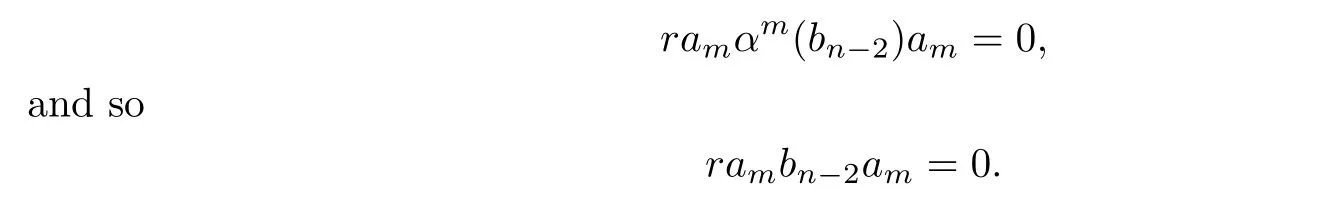
SinceMRis reduced,we have

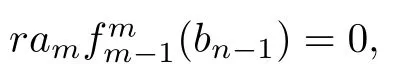
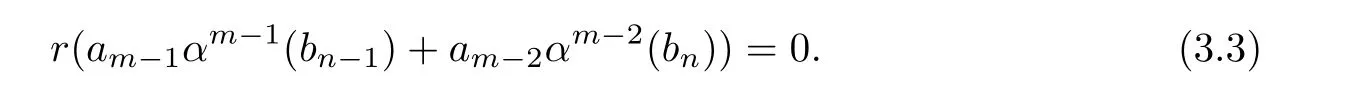
Multiplying(3.3)on the right side byam−1,then by Lemma 3.1,we can show that
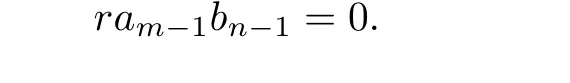
Hence(3.3)becomes
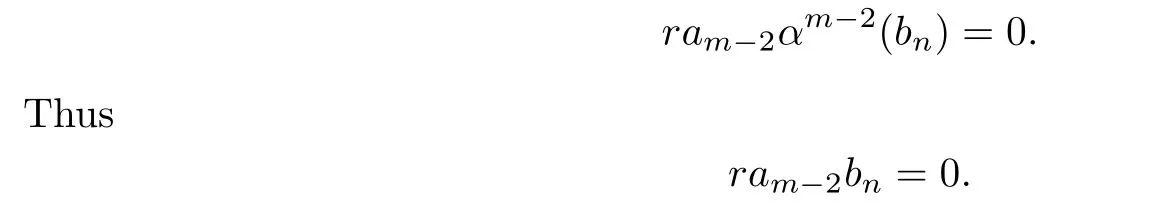
Continuing this procedure yields that
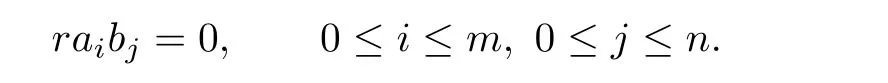

Hencer∈AnnM(AfAg)and so
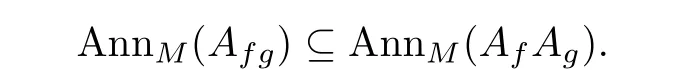
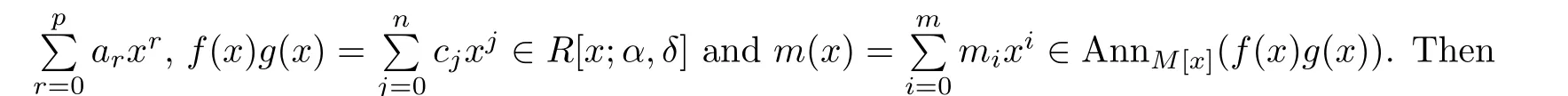
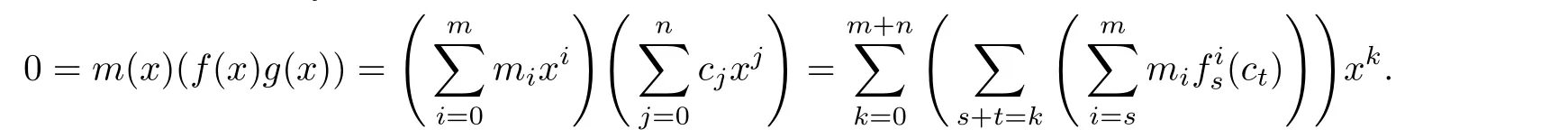
Thus we obtain a system of equations:
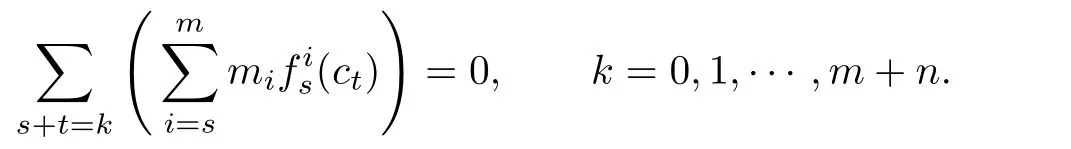
By using the same way as above,we can show that
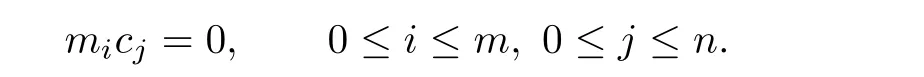
Then by Lemma 3.2,we obtain
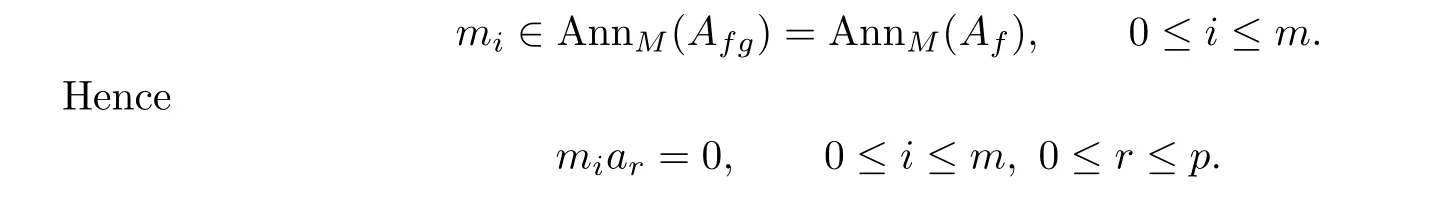
Then by a routine computations we can show that
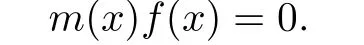
Hencem(x)∈AnnM[x](f(x))and so
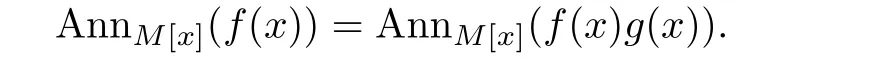
ThereforeM[x]satisfies acc ond-annihilators.
(2)⇒(1).Note that for anya∈R,AnnM(a)=AnnM[x](a)∩M.Hence the proof of(2)⇒(1)is trivial.
Corollary 3.1Let R be a ring and MRa reduced right R-module.Then we have the following results:
(1)Let α be an endomorphism of R.If MRis α-compatible,then the skew polynomial module M[x]over the skew polynomial ring R[x;α]satisfies acc on d-annihilators if and only if MRsatisfies acc on d-annihilators;
(2)Let δ be a derivation of R.If MRis δ-compatible,then the differential polynomial module M[x]over the differential ring R[x;δ]satisfies acc on d-annihilators if and only if MRsatisfies acc on d-annihilators.
Corollary 3.2Let R be a ring.If R is an(α,δ)-compatible reduced ring,then the Ore extension ring R[x;α,δ]satisfies acc on d-annihilators if and only if R satisfies acc on d-annihilators.
The following corollary is a generalization of Corollary 2.4(iii)in[2].
Corollary 3.3Let R be a reduced ring.Then the polynomial ring R[x]satisfies acc on d-annihilators if and only if R satisfies acc on d-annihilators.
We show that ifMRis(α,δ)-compatible and reduced,then the rightR[x;α,δ]-moduleM[x]satisfies acc ond-annihilators if and only ifMRsatisfies acc ond-annihilators(see Proposition 3.1).LetMRbe a module with acc ond-annihilators.IfMRdoes not be(α,δ)-compatible or not be reduced,can one provide a counterexample that the Ore extension moduleM[x]R[x;α,δ]does not has acc ond-annihilators?We do not know the answer and thus conclude with the following open problem:
Question 3.1LetMRbe a module with acc ond-annihilators.IfMRis not(α,δ)-compatible or not reduced,does there exist an Ore extension moduleM[x]over the Ore extension ringR[x;α,δ]that does not has acc ond-annihilators?
[1]Annin S.Associated primes over Ore extension rings.J.Algebra Appl.,2004,3(2):2511–2528.
[2]Frohn D.Modules withn-acc and the acc on certain types of annihilators.J.Algebra,2002,256(2):467–483.
[3]Visweswaran S.Some results on modules satisfying(C).J.Ramanujan Math.Soc.,1996,11(2):161–174.
[4]Hmaimou A,Kaidi A,Sanchez Campos E.Generalized fitting modules and rings.J.Algebra,2007,308(1):199–214.
[5]Lam T Y,Leroy A,Matczuk,J.Primeness,semiprimeness and prime radical of Ore extensions.Comm.Algebra,1997,25(80):2459–2506.
[6]Lee T K,Zhou Y.Reduced modules,rings,modules,algebras and abelian groups,365–377,Lecture Notes in Pure and Appl.Math.,236,Dekker,New York,2004.
 Communications in Mathematical Research2018年1期
Communications in Mathematical Research2018年1期
- Communications in Mathematical Research的其它文章
- Homotopy Analysis Method for Solving(2+1)-dimensional Navier-Stokes Equations with Perturbation Terms
- Growth of Solutions of Some Linear Difference Equations with Meromorphic Coefficients
- Reversible Properties of Monoid Crossed Products
- One Parameter Deformation of Symmetric Toda Lattice Hierarchy
- On Lie 2-bialgebras
- On the Coefficients of Several Classes of Bi-univalent Functions Defined by Convolution
