Discovery of the largest Carboniferous manganese deposit in Longtou-Limiao, central Guangxi, China
Xu Chen, Sha Jiang
a Central South Geo-exploration Institute, China Metallurgical Geology Bureau, Wuhan 410080, China
b Guangxi Geo-exploration Institute, China Metallurgical Geology Bureau, Nanning 530022, China
1. Objective
The Nandan-Yizhou faulting basin, which is located in Longtou-Limiao, Guangxi, is in the southern margin of the Yangtze Block, the depression zone of south Hunan and north Guangxi. It is a carbonate Manganese (Mn) ore deposit in the Baping Group, where occurs the Nongzhu large Mn deposit in a 100 km long anticlinorium with great Mn resource potential(Fig.1).
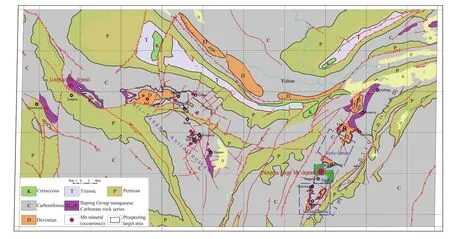
Fig. 1. Regional geological map with Mn deposits (occurrences) distribution in Longtou-Limiao, Guangxi, China.
2. Methods
The China Metallurgical Geology Bureau uses metallogenic geological setting and ore-controlling conditions of Mn deposit to identify the resource potential of this area, at the same time to support the "Mineral Geological Survey over West Hunan to East Yunnan (2016-2018)" project and Mineral Geological Survey (1∶50000).
3. Results
The Nongzhu Mn deposit, the largest Carboniferous Mn deposit in China, was discovered in the Limiao anticlinorium,the Nandan-Yizhou faulting basin, the South Hunan-North Guangxi depression zone, and the Southern Margin of the Yangtze Block. In this deposit, there are four ore bodies with stable layers that has continuous distribution in a large scale.The main ore minerals of these ore bodies are rhodochrosite,tetalite and manganocalcite. The average chemical content of Mn ore bodies is shown in Table 1 within average 0.86 m thickness. There is 3.15×107t (333+334) Mn ore reserves discovered in the Nongzhu deposit that is part of Baping Group carbonate Mn bearing rock of deep-sea sedimentary facies. The alkaline ore can be easily utilized in industry.
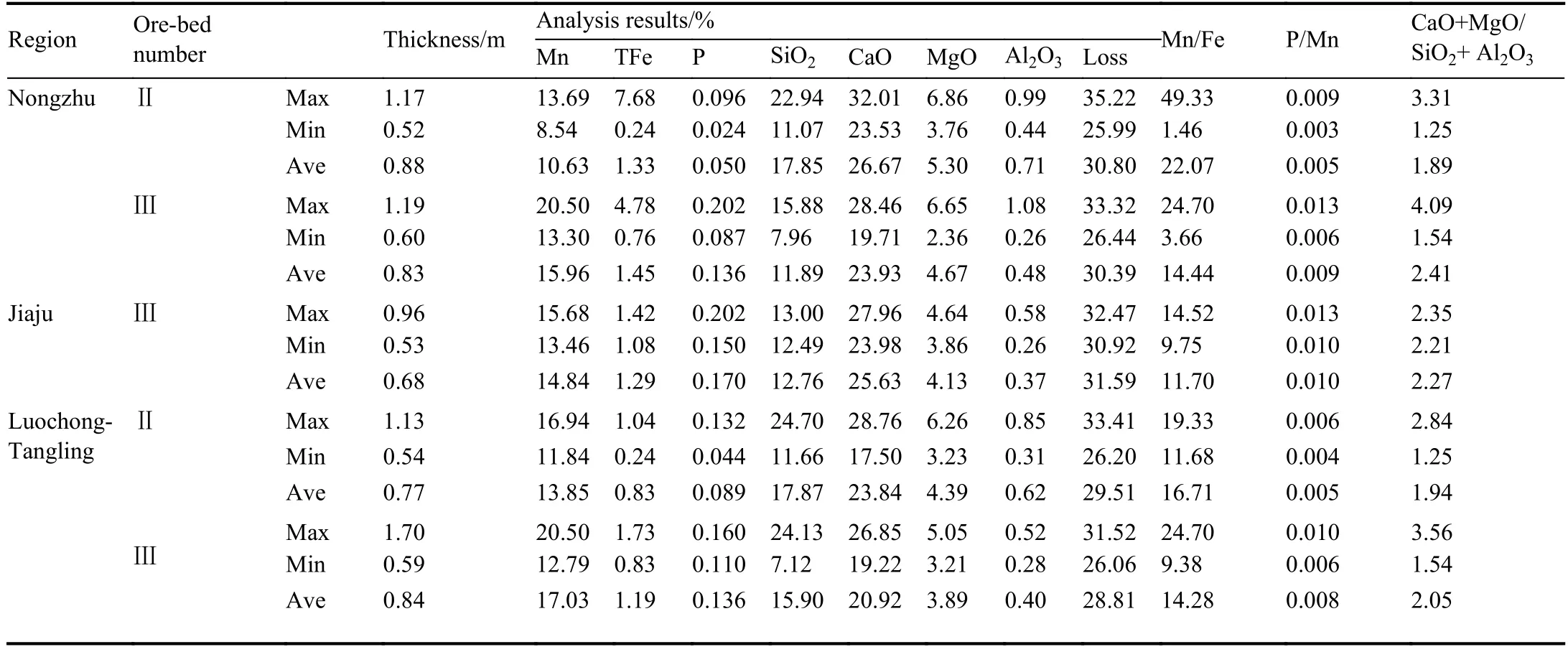
Table 1. Chemical analysis of manganese carbonate ore in Limiao-Tangling area.
The Longtou-Limiao anticlinorium, which is overlain by the Baping Group carbonate Mn bearing rock series, includes two parts, Limiao and Lali-Tangwo. The Limiao anticlinorium is about 40 km long, and is mainly distributed along NE. The Mn bearing rock was found well preserved in the sunken regions cutting by faults in its axis. The thickness of Mn ore bed is from 0.53 m to 0.98 m. The average grade is 8.96%-20.60%, and the elevation is 10-200 m. There are three Mn prospecting target areas in the Limiao anticlinorium as follows:
Nongzhu: besides the Nongzhu deposit, 2×107t Mn ore reserves was evaluated in SW section. Deep ore beds that was connected with the Nongzhu deposit is also confirmed through drilling.
Luochong-Tangling: 2.5×107t Mn ore reserves was evaluated. The metallogenic environment was similar to the Nongzhu deposit.
Luofu-Limiao: the Baping Group Mn carbonate rock are widely exposed, which is rich in Mn reserves as that of Limiao-Tangling.
There is also 6.5×106t of Mn ore reserves evaluated in Jiaju, the west periphery of Nongzhu.
Totally, there is 8.3×107t Mn ore reserves (333+334) in the Limiao anticline.
The Lali-Tangwo anticlinorium, which is 50 km long, has similar conditions of stratum, metallogenic environment and deposit preservation as the Limiao anticlinorium.
4. Conclusions
The Nongzhu large deep-sea sedimentary Mn deposit,which is located in the Nandan-Yizhou faulting basin, has been discovered 3.1×107t Mn ore reserves (12.10%/0.86 m).
Within the Nandan-Yizhou faulting basin, there is 8.3×107t of Mn ore reserves have been evaluated, and 0.2×109t Mn resource potential have been predicted.
Discovery of the Nongzhu deposit, the first large Mn deposit in Carboniferous, indicates substantial Mn ore prospecting space.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Mineral Geological Survey Project "Survey and Evaluation of Mn Ore Resource in Nandan-Yizhou, Guangxi" (12120114015401).The authors would like to express sincere thanks for professor Wang YJ and Li LT for their guidance on this work.
- China Geology的其它文章
- Deep Continental Scientific Drilling Engineering Project in Songliao Basin: progress in Earth Science research
- Main technical innovations of Songke Well No.2 Drilling Project
- Preliminary results of environmental monitoring of the natural gas hydrate production test in the South China Sea
- Episodic crustal growth in the Tanzania Craton: evidence from Nd isotope compositions
- Origin of natural sulfur-metal chimney in the Tangyin hydrothermal field, Okinawa Trough: constraints from rare earth element and sulfur isotopic compositions
- Exploration and research progress of shale gas in China

