一类温储备系统的剩余寿命及休止时间
强玉霞,张正成,温九红
(兰州交通大学 数理学院,甘肃 兰州 730070)
一类温储备系统的剩余寿命及休止时间
强玉霞,张正成,温九红
(兰州交通大学 数理学院,甘肃 兰州 730070)
本文讨论了由正常工作元件与温储备元件构成的温储备系统。在条件min(X,Y)=t下得到温储备系统中存活元件剩余寿命的可靠性函数;在系统中寿命较弱元件仍然存活的情况下,推导了系统剩余寿命及休止时间的可靠性函数,并且考虑了元件寿命与系统剩余寿命(休止时间)的关系。
随机序;温储备系统;剩余寿命;休止时间
研究可靠性工程主要的目的是提高系统的有效性与可靠性。给系统配置温储备元件是一种提高系统性能的有效方法。温储备是指元件在储备状态时是在温和的环境下工作,相较于正常工作的元件失效率较低。之前很多学者研究了各种系统的剩余寿命与休止时间,如Asadi[1]、Khaledi[2]、Hashemi[3]、Zhang[4]。 2002年,Bairamov[5]研究了具有并联和串联结构系统的剩余寿命函数;2003年,Li和Lu[6]考虑了并联和串联系统剩余寿命的随机比较;2011年,Zhang[7]研究了n中取k系统的条件剩余寿命;2013年,Zhang[8]考虑了协同系统的剩余寿命与休止时间的可靠性函数。

本文讨论了由温储备元件与正常工作元件组成的温储备系统。首先在条件min(X,Y)=t下得到温储备系统中存活元件剩余寿命的可靠性函数,比较了两个元件的剩余寿命;其次在系统中寿命较弱元件仍然存活的情况下,推导出系统剩余寿命与休止时间的可靠性函数,考虑了元件寿命不同对系统剩余寿命及休止时间的影响。
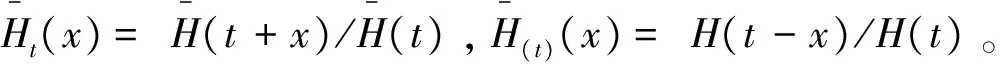
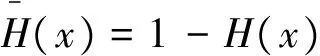

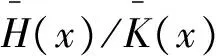

(c)若H(x)/K(x)单调递减,则称M在反失效率序意义下小于N(表示为M≤rhN)。
1 主要结论
定理1 当min(X,Y)=t时,对任意的t≥0,x≥0,有
(a)温储备系统中正常工作元件的剩余寿命函数为
(1)
(b)温储备系统中温储备元件的剩余寿命函数为
(2)
证明:(a)当x
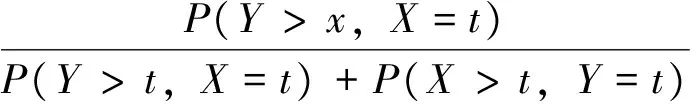
引理1[11]假设M、N是两个连续或离散的独立随机变量,对任意的t≥0,M≤hrN当且仅当(M|min(M,N)=t)≤hr(或者≤st)(N|min(M,N)=t)。
下面的定理说明引理1的结论可以推广到温储备系统中。
定理2X和Y是相互独立且连续的随机变量,对任意的t≥0,则Y≤hrX当且仅当(Y|min(X,Y)=t)≤hr(或者≤st)(X|min(X,Y)=t)。
证明:(必要性)对任意的t≥0,x≥0,由式(1)和式(2)可得
当x≥t时,

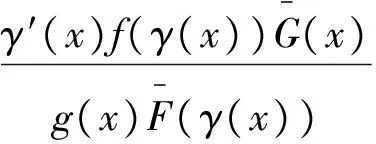
充分性由引理1即可得。 一般随机序的证明与失效率序的证明相同,此处省略。
对任意的t≥0,在温储备系统中较弱元件在t时仍然存活的情况下,考虑此时系统的剩余寿命。即(T(X,Y)-t|min(X,Y)≥t)。
定理3 (T(X,Y)-t|min(X,Y)≥t)的可靠性函数为
(3)
证明:对任意的t≥0,x≥0,有


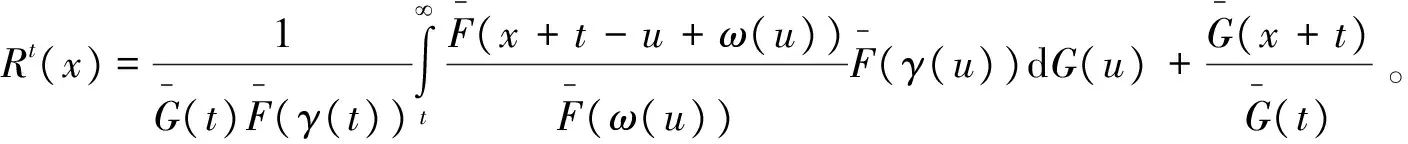
定理4 对任意的t≥0,有
(a)若X1≤hrX2,则(T(X1,Y)-t|min(X1,Y)≥t)≤st(T(X2,Y)-t|min(X2,Y)≥t);
(b)假设对任意的u≥0,有γ(u)≤ω(u)且u-ω(u)单调递增。 若Y1≤hrY2,则
(T(X,Y1)-t|min(X,Y1)≥t)≤st(T(X,Y2)-t|min(X,Y2)≥t)。




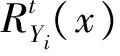

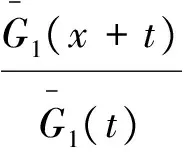
(T(X1,Y)-t|min(X1,Y)≥t)≤st(T(X2,Y)-t|min(X2,Y)≥t)。
接下来考虑了温储备系统在时刻t≥0时的休止时间,即(t-T(X,Y)|max(X,Y)≤t)。
定理5 对任意的t≥0,x≥0,(t-T(X,Y)|max(X,Y)≤t)的可靠性函数为
证明:对任意的t≥0,x≥0,有
其中:P(T(X,Y)≤t-x,max(X,Y)≤t)=P(Y≤t-x,Xμ≤t)+P(Y+X*≤t-x,Y 定理6 对任意的t≥0,有 (a)假设对任意的u≥0,有γ(u)≤ω(u),若X1≤rhX2且X1≤hrX2,则 (t-T(X1,Y)|max(X1,Y)≤t)≥st(t-T(X2,Y)|max(X2,Y)≤t); (b)假设对任意的u≥0,有γ(u)≤ω(u)且u-ω(u)单调递增。 若Y1≤rhY2,则 (t-T(X,Y1)|max(X,Y1)≤t)≥st(t-T(X,Y2)|max(X,Y2)≤t)。 证明: (a)对任意的t≥0,x≥0,有 (b)的证明与定理4(b)的证明类似,此处省略。 本文讨论了由温储备元件与正常工作元件组成的温储备系统。在条件min(X,Y)=t下考虑了温储备系统中存活元件剩余寿命的可靠性函数,比较了两个元件的剩余寿命,得到正常工作元件的剩余寿命比温储备元件的短;在系统中寿命较弱元件仍然存活的情况下,得到了温储备系统剩余寿命及休止时间的可靠性函数,并且考虑了元件寿命与系统剩余寿命及休止时间的关系,得到系统中两个元件的寿命在失效率意义下减小,则该元件对应的整个系统的剩余寿命也会减少,而休止时间增大。 [1] Asadi M,Bairamov I.A note on the mean residual life function of a parallel system[J]. Communication in Statistics-Theory and Methods,2005(34):475-484. [2] Hashemi M,Tavangar M,Asadi M.Some properties of the residual lifetime of progressively Type-Ⅱ right censored order statistics[J].Statistics and Probability Letters,2010(80):845-859. [3] Khaledi B,Shaked M.Ordering conditional lifetimes of coherent systems[J].Journal of Statistical Planning Inference,2007(137):1173-1184. [4] Zhang Z C,Yang Y.Ordered properties on the residual life and inactivity time of (n-k+1)-out-of-n systems under double monitoring[J].Statistics and Probability Letters,2010(80):711-717. [5] Bairamov I,Ahsanullah M,Akhundov I.A residual life function of a system having parallel or series structures[J].J Stat Theory Appl,2002,1(2):119-132. [6] Li X H,Lu J Y.Stochastic comparisons on residual life and inactivity time of series and parallel systems[J].Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences,2003(17):267-275. [7] Zhang Z C.Ordering new conditional residual lifetimes of k-out-of-n systems[J].Communication in Statistics-Theory and Methods,2011,40(9):1591-1600. [8] Zhang Z C,William Q,Meeker.Mixture representations of reliability in coherent systems and preservation results under double monitoring[J].Communication in Statistics-Theory and Methods,2013(42):385-397. [9] Ross S M.Stochastic process and their applications[M].New York:Wiley,1996:50-56. [10] Shaked M,Shanthikumar J G.Stochastic Orders[M].New York:Springer,2007:78-86. [11] Shaked M,Shanthikumar J G.Stochastic Orders and Their Applications[M].California:Academic Press,2007:32-45. Residual Life and Inactivity Time of the Warm Standby System JIANG Yuxia,ZHANG Zhengcheng,WEN Jiuhong (Lanzhou Jiaotong University,Lanzhou 730070,China) This article discussed the warm standby system composed of normal component and warm standby component. Under the condition min(X,Y)=t,the residual life reliability function of the surviving elements in the warm standby system is considered. Under the condition of the weaker component is still alive in the system,the reliability function of the residual life and inactivity time is deduced. The relationship between the life of component and the residual life (inactivity time) of the system is considered. stochastic order;warm Standby System;residual Life;inactivity Time 10.3969/i.issn.1674-5403.2017.03.020 O213.2 A 1674-5403(2017)03-0079-05 2017-04-05 强玉霞(1994-),女,甘肃陇南人,在读硕士研究生,主要从事系统可靠性方面的研究. 国家自然科学基金项目(71361020).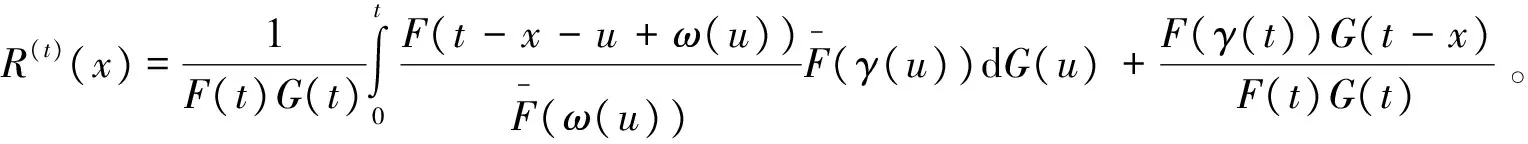


2 结 语

