先天性心脏病不同程度肺动脉高压患儿手术前后血浆脑钠肽的变化研究
郭俊晓 张玉龙 刘志平 朱宪明 赵龙 王坚
先天性心脏病不同程度肺动脉高压患儿手术前后血浆脑钠肽的变化研究
郭俊晓 张玉龙 刘志平 朱宪明 赵龙 王坚
作者单位:010050 内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市,内蒙古医科大学附属医院心脏大血管外科
目的 评价先天性心脏病伴不同程度肺动脉高压(PAH)患儿手术前后不同时间血浆脑钠肽(BNP)的变化。方法 纳入2013年12月至2014年12月内蒙古医科大学附属医院经超声心动图确诊的左向右分流先天性心脏病患儿60例,采用超声心动图评估肺动脉收缩压,比较不同程度PAH患儿手术前后不同时间血浆BNP水平差异。结果 术前及术后7 d血浆BNP水平均随PAH严重程度增高而升高,其中术前及术后7 d血浆BNP水平在无PAH,轻度、中度、重度PAH患儿间差异均有统计学意义[术前血浆BNP水平四组分别为(38.74±6.42)pg/ml、(134.36±22.40)pg/ml、(307.46±86.06)pg/ml、(661.12±66.88)pg/ml;术后血 浆 BNP 水 平四组分别为 (188.62±18.07)pg/ml、(253.78±26.00)pg/ml、(553.33±31.02)pg/ml、(789.63±108.97)pg/ml,P<0.05];而在术前及术后7 d除重度肺动脉高压组未见统计学差异,其余三组间均有统计学意义。结论 左向右分流先天性心脏病患儿手术前后血浆BNP水平随PAH严重程度的增高而逐渐升高,可作为评价PAH程度的一项指标,有助于保障患儿的健康,值得在实际中应用。
脑钠肽; 先天性心脏病; 肺动脉高压; 临床意义
先天性心脏病是我国儿童最常见的心脏疾病,占出生活产婴儿的7%~8%,其中左向右分流型占先天性心脏病的60%~70%。左向右分流型先天性心脏病患儿肺动脉高压(PAH)发生率低于复杂先天性心脏病患儿,病情进展较缓慢,85%~90%可存活至成年[1],若治疗不及时5%~10%左向右分流先天性心脏病患儿成年后将继发不同程度PAH,最终发展为艾森曼格综合征,此期PAH不因先天性心脏病矫正术后而逆转,严重影响治疗效果甚至失去手术时机[2]。肺动脉高压(pulmonary hypertension,PH)是一类以肺血管阻力进行性增高为主要特点的肺血管疾病[3,4],已成为一类严重威胁人类身心健康的常见疾病[5]。手术是治疗先天性心脏病的一个重要手段,但是,全麻体外循环下手术治疗过程复杂,需要使心脏暂时停跳,修补结束后复跳,会对心脏功能产生一定影响,在治疗上对患儿手术前后心脏功能的评价尤为重要[6]。近年来血浆脑钠肽(brain nirtie peptide,BNP)与 PAH 相关性的研究日趋增多。BNP是主要由心室合成和分泌的一种利钠多肽,心室负荷和心室壁张力的改变是刺激其分泌的主要条件[7],其对心室功能变化敏感而特异,能增加心泵量以及利钠、松弛血管平滑肌、抑制交感神经系统和拮抗肾素-血管紧张素-醛固酮系统。血浆BNP可作为监测原发和继发性PAH变化的一个观察指标[8,9]。本研究比较手术前后不同时间血浆BNP水平在先天性心脏病合并不同程度PAH患儿中的差异,旨在为临床确定手术及预后提供临床参考。
1 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象 纳入2013年12月至2014年12月经超声心动图确诊的左向右分流先天性心脏病患儿 60例,男性32例,女性 28例,年龄 3~10(7.5±2.4)岁。其中单纯室间隔缺损29例、房间隔缺损20例、动脉导管未闭11例。
1.2 PAH的测定和分级 采用Phillip 500超声心动图评估肺动脉收缩压(PASP),>30 mm Hg(1 mm Hg=0.133 Pka) 定义为 PAH[10]。轻度 PAH:PASP 30~39 mm Hg,中度 PAH:PASP 40~69 mm Hg,重度PAH:PASP≥70 mm Hg。
1.3 方法 详细询问患儿病史及家族史,体检胸部X线片、心电图、超声心动图,于入院第2天清晨及术后7 d采集外周静脉血3 ml,试管中加EDTAA(依地酸,乙二胺四乙酸)抑肽酶摇匀,4℃低温离心分离血浆(3500 r/min,10 min),采用放射免疫方法测定血浆BNP浓度。
1.4 统计学分析 采用SAS 9.0统计软件进行统计分析。计量资料以±s表示,两组间比较采用t检验。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
无PAH患儿16例,轻度PAH患儿16例,中度PAH患儿14例,重度PAH患儿14例。各组血浆BNP水平在术前及术后随PASP增高而升高,差异均有统计学意义(P均<0.05);在术前与术后各组除重度PAH组与重度PAH之间未见统计学差异,无PAH、轻度PAH、中度PAH组之间差异均有统计学意义(P均<0.05)。见表1。
表1 不同程度肺高压先天性心脏病患儿手术前后血浆 BNP 水平比较(±s)
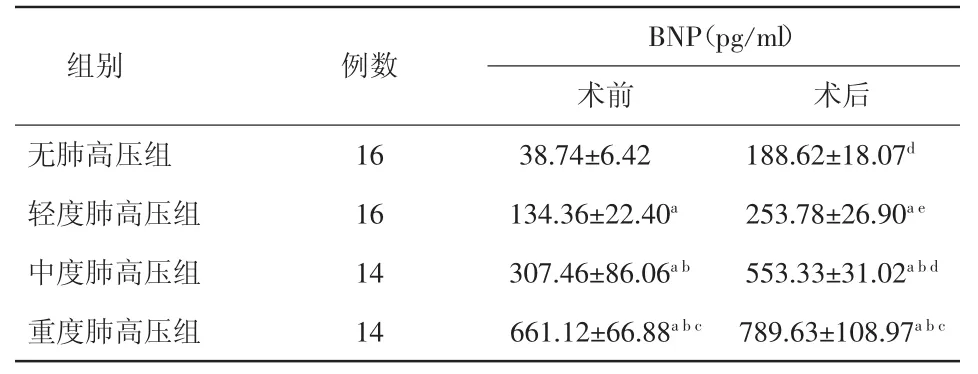
表1 不同程度肺高压先天性心脏病患儿手术前后血浆 BNP 水平比较(±s)
注:BNP:血浆脑钠肽。与无肺高压组比较,aP<0.05;与轻度肺高压组比较,bP<0.05;与中度肺高压组比较,cP<0.05。与术前比较,dP<0.05,eP<0.01
BNP(pg/ml)术前 术后无肺高压组 16 38.74±6.42 188.62±18.07d轻度肺高压组 16 134.36±22.40a 253.78±26.90ae中度肺高压组 14 307.46±86.06ab 553.33±31.02abd重度肺高压组组别 例数14 661.12±66.88abc 789.63±108.97abc
3 讨论
在先天性心脏病治疗中,BNP被认为是评定是否早期需要进行手术治疗的客观依据[11],研究显示检测手术前后BNP的变化还可以作为评估患儿预后的参考指标[12-14]。PAH是先天性心脏病最常见的并发症之一,对先天性心脏病围术期治疗具有重要影响。目前经胸超声心动图作为评价PAH的无创性检查手段已在临床广泛应用,但其对PAH的评估受多种因素的影响,诊断PAH特异度稍显不足。先天性心脏病相关性PAH早期表现为动力型,经外科手术或介入治疗矫正先天性畸形后肺动脉压力可下降或接近正常,预后良好;病情进一步发展则呈阻力型PAH,不因心脏原发病变解除而逆转甚至发展为艾森曼格综合征,称不可逆型PAH,患者失去手术时机,严重影响治疗效果。因此,评价PAH的程度及性质十分重要。目前诊断及评估PAH程度最佳指标为右心导管检查术[15],但其为有创性检查,存在一定风险。BNP临床上主要应用于心功能不全的诊断及预后评估、不同PAH的预后评估等[16]。
Cantinotti等[17]报道先天性心脏病患者血浆BNP及NT-proBNP水平明显高于对照组,并受心脏压力负荷及容量负荷的影响。Nagaya等[18]的研究表明,在特发性肺动脉高压患儿中,血清BNP水平与右室的射血分数呈负相关,提示血清BNP水平可以反映肺动脉高压右心功能的严重程度。不少国内外研究结果都提示,先天性心脏病患儿术后BNP值高于术前[19]。Koch等[20]的研究证明,手术对心脏有不同程度的损伤。相关研究证实,对于先天性心脏病患儿,在手术治疗前后血浆BNP水平会产生明显变化。本试验也对先天性心脏病合并肺动脉高压患儿术前及术后BNP水平进行研究,结果发现,左向右分流型先天性心脏病患儿,术前与术后7 d BNP水平随PASP的增高而增高,其中血浆BNP水平在术前与术后7 d重度、中度和轻度PAH患儿及无PAH患儿间差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05),提示BNP水平高低可反映PAH程度,BNP水平较NT-proBNP水平更敏感,监测术前与术后7 d血浆BNP水平对先天性心脏病所致PAH早期诊断及术后预后具有十分重要的临床意义。在术前与术后各组之间除重度PAH组与重度PAH之间未见统计学差异,无PAH、轻度PAH、中度PAH组之间差异均有统计学意义(P均<0.05)。因此检测手术前后患儿血浆BNP的变化,对临床诊断先天性心脏病合并肺动脉高压有重要价值,有利于早期诊断,干预治疗,判断预后。
测定患儿手术前后血浆BNP评估PAH不能否定超声心动图的必要性。由于应用经胸超声心动图测量肺动脉高压的误差在3~38 mm Hg[21],在诊断早期PAH时,特异性稍显不足[22],测定患儿手术前后血浆BNP水平变化与超声心动图可联合应用,互相补充,以提高诊断先天性心脏病患者合并PAH的效能,更好地评估血流动力学参数变化,从而避免进行右心导管检查术。
总之,对于左向右分流型先天性心脏病合并PAH,手术前后血浆BNP可以反映先天性心脏病合并PAH的血流动力学变化,可以有效诊断患儿病情,改善患儿心功能。由于检测血浆BNP浓度变化具有操作方便、简单、安全、可靠、无创、可重复性强的特点,在评价左向右分流型先天性心脏病合并PAH患儿的病情、预后等方面具有较好的临床价值,不失为评价PAH有益的生化指标。其临床应用价值有待进一步研究。
[1]Inglessis I,Landzberg MJ.Interventional catheterization in adult congenital heart disease.Circulation,2007,115:1622-1633.
[2]Diller GP,Gatzoulis MA.Pulmonary vascular disease in adults with congenital heart disease.Circulation,2007,115:1039-1050.
[3]Galei N,Hoeper MM,Humbert M,et al.Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension.Eur Respir J,2009,34:1219-1263.
[4]王晓峰,顾虹,张陈,等.先天性心脏病合并肺动脉高压患者可手术性分析.中国医药,2012,7:449-451.
[5]Bull TM,Clark B,MeFann K,et al.Pulmonary vascular dysfunction is associated with poor outcomes in patients with acute lung injury.Am J Respir Crit Care Med,2010,182:1123-1128.
[6]田晓瑜,王晓宁,陈惠芬,等.儿童先天性心脏病手术前后血浆脑钠肽的变化.河北医药,2014,36:168-171.
[7]Munagala VK,Burnett JC Jr,Redfield MM.The natriuretic peptides in cardiovascular medicine.Curr Probl Cardiol,2004,29:707-769.
[8]Bernus A,Wagner BD,Accurso F,et al.Brain natriuretic peptide levels in managing pediatric patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension.Chest,2009,135:745-751.
[9]Reynolds EW,Ellington JG,Vranicar M,et al.Brain-type natriuretic peptide in the diagnosis and management of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn.Pediatrics,2004,114:1297-1304.
[10]Currie PJ,Seward JB,Chan KL,et al.Continuous wave Doppler determination of right ventricular pressure:asimultaneous Doppler-catheterization study in 127 patients.J Am Coll Cardiol,1985,6:750-756.
[11]Kunii Y,Kamada M,Ohtsuki S,et al.Plasma brain natriuretic peptide and the evaluation of volume overload in infant and children with congential heart disease.Acta Med Okayama,2003,57:191-197.
[12]Norozi K,Buchhorn R,Kaiser C,et al.Plasma N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic as a marker of right ventricular dysfunction in patients with tetralogy of Fallot after surgical repair.Chest,2005,128:2563-2570.
[13]Eindhoven JA, denBosch AE, JansenPR, etal.The usefulness of brain natriuretic peptide in complex congenital heartdisease, a systematic review.J Am CollCardiol,2012,60:2140-2149.
[14]王奕.重组人脑钠肽对先天性心脏病合并肺动脉高压临床治疗观察.中国煤炭工业医学杂志,2013,16:1123-1124.
[15]Galiè N,Hoeper MM,Humbert M,et al.Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension:the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology(ESC)and theEuropeanRespiratorySociety (ERS), endorsed bythe International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation(ISHLT).Eur Heart J,2009,30:2493-2537.
[16]李丽,方臻飞,朱丹.成人左向右分流先天性心脏病封堵术前NT-proBNP浓度与PAH的临床意义.中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2012,10:670-672.
[17]Cantinotti M,Vittorini S,Storti S,et al.Diagnostic accuracy and clinical relevance of brain natriuretic peptide assay in pediatric patients with congenital heart diseases.J Cardiovasc Med(Hagerstown),2009,10:706-713.
[18]Nagaya N,Nishikimi T, Okano Y, et al.Plasma brain natriuretic peptide levels increase in proportion to the extend of right ventricular dysfunction in pulmonary hypertension.J Am Coll Cardiol,1998,31:202-208.
[19]Koch A,kitzsteiner T,Zink S,et al.Impact of cardiac surgery on plasma levels of B-type natriuretic peptide in children with congential heart disease.Int J Cardiol,2007,114:339-344.
[20]Koch A,Singer H.Normal value of B type natriuetic peptide in-fants,children,and adolescents.Heart,2003,89:875-878.
[21]McGoon,Gutterman D,Steen V,et al.Screening,early detection,and diagnosis of pulmonary arterial hypertension:ACCP evidencebased clinicalpractice guideline.Chest,2004,126:14S-34S.
[22]Casserly B,Klinger JR.Brain natriuretic peptide in pulmonary arterial hypertension:biomarker and potential therapeutic agent.Drug Des Devel Ther,2009,29:269-287.
The perioperation change of plasma brain natriuretic peptide in children with congenital heart disease combined pulmonary hypertension
GUO Jun-xiao,ZHANG Yu-long,LIU Zhi-ping,et al.Department of Heart Vascular Surgery,Inner Mogalin Medical College Affiliated Hospital,Hohhot 010050,China
Objective To study the perioperation change of plasma brain natriuretic peptide(BNP)in children with congenital heart disease combined pulmonary hypertension.Methods 60 cases with left to right shunt congenital heart admitted in Inner Mongolia medical university affiliated hospital from December 2013 to De-cember 2014 were enrolled.The pulmonary artery systolic pressure was evaluated by the echocardiography,and the different degree PAH plasma,BNP levels before and after surgery were compared.Results The blood plasma BNP levels in preoperative and seventh day of postoperative were rised with the increasing severity of PAH,and there were statistical significance among the absence of PAH,mild,moderate and severe PAH patients(P<0.05).In preoperative and postoperative 7th day,the level of BNP was no statistical significance in the severe pulmonary hypertension group,but in the other three groups there were statistical significance(P>0.05).Conclusion The level of plasma BNP increases with increasing of PAH in children with congenital heart disease combined pulmonary hypertension,and may be used as an evaluation of the degree of PAH.
Brain natriuretic peptide; Congenital heart disease; Pulmonary arterial hypertension;Clinical significance
10.3969/j.issn.1672-5301.2017.09.016
R654.2
A
1672-5301(2017)09-0829-04
2016-06-17)