结肠癌患者外周血Th17和Th22细胞分布及IL-17A和IL-22的作用研究
李树斌,苏冬梅
中国中医科学院广安门医院南区内1科,北京102618
结肠癌患者外周血Th17和Th22细胞分布及IL-17A和IL-22的作用研究
李树斌,苏冬梅
中国中医科学院广安门医院南区内1科,北京102618
目的 研究结肠癌患者外周血Th17和Th22亚群分布及血清IL-17A和IL-22含量与临床病理的相关性及IL-17A和IL-22对结肠癌细胞的作用。方法 收集结肠癌患者全血和血清样本,流式细胞术检测Th17和Th22亚群比例;ELISA法检测血清细胞因子IL-17A和IL-22含量;流式细胞术检测IL-17A和IL-22对结肠癌细胞增殖和凋亡的影响。结果 结肠癌患者外周血Th17和Th22含量较健康对照组显著升高;血清IL-22表达水平显著升高;IL-17A和IL-22促进结肠癌细胞增殖,抑制细胞凋亡。结论Th17和Th22细胞及其相关细胞因子与结肠癌的发生、发展密切相关。
结肠癌;Th22细胞;IL-22;Th17细胞;IL-17A
结肠癌是高发肿瘤,尤其在中国,近年来结肠癌的发病率呈上升趋势。虽然伴随着结肠癌的筛查和早期诊断及治疗方法的不断改进,结肠癌患者的总体生存率已大大提高。但是晚期结肠癌的死亡率依然很高。因此,深入研究结肠癌的分子机制有助于提高诊断和治疗效果[1]。
越来越多的证据表明,淋巴细胞亚群分布和细胞因子表达水平失调与结肠癌的发生、发展密切相关[2-3]。Th17细胞是一个CD4+T淋巴细胞亚群 (主要分泌IL-17A),广泛参与多种自身免疫性疾病和慢性炎症。目前对于小鼠和人类的Th17细胞的分化和功能研究已取得了可喜的进展,但在肿瘤特别是结肠癌中Th17细胞的产生和调控仍有许多问题不明确[4]。Th22细胞是分泌IL-22的一类CD4+辅助性T细胞。这类细胞在炎症和自身免疫性疾病中的功能特点也已被广泛研究。但是其在肿瘤免疫中的作用研究相对有限,特别是在结肠癌中[5]。本研究通过检测并分析结肠癌患者外周血Th17和Th22细胞与相关细胞因子的表达差异及与临床病理的相关性,旨在探讨Th17和Th22细胞在结肠癌发生、发展中的作用,为临床个体化治疗提供实验依据。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 收集中国中医科学院广安门医院2014年12月-2015年12月经病理确诊的结肠癌患者外周血和血清样本53例,男33例,女20例,年龄38~81岁,平均年龄60岁;TNM分期StageⅠ~Ⅱ23例,StageⅢ~Ⅳ30例;患者均接受手术治疗,在未开始放化疗或免疫治疗之前取样。入组患者排除自身免疫性疾病、传染病、多发性原发癌、肠炎和家族性息肉。健康对照来自我院体检人群,共50名,男23名,女27名,年龄(57±6.21)岁(40~75岁)。血液样本的流式检测在24 h内完成,血清样本保存于-80℃备用。
1.2 试剂 FITC Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kit I、Anti-humanCD3-PerCP、CD4-FITC/APC、CD8-FITC/APC、IL-17A-PE抗体和相应同型对照购自BD Bioscience。Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate(PMA),ionomycin,Brefeldin A,FIX & PERM Kit Reagent、Anti-human IL-22-PE抗体、IL-17A和 IL-22 ELISA kit购自 eBioscience。
1.3 流式检测 细胞表面染色按试剂说明操作,室温避光孵育20 min;胞内染色时细胞 (1×106)被刺激培养4 h 用50 ng/ml PMA、1 μg/ml ionomycin、10 μg/ml Brefeldin A,染色前细胞用FIX&PERM Kit破膜和固定。实验使用FACSCalibur流式细胞仪检测,CellQuest software分析数据。
1.4 ELISA法检测结肠癌患者血清IL-17A、IL-22表达水平 按说明书操作,酶标仪检测(490 nm)。
1.5 细胞培养 人结肠癌细胞系HT-29购自中国科学院细胞库。Recombinant human IL-17A、IL-22购自PeproTech Company。细胞常规培养在DMEM培养基中,辅以100 g/L FBS。待进入指数期后,分别加入IL-17A(50 ng/ml)和IL-22(50 ng/ml)。48 h后收集细胞,进行胞内Ki-67染色,Annexin V和PI染色检测细胞凋亡。
1.6 统计学分析 采用GraphPad Prism 5.0和SPSS 17.0软件进行统计学分析。组间比较采用Student’s t-test、a paired t-test和one-way ANOVA。外周血清细胞含量用±s表示,流式检测外周血Th22及Th17细胞比例用中位数(P25,P75)表示。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 结肠癌患者外周血Th22、Th17细胞显著增加流式检测结果显示,与健康对照组[1.20%(0.91%,1.51%)]相比,结肠癌患者的CD4+T细胞中Th17细胞显著增加[3.00%(1.90%,5.00%),P <0.0001]。晚期结肠癌(StageⅢ~Ⅳ)患者的Th17细胞含量高于早期患者 (StageⅠ~Ⅱ),但差异无统计学意义 (见图1A~1B)。与健康对照组[1.68%(1.31%,2.67%)]相比,结肠癌患者的CD4+T细胞中Th22细胞显著增加[(2.70%(1.70%,4.70%),P=0.0010)];晚期结肠癌患者的Th22细胞含量(StageⅢ~Ⅳ)[3.25%(2.40%,6.15%)]高于早期患者 (StageⅠ~Ⅱ)[2.00%(1.45%,3.10%),P=0.0478](见图1C ~1D)。
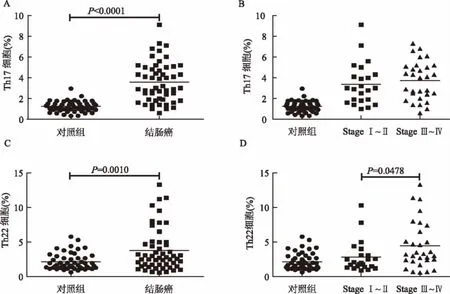
图1 结肠癌患者外周血CD4+T细胞中Th17和Th22细胞亚群分布 A:结肠癌患者和健康对照组Th17细胞百分比;B:不同分期的结肠癌患者的Th17细胞百分比;C:结肠癌患者和健康对照组Th22细胞百分比;D:不同分期的结直肠癌患者的Th22细胞百分比Fig 1 Peripheral CD4+T cell Th17 and Th22 cell subsets in colon cancer patients A:percentage of Th17 cells in colon cancer patients and healthy controls;B:percentage of Th17 cells in patients with different stages of colon cancer;C:percentage of Th22 cells in colon cancer patients and healthy controls;D:percentage of Th22 cells in patients with different stages of colon cancer
2.2 结肠癌患者血清IL-17A和IL-22含量 如图2所示,结肠癌患者血清IL-17A含量 (13.85±5.14)pg/ml高于健康对照 [(4.10 ±2.22)pg/ml,P <0.0001]。随着临床进展,晚期结肠癌患者血清IL-17A含量与早期患者相比无明显变化[StageⅢ-Ⅳ:(13.74±4.97)pg/ml;StageⅠ~Ⅱ:(13.98 ±5.46)pg/ml];结肠癌患者血清 IL-22含量(37.75±10.29)pg/ml高于健康对照[(25.53 ±9.86)pg/ml,P <0.0001]。晚期结肠癌患者血清IL-22水平升高[StageⅢ~Ⅳ:(40.41±9.09)pg/ml;StageⅠ~Ⅱ:(34.28 ±10.91)pg/ml,P=0.0301]。
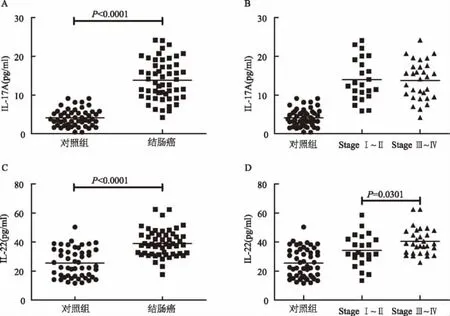
图2 结肠癌患者血清IL-17A和IL-22含量 A:结肠癌患者和健康对照组血清IL-17A含量;B:不同分期的结肠癌患者血清IL-17A含量;C:结肠癌患者和健康对照组血清IL-22含量;D:不同分期的结直肠癌患者血清IL-22含量Fig 2 Serum IL-17A and IL-22 levels in patients with colon cancer A:serum IL-17A level in colon cancer patients and healthy controls;B:serum IL-17A level in patients with different stages of colon cancer;C:serum IL-22 level in colon cancer patients and healthy controls;D:serum IL-22 level in patients with different stages of colon cancer
2.3 体外IL-17A和IL-22对结肠癌细胞的作用 如图3所示,IL-17A和IL-22促进结肠癌细胞HT-29增殖,抑制癌细胞凋亡。与对照组相比,IL-22处理后,HT-29细胞的增殖率升高和凋亡率降低,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05);IL-17A处理的HT-29细胞增殖率和凋亡率与对照组相比,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
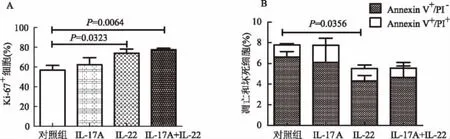
图3 IL-17A和IL-22对结肠癌HT-29细胞的作用 A:流式细胞术检测IL-17A和IL-22作用后结肠癌细胞增殖;B:流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡实验结果Fig 3 Effects of IL-17A and IL-22 on colon cancer HT-29 cells A:the proliferation of colon cancer cells after the action of IL-17A and IL-22 detected by flow cytometry;B:experimental results of apoptosis detected by flow cytometry
3 讨论
本研究首先检测了结肠癌患者外周血Th17、Th22细胞和血清细胞因子IL-17A和IL-22的变化,结果表明,结肠癌患者早期循环Th17细胞增加。随着疾病进展,虽然晚期结肠癌 (StageⅢ~Ⅳ)患者的Th17细胞含量高于早期患者 (StageⅠ~Ⅱ),但差异无统计学意义。晚期结肠癌患者血清IL-17A含量与早期患者相比也无明显变化。Th17细胞是一群异质性细胞,能产生大量的IL-17A和其他细胞因子如IL-17F等,这些细胞因子可通过IL-17受体A(IL-17RA)触发MAPK和 NF-κB信号通路,刺激产生促炎症细胞因子、趋化因子和前列腺素[7-8]。Th17细胞的功能具有可塑性[9],已有证据[10]表明,Th17 细胞参与肿瘤发生,但Th17及其细胞因子对于恶性肿瘤细胞的存活和生长有正反两方面的作用。目前对于产生这种双重作用的原因尚不明确。本文的临床检测和体外细胞实验结果印证了前人的报道。
CD4+Th22细胞是一个T辅助细胞亚群。与Th1、Th2、Th17细胞不同,Th22细胞仅产生 IL-22。但IL-22还可由Th1和Th17细胞产生。Jiang等[11]研究表明,高水平的IL-22促进免疫缺陷小鼠体内人大肠癌细胞 (HCT-116)的生长,这种作用与STAT3活化和STAT3下游效应分子如cyclin D1上调有关。其他的报道[12-13]也证明,Th22细胞参与消化道恶性肿瘤的发生、发展。本研究结果显示,与健康对照组相比,结肠癌患者的CD4+T细胞中Th22细胞显著增加;晚期结肠癌患者的Th22细胞含量高于早期患者。同时结肠癌患者血清IL-22含量也呈一致的变化趋势。
我们随后检测了体外IL-17A和IL-22对结肠癌HT-29细胞增殖和凋亡的影响。结果表明,与对照组相比,IL-22处理后,HT-29细胞的增殖率升高,凋亡率降低;IL-17A处理的HT-29细胞无论是增殖还是细胞凋亡,与对照组相比,均无显著改变。IL-17A和IL-22联合作用后,与对照组相比HT-29细胞的增殖显著增加,但与单用IL-17A或IL-22处理组相比,差异无统计学意义;IL-17A和IL-22联合作用后,HT-29细胞凋亡率与其他组相比,差异均无统计学意义。分析结果产生的原因可能与实验采用的细胞因子浓度和选择的肿瘤细胞系及其他实验条件的设定有关。进一步的研究需要通过体内外实验比较不同浓度和组合的细胞因子对结肠癌发生、发展的影响,并深入分析背后的作用机制。
[1]Jiang Z,Wang X,Tan X,et al.Effect of age on survival outcome in operated and non-operated patients with colon cancer:a populationbased study[J].PLoS One,2016,11(1):e0147383.
[2]Scurr M,Gallimore A,Godkin A.T cell subsets and colorectal cancer:discerning the good from the bad [J].Cell Immunol,2012,279(1):21-24.
[3]Ling KL,Pratap SE,Bates GJ,et al.Increased frequency of regulatory T cells in peripheral blood and tumour infiltrating lymphocytes in colorectal cancer patients[J].Cancer Immun,2007,7:7.
[4]Wang J,Xu K,Wu J,et al.The changes of Th17 cells and the related cytokines in the progression of human colorectal cancers[J].BMC Cancer,2012,12:418.
[5]Huang YH,Cao YF,Jiang ZY,et al.Th22 cell accumulation is associated with colorectal cancer development[J].World J Gastroenterol,2015,21(14):4216-4224.
[6]Amicarella F,Muraro MG,Hirt C,et al.Dual role of tumour-infiltrating T helper 17 cells in human colorectal cancer[J].Gut,2015,66(4):692-704.
[7]De Simone V,Pallone F,Monteleone G,et al.Role of TH17 cytokines in the control of colorectal cancer[J].Oncoimmunology,2013,2(12):e26617.
[8]Liu J,Duan Y,Cheng X,et al.IL-17 is associated with poor prognosis and promotes angiogenesis via stimulating VEGF production of cancer cells in colorectal carcinoma[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2011,407(2):348-354.
[9]Karczewski J,Mazur M,Rychlewska-Hańczewska A,et al.Role of Th17 lymphocytes in pathogenesis of colorectal cancer[J].Postepy Hig Med Dosw(Online),2014,68:42-47.
[10]Tosolini M,Kirilovsky A,Mlecnik B,et al.Clinical impact of different classes of infiltrating T cytotoxic and helper cells(Th1,Th2,treg,Th17)in patients with colorectal cancer [J].Cancer Res,2011,71(4):1263-1271.
[11]Jiang R,Wang H,Deng L,et al.IL-22 is related to development of human colon cancer by activation of STAT3 [J].BMC Cancer,2013,13:59.
[12]Kryczek I,Lin Y,Nagarsheth N,et al.IL-22(+)CD4(+)T cells promote colorectal cancer stemness via STAT3 transcription factor activation and inductionof the methyltransferase DOT1L [J].Immunity,2014,40(5):772-784.
[13]Koltsova EK,Grivennikov SI.IL-22 gets to the stem of colorectal cancer[J].Immunity,2014,40(5):639-641.
(责任编辑:王全楚)
The distribution of peripheral Th17 and Th22 cells and the roles of IL-17A and IL-22 in colon cancer patients
LI Shubin,SU Dongmei
Department of Internal Medicine,Guang’anmen Hospital(South Region),China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences,Beijing 102618,China
ObjectiveTo determine the distribution of peripheral Th17 and Th22 cells and the roles of IL-17A and IL-22 in colon cancer patients.MethodsFlow cytometry was used to determine the percentages of Th22 cells and Th17 cells in the peripheral blood of colon cancer patients.ELISA assay was adopted to examine the serum levels of IL-17A and IL-22.The effects of IL-17A and IL-22 on the proliferation and apoptosis of colon cancer cell line were detected by flow cytometry.ResultsThe percentages of peripheral Th17 and Th22 cells in colon cancer patients were significantly increased compared with controls.The level of IL-22 in serum was significantly increased in colon cancer patients compared with controls.IL-17A and IL-22 promoted cell proliferation and inhibited apoptosis in colon cancer cells.ConclusionThere are high percentages of Th22 and Th17 cells in colon cancer patients.Th22 and Th17 cells may jointly participate in the pathogenesis and progression of colon cancer.
Colon cancer;Th22 cells;Interleukin-22;Th17 cells;Interleukin-17A
R735.3
A
1006-5709(2017)08-0882-04
2016-12-27
10.3969/j.issn.1006-5709.2017.08.011
李树斌,主任医师,研究方向:消化内科及消化系肿瘤临床研究。E-mail:lishb69@126.com
苏冬梅,主治医师,研究方向:中医药防治脾胃病及消化系肿瘤。E-mail:sdm1983@163.com

