GDSL脂肪酶增强棉花对大丽轮枝菌的抗性
安晶,潘泽,李鸿彬*
(石河子大学生命科学学院/石河子大学农业生物技术重点实验室,新疆 石河子832003)
GDSL脂肪酶增强棉花对大丽轮枝菌的抗性
安晶,潘泽,李鸿彬*
(石河子大学生命科学学院/石河子大学农业生物技术重点实验室,新疆 石河子832003)
大丽轮枝菌是影响棉花生长发育的一种通过土传真菌维管束的病菌,严重影响棉花纤维的产量和品质。为研究棉花GDSL脂肪酶(GDSL lipase,GLIP)在植物响应大丽轮枝菌中的重要功能,本研究利用大丽轮枝菌悬浮液对新陆早42号及其转GhGLIP基因的棉花株系叶片进行处理,分析转GhGLIP棉花株系对大丽轮枝菌的生理生化响应。结果表明,棉花GDSL脂肪酶基因GhGLIP能够响应大丽轮枝菌的刺激,转GhGLIP基因棉花株系可显著抑制大丽轮枝菌导致的叶片细胞死亡。与未处理相比,经大丽轮枝菌处理后的野生型和转基因棉花株系植株的GDSL脂肪酶活力显著增加。同时,转基因棉花株系植株过氧化氢酶、过氧化物酶、超氧化物歧化酶、苯丙氨酸解氨酶和多酚氧化物酶的表达显著提升,说明GhGLIP基因诱导了棉花对大丽轮枝菌的抗性。本研究为棉花抵抗大丽轮枝菌的分子机制解析,及进一步利用基因工程技术培育抗病棉花材料提供了有效参考。
GDSL脂肪酶;大丽轮枝菌;棉花抗病;抗氧化系统酶类
棉花是我国重要的经济作物,但是其生长发育受到多种病害的影响,尤其是大丽轮枝菌引起的棉花黄萎病是较为严重的影响棉花产量的真菌病害。该病害广泛分布于各个产棉地区,且有逐年加重的趋势[1]。针对黄萎病的防治,目前未见对环境无污染的化学防治药剂[2],因此,运用基因工程技术培育抗病棉花品种是当前主要的防治措施之一[3]。
植物GDSL脂肪酶是一个相对较大的家族酶类,具有多种功能,在植物生长发育、器官形态构成、次生代谢以及防御反应等生理活动中起到十分重要的作用[4]。植物GDSL脂肪酶基因的表达可以被多种生物因素及非生物因素的诱导,也受到植物激素如水杨酸(salicylic acid)、乙烯(ethylene)、茉莉酸(jasmonic acid)等的调控[5]。植物抗病性的表现是在一定的环境条件影响下寄主植物的抗病性基因和病原物的致病基因相互作用的结果[6],GDSL脂肪酶能够通过信号的转导调节或者直接破坏真菌孢子在植物体中结构的完整性,限制其正常繁殖[7]。棉花在生长过程中会遇到各种生物和非生物胁迫,例如大丽轮枝菌会严重危害棉花的生长发育。植物在受到病害胁迫时,细胞内会产生大量的活性氧(reactive oxygen species,ROS)[5],从而影响植物的正常生长发育,细胞内的抗氧化酶可以清除ROS并保持细胞的氧化还原平衡[8-9]。
棉花GDSL脂肪酶与黄萎病相关的研究少有报道。本研究以前期获得的过量表达GDSL脂肪酶基因GhGLIP的棉花株系为对象,利用大丽轮枝菌分别处理野生型和转基因棉花叶片,GDSL脂肪酶显著增强了转基因棉花植株对于大丽轮枝菌的抗性,以期为解析棉花大丽轮枝菌的分子机制及培育抗病品种奠定一定基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1 供试材料
陆地棉新陆早-42号野生型和转基因棉花、大丽轮枝菌为本实验室保存,大丽轮枝菌处理后的各种野生型和转基因棉花材料氮速冻后,于-80℃冰箱保存。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 RNA的提取和qRT-PCR表达分析
各棉花材料采用CTAB方法提取棉花总RNA,参照试剂盒的实验步骤说明,以棉花RNA为模板反转录成cDNA,用反转录后的cDNA作为模板进行qRT-PCR分析,所使用的引物利用Primer 5.0软件进行设计,并送生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司合成,引物序列见表1。
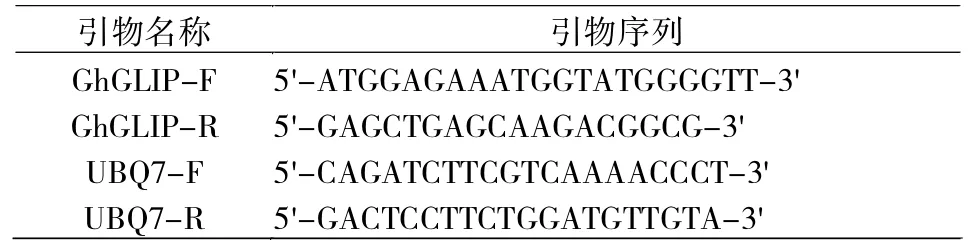
表1 使用的引物序列Tab.1 Primers used in this study
1.2.2 大丽轮枝菌培养与接种处理
参照张兴华等[10]的方法,配制大丽轮枝菌孢子浓度为1×107个/mL的悬浮液,棉签沾取菌液后在叶片表面涂抹,用水做对照处理,每棵植株处理3片叶片,每个处理设置9株作为重复。分别在接种0、1、3、5和 7 d后,摘下处理的叶片,置于 -80 ℃的冰箱,备用,用于酶活测定。
1.2.3 细胞染色
将经过大丽轮枝菌处理后3 d的叶片,置于DAB(1 mg/mL,pH 3.8)中染色 12 h,用脱色液(无水乙醇∶乙酸∶甘油∶水 =8∶1∶1∶1)于 37 ℃条件下脱色36 h,将叶片放置在干净的载玻片上,将Trypan blue染液均匀滴于叶面上,盖上盖玻片,静置20 min,用光学显微镜观察并拍照,统计叶片的坏死面积。细胞死亡率=细胞坏死面积/叶片总面积。
1.2.4 酶活力测定
脂肪酶(Lipase)的活力测定使用对硝基苯酚法[11]测定,并参照程璐等[12]的方法;多酚氧化酶(Polyphenolo-xi das,PPO)活力测定使用邻苯二酚法;超氧化物岐化酶(Superoxide dismutase,SOD)活力测定使用NBT方法;过氧化物酶(Peroxidase,POD)活力测定使用愈创木酚法;过氧化氢酶(Catalase,CAT)测定使用紫外分光光度碘量方法;苯丙氨酸解氨酶(Phenylalanine ammonialyase,PAL)参照邢会琴等[13]的方法。
1.2.5 数据统计与分析
试验所获数据为独立3次重复实验的平均值,数据差异性检验分析用Student t test方法检测,图表制作运用Orgin 8.0完成。
2 结果与分析
2.1 GhGLIP响应大丽轮枝菌处理的表达分析
由图1可见:经大丽轮枝菌处理1 d时,转基因棉花植株叶片中GhGLIP基因的转录表达和酶活力均显著增加,在处理5 d时达到最大值,随后保持稳定,表明GhGLIP基因对于大丽轮枝菌刺激的响应迅速。

图1 转基因棉花中GhGLIP响应大丽轮枝菌刺激的表达分析Fig.1 Analysis of GhGLIP expression in the transgenic cotton plants in response toVerticillium dahilaestimulus
2.2大丽轮枝菌处理棉花叶片的表型分析
利用大丽轮枝菌处理野生型和转基因棉花叶片,野生型棉花在处理2 d时表面有褐色斑点出现,处理3 d时出现萎蔫现象,并且出现较多的坏死斑点。转基因棉花植株仅出现少量褐色斑点,无严重的萎蔫现象。DAB-台盼蓝染色定量分析细胞坏死的结果(图2)显示:野生型棉花叶片有大面积的死亡,死亡面积达55%以上,转基因棉花植株叶片细胞死亡率为20%左右,表明GDSL脂肪酶显著增强了棉花植株对大丽轮枝菌的抗性。

图2 大丽轮枝菌处理转基因棉花叶片的表型分析Fig.2 Phenotypic analysis of transgenic cotton leaf afterVerticillium dahilaetreatment
2.3 大丽轮枝菌处理后的棉花脂肪酶活性测定
大丽轮枝菌处理后的棉花脂肪酶活性测见图3。
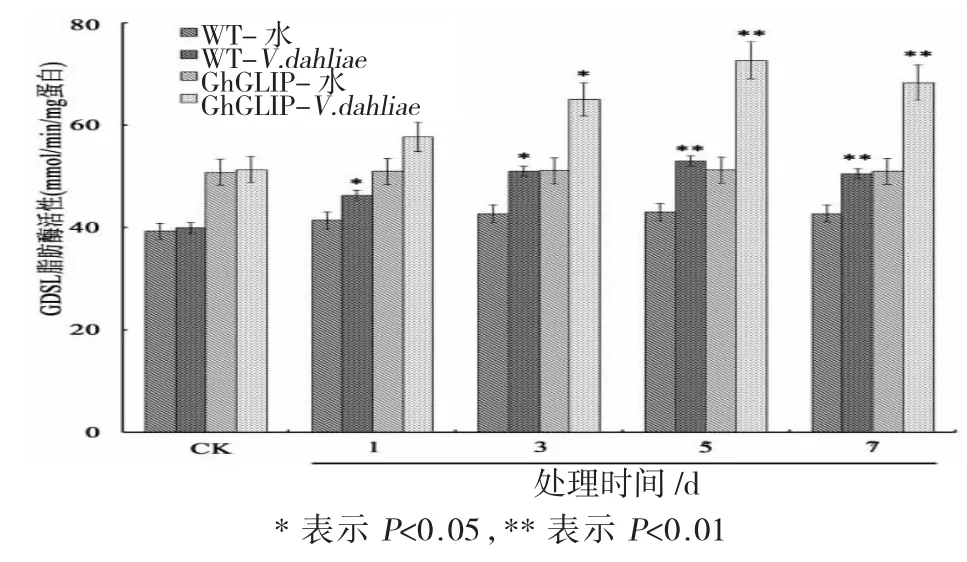
图3 转基因棉花中GDSL脂肪酶活性测定Fig.3 Measurement of GDSL lipase enzyme activity of transgenic cotton plants underVerticillium dahilaetreatment
由图3可见:经大丽轮枝菌处理后,野生型和转基因棉花中的脂肪酶活性均呈逐步增长的趋势,在处理5 d时酶活力达到最高值,而后趋于稳定;与野生型相比,转基因棉花中的脂肪酶活力显著增加。这表明GDSL脂肪酶的表达与植物响应大丽轮枝菌的刺激密切相关。
2.4 转基因棉花抗氧化酶活分析
经大丽轮枝菌处理后,以水处理作为对照,与野生型棉花相比,转基因棉花植株中的CAT、POD和SOD的表达均有显著的提升。CAT和POD的酶活力在大丽轮枝菌处理5 d时达到峰值并保持稳定表达,SOD酶活力在大丽轮枝菌处理3 d时,表现出快速的响应表达(图4)。这表明转基因棉花中的抗氧化系统酶类对于大丽轮枝菌的刺激响应具有较高的敏感性,并与棉花的抗病性获得联系紧密。
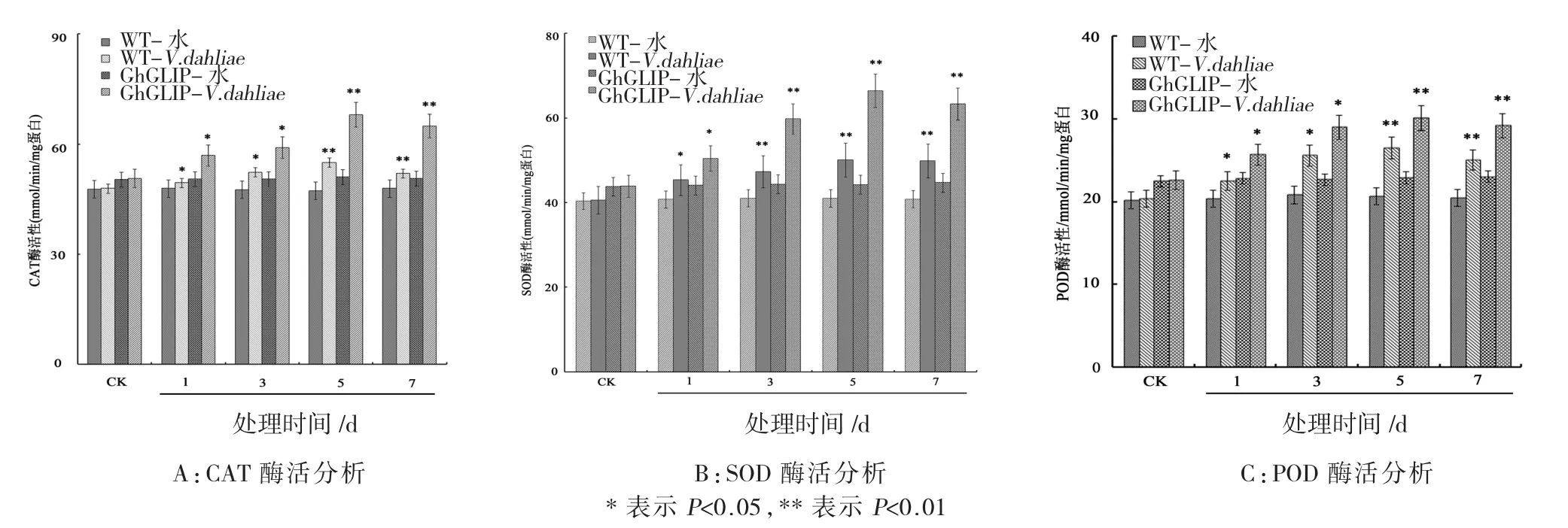
图4 转基因棉花植株的抗氧化酶活性分析Fig.4 Activity analysis of antioxidant enzyme in the transgenic cotton plants
2.5 转基因棉花PAL和PPO酶活性分析
大丽轮枝菌处理棉花后,野生型和转基因棉花中的PAL和 PPO的表达均显著升高,且在转基因棉花中的表达高于野生型棉花。PAL和PPO酶活力均在处理5 d时达到峰值;PPO对于大丽轮枝菌的刺激响应更敏感,处理3 d时呈现出显著提升(图5)。

图5 转基因棉花植株PAL和PPO酶活性分析Fig.5 Activity analyses of PAL and PPO enzymes in the transgenic cotton plants
3 讨论
GDSL脂肪酶在植物响应生物和非生物胁迫过程中发挥重要作用[14-15]。GDSL脂肪酶能够诱导植物对真菌产生抗病性,与野生型植株相比,glip-1突变体植株对腐生真菌芸苔表现为更强的敏感性[16-17]。许多研究表明植物的体内过量表达GDSL1可以增强对多种病原真菌和细菌的抗性,并且在这个过程中乙烯介导的信号途径诱导植物的系统抗病性发挥着重要作用[18-19]。本研究以过量表达GDSL脂肪酶基因的转基因棉花为对象,转基因棉花对于大丽轮枝菌的抗性获得了显著增强。
GDSL脂肪酶具有引起对多种病原体的广谱抗性的活性[20],植物可利用多层免疫系统来抵抗病原体的攻击[21]。植物被病原菌侵染时,一些生理生化反应如植保素等次级代谢产物的合成、β-1、与3-葡聚糖酶以及几丁酶等与病原相关蛋白的激活、富含羟脯氨酸蛋白在细胞壁中的积累等不会被诱导[22]。一些抗氧化酶类如PPO和PAL等则会大量累积。PPO在植物抗病反应中起到重要的作用,PPO能够催化木质素及其它酚类氧化产物的生成,构成保护性屏障从而抵抗病菌的侵入[23-24];PAL是苯丙氨代谢的第一关键酶,与包括木质素、香豆素、类黄酮、羟基肉桂酸酯以及异类黄酮衍生物等在内的植物抗毒素的合成有密切关系[25]。本研究中转基因棉花的抗氧化系统酶类CAT、SOD和POD,以及PAL和PPO的均能响应大丽轮枝菌菌刺激并具有较高的表达,表明了这些酶表达在病菌响应过程中的重要作用。
植物响应大丽轮枝菌的过程十分复杂,与多个生理生化过程密切相关,本研究为棉花抗病分子机制解析和利用基因工程技术培育抗病棉花新材料奠定了一定基础。
[1]林玲,张昕,邓晟.棉花黄萎病研究进展[J]棉花学报,2014,26(3):260-267.Lin L,Zhang X,Deng C.Research advance in cottonVerticllium wilt[J].Cotton Science,2014,26(3):260-267.
[2]郭宝生,师恭曜,王凯辉,等.黄萎病菌侵染下陆地棉Dirigent-like蛋白基因表达差异分析[J].中国农业科学.2014,47(22):4349-4359.Guo B S,Shi G Y,Wang K H,et al.Expression differences of Dirigent like protein genes in upland cotton responsed to infection byVerticillium dahlia[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2014,47(22):4349-4359.
[3]Cary J W,Rajasekaran K J,Jesse M.Transgenic expression of a gene encoding a synthetic antimicrobial peptide results in inhibition of fungal growth in vitro and in planta[J].Plant Science,2000,154(2):171-181.
[4]II Seok O,Ae R P,Seok B M,et al.Secretome analysis reveals anArabidopsis lipaseinvolved in defense againstAlternaria brassicicola[J].Plant Cell,2005,17(10):2832-2847.
[5]Lee D S,Kim B K,Kwon S J,et al.Arabidopsis GDSL lipase 2 plays a role in pathogen defense via negative regulation of auxin signaling[J].Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2009,379(4):1038-1042.
[6]劭佳丽,缪卫国,刘海洋,等.新疆主要棉区棉花黄萎病菌致病力分化及其遗传多样性分析[J].新疆农业科学,2009,46(1):122-127.Shao J L,Niu W G,Liu H Y,et al.Analysis on pathogenicity differentiation of cottonVerticillium dahliaestrainsand its genetic diversity in Xinjiang[J].Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences,2009,46(1):122-127.
[7]Naranjo M A,Forment J M,Serrano R,et al.Overexpression ofArabidopsis thalianaLTL1,a salt-induced gene encoding a GDSL-motif lipase,increases salt tolerance in yeast and transgenic plants[J].Plant Cell&Environment,2006,29(10):1890-1900.
[8]田秀明,徐利锋.棉花对枯黄萎病的抗性与过氧化物酶活性的关系[J].植物病理学报,1991,21(2):94.Tian X M.,Xu L F.The relations between resistance of cotton toVerticilliumandFusarium wiltand peroxidase activity[J].Acta Phytopathologica Sinia,1991,21(2):94.
[9]汪红,刘辉,袁红霞,等.棉花黄萎病不同抗性品种接菌前后体内酶活性及酚类物质含量的变化 [J].华北农学报,2001,16(3):46-51.Wang H,Liu H,Yuan H X,et al.The Change of enzymes activity and phenois content in cotton cultivars with different esistanrce toV.dahliaeafter inoculation[J].Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica,2001,16(3):46-51.
[10]张兴华,李捷.棉花抗枯、黄萎病研究进展及其抗性鉴定方法[J].江西农业学报,2008,20(3):43-49.Zhang X H,Li J.Study progress and resistance identification method of cotton to fusarium wilt andVerticillium wilt[J].Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi,2008,20(3):43-49.
[11]江慧芳,王雅琴,刘春国.三种脂肪酶活力测定方法的比较[J].化学与生物工程,2007,24(8):72-75.Jiang H F,Wang Y Q,Liu C G.Comparison and improvement of three determination methods for lipase activity[J].Chemistry and Bioengineering,2007,24(8):72-75.
[12]程璐,贺春贵,胡桂馨,等.苜蓿斑蚜危害对5种苜蓿品种(系)PAL、POD、PPO 酶活性的影响[J].植物保护,2009,35(6):87-90.Chen L,Hei C G,Hu G X,et al.The effects of Therioaphis trifolii on the activities of PAL,POD and PPO in five alfalfa varieties[J].Plant Protection,2009,35(6):87-90.
[13]邢会琴,李敏权,徐炳良,等.过氧化氢酶和苯丙氨酸解氨酶与苜蓿白粉病抗性的关系 [J].草地学报,2007,15(4):376-380.Xing H Q,Li M Q,Xu B L,et al.Relationships between leaf POD and PAL and the resistance of alfalfa cultivars against powdery mildew[J].Acta Agrestia Sinica,2007,15(4):376-380.
[14]Huang L M,Lai C P,Chen L F,et al.Arabidopsis SFAR4 is a novel GDSL-type esterase involved in fatty acid degradation and glucose tolerance[J].Botanical Studies,2015,56(1):1-12.
[15]Sugui J A,Julian P,Yun C C,et al.Role of laeA in the regulation of alb1,gliP,conidial morphology and virulence inAspergillus fumigatus[J].Eukaryotic Cell,2007,6(9):1552-1561.
[16]Zuo K J,Wang J,Wu W,et al.Identification and characterization of differentially expressed ESTs ofGossypium barbadenseinfected byVerticillium dahliaewith suppression subtractive hybridization[J].Mol Biol(Mosk),2005,39(2):214-223.
[17]袁哈利,郝晓云,郑学伟,等.陆地棉GDSL脂肪酶增强拟南芥对黄萎病菌的抗性[J].石河子大学(自然科学版),2015,33(5):529-534:Yuan H L,Hao X Y,Zheng X W,et al.Cotton GDSL lipase increases the resistance againstVerticillium dahilae[J].Journal of Shihezi University(Natural Science),2015,33(5):529-534.
[18]Tian J,Zhang X,Liang B,et al.Expression of baculovirus anti-apoptotic genes p35 and op-iap in cotton(Gossypium hirsutumL.)enhances tolerance toVerticillium wilt[J].PlosOne,2010,5(12):e14218.
[19]Hye G K,Sun J K,Young J J,et al.GDSL lipase 1 regulates ethylene signaling and ethylene-associated systemic immunity in arabidopsis[J].FEBS Letters,2014,588:165-1658.
[20]Hong J K,Choi H W,Hwang I S,et al.Function of a novel GDSL-type pepper lipase gene GLIP1 in disease susceptibility and abiotic stress tolerance[J].Planta,2008,227(3):539-558.
[21]韩盛,向本春.植物病毒分子检测方法研究进展[J].石河子大学学报(自然科学版),2006,24(5):550-553.Han S,Xiang B C.Advances of methods for the molecular detection of plant virus[J].Journal of Shihezi University(Natural Science),2006,24(5):550-553.
[22]巧汪.植物抗病机理研究进展综述[J].安徽农业通报,2015,21(8):25-30.Wang Q,Advances on the mechanism of plant disease resistance[J].Anhui Agri Sci Bull,2015,21(08):25-30.
[23]王志卫,贝学军,朱世平,等.植物激素在植物抗病过程中的作用研究进展[J].安徽农业科学,2011,39(15):9035-9038.Wang Z W,Bei X J,Zhu S P,et al.Recent advances in phytohormone regulated plant resistance to pathogens[J].Journal of Anhui Agri Sci,2011,39(15):9035-9038.
[24]赵凤轩,戴小枫.棉花黄萎病菌的侵染过程[J].基因组学与应用生物学,2009,28(4):786-792.Zhao F X,Dai X F.Infection process ofVerticillium dahliaeKlebahn in cotton[J].Genomics and Applied Biology,2009,28(4):786-792.
[25]Gayoso C,Pomar F,Novouzal E,et al.The Ve-mediated resistance response of the tomato toVerticillium dahliaeinvolvesH2O2peroxidaseand ligninsand drivesPAL gene expression[J].BMC Plant Biol,2010,10(1):232-239.
GDSL lipase increases the resistance againstVerticillium dahilaeinGossypium hirsutum
An Jing,Pan Ze,Li Hongbin*
(College of Life Sciences/Key laboratory of Agrobiotechnology,Shihezi University,Shihezi,Xinjiang 832003,China)
Verticillium dahilaeis a soil-brone fungal pathogen through vasculature,and affects the yield and quality of cotton fiber seriously.To investigate the important function of cotton GDSL lipase (GLIP)in response toVerticillium dahilae,physiological analyses of wild-type (WT)cotton (Xinluzao 42)and transgenic cotton overexpressing GhGLIP underVerticillium dahilaetreatment were performed in this study.The results indicated that the expression of GhGLIP gene was induced underVerticillium dahilaestimulation,and transgenic cotton plants showed obviously inhibition of leaf cell death that was caused byVerticillium dahliae.Compared with the untreated control,GDSL lipase enzyme activity of both WT and transgenic cotton plants increased significantly afterVerticillium dahilaetreatment.Meanwhile,in transgenic cotton plants,the enzyme activities of catalase(CAT),superoxide dismutase(SOD),peroxidase(POD),phenylalanine ammonialyas(PAL)and polyphenoloxidase(PPO)were significantly enhanced,demonstrating that GhGLIP induced the resistance of cotton plants toVerticillium dahilae.These results provided an effective reference for elucidating the molecular mechanism of cotton resistance toVerticillium dahliaeand improvement of cotton breeding through genetic engineering technology.
GDSL lipase;Verticillium dahilae;cotton resistance;antioxidant enzymes
S562;S432.44
A
10.13880/j.cnki.65-1174/n.2017.04.005
1007-7383(2017)04-0420-05
2017-03-24
国家自然科学基金项目(31660408),新疆兵团现代农业科技攻关与成果转化项目(2016AC017)
安晶(1991-),女,硕士研究生,专业方向为生物化学与分子生物学,e-mail:605805134@qq.com。
*通信作者:李鸿彬(1980-),男,教授,博士生导师,从事植物分子生物学与基因工程研究,e-mail:lihb@shzu.edu.cn。

