超声造影半定量方法评估斑块内新生血管与斑块狭窄程度及C反应蛋白的关系研究
郑 军,何晨晖,徐翠霞
超声造影半定量方法评估斑块内新生血管与斑块狭窄程度及C反应蛋白的关系研究
郑 军,何晨晖,徐翠霞
目的 通过超声造影(CEUS) 半定量方法评估颈动脉斑块内新生血管(IPN ),探讨斑块内新生血管增强程度与狭窄程度及C反应蛋白(CRP)的关系。方法 收集134例颈动脉斑块患者,均行颈动脉超声检查及颈动脉超声造影。颈动脉超声检查后根据斑块致管腔狭窄程度分为<50%组,50%~69%组,70%~99%组。造影后斑块内新生血管根据视觉上斑块内微泡进行分级:G0,斑块内没有微泡进入;G1,微泡进入到斑块的肩部和(或)外侧壁;G2,大量的微泡进入到斑块内。分析不同狭窄程度患者颈动脉斑块内新生血管增强程度分级,斑块内新生血管与CRP的关系。结果 不同狭窄程度斑块内新生血管增强程度分级差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),两两组间比较差异有统计学意义(<50%组和50~69%组,P<0.05;<50%组和70~99%组,P<0.05;50~69%组和70~99%组,P<0.05)。斑块厚度与增强程度分级间呈正相关性(r=0.641,P<0.05),3组间比较CRP差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。斑块内新生血管不同增强程度分级间比较,斑块内新生血管增强程度越高、CRP值就越高,且组间比较差异有统计学意义;相关性分析显示,斑块内新生血管增强程度与CRP有显著相关性(r=0.502,P<0.05)。结论 超声造影半定量方法所评估的斑块内新生血管与斑块的狭窄严重程度有关,并与CRP呈正相关性,提示斑块狭窄程度越重、斑块内新生血管越丰富,斑块内新生血管越丰富、炎症越厉害,斑块越容易成为易损性斑块。
斑块;新生血管;狭窄;C反应蛋白;易损性
目前颈动脉粥样硬化的危险分层是基于多普勒超声所评估斑块的狭窄程度和形态[1]。研究指出,斑块的进展与斑块内新生血管(IPN )的形成有关,并且最终这些微血管导致了斑块成为不稳定斑块[2]。六氟化硫微泡造影剂用于颈动脉超声造影(CEUS),可以直接显示斑块内新生血管[3],通过CEUS所观察到颈动脉粥样硬化斑块的新生血管程度与组织学所显示新生血管的密度[4]。本研究目的是评估普通超声所显示斑块狭窄程度与CEUS所显示的斑块内新生血管的关系,并探讨斑块内新生血管与炎症指标C反应蛋白(CRP)的关系。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料:选择2012年3月-2016年5月在本院住院或门诊就诊的颈动脉粥样硬化斑块患者134例为研究对象,其中男性115例(86%),女性19例(14%)。将二维超声测量的颈动脉内中膜厚度≥1.5 mm定义为粥样硬化斑块[5],选取造影斑块是双侧颈总动脉中最厚的斑块,并且斑块内没有强回声导致的声影出现。
1.2 仪器和方法
1.2.1 常规颈动脉超声检查:采用美国GE公司Logiq E9超声诊断仪器,线阵ML6-15探头,扫查双侧颈总动脉、长轴测量颈总动脉内最厚处斑块的厚度,并且计算狭窄率。狭窄的诊断根据最新的指南标准进行[6]。
1.2.2 颈动脉超声造影检查:采用9L线阵探头,频率为7 MHz。启用造影模式,造影时机械指数设定为0.13,增益10,深度设置在3~5 cm处。造影剂使用Sonovue(声诺维),生理盐水配置成5 mL悬浊液,肘正中静脉注射2.0 mL,随后立即团注5 mL生理盐水。动态记录超声造影过程,时间为2 min。斑块内新生血管是根据其内造影剂的微泡的回声反射以及快速移动的微泡为标准。造影后斑块内新生血管根据视觉上斑块内微泡进行分级:G0,斑块内没有微泡进入;G1,微泡进入到斑块的肩部和(或)外侧壁;G2,大量的微泡进入到斑块内[3]。
血液标本是收集住院或门诊患者晨起空腹采取静脉血测得。

2 结果
2.1 3组患者一般临床资料的比较:134例颈动脉斑块患者根据斑块致管腔狭窄程度分为<50%组,50~69%组,70~99%组,3组间比较,斑块厚度和CRP差异有统计学意义,其余各组间比较差异无统计学意义,见表1。
2.2 不同狭窄程度斑块内新生血管增强程度分级比较:3组患者间增强程度分级分析,<50%组G0级15例(25%),G1级33例(55%),G2级12例(20%);50%~69%组G0级0例(0%),G1级18例(41%),G2级26例(59%);70%~99%组G0级0例(0%),G1级6例(20%),G2级24例(80%)。3组患者间随着狭窄程度的加重,G0、G1级病例数减少,G2级病例数增加,3组间比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);两两组间比较差异有统计学意义(<50%组和50%~69%组,P<0.05;<50%组和70%~99%组,P<0.05;50%~69%组和70%~99%组,P<0.05)。相关性分析斑块厚度与增强程度分级之间的关系,结果显示斑块厚度与增强程度分级之间呈正相关性(r=0.641,P<0.05)。
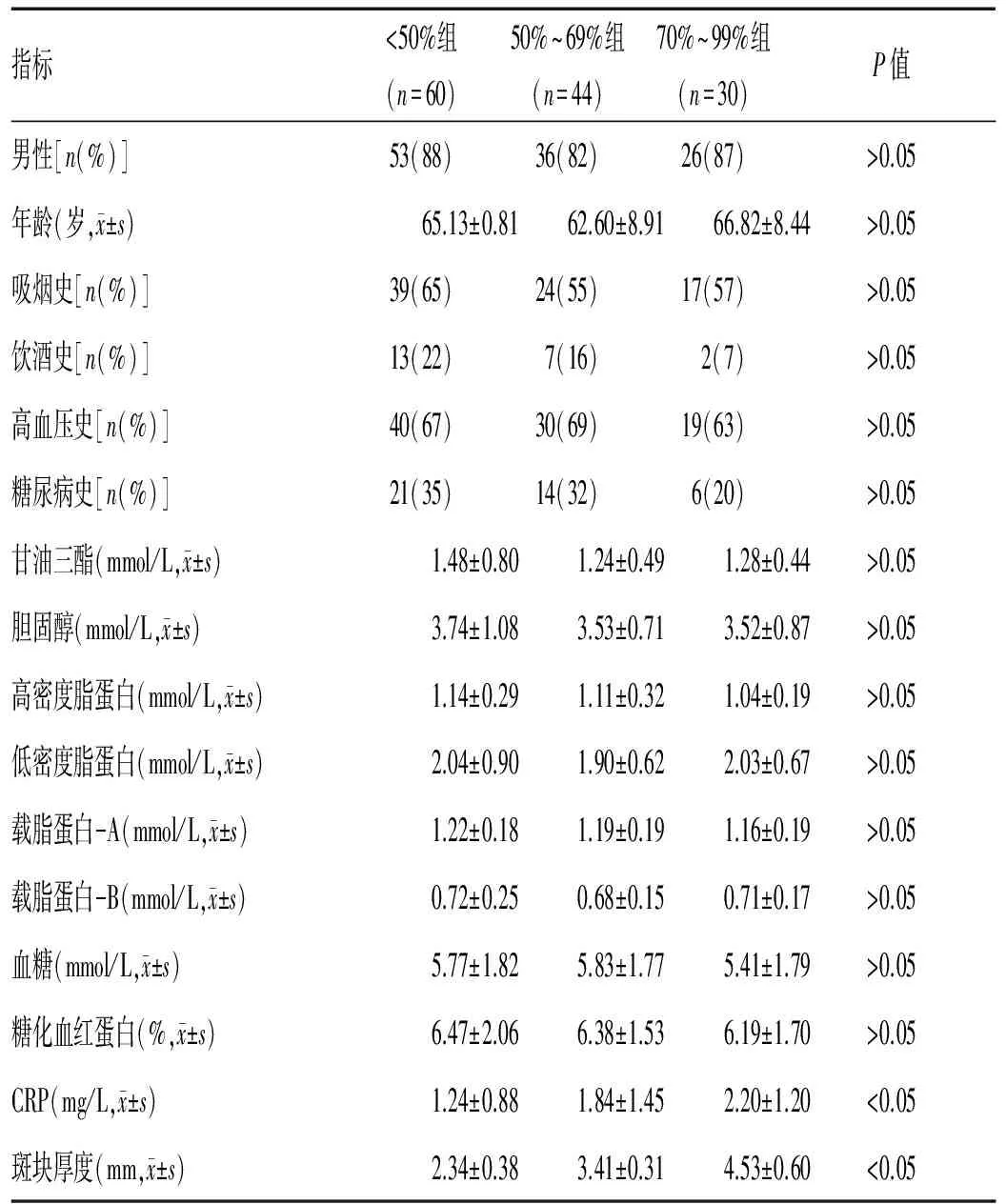
表1 3组患者一般临床资料的比较
2.3 斑块内新生血管增强程度分级与CRP的关系:斑块内新生血管增强程度分级方法,CRP分别为:G0级,(0.50±0.25)mg/L;G1级,(1.33±1.21)mg/L;G2级,(2.17±1.35)mg/L。随着斑块内新生血管增强程度分级的增高,CRP水平也随着增加,且3组患者间比较差异有统计学意义(F=23.793,P<0.05);两两组间比较差异有统计学意义(G0级和G1级,P<0.05;G1级和G2级,P<0.05;G0级和G2级,P<0.05)。
斑块内新生血管增强程度分级与CRP的相关性分析显示,增强程度分级与CRP呈正相关性(r=0.502,P<0.05),提示斑块内新生血管与CRP呈正相关关系。
3 讨论
本研究通过颈动脉超声造影半定量分析方法对斑块内新生血管增强程度进行分级,结果显示随着斑块致管腔狭窄程度的加重,斑块内新生血管增强程度分级也随之增加,斑块越厚、斑块内新生血管越丰富,这与既往的研究观点一致[7]。颈动脉超声造影是一种非侵入性的影像学方法,可以通过评估斑块内新生血管评估斑块发生破溃的风险[7]。斑块内这些新生血管大多数来自于颈动脉外膜侧的滋养血管,由于斑块增厚致缺氧,缺氧诱导因子信号传导,以及炎症的刺激,诱发了新生血管由外膜侧向中膜、内膜侧延伸[8]。斑块内新生血管最丰富的地方是巨噬细胞聚集最多以及纤维帽最薄弱处,同样也是含有脂质最丰富的地方,所有这些特点都是易损性斑块所具有的[9]。易损性斑块的炎症聚集、斑块内出血、异位新生血管的破裂,导致了斑块破溃,最后出现心脑血管事件。
本文研究显示CRP不仅在3组患者间存在差异,任意2组间比较都有差异,这与既往研究结果一致[10]。CRP主要可能通过以下三条路径参与了易损性斑块的形成:第一,CRP参与炎症反应。有研究指出斑块内的炎症细胞因子能刺激血管平滑肌细胞和巨噬细胞分泌基质金属蛋白酶,分解纤维帽,从而形成易损性斑块[11]。第二,CRP影响斑块内脂质核的大小。有研究报道了在尸检的病例中,正常的冠状动脉内没有CRP沉积,而在有斑块形成的冠状动脉中,可以检测到CRP的聚集,同时发现CRP免疫反应最激烈的部位是脂质核[12]。第三,CRP影响了斑块纤维帽的厚度。有研究发现,血清CRP水平较高的冠心病患者斑块的纤维帽更薄,更容易发生破溃[13]。
本研究根据颈动脉超声造影后斑块的增强程度将患者分为3组,G0级斑块内没有造影剂进入;G1级,斑块的肩部和外膜侧有造影剂进入;G2级,斑块内有广泛的造影剂进入。分析结果显示,G2级患者血清CRP水平最高,3组间比较差异有统计学意义,这提示新生血管的增加与炎症反应有关。任意2组比较均存在差异,提示CRP是一个较为敏感的不稳定斑块的指标,这与既往研究结果一致[11]。
总之,超声造影半定量方法所评估的斑块内新生血管与斑块的狭窄严重程度有关,并与CRP呈显著正相关性,提示斑块狭窄程度越重、斑块内新生血管越丰富,斑块内新生血管越丰富、炎症越厉害,斑块越容易成为易损性斑块。
[1] Hobson RW,Mackey WC,Ascher E,et al.Management of atherosclerotic carotid artery disease:clinical practice guidelines of the Society for Vascular Surgery[J].Journal of Vascular Surgery,2008,48(2):480-486.
[2] Sluimer JC,Daemen MJ.Novel concepts in atherogenesis:angiogenesis and hypoxia in atherosclerosis[J].The Journal of Pathology,2009,218(1):7-29.
[3] Deyama J,Nakamura T,Takishima I,et al.Contrast-enhancement ultrasound imaging of carotid plaque neovascularization is useful for identifying high-risk patients with oronary artery disease[J].Circ,2013,77(6):1499-1507.
[4] Eriksson EE.Intravital microscopy on atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein e-deficient mice establishes microvessels as major entry pathways for leukocytes to advanced lesions[J].Circulation,2011,124(19):2129-2138.
[5] 勇强,张蕾,王丽娟,等.颈动脉斑块风险等级的超声评价[J].血管与腔内血管外科杂志,2016,2(4):278-281.
[6] Brott TG,Halperin JL,Abbara S,et al.ASA/ACCF/AHA/AANN/AANS/ACR/ASNR/CNS/SAIP/SCAI/SIR/SNIS/SVM/SVS guideline on the management of patients with extracranial carotid and vertebral artery disease[J].J AM Coll Cardiol,2011,57:1002.
[7] Staub D,Partovi S,Schinkel AF,et al.Correlation of carotid artery atherosclerotic lesion echogenicity and severity at standard US with intraplaque neovascularization detected at contrast-enhanced US[J].Radiology,2011,258(2):618-626.
[8] Sluimer JC,Gasc JM,Van Wanroij JL,et al.Hypoxia,hypoxia-inducible transcription factor,and macrophages in human atherosclerotic plaques are correlated with intraplaque angiogenesis[J].Journal of the American College of Cardiology,2008,51(13):1258-1265.
[9] Naghavi M,Falk E,Hecht HS,et al.From vulnerable plaque to vulnerable patient-Part Ⅲ:Executive summary of the Screening for Heart Attack Prevention and Education (SHAPE) Task Force report[J].The American Journal of Cardiology,2006,98(2A):2-15.
[10] Chang Xiaoni,Feng Jun,Ruan Litao,et al.Positive correlation between neovascularization degree of carotid atherosclerosis determined by contrast-enhanced ultrasound and level of serum C-reactive protein[J].Zeitschrift Fur Gefasskrankheiten,2015,44(3):187-194.
[11] Ishikawa T,Imamura T,Hatakeyama K,et al.Possible contribution of C-reactive protein within coronary plaque to increasing its own plasma levels across coronary circulation[J].American Journal of Cardiology,2004,93(5):611-614.
[12] Zhang YX,Cliff WJ,Schoefl GI,et al.Coronary C-reactive protein distribution:its relation to development of atherosclerosis[J].Atherosclerosis,1999,145(2):375-379.
[13] Zwaka TP,Hombach V,Torzewski J.C-reactive protein-mediated low density lipoprotein uptake by macrophages:implications for atherosclerosis[J].Circulation,2001,103(9):1194-1197.
Relationship between intraplaque neovascularization(IPN) degree of carotid atherosclerosis determined by semi-quantitative method of contrast-enhanced ultrasound(CEUS) and the stenosis and the level of serum C-reactive protein(CRP)
ZHENGJun,HEChenhui,XUCuixia.
DepartmentofUltrasound,thePeople’sofGuyuanCity,Guyuan,Ningxia756000,China
Objective To Assess the intraplaque neovascularization(IPN) by semi-quantitative method of contrast-enhanced ultrasound(CEUS) and explore the relationship between the IPN and the stenosis and the level of serum C-reactive protein(CRP).Methods A total of 134 cases with carotid artery plaque.All the patients underwent the standard ultrasound and CEUS.the patients were divided into three groups based on the stenosis,they are<50% group,50~69% group,70~99% group.IPN was identified by rapid movement of echogenic reflectors of microbubbles within the plaque and graded as G0,no microbubbles in the plaque;G1,moderate microbubbles confined to the shoulder and/or adventitial side of the plaque;G2,extensive microbubbles throughout the plaque.Analysis the relationship between the IPN and the stenosis and the level of serum C-reactive protein.Results There are significant differences of the degree of plaque enhancement in the three groups of different stenosises(P<0.05),there are also significant differences between the two groups(<50% group and 50~69% group:P<0.05;<50% group and 70-99% group:P<0.05;50~69% group and 70~99% group:P<0.05).There was positive correlation between plaque thickness and the grade of plaque enhancement(r=0.641,P<0.05).The level of serum CRP were different among the three groups and there were significant difference among the three groups(F=23.793,P<0.05).The higher of the grade of the plaque enhancement,the higher of the level CRP and there was significant difference between these groups.There was positive correlation between the neovascularization and the level of serum CRP(r=0.502,P<0.05).Conclusion There are positive correlation between the neovascularization of carotid atherosclerosis determined by contrast-enhanced ultrasound and the severity of stenosis and the level of serum CRP.This is suggesting that the severitier of the stenosis is,the richer of IPN is.If the IPN is richer,the more powerful inflammation and plaque more easily become vulnerable plaque.
Plaque;Neovascularization;Stenosis;CRP;Vulnerability
10.13621/j.1001-5949.2017.06.0522
宁夏固原市人民医院,宁夏 固原 756000
http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/64.1008.R.20170614.1315.030.html
R737.9
A
2016-10-22 [责任编辑]马兴忠

