TRIM蛋白家族调节NF-κB信号通路的研究进展①
金 争 李 冬 闫东梅 朱 迅
(吉林大学基础医学院免疫学系,长春130021)
·专题综述·
TRIM蛋白家族调节NF-κB信号通路的研究进展①
金 争 李 冬 闫东梅 朱 迅
(吉林大学基础医学院免疫学系,长春130021)
核因子-κB(Nuclear factor-kappa B,NF-κB)作为重要的核转录因子参与调节机体的免疫应答,一旦其调节发生异常将会导致免疫疾病、神经退行性病变、新陈代谢疾病、肿瘤等。磷酸化、泛素化等转录后修饰可调节NF-κB信号通路。E3泛素连接酶在泛素化的过程中起重要作用[1]。TRIM(Tripartite motif)蛋白是E3泛素连接酶中RING家族成员,由RING、B-Box、Coil-coiled和C端结构域构成[2]。已有研究证明在感染等病理条件下,TRIM蛋白能调节固有免疫应答[3]。最近研究表明,TRIM作为泛素连接酶调节NF-κB信号通路[4]。我们将对TRIM家族蛋白调节NF-κB信号通路及其在免疫疾病中的研究进展做简要综述。
1 TRIM蛋白家族
近年来,随着对TRIM蛋白家族研究的不断深入,TRIM蛋白的重要性也越来越突出。TRIM蛋白属于E3泛素连接酶中RING家族,所有的哺乳动物都表达TRIM蛋白,人类大约表达60种TRIM蛋白及8种TRIM样蛋白,小鼠表达64种TRIM蛋白,蠕虫和苍蝇只表达10~20种TRIM蛋白[3]。TRIM蛋白家族最显著的特点是具有三结构域(Tripartite-motif domain)结构,从N端到C端依次是一个锌指结构域(RING domain)、一个或两个B-Box结构域(B-Box domain)、一个卷曲螺旋结构域(Coiled-coil domain)和C端的非特异性的结构域(C-terminal domain),故TRIM蛋白也被称为RBCC蛋白[5]。大多数研究认为,RING结构域能特异性结合E2泛素结合酶,从而发挥E3泛素连接酶的作用[6,7]。也有研究表明,RING结构域在蛋白相互作用中也有一定作用,可能参与NF-κB信号通路的调节[6,8]。现有的研究对B-Box结构与功能的了解十分有限,TRIM蛋白中的B-Box被证实与自身免疫疾病有关。B-Box在结构上与RING类似,有人认为它也可以作为E2的结合位点发挥E3泛素连接酶的作用,如TRIM16缺少RING结构域,在体外实验中仍发挥E3泛素连接酶的作用[9]。Coiled-coil结构域主要参与同源二聚体的相互作用和低聚反应[10-12],促进大分子复合物的形成,影响蛋白的亚细胞定位[12],并且异源二聚体的形成使卷曲螺旋结构域的功能更加多元化[5]。
TRIM蛋白有多种表达形式,细胞质、细胞核中均有表达。表达的部位大多数与明确定义的亚细胞结构如内质网、高尔基体无关,而是表达于其他亚细胞区域[12,13],如TRIM19表达于核体,参与转录的调节[14,15]。
TRIM蛋白因有RING结构而被归为E3泛素连接酶的RING家族,在泛素化中发挥作用[3]。泛素化是泛素分子以共价键结合特异性目的蛋白的赖氨酸残基,发生转录后修饰的过程[16]。泛素活化酶(E1)、泛素交联酶(E2)、泛素连接酶(E3)是泛素化的重要组成部分,其中E3的作用是将E2与目的蛋白连接[16]。最初,泛素化被认为是蛋白酶降解的一种机制,随着研究的深入,人们发现泛素化也可以调节其他的细胞过程,如转录、蛋白质的运输[16]。泛素化参与了许多病理过程,如肿瘤、炎症及自身免疫紊乱[17-19]。TRIM蛋白作为泛素连接酶参与抗病毒和调节免疫相关信号通路的过程。但是,TRIM蛋白家族所有成员是否都具有泛素连接酶作用并未得到证实[20]。
2 TRIM家族蛋白对NF-κB信号通路的调节
NF-κB信号通路和TRIM蛋白之间存在相互作用。有研究表明,NF-κB信号通路能调节TRIM家族蛋白的表达,TRIM家族蛋白也能双向调节NF-κB信号通路。如肿瘤坏死因子(Tumor necrosis factor alpha,TNF-α)介导的NF-κB信号通路活化能上调TRIM9、TRIM21、TRIM62的表达,而这些TRIM蛋白反过来又可对NF-κB信号通路产生正向或负向调节[2,21,22],见表1。
3 TRIM家族蛋白调节NF-κB信号通路的机制
NF-κB是一个转录因子蛋白家族,包括5个亚单位:RelA(p65)、RelB、c-Rel、p50和p52。NF-κB分为经典通路和非经典通路两大部分,二者既相互影响又相互独立。经典通路中,TNF-α、脂多糖(LPS)、IL-1等通过受体将信号传递至细胞内,接头蛋白MyD88(Myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88)招募TRAF6(TNF receptor associated factor 6),后者通过自身泛素化形成一个包括在内IKK(Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase)复合物激酶(TAK1、TAB2/3)的复合物,复合物中的TAK1能激活IKK复合物(IKK-α、IKK-β、NEMO),IKK复合物被激活后,作用于NF-κB抑制物IκBα(Inhibitor of NF-κB),使之磷酸化,进而发生泛素化修饰并通过蛋白酶体通路降解,从而释放核因子p65/RelA和p50/52复合物入核,结合相应的DNA位点,调控相关基因转录[23]。在非经典通路中,CD40L(肿瘤坏死因子相关激活蛋白)、B细胞激活因子(BAFF/Blys)、LT-β(Lymphotoxin-β)等刺激下,TRAF3、TRAF2被招募与受体形成复合物,TRAF2的RING结构使TRAF3发生多聚泛素化,复合物降解,NIK(NF-κB-inducing kinase)被激活,促进IKK-α的磷酸化,被激活的NIK和IKK-α 一起磷酸化p100并加工成p52,使p52/RelB复合物活化,启动NF-κB非经典通路[24,25]。近年来大量的研究证实,RIG-Ⅰ(Retinoic acid inducible gene Ⅰ)也可激活NF-κB信号通路。RIG-Ⅰ能够识别病毒的RNA组分,并通过自身的CARD(Anino-terminal caspase recruitment domain)与下游信号分子MAVS(Mitochondrial antiviral signaling proteinprovided)的CARD相互作用来传递信号,MAVS含有两个TRAF6结合模序,能够与TRAF6结合,激活细胞转录因子NF-κB,使其进入细胞核内,结合相应的DNA序列,增强机体抵抗病毒的能力[26]。TRIF(TIR-domain-containing adaptor inducing interferon-β)及RIP1(Receptor-interacting protein 1)也可介导NF-κB信号通路。在LPS等刺激下,Toll样受体招募TRIF,RIP1结合于TRIF C端,并通过同型DD结构域与TRADD(TNF receptor associated death domain protein)结合,TRADD连接E3泛素连接酶,使RIP1发生K63位多聚泛素化修饰,泛素化的RIP1被TAB2/TAB3识别,并由此激活TAK1,从而激活NF-κB信号通路[27]。TRIM家族蛋白可结合以上通路中的多个靶点,正向或负向调节NF-κB信号通路,从而调节各种生理或病理活动,见图1。
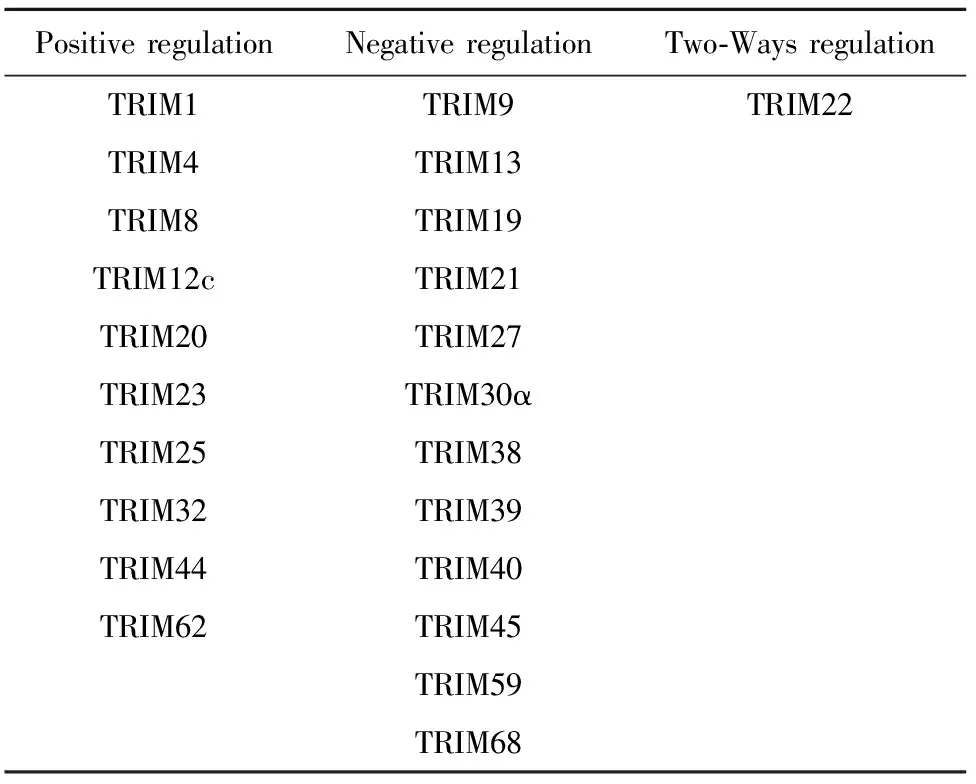
表1 TRIM家族蛋白对NF-κB信号通路的调节

图1 NF-κB信号通路Fig.1 NF-κB signaling pathways
3.1TRIM家族蛋白对TRAF6调节 TRAF6蛋白属于TRAF家族,能介导多种信号通路,其中包括NF-κB信号通路。在LPS等刺激物激活的NF-κB信号通路中,TRAF6通过自身泛素化而活化IKK激酶TAK1,调节NF-κB信号通路[28]。TRIM12c是TRIM5样蛋白,在巨噬细胞和树突状细胞中,能结合TRAF6,促进其泛素化,激活TAK1,正向调节NF-κB信号通路[29]。人巨细胞病毒与TRIM23结合,后者促进 TRAF6的自身泛素化,从而实现对 NF-κB信号通路的正向调节[30]。TFG(TPK-fused gene)能作用于TRAF6,激活NF-κB。在TLR3(Toll-like receptor 3)介导的信号通路中,TRIM68通过结合TFG抑制TRAF6激活,负向调节NF-κB信号通路[31]。在巨噬细胞中,TRIM38结合TRAF6,对其进行K48位的多聚泛素化修饰,促进TRAF6蛋白酶体通路的降解,抑制TLR(Toll-like receptor)介导的NF-κB信号通路[32]。
3.2TRIM家族蛋白对IKK复合物激酶的调节 IKK复合物激酶(TAK1、TAB2/3)对IKK复合物的激活至关重要。在IL-1β、TNF-α等介导的NF-κB信号通路中,TRIM8结合TAK1,介导其K63位的多聚泛素化,激活TAK1,正向调节NF-κB信号通路[33]。TRIM30α结合TAB2-TAB3-TAK1复合物,促进TAB2-TAB3的降解,抑制TLRs介导的NF-κB信号通路的激活[34]。TRIM22能激活人巨噬细胞中的NF-κB信号通路,但其机制不清[35,36]。也有研究发现TRIM22通过RING结构域降解TAB2,负向调节TRAF6介导的NF-κB信号通路[36]。最近研究显示,TRIM38作为E3泛素连接酶促进TAB2/3的溶酶体降解,抑制TNF-α和IL-1β介导的NF-κB信号通路[37]。
3.3TRIM家族蛋白对IKK复合物的调节 IKK复合物能激活IκB,使其降解,解除IκB对NF-κB的抑制作用。TRIM23不仅能通过TRAF6调节NF-κB信号通路,还可通过调节IKK复合物影响NF-κB信号通路。有研究证明在抗病毒的免疫应答中,TRIM23作为E3泛素连接酶介导NEMO(IKKγ)的K27位多聚泛素化,激活下游通路,正向调节NF-κB通路[38]。TRIM13是内质网上的E3泛素连接酶,能通过抑制NEMO泛素化,抑制NF-κB信号通路[39]。NEDD8(Neural precursor cell-expressed developm-entally downregulated 8)分子是一类结构上与泛素相似的分子,参与蛋白质翻译后修饰,这一过程被称为Neddylation。在消化道肿瘤的研究中,NEDD8能特异性结合并修饰NEMO,抑制NEMO的活化,从而抑制NF-κB信号通路。TRIM40结合NEDD8,增强NEDD8对NEMO的抑制作用,从而负向调节NF-κB信号通路。进一步研究发现,TRIM40在正常胃肠道上皮细胞中高表达,在胃肠道的炎症和肿瘤中低表达[40]。TRIM68不仅能通过结合TFG抑制TRAF6激活,也可通过结合TFG 抑制NEMO的激活,从而抑制NF-κB信号通路[31]。在感染HTLV1(Human T-lymphotropic virus 1)的细胞中,Tax蛋白使IKK-β持续磷酸化,激活NF-κB信号通路,促进细胞增殖。TRIM21抑制Tax蛋白的表达,介导寡聚泛素化使IKK-β发生自噬降解,从而抑制NF-κB信号通路[41]。TRIM27结合IKK复合物,抑制后者的激活,负向调节TNF、IL-1、TLR3及病毒感染激活的NF-κB信号通路[42]。
3.4TRIM家族蛋白对IκB的调节 在静息状态下,IκB与NF-κB结合,抑制NF-κB信号通路。TRIM20,也称为MEFV(Mediterranean fever)蛋白,是Caspase-1的靶蛋白,其N端结构域结合IκBα,促进钙蛋白酶介导的IκBα的降解,从而正向调节NF-κB信号通路[43]。TRIM9结合β-TrCP(E3泛素连接酶复合物),阻止β-TrCP与IκBα结合,并防止β-TrCP降解,负向调节NF-κB信号通路[44]。
3.5TRIM家族蛋白对NF-κB转录的调节 TRIM家族蛋白对NF-κB也有一定的调节作用。TRIM19,又称PML(Promyelocytic leukemia)蛋白,其C端结构域能结合RelA和p65,阻止RelA和p65与同源增强子的结合,抑制NF-κB信号通路[45]。PIAS3(Protein inhibitor of activated STAT 3)可作为SUMO(Small ubiquitin-like modifier)的E3连接酶,通过加强SUMO与NF-κB的结合促进NF-κB的SUMO化修饰,使p65从细胞核转移至细胞质,抑制NF-κB信号通路。TRIM8不仅能通过TAK1激活NF-κB,同时它也是一个核蛋白,在核内通过抑制PIAS3,促进p65从细胞质转移至细胞核,正向调节NF-κB信号通路[46]。TRIM20的N端结构域不仅能结合IκBα,还能结合p65,促进p65入核,正向调节NF-κB信号通路[43]。
3.6TRIM家族蛋白对NF-κB信号通路其他分子的调节 除上述分子外,TRIM家族蛋白还通过其他分子调节NF-κB信号通路。仙人掌素(Cactin)是NF-κB的抑制剂,在TNF-α介导的NF-κB信号通路中,TRIM39通过增强仙人掌素的稳定性,间接负向调节NF-κB信号通路[47]。非小细胞肺癌中,TRIM44通过上调CXCL16(C-X-C chemokine ligand 16)和MMP9(Matrix metallopeptidase 9)激活NF-κB信号通路,促进非小细胞肺癌的发展,但其机制不清[48]。另有研究表明,在抗病毒感染中,TRIM44通过B-Box结合MAVS,阻止MAVS的K48位多聚泛素化修饰,避免其降解,增强了稳定性,正向调节NF-κB信号通路[49]。ECSIT(Evolutionarily conserved signaling intermediate in Toll pathways)是RLR信号通路中的关键分子,TRIM59结合并抑制ECSIT的激活,抑制RIG-Ⅰ介导的NF-κB信号通路[50]。 TRIM25羧基末端的SYBR结构域结合于RIG-Ⅰ N端的CARD结构域,促进了CARD结构域K63位的泛素化修饰,正向调节NF-κB信号通路[51]。通过调节RIG-Ⅰ多聚泛素化正向调节NF-κB信号通路。TRIM4也是通过对RIG-Ⅰ进行K63位的泛素化修饰,正向调节NF-κB信号通路[52]。TRIM1、TRIM62和TRIM32正向调节NF-κB信号通路,TRIM45负向调节NF-κB信号通路,但其机制尚不十分明确[53,54]。以上研究表明,在生理或病理情况下,TRIM家族蛋白对NF-κB信号通路的调节具有重要意义。
4 展望
TRIM家族蛋白对NF-κB信号通路的调节在炎症、细胞信号通路中起重要作用。对于许多疾病,如肿瘤、炎症、自身免疫病,NK-κB是有效的药物作用靶点[55,56]。但是目前针对NF-κB的非选择性或完全性抑制存在一定的局限性及副作用。非甾体类抗炎药最早应用于炎症的治疗中,阿司匹林和水杨酸钠通过作用于IKK-β上三磷酸腺苷(ATP)的结合位点抑制NF-κB信号通路[57],但其可引发严重的超敏反应[58]。糖皮质激素类药物用于过敏及自身免疫病,是利用其对NF-κB信号通路的抑制作用[59],而随之而来的是肝、肌肉等葡萄糖不耐受疾病[60]。硼替佐米是蛋白酶体抑制剂,能阻断IκBα的降解,抑制NF-κB,目前已成功应用于血液肿瘤的治疗[61,62],但在实体瘤中应用十分有限。TRIM家族蛋白能适度调节NF-κB信号通路,在特定的生理病理条件下,可以形成高级结构作为信号转导体,因此可以作为一个有效的作用靶点,为临床许多与NF-κB信号通路异常有关疾病的治疗提供新思路。
[1] Won M,Byun HS,Park KA,etal.Post-translational control of NF-κB signaling by ubiquitination[J].Archives Pharmacal Res,2016,39(8):1075-1084.
[2] Tomar D,Singh R.TRIM family proteins:emerging class of RING E3 ligases as regulator of NF-kappaB pathway[J].Biol Cell,2015,107(1):22-40.
[3] Kawai T,Akira S.Regulation of innate immune signalling pathways by the tripartite motif (TRIM) family proteins[J].EMBO Mole Med,2011,3(9):513-527.
[4] Rajsbaum R,Garcia-Sastre A,Versteeg GA.TRIMmunity:the roles of the TRIM E3-ubiquitin ligase family in innate antiviral immunity[J].J Mole Biol,2014,426(6):1265-1284.
[5] Napolitano LM,Meroni G.TRIM family:Pleiotropy and diversi-fication through homomultimer and heteromultimer formation[J].IUBMB life,2012,64(1):64-71.
[6] Kentsis A,Borden KL.Construction of macromolecular assemblages in eukaryotic processes and their role in human disease:linking RINGs together[J].Current Protein Peptide Sci,2000,1(1):49-73.
[7] Meroni G,Diez-Roux G.TRIM/RBCC,a novel class of ′single protein RING finger′ E3 ubiquitin ligases[J].Bio Essays,2005,27(11):114711-114757.
[8] Borden KL.RING fingers and B-boxes:zinc-binding protein-protein interaction domains[J].Biochem Cell Biol,1998,76(2-3):351-358.
[9] Bell JL,Malyukova A,Holien JK,etal.TRIM16 acts as an E3 ubiquitin ligase and can heterodimerize with other TRIM family members[J].PLoS One,2012,7(5):e37470.
[10] Cao T,Borden KL,Freemont PS,etal.Involvement of the rfp tripartite motif in protein-protein interactions and subcellular distribution[J].J Cell Sci,1997,110 (14):1563-1571.
[11] Cainarca S,Messali S,Ballabio A,etal.Functional characterization of the Opitz syndrome gene product (midin):evidence for homodimerization and association with microtubules throughout the cell cycle[J].Human Mole Genetics,1999,8(8):1387-1396.
[12] Reymond A,Meroni G,Fantozzi A,etal.The tripartite motif family identifies cell compartments[J].EMBO J,2001,20(9):2140-2151.
[13] Short KM,Cox TC.Subclassification of the RBCC/TRIM superfamily reveals a novel motif necessary for microtubule binding[J].J Biological Chemis,2006,281(13):8970-8980.
[14] Bernardi R,Pandolfi PP.Structure,dynamics and functions of promyelocytic leukaemia nuclear bodies[J].Nat Rev Mole Cell Biol,2007,8(12):1006-1016.
[15] Van damme E,Laukens K,Dang TH,etal.A manually curated network of the PML nuclear body interactome reveals an important role for PML-NBs in SUMO ylation dynamics[J].Int J Biological Sci,2010,6(1):51-67.
[16] Pickart CM,Eddins MJ.Ubiquitin:structures,functions,mechanisms[J].Biochimicaet Biophysica Acta,2004,1695(1-3):55-72.
[17] Cambiaghi V,Giuliani V,Lombardi S,etal.TRIM proteins in cancer[J].Adv Experimental Med Biol,2012,770:77-91.
[18] Micale L,Chaignat E,Fusco C,etal.The tripartite motif:structure and function[J].Adv Experimental Med Biol,2012,770:11-25.
[19] Petrera F,Meroni G.TRIM proteins in development[J].Adv Experimental Med Biol,2012,770:131-141.
[20] Ozato K,Shin DM,Chang TH,etal.TRIM family proteins and their emerging roles in innate immunity[J].Nat Rev Immunol,2008,8(11):849-860.
[21] Schwamborn J,Lindecke A,Elvers M,etal.Microarray analysis of tumor necrosis factor alpha induced gene expression in U373 human glioblastoma cells[J].BMC genomics,2003,4(1):46.
[22] Dos santos CC,Han B,Andrade CF,etal.DNA microarray analysis of gene expression in alveolar epithelial cells in response to TNFalpha,LPS,and cyclic stretch[J].Physiological Genomics,2004,19(3):331-342.
[23] Mitchell S,Vargas J.Signaling via the NFkappaB system[J].2016,8(3):227-241.
[24] Hayden MS,Ghosh S.NF-kappaB in immunobiology[J].Cell Res,2011,21(2):223-244.
[25] Sanjo H,Zajonc DM,Braden R,etal.Allosteric regulation of the ubiquitin:NIK and ubiquitin:TRAF3 E3 ligases by the lymphotoxin-beta receptor[J].J Biological Chem,2010,285(22):17148-17155.
[26] Seth RB,Sun L,Ea CK,etal.Identification and characterization of MAVS,a mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein that activates NF-kappaB and IRF 3[J].Cell,2005,122(5):669-682.
[27] Ermolaeva MA,Michallet MC,Papadopoulou N,etal.Function of TRADD in tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 signaling and in TRIF-dependent inflammatory responses[J].Nat Immunol,2008,9(9):1037-1046.
[28] Wang C,Deng L,Hong M,etal.TAK1 is a ubiquitin-dependent kinase of MKK and IKK[J].Nature,2001,412(6844):346-351.
[29] Chang TH,Yoshimi R.Tripartite Motif (TRIM) 12c,a mouse homolog of TRIM5,is a ubiquitin ligase that stimulates Type I IFN and NF-kappaB pathways along with TNFR-associated factor 6[J].J Immunol,2015,195(11):5367-5379.
[30] Poole E,Groves I,Macdonald A,etal.Identification of TRIM23 as a cofactor involved in the regulation of NF-kappaB by human cytomegalovirus[J].J Virol,2009,83(8):3581-3590.
[31] Wynne C,Lazzari E,Smith S,etal.TRIM68 negatively regulates IFN-beta production by degrading TRK fused gene,a novel driver of IFN-beta downstream of anti-viral detection systems[J].PLoS One,2014,9(7):e101503.
[32] Zhao W,Wang L,Zhang M,etal.E3 ubiquitin ligase tripartite motif 38 negatively regulates TLR-mediated immune responses by proteasomal degradation of TNF receptor-associated factor 6 in macrophages[J].J Immunol(Baltimore,Md :1950),2012,188(6):2567-2574.
[33] Li Q,Yan J,Mao AP,etal.Tripartite motif 8 (TRIM8) modulates TNFalpha-and IL-1beta-triggered NF-kappaB activation by targeting TAK1 for K63-linked polyubiquitination[J].Proc Nat Acad Sci U S A,2011,108(48):19341-19346.
[34] Shi M,Deng W,Bi E,etal.TRIM30 alpha negatively regulates TLR-mediated NF-kappa B activation by targeting TAB2 and TAB3 for degradation[J].Nat Immunol,2008,9(4):369-377.
[35] Yu S,Gao B,Duan Z,etal.Identification of tripartite motif-containing 22 (TRIM22) as a novel NF-kappaB activator[J].Biochemical Biophysical Res Communicat,2011,410(2):247-251.
[36] Qiu H,Huang F,Xiao H,etal.TRIM22 inhibits the TRAF6-stimulated NF-kappaB pathway by targeting TAB2 for degradation[J].Virologica Sinica,2013,28(4):209-215.
[37] Hu MM,Yang Q,Zhang J,etal.TRIM38 inhibits TNFalpha-and IL-1beta-triggered NF-kappaB activation by mediating lysosome-dependent degradation of TAB2/3[J].Proc Nat Acad Sci U S A,2014,111(4):1509-1514.
[38] Arimoto K,Funami K,Saeki Y,etal.Polyubiquitin conjugation to NEMO by triparite motif protein 23 (TRIM23) is critical in antiviral defense[J].Proc Nat Acad Sci U S A,2010,107(36):15856-15861.
[39] Tomar D,Singh R.TRIM13 regulates ubiquitination and turnover of NEMO to suppress TNF induced NF-kappaB activation[J].Cellular Signal,2014,26(12):2606-2613.
[40] Noguchi K,Okumura F,Takahashi N,etal.TRIM40 promotes neddylation of IKKgamma and is downregulated in gastrointestinal cancers[J].Carcinogenesis,2011,32(7):995-1004.
[41] Niida M,Tanaka M,Kamitani T.Downregulation of active IKK beta by Ro52-mediated autophagy[J].Mole Immunol,2010,47(14):2378-2387.
[42] Zha J,Han KJ,Xu LG,etal.The Ret finger protein inhibits signaling mediated by the noncanonical and canonical IkappaB kinase family members[J].J Immunol(Baltimore,Md :1950),2006,176(2):1072-1080.
[43] Chae JJ,Wood G,Richard K,etal.The familial Mediterranean fever protein,pyrin,is cleaved by caspase-1 and activates NF-kappaB through its N-terminal fragment[J].Blood,2008,112(5):1794-1803.
[44] Shi M,Cho H,Inn KS,etal.Negative regulation of NF-kappaB activity by brain-specific TRIpartite motif protein 9[J].Nat Communicat,2014,5(26):4820-4820.
[45] Wu WS,Xu ZX,Hittelman WN,etal.Promyelocytic leukemia protein sensitizes tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced apoptosis by inhibiting the NF-kappaB survival pathway[J].J Biological Chemist,2003,278(14):12294-12304.
[46] Tomar D,Sripada L,Prajapati P,etal.Nucleo-cytoplasmic trafficking of TRIM8,a novel oncogene,is involved in positive regulation of TNF induced NF-kappaB pathway[J].PLoS One,2012,7(11):e48662.
[47] Suzuki M,Watanabe M,Nakamaru Y,etal.TRIM39 negatively regulates the NFkappaB-mediated signaling pathway through stabilization of cactin[J].Cell Mole Life Sci,2016,73(5):1085-1101.
[48] Luo Q,Lin H,Ye X,etal.Trim44 facilitates the migration and invasion of human lung cancer cells via the NF-kappaB signaling pathway[J].Int J Clin Oncol,2015,20(3):508-517.
[49] Yang B,Wang J,Wang Y,etal.Novel function of Trim44 promotes an antiviral response by stabilizing VISA[J].J Immunol(Baltimore,Md :1950),2013,190(7):3613-3619.
[50] Kondo T,Watanabe M,Hatakeyama S.TRIM59 interacts with ECSIT and negatively regulates NF-kappaB and IRF-3/7-mediated signal pathways[J].Biochemical Biophysical Res Communicat,2012,422(3):501-557.
[51] Gack MU,Shin YC,Joo CH,etal.TRIM25 RING-finger E3 ubiquitin ligase is essential for RIG-I-mediated antiviral activity[J].Nature,2007,446(7138):916-920.
[52] Yan J,Li Q,Mao AP,etal.TRIM4 modulates type I interferon induction and cellular antiviral response by targeting RIG-I for K63-linked ubiquitination[J].J Mole Cell Biol,2014,6(2):154-163.
[53] Uchil PD,Hinz A,Siegel S,etal.TRIM protein-mediated regulation of inflammatory and innate immune signaling and its association with antiretroviral activity[J].J Virol,2013,87(1):257-272.
[54] Shibata M,Sato T,Nukiwa R,etal.TRIM45 negatively regulates NF-kappaB-mediated transcription and suppresses cell proliferation[J].Biochemical Biophysical Res Communicat,2012,423(1):104-109.
[55] Niederberger E,Geisslinger G.The IKK-NF-kappaB pathway:a source for novel molecular drug targets in pain therapy?[J].FASEB J,2008,22(10):3432-3442.
[56] Perkins ND.The diverse and complex roles of NF-kappaB subunits in cancer[J].Nat Rev Cancer,2012,12(2):121-132.
[57] Yin MJ,Yamamoto Y,Gaynor RB.The anti-inflammatory agents aspirin and salicylate inhibit the activity of I(kappa)B kinase-beta[J].Nature,1998,396(6706):77-80.
[58] Saff RR,Banerji A.Management of patients with nonaspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease aspirin hypersensitivity reactions[J].Allergy Asthma Proc,2015,36(1):34-39.
[59] Auphan N,Didonato JA,Rosette C,etal.Immunosuppression by glucocorticoids:inhibition of NF-kappa B activity through induction of I kappa B synthesis[J].Science (New York,NY),1995,270(5234):286-290.
[60] Pasieka AM,Rafacho A.Impact of glucocorticoid excess on glucose tolerance:clinical and preclinical evidence[J].Metabolites,2016,6(3):E24.
[61] Gilmore TD,Herscovitch M.Inhibitors of NF-kappaB signaling:785 and counting[J].Oncogene,2006,25(51):6887-6899.
[62] Baud V,Karin M.Is NF-kappaB a good target for cancer therapy? Hopes and pitfalls[J].Nat Rev Drug Discovery,2009,8(1):33-40.
[收稿2017-10-27 修回2017-12-20]
(编辑 许四平)
10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2017.06.025
①本文受国家自然科学基金(81571530)资助。
金 争(1992年-),女,在读硕士,主要从事肿瘤免疫相关研究,E-mail:jzjinzhengjz@163.com。
及指导教师:闫东梅(1978年-),女,博士,副教授,硕士生导师,主要从事细胞免疫相关研究,E-mail:dmyan@jlu.edu.cn。 朱 迅(1958年-),男,博士,教授,博士生导师,主要从事分子免疫与肿瘤免疫相关研究,E-mail:zxunzhux@vip.sohu.com。
R292.9
A
1000-484X(2017)06-0924-06

