多自由度拟不可积哈密顿系统的随机分数阶最优控制*
钱佳敏 陈林聪 陈虹霖
(华侨大学土木工程学院,厦门 361021)
多自由度拟不可积哈密顿系统的随机分数阶最优控制*
钱佳敏 陈林聪†陈虹霖
(华侨大学土木工程学院,厦门 361021)
推广了适用于分数阶系统控制的随机分数阶最优控制策略,提出了高斯白噪声激励下多自由度拟不可积哈密顿系统以响应最小化为目标的随机分数阶最优控制策略.首先,应用拟不可积哈密顿系统随机平均法,将受控系统简化为关于能量的部分平均伊藤方程.然后,将控制性能指标中关于控制力的部分表示为分数阶形式,结合随机动态规划原理,建立并求解部分平均系统的无界遍历控制的随机动态规划方程,获得了随机分数阶最优控制律.最后,采用一个算例验证了随机分数阶控制策略的控制效果和控制效率.研究表明,随机分数阶最优控制策略对传统的整数阶随机动力学系统同样适用,能比传统的整数阶控制策略取得更好的控制效果.另外,随着激励强度增加,整数阶控制策略的控制效率显著降低;而分数阶控制策略的控制效率虽比整数阶控制策略的控制效率略低,但随着激励强度的增加,分数阶控制策略的控制效率缓慢上升并趋于平稳, 可以有效地缓解控制效率与控制效果之间的矛盾.
随机分数阶最优控制, 随机平均法, 随机动态规划原理, 多自由度系统, 拟不可积哈密顿系统
引言
随机最优控制具有广泛的应用前景,亦是相当具有挑战性的课题.经过几十年的发展,随机最优控制已取得了长足的发展,出现了许多重要的研究成果,如文献[1-4].但在工程中,应用最广泛的随机最优控制依然是基于线性系统模型的LGQ控制或最优Bang-bang控制.因此,越来越多的学者开始研究非线性系统的随机最优控制.如,Beaman[5],Yohsida[6],以及Young和Chang[7]用统计线性化法将非线性随机系统转化为拟线性系统, 再应用LGQ控制策略;Crespo和Sun[8]用广义胞映射法求解受控非线性随机系统的动态规划方程;Crespo和Sun[9]还提出了另一种非线性控制方法,即无论系统初始条件如何,系统响应最终都可达到一个预先设计好的概率密度函数.Dimentberg等[10]提出线性随机振动系统最优有界控制问题的动态规划方程的混合解法;李杰等[11]将广义概率密度演化方程用于随机结构系统的最优控制;朱位秋及其合作者[12,13]提出了基于随机平均法和随机动态规划原理的拟哈密顿系统的非线性随机最优控制策略.然而,控制效率和控制效果这一对矛盾仍未得到很好解决.
近年来,越来越多的学者开始从事分数阶最优控制问题的研究.如,Agrawal[14]给出了分数阶最优控制问题的一般求解方法.曾庆山和杨增芳[15]将求解整数阶系统最优控制的方法和步骤拓展到分数阶系统的最优控制,获得指标函数终端自由和受函数约束的分数阶系统的最优控制.纪增浩[16]采用分数阶变分法推导出分数阶最优控制问题的必要条件,然后采用多段线性插值法来求解,最终得到最优控制律.分数阶最优控制的意义是对整数阶最优控制理论的进一步推广,可获得具有更佳的动态性能和鲁棒性的控制结果.然而,分数阶最优控制问题研究还处于起步阶段,许多方面都需要进一步完善,尤其是针对随机激励下非线性动力学系统.
最近,Hu及其合作者[17]提出了一种随机分数阶最优控制策略,对随机激励下具有分数阶导数型阻尼的拟可积哈密顿系统进行控制,取得了较好的控制效率和控制效果.本文将进一步推广随机分数阶最优控制策略,对多自由度非线性拟不可积哈密顿系统的随机响应进行控制.研究表明,分数阶随机控制策略对传统的整数阶随机动力学系统仍然适用,能比整数阶控制策略取得更佳的控制效果,同时还能有效地缓解控制效率与控制效果之间的矛盾.
1 随机平均法
考虑受控拟哈密顿系统,其运动方程型为:
Qi(0)=Qi0,Pi(0)=Pi0
i,j=1,2,…n,k=1,2,…m
(1)
式中Qi,Pi分别是广义位移与广义动量;H′=H′(Q,P)是相应哈密顿系统的哈密顿函数;c′=c′(Q,P)是拟线性阻尼系数;ε1/2fik=ε1/2fik(Q,P)为激励的幅值;Wk(t)是相关函数为2Dklδ(t)的高斯白噪声;ui=ui(Q,P)为反馈控制力.经Wong-Zakai修正项修正后,(1)式可以转化为如下的It随机微分方程:
(2)
式中H与cij分别为修正后的哈密顿函数与拟线性阻尼系数;Bk(t)为Wiener过程.
设与系统(2)相应的哈密顿系统为不可积,即H是与(2)相应的哈密顿系统的唯一独立对合的首次积分.应用拟不可积哈密顿系统随机平均法,可由(2)式导出如下关于H的部分平均It随机微分方程:
(3)
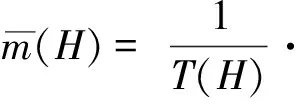
·dq1dq2…dqndp2…dpn
·dq1dq2…dqndp2…dpn
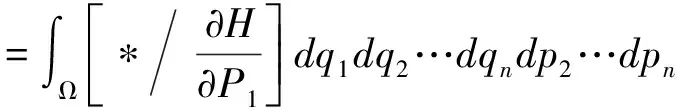
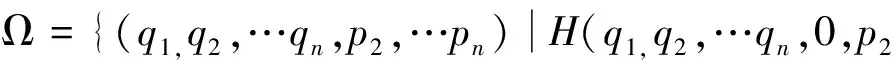
p3,…pn)≤H}
(4)
2 随机动态规划方程
考虑系统(3)在半无限长时间区间上的控制.设性能指标为:
(5)
引入值函数:
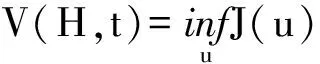
(6)
应用随机动态规划原理,可以导出如下形式的动态规划方程:
(7)
其中,
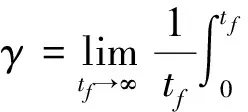
(8)
表示最优平均成本.式(7)右边取极小值的必要条件为:
(9)
设
f(H,
(10)
其中R为正定对称常数矩阵,则最优控制律为:
(11)
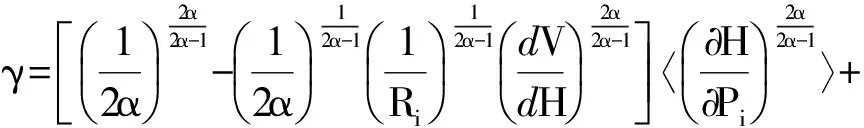
(12)
求解上式,可获得dV/dH.然后,再将dV/dH代入方程(11)可得最优控制律的表达式.最后,将最优控制律,代入部分平均It随机微分方程(3)以取代ui,完成平均,得到最优控制系统的平均It随机微分方程:
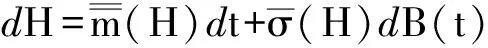
(13)
其中,
(14)
求解与方程(13)相应的FPK方程,可得最优控制或未控系统的响应统计量.为评价分数阶最优控制策略的效果与效率,引入如下两个准则:
(15)
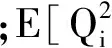
3 算例
考虑一个两自由度受控的拟不可积哈密顿系统,其运动方程为:
(16)
其中,w1,w2与a为正常数;ξi(i=1,2)为强度2Di的高斯白噪声;ui(i=1,2)为反馈控制力.
与系统(16)相应的哈密顿函数为:
(17)
(18)
式中,
(19)
取成本函数形为式(10),其中u=[u1,u2]T,
R=diag(R1,R2)及
f1(H)=s0+s1H+s2H2+s3H3
(20)
运用随机动态规划原理,建立并求解形如式(7)的随机动态规划方程,得到最优控制律为:
(21)

(22)

pcon(H)=
(23)
其中C1为归一化系数.令u=0,求解与之相应的平稳FPK方程可得未控系统的平稳概率密度:puncon(H)=
(24)
最优控制和未控系统的广义位移与广义速度的联合平稳概率密度为:
(25)
(26)
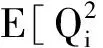
(27)
以及最优控制力的均方值
(28)最后,按方程(15)计算控制效果K1和控制效率K2.对如下系统参数:b1=b2=0.05, a=2.0, w1=1.0,w2=1.414, s1=0.05,s2=0.0, s3=1.5,dV(0)/dH=13.0,R1=R2=R=2.1,图1与图2给出了上述最优控制下系统第一个自由度的若干个数值结果.
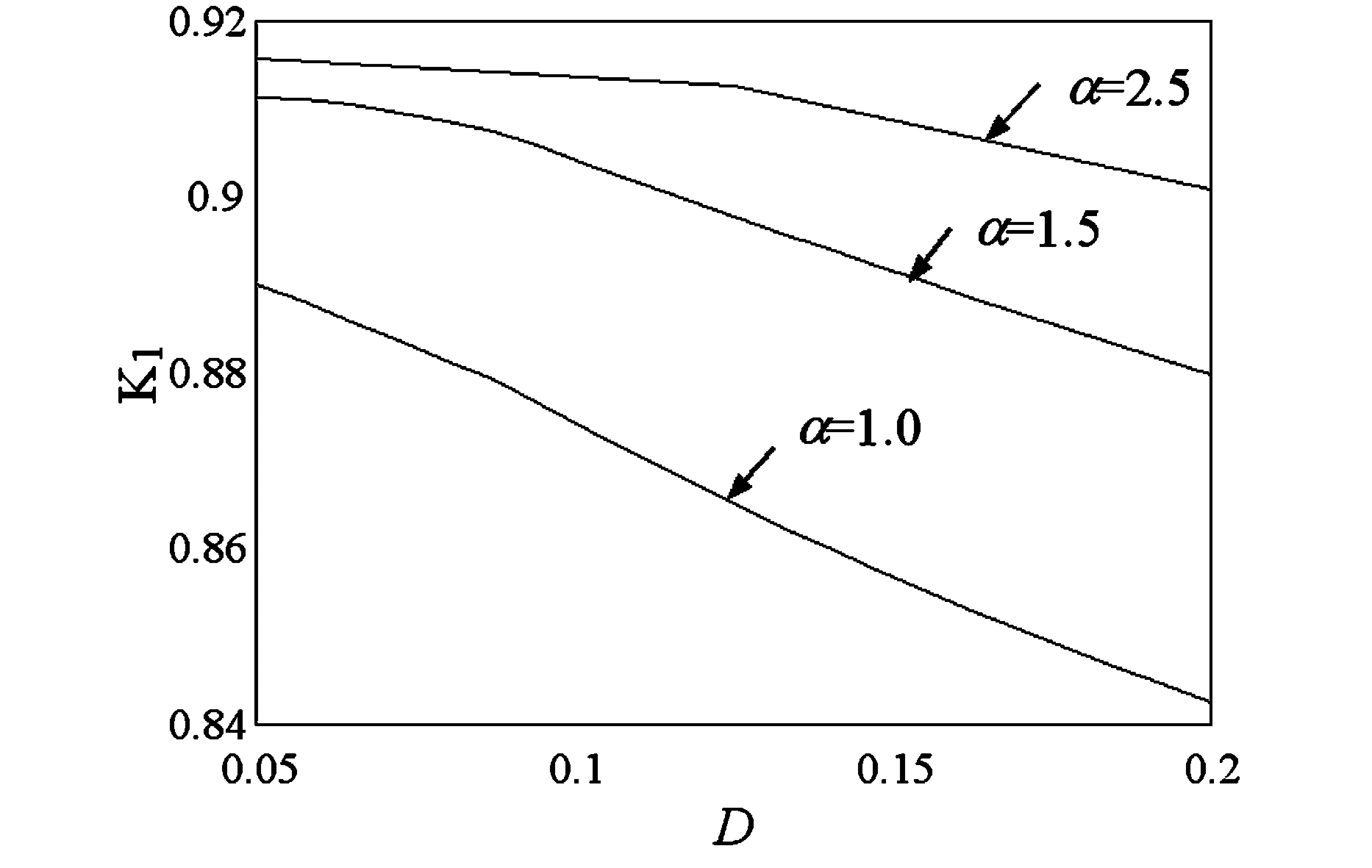
图1 不同分数阶数时控制效果与激励强度变化的关系Fig.1 Relationship between control effect and excitation intensity under different fractional orders

图2 不同分数阶数时控制效率与激励强度变化的关系Fig.2 Relationship between control efficiency and excitation intensity under different fractional orders
由图1可知,本文提出的分数阶最优控制策略在控制效果上比传统的整数阶要好,并且控制效果随着分数阶阶数的增加而提高.另外,随着激励强度增加,控制效果均变差.图2给出了不同分数阶阶数下随激励强度变化的最优控制效率.由图可知,当a=1.0,即分数阶最优控制策略退为整数阶最优控制策略,此时控制效率随着激励强度的增加而降低.然而,当分数阶数a=1.5或2.5时,随着激励强度的增加,分数阶控制策略的控制效率开始缓慢提高,并趋于平稳.因此,为了缓解控制效率与控制效果这一对矛盾,采用随机分数阶最优控制策略取代传统的整数阶控制策略是一种可行的方案.
4 小结
本文进一步推广了适用于分数阶系统控制的随机分数阶最优控制策略,提出了多自由度拟不可积哈密顿系统以响应最小化为目标的随机分数阶最优控制策略.数值算例表明,控制效果随着分数阶阶数的增加而提高;整数阶控制策略的控制效果随着激励强度增加而显著降低;分数阶控制效率比整数阶控制效率略低,但是随着激励强度的增加而缓慢上升并趋于平缓,可为解决控制效果与控制效率是一对矛盾提供可行方案.
1Stengel R F. Stochastic Optimal Control: Theory and application. New York: Wiley, 1986
2Fleming W H, Soner H M. Controlled markov processes and viscosity solutions. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1992
3Yong J M, Zhou X Y. Stochastic control, Hamiltonian systems and HJB equations. New York: Springer-Verlag,1999
4Soong T T. Active structural control: theory and practice. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1990
5Beaman J J. Non-linear quadratic Gaussian control.InternationalJournalofControl, 1984,39(2):343~361
6Yoshida K. A method of optimal control of non-linear stochastic systems with non-quadratic criteria.InternationalJournalofControl, 1984,39(2):279~291
7Young G E, Chang C J. Optimal control of stochastic parametrically and externally excited nonlinear control systems.JournalofDynamicsandSystemMeasureControl, 1988,110(2):114~119
8Crespo L G, Sun J Q. Stochastic optimal control of nonlinear dynamical systems via Bellman′s principle and cell mapping.Automatica, 2003,39(11):2109~2114
9Crespo L G, Sun J Q. Non-linear stochastic control via stationary response design.ProbabilisticEngineeringMechanics, 2003,18(1):79~86
10 Dimentberg M F, Iourtchenko A S, Brautus A S. Optimal bounded control of steady-state random vibrations.ProbabilisticEngineeringMechanics, 2000,15(4):381~386
11 Li J, Peng Y B, Chen J B. A physical approach to structural stochastic optimal controls.ProbabilisticEngineeringMechanics, 2010,25(1):127~141
12 Zhu W Q. Nonlinear stochastic dynamics and control in Hamiltonian formulation.ASMEAppliedMechanicsReview, 2006,59(4):230~248
13 朱位秋,应祖光. 拟哈密顿系统非线性随机最优控制. 力学进展, 2013,43(1):39~55 (Zhu W Q, Ying Z G. Nonlinear stochastic optimal control of quasi Hamiltonian systems.AdvancesinMechanics, 2013,43(1):39~551(in Chinese))
14 Agrawal O P. A general formulation and solution scheme for fractional optimal control problems.NonlinearDynamics, 2004,38(1-4):323~337
15 曾庆山,杨增芳. 指标函数终端自由和受函数约束的分数阶系统的最优控制. 郑州大学学报工学版, 2012,33(3):71~74 (Zeng Q S,Yang Z F. Optimal control of fractional-order system with freedom end-point and function constrained end-point.JournalofZhengzhouUniversity(EngineeringEdition), 2012,33(3):71~74 (in Chinese))
16 纪增浩. 分数阶系统的状态估计及其最优控制问题研究[硕士学位论文]. 北京:北京化工大学,2013 (Ji Z H. Study on state estimation and optimal control of fractional order system[Master Thesis]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Master Thesis, 2013(in Chinese))
17 Hu F, Zhu W Q, Chen L C. Stochastic fractional optimal control of quasi-integrable Hamiltonian system with fractional derivative damping.NonlinearDynamics, 2012,70(2):1459~ 1472
*The project supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China through the Grants (11672111), by the Research Award Fund for Outstanding Young Researcher in Higher Education Institutions of Fujian Province and by the Research Fund for Excellent Young Scientific and Technological Project of Huaqiao University under the Grant (ZQN-YX307)
† Corresponding author E-mail:lincongchen@hqu.edu.cn
17 March 2017,revised 18 April 2017.
STOCHASCTICFRACTIONAL OPTIMAL CONTROL OF MDOF QUASI NON-INTEGRABLE HAMILTONIAN SYSTEMS*
Qian Jiamin Chen Lincong†Chen Honglin
(CollegeofCivilEngineering,HuaqiaoUniversity,Xiamen361021,China)
In this paper, a fractional optimal control strategy suitable for the fractional order dynamical system is extended to the classical integral dynamical system. A stochastic fractional optimal control strategy is proposed to minimize the response of the multi-degree-of-freedom (MDOF) quasi-non-integrable Hamiltonian systems under Gaussian white noise excitations. First, the controlled system is reduced to a partially averaged Itequation for the energy process by applying the stochastic averaging method of quasi-non-integrable Hamiltonian systems. The control force part in the control performance index is then formulated as the form of fractional-order. By combining with the stochastic dynamics programming principle, the dynamical programming equation for the ergodic control of the partially averaged system is established and then solved to yield the fractional optimal control law. Finally, an example is given to illustrate the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed control design procedure. The numerical results indicate that the stochastic fractional optimal control strategy can be suitable for the classical integral order stochastic dynamical systems. The proposed control strategy can obtain the better control effectiveness than that of the classical integral-order optimal control strategy. Furthermore, the efficiency of integral-order control strategy becomes worse remarkably as the excitation intensity increases, while the efficiency of fractional order control strategy is a bit lower than that of integral-order control strategy, but it slowly rises and then tends to stable. The proposed stochastic fractional order optimal control strategy effectively mitigates the contradiction between the control effectiveness and control efficiency.
stochastic fractional optimal control, stochastic averaging method, stochastic dynamics programming principle, multi-degree-of-freedom system, quasi non-integrable Hamiltonian systems
*国家自然科学基金资助项目(11672111)、福建省高校青年杰出项目、华侨大学优秀青年科技创新人才(ZQN-YX307)
10.6052/1672-6553-2017-024
2017-03-17收到第1稿,2017-4-18收到修改稿.
† 通讯作者 E-mail: lincongchen@hqu.edu.cn

