胞映射方法及其在非线性随机动力学中的应用*
徐伟 岳晓乐 韩群,2
(1.西北工业大学应用数学系,西安 710072) (2.华中农业大学理学院,武汉 430070)
胞映射方法及其在非线性随机动力学中的应用*
徐伟1†岳晓乐1韩群1,2
(1.西北工业大学应用数学系,西安 710072) (2.华中农业大学理学院,武汉 430070)
介绍了与非线性随机动力学研究密切相关的几类胞映射方法的研究和进展,主要有广义胞映射图方法、基于短时高斯逼近的胞映射方法、并行胞映射方法等.简述了胞映射方法在随机动力学中的应用情况,重点关注随机响应、分岔、离出和碰撞振动系统.给出了胞映射方法面临的挑战,以及未来研究可能的发展方向.
胞映射方法, 并行算法, 离出, 短时高斯逼近
引言
在自然界和实际工程问题当中,往往受到像大气湍流、地面强风、海浪运动和路面不平整等因素的影响,这些作用都带有随机性,由此诱发了非线性随机动力学的研究[1-2],已成为数学、力学、物理、经济金融等领域较活跃的科学前沿,其主要研究内容包括随机响应、随机分岔、随机控制和随机离出问题等[3-4],研究方法有从确定性系统推广而来的随机摄动法、随机多尺度法、随机平均法等近似解析方法,也有像胞映射方法、路径积分法等有效的数值方法[5].由于解析方法难以处理强非线性或强随机激励问题,借助一定的数值方法,可以揭示很多非常复杂动力学现象,因此数值方法对非线性随机动力学的研究具有不可替代的作用.目前,随着计算机水平的快速发展,计算性能越来越高,速度越来越快,成本逐步降低,这为数值方法的应用研究提供了更广阔的舞台.
胞映射方法[6]是分析非线性动力系统全局特性的有效数值工具,因其快速、准确和适用范围广等特点而备受关注,尤其是改进后的广义胞映射方法,通过引入Markov链使得计算优势更加明显,不仅能够计算系统的拓扑结构等定性性质(如吸引子和吸引域的空间分布),而且还能从统计意义上反映动力系统的定量性质,因此广义胞映射方法在随机动力系统中逐步展现出了良好的应用前景[7].当前,由于一些实际问题的需求,系统规模由低维走向高维,随机激励从高斯变成非高斯,数值方法在科学研究中扮演着越来越重要的角色,因此,开展广义胞映射方法在非线性随机动力学中的应用研究具有重要的科学意义.
1 非线性随机动力学中的胞映射方法研究进展
胞映射方法最初由Hsu[6]于上世纪80年代提出,主要用于强非线性系统的全局分析,基本思想是将动力系统的连续状态空间离散成胞状态空间,其中包含大量的规则几何体,称之为胞,并用整数序号标示.每个胞都是一些状态点的集合,以胞中的点为起始点向前积分,构造点到点的映射,而积分终点所在的胞称为像胞.点与点之间的映射关系就转化成了胞与胞之间的映射关系,用胞动力系统来分析原始动力系统的性质.相比传统的点映射,胞映射方法的显著特点是它数值积分时不用记录长时间的轨线,只需要计算一个映射时间步长后的轨线终点,从而达到提高计算效率的目的.胞映射方法自提出之后,众多学者参与胞映射的研究工作,发展了一系列改进版本,较有代表性的有简单胞映射方法[6,8]、广义胞映射方法[7,8]、图胞映射方法[9-11]、胞参照点映射方法[12,13]、插值胞映射方法[14]、面向集合法[15]等等.
众多改进方法中,广义胞映射方法由于能够同时分析动力系统的定性性质和定量性质,地位变得尤为重要.其基本思想是在寻找像胞时,每个胞内需选取多个采样点,分别从每个采样点出发计算一条轨线,每个胞可以有多个像胞,并以一定的概率转移到它的像胞,这样可以得到任意两个胞之间的一步转移概率.胞与胞的转移关系等价于一个有限的Markov链,因此可运用Markov链的相关理论对胞映射动力系统进行分析,并用于随机动力系统的响应分析.Sun利用广义胞映射方法研究随机系统的首次穿越和响应分析[16,17],Wu和Zhu[18]研究了一类脉冲激励下捕食和被捕食者模型的随机响应分析,Yue等[19,20]分别给出了有界噪声和泊松白噪声激励下典型动力系统的响应概率密度函数,Hong等[21,22]运用研究了几类模糊动力系统瞬态和稳态隶属分布函数的演化过程.
非线性随机动力系统响应的概率密度函数可以通过求解相应的Fokker-Planck-Kolmogorov(FPK)方程来获得,通过构造从某些给定初始条件出发的短时解是求解问题的一种有效途径.为了提高非线性系统短时解的精度,Sun和Hsu[23]成功构造了高斯白噪声激励下非线性系统FPK方程的一种短时高斯解,将系统的短时概率密度函数近似为高斯分布,其均值和方差可通过数值求解高斯闭包后的矩方程得到,然后运用这种短时高斯解计算广义胞映射方法中的胞转移概率,并研究了几类典型系统的随机振动分析.基于短时高斯逼近胞映射方法,Sun[24]还研究了非线性系统的最优控制问题,以及含干摩擦系统的非线性系统的随机振动问题[25].针对含周期和高斯白噪声激励的非线性系统,Han等[26]通过短时高斯逼近方法计算含周期激励系统的转移概率矩阵,提高了广义胞映射方法在计算响应概率密度函数时的效率,研究发现确定性混沌鞍会影响随机响应概率密度函数.Li等[27,28]通过引入演化概率向量的概念,利用广义胞映射方法研究了Mathieu-Duffing振子在加性和乘性噪声共同作用下的分岔行为.
图论分析方法的引入,进一步扩展了广义胞映射方法在定性分析中应用范围.Xu等从全局的角度分析了随机吸引子和随机鞍的演化特性,提出了新的随机分岔定义,研究了高斯白噪声激励下几类典型非线性动力系统的随机分岔行为[29-31].Yue和Xu[32,33]研究了有界噪声激励下单势井Duffing振子和SD振子的随机分岔,发现随机吸引子和随机鞍形状及大小改变的方向与系统不稳定流形的形状始终保持一致.Hong和Sun[34,35]通过提出模糊胞映射方法,研究了模糊噪声激励下非线性动力系统的分岔现象.Liu等利用广义胞映射图方法研究了高斯白噪声激励下分段线性系统的全局动力学[36],以及噪声诱导周期激励系统的逃逸问题[37].最近,基于分数阶导数的短记忆原理,广义胞映射图方法又成功地应用于分数阶动力系统全局特性的研究中[38-40].
胞映射方法自提出以来,面临的最主要问题就是计算精度与计算速度之间的矛盾,随着计算机水平的提高,并行技术为胞映射方法提供了新的途径.Kreuzer和Lagemann[41]通过分析给出了胞映射方法中引入并行技术的可行性,并应用于二维动力系统中.Eason和Dick[42]基于多核CPU提出了并行多自由度胞映射方法,用于分析维数较高的动力系统.Belardinelli和Lenci[43]研究了一种基于分布式计算的胞映射方法,针对高维非线性系统的大范围吸引域提出了有效的并行算法.Sun和其合作者[44]基于GPU多线程实现技术,结合简单胞映射、广义胞映射、迭代细分算法和有效后处理方法提出了并行胞映射方法,该方法被运用到高维非线性动力系统的全局分析中,表现出了非常高的计算效率.随后,他们运用并行胞映射方法计算了非线性向量函数的简单零点问题[45].Yue[46]基于并行和细分技术,有效地提高了胞映射方法的计算精度和速度,该方法能够处理动力系统的复杂吸引域边界.在基于演化概率向量的胞映射方法基础上,Li等[47]进一步利用GPU并行技术提高计算效率,研究了噪声诱导一类二自由度分段线性系统的转迁行为.
本文仅介绍了与随机动力学密切相关的几类胞映射方法的最新进展,其他有关的改进方法的进展情况,可参考文献及专著[48-51].
2 胞映射方法在随机动力系统中的若干应用研究
2.1 随机响应与分岔
考虑n维随机动力系统[23]

(1)
其中t为时间变量,ζ(t)为随机激励,f为向量值函数,D为给定的状态空间区域.x(t)为稳态Markov过程,令p(x,t)为x(t)在时刻t的概率密度函数,则有
(2)

(3)
令t0=(m-1)Δt和t=mΔt,那么在式(3)条件下式(2)又可以写为:
(4)
运用广义胞映射方法时,将连续状态空间离散成胞化空间,得到系统状态胞之间的转移关系,上述式(4)变为:
(5)
矩阵形式为:
p(n+1)=P·p(n)
(6)
其中P={pji}表示一步转移概率矩阵,p(n)指的是n步迭代之后系统在状态空间中的概率分布,也即系统在时刻tn=t0+nΔT时的概率分布.若给定初始概率分布p(0),可以计算得到系统在tn时刻的瞬态响应的概率分布:
p(n)=P·p(n-1)=P2·p(n-2)=…=Pn·p(0)
(7)
数值计算时不需要求出Pn,只需计算n次矩阵P和向量p(i),i=0,1,2,…,n-1的乘积即可.
对于含周期激励的系统[26],在计算一步转移概率时,转移概率求解时的时间长度直接取为系统的周期,虽然这样在形式上显得很简单,但是运算过程却相当费时,短时高斯逼近方法构造FPK方程的短时解是提高胞映射方法计算效率的有效途径.考虑含周期和高斯白噪声激励的n维非线性随机动力系统,其对应的It随机微分方程为
dX(t)=f(X,t)dt+σ(X)dB(t)
(8)
求解短时高斯逼近解时,首先考虑响应过程X(t)的一阶矩和二阶矩
m(t)=E[X(t)]
C(t)=E[(X-m)(X-m)T]
(9)
(10)
其中m(kτ)和C(kτ)是方程(9)满足初始条件m[(k-1)τ]=x0和C[(k-1)τ]=0时的短时解.需要指出的是计算条件概率需要进行数值积分,用到了Gauss-Legendre积分方法[52-53].
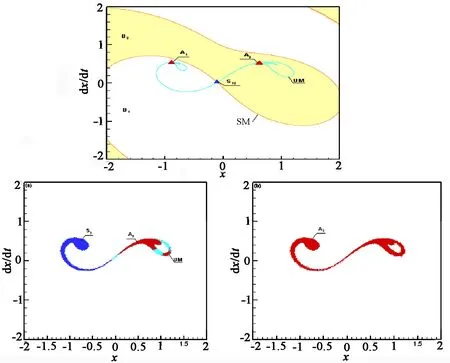
图1 系统(11)的全局特性图 μ1=μ2=0.0; μ1=0.09,μ2=0.133; μ1=0.09,μ2=0.134Fig.1 Global properties of system (11) μ1=μ2=0.0; μ1=0.09,μ2=0.133; μ1=0.09,μ2=0.134
考虑随机激励下的光滑非连续(SD)振子[54-55]:

(11)
其中β为阻尼系数,f和ω为谐和激励的幅值和频率,α为光滑参数,ξ1(t)和ξ2(t)为两个有界噪声过程,取参数β=0.2,α=0.42,f=0.22,ω=0.85时,利用广义胞映射图方法得到确定性系统,以及噪声激励下系统的全局特性,如图1,发现随机分岔的发生是随机吸引子与随机鞍发生碰撞的结果,且随机吸引子和随机鞍的形状和大小的改变方向和系统的不稳定流形形状始终保持一致[33].
考虑SD振子受周期和高斯白噪声共同作用,即μ1=0.01,μ2=0.0,ξ1(t)为高斯白噪声,取β=0.04,α=0.6,f=0.83,ω=1.0606时,确定系统的全局特性如图2所示.图3进一步给出了不同时刻瞬态联合概率密度函数的等高线图,可以发现瞬态联合概率密度函数的形状逐渐演化成了确定系统混沌鞍的形状[26].
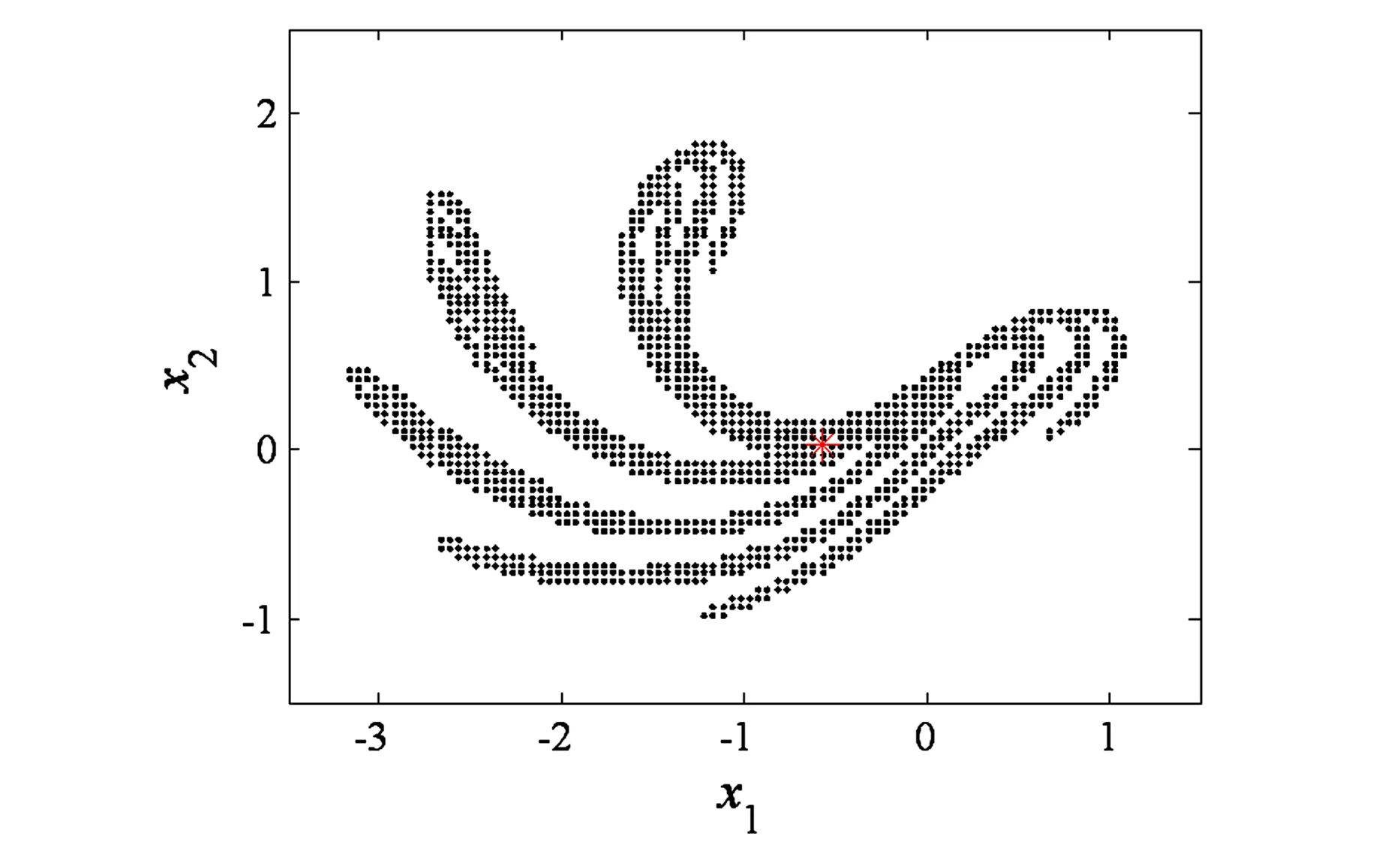
图2 确定性系统(11)的吸引子A(星号)和混沌鞍S(点)Fig.2 Attractor A (asterisk) and chaotic saddle S (dots) of system (11)
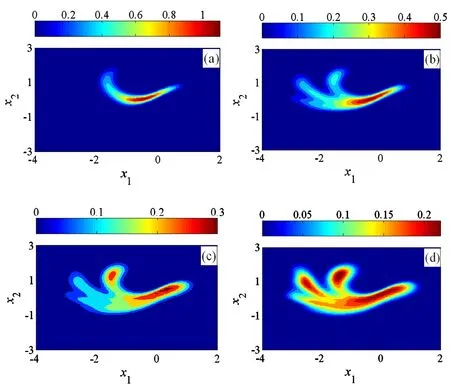
图3 系统(11)在不同时刻瞬态联合概率密度函数的等高线图(a) t=1T;(b) t=2T;(c) t=3T;(d) t=4TFig.3 The contour plots of transient joint probability density function of system (10) at different times(a) t=1T;(b) t=2T;(c) t=3T;(d) t=4T
2.2 首次穿越时间
首次穿越时间是研究非线性随机动力系统离出问题的重要指标之一,关注的是系统响应会在何时从一个稳态出发首次穿过其安全域的边界到达另一个稳态的安全域.需要计算系统首次穿越时间的统计分布,包括首次穿越时间的概率密度函数及平均首次穿越时间.近年来,许多学者研究了随机游走模型的首次穿越时间[56,57]和双稳动力系统的平均首次穿越时间[58],但是这些研究对象往往都局限在一阶系统.二阶非线性系统首次穿越时间的精确解一般很难获取,因此需要借助一些近似方法或数值方法来进行研究.胞映射方法是研究首次穿越时间问题一种有效的数值方法[16],比直接数值模拟方法有明显优势.
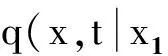
x,x1∈Rm
(12)
式中L[·]表示后向Kolmogorov方程的微分算子.
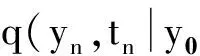
dy1…dyn-1
(13)
若假设系统的响应为齐次Markov过程,则有:
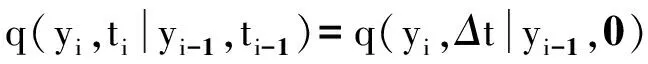
i=1,2,…,n
(14)
然后基于广义胞映射方法求解含吸收边界条件的一步转移概率矩阵,并在初始分布中考虑对应的初始条件,即可得到首次穿越时间的概率密度,以及平均首次穿越时间.通过比较,发现胞映射方法和直接数值模拟结果吻合较好,如图4所示[59].
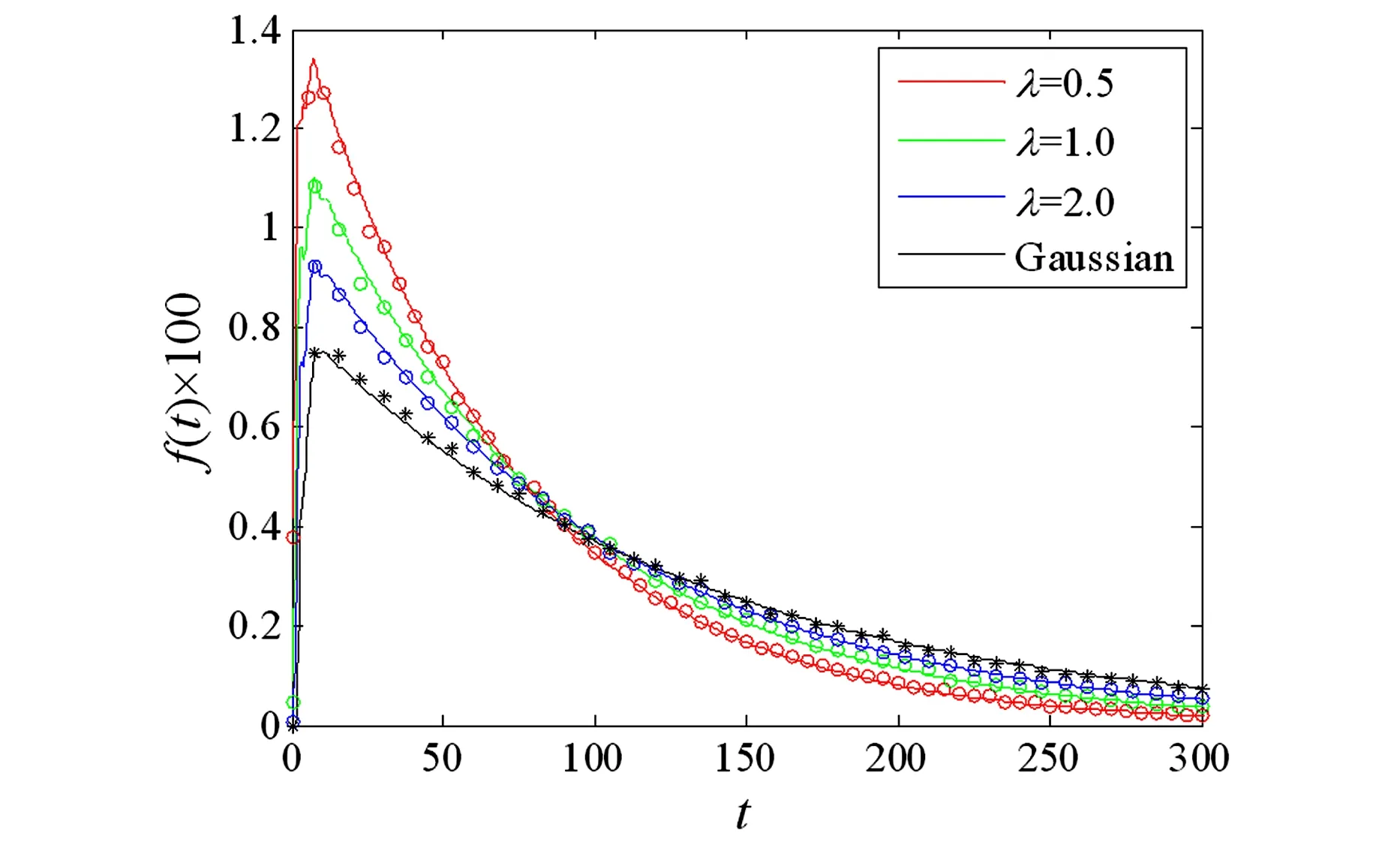
图4 对称双稳系统首次穿越时间的概率密度函数f(t)实线表示广义胞映射方法的结果,圆圈和星号表示直接模拟的结果Fig.4 First-passage time probability density functions f(t) in the asymmetric bistable system solid lines are results from the generalized cell mapping method, circles and stars are results from direct Monte Carlo simulation
2.3 离出位置分布
离出位置分布是刻画非线性随机动力系统离出问题的另一个重要指标.系统在噪声激励下的逃逸路线与确定性吸引域边界的交点被称为离出点.离出点的位置与首次穿越时间一样具有随机性,因此需要计算离出位置统计分布的概率密度函数.Bobrovsky和Schuss[60]运用渐进展开法研究时观察到了离出位置分布的一种非常规偏移,也被称作为鞍点回避现象[61,62].2013年,Khovanov等[63]发展了一种非线性非局部稳定性方法,借此描述了可激发FHN系统中噪声诱导逃逸问题,并计算了离出位置分布.这两种解析方法在运用过程中也难免存在一些局限性[64],经常需要借助数值方法来计算离出位置分布,胞映射方法即是其中一种有效的数值方法[37-65].
考虑Kramers离出问题[66,67],布朗粒子在噪声作用下从一个势阱越过势垒到达另一个势阱.其运动可表示为下面的标准化随机微分方程:
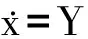
(15)
其中X和Y分别表示粒子运动的位移和速度,β是标准化电离常数,取值为2.0,ε是一个表示温度的标准化小参数,W(t)是标准的高斯白噪声.图5给出了确定系统的全局行为,以及随噪声强度ε取不同时系统离出位置分布.可以发现分布曲线随着ε的减小而慢慢往右移动,且峰值变高,这种变化的原因在于,随着噪声的越来越弱,系统最大可能的离出位置会慢慢逼近鞍点S.

图5 系统(15)全局特性及离出位置分布(a)全局性质(ε=0), A为吸引子,B为A的吸引域; (b)离出位置分布,实线表示广义胞映射方法的结果,圆圈表示直接数值模拟的结果Fig.5 Global properties and exit location distribution of system (15)(a) global properties, A is attractor and B is the basin of attraction of attractor A; (b) exit location distribution, solid lines are results from the generalized cell mapping method, circles are results from direct Monte Carlo simulation
2.4 碰撞振动系统
对于含高碰撞损失或碰撞约束不在平衡位置的碰撞振动系统,一般的近似解析方法不再适用,只能依赖数值方法来求解,路径积分法就是其中一种.Dimentberg 等[68]基于短时高斯近似的路径积分法研究了具有高碰撞损失的碰撞振动系统,验证了方法的有效性,但该结果只针对运动约束在平衡位置的情形.Li[69]试图利用通过改进广义胞映射方法,使其适用于一般噪声激励下碰撞振动系统的响应概率密度函数求解.广义胞映射方法在非光滑系统定性分析中已经取得了一些研究进展[36,70-73].
考虑随机激励下的单自由度碰撞振动系统[69]:

(16)

(17)
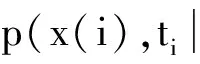
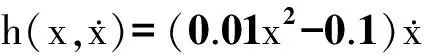

图6 系统(16)的稳态联合概率密度函数(a)q=-0.5;(b)q=-0.8;(c)q=-1.0;(d)q=-1.2Fig.6 The stationary joint probability density function of system (16)(a)q=-0.5;(b)q=-0.8;(c)q=-1.0;(d)q=-1.2
另外,胞映射方法在随机最优控制等领域还有一些重要的研究成果与进展,详情可参考综述文献[50-51].
3 结语
胞映射方法作为一种高效的数值方法,不仅在研究确定性系统全局分析中发挥巨大作用,还在随机动力系统中展现出了良好的应用前景,且已有一定的研究基础.本文重点讨论了胞映射方法在随机动力学领域的最新研究进展,以及所取得的一些成果,包括随机响应与分岔、离出问题以及在随机非光滑系统中的应用.用胞映射方法来研究随机动力系统有明显的优势,但又面临众多挑战,比如:
(1)高维问题一直以来是众多研究者所密切关注的难题,目前的改进方法已取得重大研究进展,特别是并行胞映射方法的提出大大提升了计算维数.对高维非线性随机动力系统而言,如何改进短时高斯逼近策略,并结合并行技术应该是有效的途径.
(2)胞映射方法已经在众多非线性动力学领域有重要应用,如逃逸问题、碰撞振动系统、分数阶系统等,未来的研究可以结果高效胞映射方法进一步拓展在随机动力系统中的应用范围,发现新的动力学现象.
1方同. 工程随机振动. 北京:国防工业出版社, 1995 (Fang T. Random vibration in engineering. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 1995 (in Chinese))
2Lin Y K, Cai G Q. Probabilistic structural dynamics: advanced theory and applications. New York: Mcgraw-Hill, 1995
3朱位秋. 随机振动. 北京:科学出版社, 1992 (Zhu W Q. Random vibration. Beijing: Science Press, 1992 (in Chinese))
4朱位秋. 非线性随机动力学与控制: Hamilton 理论体系框架. 北京:科学出版社, 2003 (Zhu W Q. Nonlinear stochastic dynamics and control: Hamilton theoretic frame. Beijing: Science Press, 2003 (in Chinese))
5徐伟. 非线性随机动力学的若干数值方法及应用. 北京:科学出版社, 2013 (Xu W. Numerical analysis methods for stochastic dynamical systems. Beijing: Science Press, 2013 (in Chinese))
6Hsu C S. A theory of cell to cell mapping dynamical systems.ASMEJournalofAppliedMechanics, 1980,47(4):931~939
7Hsu C S. A generalized theory of cell to cell mapping for nonlinear dynamical systems.ASMEJournalofAppliedMechanics, 1981,48(3):634~642
8Hsu C S. Global analysis by cell mapping.InternationalJournalofBifurcationandChaos, 1992,2(4):727~771
9Hsu C S. Global analysis of dynamical systems using posets and digraphs.InternationalJournalofBifurcationandChaos, 1995,5(4):1085~1118
10 Hong L, Xu J X. Crises and chaotic transients studied by the generalized cell mapping digraph method.PhysicsLettersA, 1999,262(4):361~375
11 Xu W, He Q, Li S. The cell mapping method for approximating the invariant manifolds, IUTAM symposium on dynamics and control of nonlinear systems with uncertainty.SpringerNetherlands, 2007:117~126
12 Jiang J, Xu J X. A method of point mapping under cell reference for global analysis of nonlinear dynamical systems.PhysicsLettersA, 1994,188(2):137~145
13 Jiang J, Xu J X. An iterative method of point mapping under cell reference for the global analysis: theory and a multiscale reference technique.NonlinearDynamics, 1998,15(2):103~114
14 Tongue B H. On obtaining global nonlinear system characteristics through interpolated cell mapping.PhysicaD, 1987,28(3):401~408
15 Dellnitz M, Junge O. Set oriented numerical methods for dynamical systems.HandbookofDynamicalSystemsII:TowardsApplications, 2002,2:221~264
16 Sun J Q, Hsu C S, First-passage time probability of nonlinear stochastic systems by generalized cell mapping method.JournalofSoundandVibration, 1988,124(2):233~248
17 Sun J Q, Hsu C S. Effects of small random uncertainties on nonlinear systems studied by the generalized cell mapping method.JournalofSoundandVibration, 1991,147(2):185~201
18 Wu Y, Zhu W Q. Stochastic analysis of a pulse-type prey-predator model.PhysicalReviewE, 2008,77(4):041911.
19 Yue X L, Xu W, Wang L, Zhou B C. Transient and steady-state responses in a self-sustained oscillator with harmonic and bounded noise excitations.ProbabilisticEngineeringMechanics, 2012,30:70~76
20 Yue X L, Xu W, Jia W T, Wang L. Stochastic response of a φ6oscillator subjected to combined harmonic and Poisson white noise excitations.PhysicaA:StatisticalMechanicsanditsApplications, 2013,392(14):2988~2998
21 Hong L, Jiang J, Sun J Q. Response analysis of fuzzy nonlinear dynamical systems.NonlinearDynamics, 2014,78(2):1221~1232
22 Hong L, Jiang J, Sun J Q. Fuzzy responses and bifurcations of a forced duffing oscillator with a triple-well potential.InternationalJournalofBifurcationandChaos, 2015,25(1):1550005
23 Sun J Q, Hsu C S. The generalized cell mapping method in nonlinear random vibration based upon short-time Gaussian approximation.ASMEJournalofAppliedMechanics, 1990,57(4):1018~1025
24 Crespo L G, Sun J Q. Stochastic optimal control of nonlinear systems via short-time Gaussian approximation and cell mapping.NonlinearDynamics, 2002,28(3):323~342
25 Sun J Q. Random vibration analysis of a non-linear system with dry friction damping by the short-time Gaussian cell mapping method.JournalofSoundandVibration, 1995,180(5):785~795
26 Han Q, Xu W, Sun J Q. Stochastic response and bifurcation of periodically driven nonlinear oscillators by the generalized cell mapping method.PhysicaA:StatisticalMechanicsanditsApplications, 2016,458:115~125
27 Li Z, Jiang J, Hong L. Transient behaviors in noise-induced bifurcations captured by generalized cell mapping method with an evolving probabilistic vector.InternationalJournalofBifurcationandChaos, 2015,25(8):1550109
28 Li Z, Guo K, Jiang J, et al. Study on Critical Conditions and Transient Behavior in Noise-Induced Bifurcations//Control of Self-Organizing Nonlinear Systems.SpringerInternationalPublishing, 2016:169~187
29 He Q, Xu W, Rong H W, Fang T. Stochastic bifurcation in Duffing-van der Pol oscillators.PhysicaA:StatisticalMechanicsanditsApplications, 2004,338(3):319~334
30 Xu W, He Q, Fang T, Rong H W. Global analysis of crisis in twin-well Duffing system under harmonic excitation in presence of noise.ChaosSolitions&Fractals, 2005,23(1):141~150
31 Xu W, He Q, Fang T, Rong H W. Stochastic bifurcation in Duffing system subject to harmonic excitation and in presence of random noise.InternationalJournalofNon-LinearMechanics, 2004,39(9):1473~1479
32 Yue X L, Xu W. Stochastic bifurcation of an asymmetric single-well potential Duffing oscillator under bounded noise excitation.InternationalJournalofBifurcationandChaos, 2010,20(10):3359~3371
33 Yue X L, Xu W, Wang L. Stochastic bifurcations in the SD (smooth and discontinuous) oscillator under bounded noise excitation.ScienceChinaPhysics.MechanicsandAstronomy, 2013,56(5):1010~1016
34 Hong L, Sun J Q. Bifurcations of fuzzy nonlinear dynamical systems.CommunicationsinNonlinearScienceandNumericalSimulation, 2006,11(1):1~12
35 Hong L, Sun J Q. Codimension two bifurcations of nonlinear systems driven by fuzzy noise.PhysicaD:NonlinearPhenomena, 2006,213(2):181~189
36 Kong C, Gao X, Liu X. On the global analysis of a piecewise linear system that is excited by a gaussian white noise.JournalofComputationalandNonlinearDynamics, 2016,11(5):051029.
37 Chen Z, Li Y, Liu X. Noise induced escape from a nonhyperbolic chaotic attractor of a periodically driven nonlinear oscillator.Chaos:AnInterdisciplinaryJournalofNonlinearScience, 2016,26(6):063112.
38 Liu T, Xu W, Xu Y, et al. Long-term dynamics of autonomous fractional differential equations.InternationalJournalofBifurcationandChaos, 2016,26(4):1650055.
39 Liu X, Hong L, Jiang J, et al. Global dynamics of fractional-order systems with an extended generalized cell mapping method.NonlinearDynamics, 2016,83(3):1419~1428.
40 Liu X, Hong L, Jiang J. Global bifurcations in fractional-order chaotic systems with an extended generalized cell mapping method.Chaos:AnInterdisciplinaryJournalofNonlinearScience, 2016,26(8):084304.
41 Kreuzer E, Lagemann B. Cell mappings for multi-degree-of-freedom-systems-Parallel computing in nonlinear dynamics.Chaos,Solitons&Fractals, 1996,7(10):1683~1691.
42 Eason R P, Dick A J. A parallelized multi-degrees-of-freedom cell mapping method.NonlinearDynamics, 2014,77(3):467~479.
43 Belardinelli P, Lenci S. An efficient parallel implementation of cell mapping methods for MDOF systems.NonlinearDynamics, 2016,86(4):2279~2290.
44 Xiong F R, Qin Z C, Ding Q, et al. Parallel cell mapping method for global analysis of high-dimensional nonlinear dynamical systems.ASMEJournalofAppliedMechanics, 2015,82(11):111001.
45 Xiong F R, Schütze O, Ding Q, Sun J Q. Finding zeros of nonlinear functions using the hybrid parallel cell mapping method.CommunicationsinNonlinearScienceandNumericalSimulation, 2016,34:23~37.
46 岳晓乐. 一类高效胞映射方法及其在动力系统中的应用研究[博士学位论文]. 西安:西北工业大学, 2012 (Yue X L. The research on a high efficient cell mapping method and its application in dynamical systems[PhD Thesis]. Xi′an, Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2012 (in Chinese))
47 Li Z, Jiang J, Hong L. Noise-induced transition in a piecewise smooth system by generalized cell mapping method with evolving probabilistic vector.NonlinearDynamics, 2017:88(2):1473~1485
48 Hsu C S. Cell-to-cell mapping: A method of global analysis for nonlinear systems. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1987
49 Sun J Q, Albert C J L, et al. Global analysis of nonlinear dynamics. Springer Science & Business Media, 2012
50 徐伟,孙春艳,孙建桥,贺群. 胞映射方法的研究和进展. 力学进展, 2013,43(1):91~100 (Xu W, Sun C Y, Sun J Q, He Q. Development and study on cell mapping methods.AdvancesinMechanics, 2013,43(1):91~100(in Chinese))
51 孙建桥,熊夫睿.非线性动力学系统全局分析之外的胞映射方法新发展. 力学进展, 2016,47:201705 (Sun J Q, Xiong F. Cell mapping methods-beyond global analysis of nonlinear dynamic systems.AdvancesinMechanics, 2016,47:201705 (in Chinese))
52 Yu J S, Cai G Q, Lin Y K. A new path integration procedure based on Gauss-Legendre scheme.InternationalJournalofNon-LinearMechanics, 1997,32(4):759~768
53 Stroud A H. Numerical Quadrature and Solution of Ordinary Differential Equations. New York: Springer, 1974
54 Cao Q J, Wiercigroch M, Pavlovskaia E E, Grebogi C, Thompson J M T. Archetypal oscillator for smooth and discontinuous dynamics.PhysicalReviewE, 2006,74(4):046218
55 Cao Q J, Wiercigroch M, Pavlovskaia E E, Grebogi C, Thompson JMT. The limit case response of the archetypal oscillator for smooth and discontinuous dynamics.InternationalJournalofNon-LinearMechanics, 2008,43(6):462~473
56 Meroz Y, Sokolov I M, Klafter J. Distribution of first-passage times to specific targets on compactly explored fractal structures.PhysicalReviewE, 2011,83(2):020104
57 Hwang S, Lee D S, Kahng B. First passage time for random walks in heterogeneous networks.PhysicalReviewLetters, 2012,109(8):088701
58 Jin YF, Xu W. Mean first-passage time of a bistable kinetic model driven by two different kinds of coloured noises.Chaos,Solitons&Fractals, 2005,23(1):275~280
59 Han Q, Xu W, Yue X L, Zhang Y. First-passage time statistics in a bistable system subject to Poisson white noise by the generalized cell mapping method.CommunicationsinNonlinearScienceandNumericalSimulation, 2015,23(1-3):220~228
60 Bobrovsky B Z, Schuss Z. A singular perturbation method for the computation of the mean first passage time in a nonlinear filter.SIAMJournalonAppliedMathematics, 1982,42(1):174~187.
61 Luchinsky D G, Maier R S, Mannella R, McClintock P V E, Stein D L. Observation of saddle-point avoidance in noise-induced escape.PhysicalReviewLetters, 1999,82(9):1806.
62 Maier R S, Stein D L. Effect of focusing and caustics on exit phenomena in systems lacking detailed balance.PhysicalReviewLetters, 1993,71(12):1783
63 Khovanov I A, Polovinkin A V, Luchinsky D G, McClintock P V E. Noise-induced escape in an excitable system.PhysicalReviewE, 2013,87(3):032116
64 Bobrovsky B Z, Zeitouni O. Some results on the problem of exit from a domain.StochasticProcessesandtheirApplications, 1992,41(2):241~256.
65 Han Q., Xu W, Yue X L. Exit location distribution in the stochastic exit problem by the generalized cell mapping method.Chaos,Solitons&Fractals, 2016,87:302~306
66 Spivak A, Schuss Z. Analytical and numerical study of kramers′ exit problem I.AppliedMathematicsE-Notes, 2002,2:132~140
67 Spivak A, Schuss Z. Analytical and numerical study of kramers′ exit problem II.AppliedMathematicsE-Notes, 2003,3:147~155
68 Dimentberg M F, Gaidai O, Naess A. Random vibrations with strongly inelastic impacts: response PDF by the path integration method.InternationalJournalofNon-LinearMechanics, 2009,44(7):791~796.
69 Li C, Xu W, Yue X. Stochastic response of a vibro-impact system by path integration based on generalized cell mapping method.InternationalJournalofBifurcationandChaos, 2014,24(10):1450129.
70 李爽,贺群, 非光滑动力系统的迭代图胞映射法. 力学学报, 2011,43(3):579~585 (Li S, He Q. The iterative digraph cell mapping method of non-smooth dynamical systems.ChineseJournalofTheoreticalandAppliedMechanics, 2011,43(3):579~585 (in Chinese))
71 Gan C B, Lei H. Stochastic dynamical analysis of a kind of vibro-impact system under multiple harmonic and random excitations.JournalofSoundandVibration, 2011,330(10):2174~2184
72 Wang L, Yue X L, Sun C Y, Xu W. The effect of the random parameter on the basins and attractors of the elastic impact system.NonlinearDynamics, 2013,71(3):597~602
73 Feng J.Analysis of chaotic saddles in a nonlinear vibro-impact system.CommunicationsinNonlinearScienceandNumericalSimulation, 2017,48:39~50
*The project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(11472212, 11672230).
† Corresponding author E-mail:weixu@nwpu.edu.cn
17 March 2017,revised 18 April 2017.
CELL MAPPING METHOD AND ITS APPLICATIONS IN NONLINEAR STOCHASTIC DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS*
Xu Wei1†Yue Xiaole1Han Qun1,2
(1.DepartmentofAppliedMathematics,NorthwesternPolytechnicalUniversity,Xi′an710072,China) (2.CollegeofScience,HuazhongAgriculturalUniversity,Wuhan430070,China)
This paper introduces the development of several cell mapping methods closely associated with nonlinear stochastic dynamical systems, including generalized cell mapping method with digraph, cell mapping method based on short-time Gaussian approximation, parallel cell mapping method etc. The applications of cell mapping method in stochastic dynamical systems are also shown, focusing on stochastic response、bifurcation、exit and vibro-impact system. Finally, some challenges and possible future researches about cell mapping method are presented.
cell mapping method, parallel algorithm, exit, short-time Gaussian approximation
*国家自然科学基金资助项目(11472212, 11672230)
10.6052/1672-6553-2017-023
2017-03-17收到第1稿,2017-4-18收到修改稿.
† 通讯作者 E-mail:weixu@nwpu.edu.cn

