大型喷杆及其摆式悬架减振系统动力学特性分析与试验
崔龙飞,薛新宇,丁素明,乔白羽,乐飞翔
大型喷杆及其摆式悬架减振系统动力学特性分析与试验
崔龙飞1,2,薛新宇1※,丁素明1,乔白羽1,乐飞翔1
(1. 农业部南京农业机械化研究所,南京 210014; 2. 江苏大学农业工程研究院,镇江 212013)
针对摆式悬架减振系统对喷杆动力学行为影响机理的复杂性,利用第二类拉格朗日方法建立了描述喷杆-悬架系统倾斜运动、垂向运动的数学模型。在MATLAB/Simulink中进行了瞬态响应分析、频率响应分析,研究了动力参数对其特性的影响。在此基础上,以某大型喷杆及其摆式减振悬架为试验对象,通过六自由度运动模拟平台输出翻滚和垂向运动激励,采用超声波距离传感器、LVDT位移传感器等进行数据采样分析,测得喷杆瞬态动力学响应及频率响应特性,并与模型预测进行对比,验证了数学模型的准确性。最后通过扫频振动试验确定了系统的频率响应峰值及对应频率,着重分析了阻尼、刚度系数对喷杆振动特性的影响规律:在一定范围内增加阻尼可以减弱系统振荡,增加刚度有利于提高悬架响应速度。研究为大型喷杆悬架参数优化配置提供理论依据与试验方法,有利于中国大型喷杆(大于12 m)动力学特性试验方法、检测标准的完善。
机械化;模型;试验;喷杆喷雾机;喷杆运动;摆式悬架;动力学特性
0 引 言
喷杆式喷雾机作为大田植保的主要机具之一,由于田间不平地面的激励导致喷杆的倾斜、振荡等不规律运动(undesired motion),极大的影响喷雾分布形态,降低农药化肥的作用效果[1-4]。在喷杆与车体之间增设悬架系统是提高喷杆稳定性与防治效果的重要途径[4-8]。摆式悬架在12~28 m进口喷杆喷雾机上使用较多,利用阻尼弹簧摆的原理,使喷杆能够随着机身的低频摆动而摆动,以适应长波段的地形起伏,隔离由于短波段地表不平度造成的高频振动,使喷杆保持相对稳定。
喷杆悬架系统动力学特性方面的研究,英国农业工程研究院、鲁汶大学农业工程与经济系等开展较早,Nation等[9]对多种喷雾机田间作业时的动力学特性分别进行了测试,研究了喷杆末梢垂直、水平方向振动,认为喷杆悬架设计时应重点考虑衰减来自喷雾机的翻滚运动。Frost等[10]对双连杆悬架系统的动力学特性进行了数学建模和试验验证。Anthonis等[11-13]针对John Deere 39 m喷杆喷雾机进行研究,用数学模型描述喷杆的滚转动力学行为,对悬架上弹簧缓冲器的安装位置提出了优化方案,并通过田间试验验证优化方案的可行性。Kennes等[14-16]通过喷雾机整机有限元分析的方法,对不同悬架结构下喷杆的动力学响应特性进行了对比。Ooms等[17-20]提出了基于多传感器信息融合的喷杆运动特性测量方法。张际先[21-22]对“Patriot”喷雾机的双连杆悬架性能和优化曾进行过初步探索;Sun等[23-24]建立了宽幅4弹簧阻尼器型悬架-喷杆系统模型,研究了不同(脉冲、阶跃、正弦)激励下喷杆的动力学特性,发现车体翻滚运动对喷杆的影响远大于平移运动的影响;邱白晶等[25-27]研究了当路面激励相继作用于喷雾机前、后轮时的喷杆运动响应的提取方法,并用于喷杆运动响应特性分析。
目前摆式悬架动力参数的对喷杆动力学行为影响的研究较少,本文针对摆式悬架减振系统的翻滚运动、垂向运动分别进行建模仿真,并借助Stewart六自由度运动模拟平台进行样机动力学特性测试,研究悬架阻尼系数、弹簧刚度等动力参数对喷杆瞬态响应特性、振动传递特性的影响规律,为大型喷杆悬架参数配置提供参考。
1 摆式减振悬架结构与工作原理
1.1 基本结构
喷杆与机体之间安装悬架的主要目的:一方面可以减小喷杆与机架间的机械应力;另一方面可以衰减喷雾机机体的晃动干扰,提供一个可以均匀喷雾的平台。
弹簧摆式悬架结构如图1所示,支架1用来承担喷杆系统的重力及惯性负载,钟摆机构通过吊环与支架在点铰接,摆式悬架机构由摆杆2、中心架3、托架4、垂向减振器5、侧倾减振器6、喷杆7等组成。设点为整个喷杆(左喷杆、中心架、右喷杆)的质心,中心架3可以沿摆杆滑动,托架与摆杆固连。2个弹簧减振器一端与托架固连,另一端支撑中心架。中心架连接左右喷杆,由于导向机构的约束,喷杆在竖直平面的运动主要表现为绕转轴的转动、沿着钟摆长度方向的平动,2种运动相互耦合。
1.支架 2.单摆机构 3.浮动架 4.托架 5.垂向减振器 6.侧倾减振器 7.喷杆
1.Bracket 2.Pendulum mechanism 3.Floating frame 4.Carrier fame 5.Vertical vibration damper 6. Roll vibration damper 7. Spray boom
注:表示喷杆质心位置,表示单摆机构的转动中心。
Note:is centroid position of spray boom;is rotation center of pendulum mechanism.
图1 喷杆及悬架装置
Fig.1 Spray boom and suspension device
1.2 工作原理
弹簧摆式减振悬架利用单摆原理,喷杆运动过程中质心常处于过点竖直线的左边或者右边,设摆杆与竖直线的夹角为,喷杆及中心架总质量为,喷杆质心由于受到重力和弹簧提供的回复力在平衡位置往复摆动,可调式液压减振器安装于机架与钟摆之间,喷杆的动能经阻尼器、摩擦等消耗,喷杆最终回到平衡位置。在垂直摆杆方向则使用2个大螺旋弹簧及阻尼器直接衰减来自地面的起伏运动。
2 悬架动力学模型
2.1 模型描述
如图2所示悬架系统原理图。喷杆12通过滑动副与摆杆连接,喷杆质心可以沿滑动,喷杆12与摆杆上的点通过弹簧和阻尼器连接,摆杆与在点铰接。图中3表示倾斜的地面,车体的侧倾运动简化为绕的摆动,多数喷雾机使用拖拉机作为运载车辆,研究喷杆滚转运动暂不考虑轮胎的刚度、阻尼的影响。喷杆与摆式悬架减振系统即简化为三自由度刚性杆-弹簧摆模型,3个自由度分别指连杆绕点的转动、连杆绕点的转动和喷杆(沿方向)的平动,三者之间相互耦合。
1.喷杆 2.弹簧摆悬架 3.地面 4.轮胎和机架
1.Spray room 2.Spring pendulum suspension 3.Ground 4.Tire and frame of vehicle
注:为地面坡度,rad;为喷杆与水平面的夹角,rad;为摆杆与机架的夹角,rad;1为喷杆旋转刚度系数,m·N·rad-1;2为垂向弹簧的刚度系数,N·m-1;1为喷杆旋转阻尼系数,m·s N·rad-1;2垂向滑动阻尼器的阻尼系数,N·s·m-1。
Note:is inclination angle of ground to horizontal, rad;isinclination angle of spray boom to horizontal, rad;is included angle between pendulum link () and link (), rad;1is rotational stiffness coefficient of spray boom, m·N·rad-1;2is stiffness coefficient of vertical spring, N·m-1;1 isrotational damping coefficient of spray boom, m·s N·rad-1;2 isdamping coefficient of vertical damper, N·s·m-1.
图2 喷杆喷雾机及其摆式悬架减振系统
Fig1 Boom sprayer and pendulum suspension damping system
2.2 动力学方程与频响函数
喷杆与摆杆的端点通过减振弹簧、阻尼器连接,摆杆可绕机架上点转动,与机架之间装有旋转阻尼缓冲器。设地面坡度,不考虑轮胎变形,则车体与重力方向的夹角大小也为,喷杆与水平面的夹角,摆杆相对机架的夹角为。以点为重力势能零点。喷杆的运动用拉格朗日方程描述
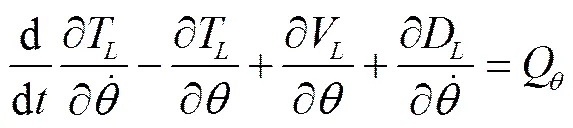
式中T为总动能,N·m;V为系统的势能,N·m;D为瑞利耗散能,N·m·rad/s。
喷杆悬架原理图2中喷杆的质心在到转轴点的距离为,机架上距离地面瞬时摆动中心的距离为,以为坐标原点,设喷杆重心的纵坐标=cos-cos(+),重心的横坐标=-sin+sin(+)。
系统的势能V
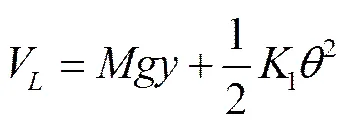
式中为喷杆的质量,kg;为重力加速度,m/s2。
系统的总动能T
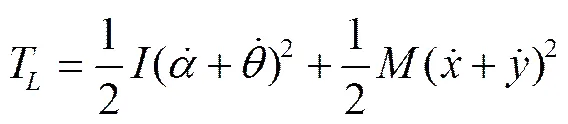
式中为绕质心的转动惯量,kg·m2。
设转轴处的摩擦力矩为1(N·m),系统瑞利耗散函数D
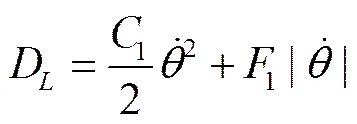
对于被动悬架系统,无外界动力源,所以广义力=0。将式(2)-(4)代入式(1),即可得到系统的动力学方程组,由于田间作业时地面坡度、喷杆水平倾角都非常小,假设sin(+)≈+,cos(+)≈1,忽略二阶小量,将动力学方程组化简
(5)
通过以上方程(5)描述喷杆在车体扰动输入下的动力学行为,悬架各关节运动副润滑良好的情况下,≈0。
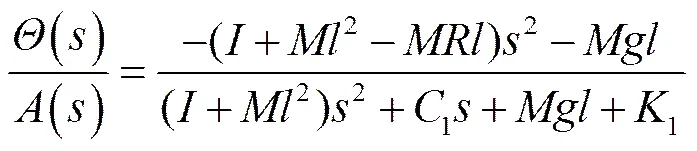
式中为拉普拉斯算子,表示复数频率;同理可得喷杆水平倾角与地面坡度角的传递函数
(7)
被动悬架系统属于二阶系统,系统的特征方程
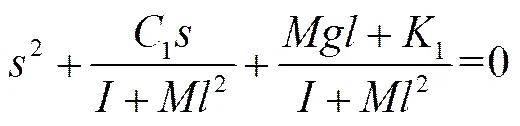
系统的悬架翻滚运动阻尼比1为
(9)
系统固有频率ω
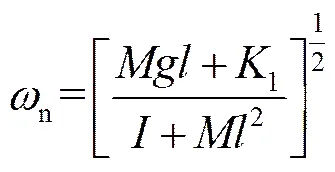
系统的有阻尼频率为ω
(11)
令=,为虚数,为频率,rad/s;代入传递函数(7)中,系统频率响应函数表达式

(13)
在运载车辆属性却确定的情况下,喷杆的翻滚运动(roll movement)特性主要由等效回转半径l、喷杆旋转阻尼系数1、喷杆旋转刚度系数1、摆长和决定。
在研究竖直激励作用下喷杆振动情况时,喷杆悬架系统可简化为质量-弹簧-阻尼系统,该二阶系统动力学方程为
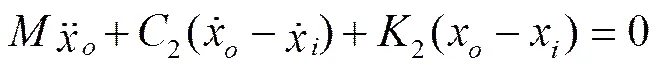
对方程(14)两端进行拉氏变换,可得系统传递函数
(15)
由式(15)可以推导出垂向振动幅频特性函数,也即位移传递函数
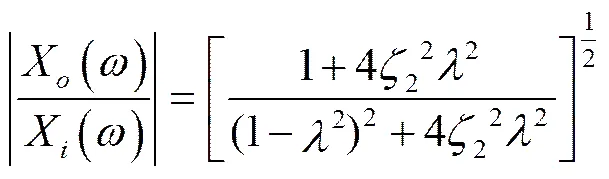
通过传递函数对输入激励进行运算就可以得出系统的响应,在MATLAB/Simulink环境中对悬架数学模型进行瞬态响应分析、频率响应分析,对喷杆悬架系统动力学参数如喷杆旋转阻尼系数1、垂向滑动阻尼器的阻尼系数2、喷杆旋转刚度系数1垂向弹簧刚度系数2进行研究,并进行台架试验验证,以期达到提升悬架减振效果及喷杆的稳定性的目的。
3 悬架关键参数测定
试验时设计分体式液压阻尼器(阻尼调节采用插装式电磁节流阀)抑制喷杆横滚运动,且节流阀开度可调,在叠加套管内置复位弹簧。通过机电伺服万能试验机测得试阻尼器的拉(压)力F(N)及对应的伸(缩)速度v(m/s),通过对试验数据拟合如图3a所示,线性拟合方程F11 389.7v,决定系数2=0.921,即得缓冲器伸缩阻尼系数11 389.7 N·s/m,根据单摆机构几何关系折算出喷杆旋转阻尼系数1为25 758 N·m·s/rad;同理测得垂向滑动阻尼器的阻尼系数2为5.11 N·s/m。
弹簧刚度系数也使用万能试验机测试,匀速压缩弹簧,测得力与变形关系曲线如图3b所示,图中斜线的斜率即刚度系数阻尼器内置弹簧刚度系数26 320 N/m,根据几何关系折算出喷杆旋转刚度系数1为51 521 N·m/rad;同理测得垂向弹簧刚度系数2为13 350 N/m。
喷杆整体质量通过行吊上的电子磅测得,为922.6 kg。利用SolidWorks三维模型测得喷杆绕质心惯量2为3.27×104kg·m2。悬架主要参数测试、换算之后如表1所示。

表1 悬架参数
4 动力学仿真与台架试验
悬架的动力学特性通常从时域和频域2个方面分别采用瞬态响应法和频率响应法来分析,在时域内研究悬架响应特性时,采用阶跃输入研究悬架的时域瞬态响应,表征参数为峰值时间、超调量等[28-30];采用正弦激励信号研究传感器的频域动力学特性时,常用幅频特性(位移传递率)来描述悬架动力学特性。本文通过模型仿真和试验相结合的方法分析悬架的瞬态响应特性和频率响应特性,通过阻尼系数、弹簧刚度等参数对动力学特性的影响规律,指导悬架参数合理配置。
4.1 试验装置与数据采集
Stewart六自由度运动平台即由动平台、铰支座、驱动腿和固定平台组成6UPU并联机构,如图4a所示。动平台和固定平台通过虎克铰与驱动腿相连,通过控制驱动腿的长度即可改变动平台的位置和姿态,伺服电机进行驱动,具有刚度大、体积小、运动精度高、动力性能好等优点[31-32]。在控制台输入动平台的运动指令,接着运动控制计算机进行位姿反解,得到各驱动支路的驱动信号,控制各个电动缸运动,进而带动上平台和喷杆运动,伺服电机的运动信息通过旋转编码器和脉冲计数器反馈至主控计算机,计算机将脉冲数据转换为电动丝杠位移量,形成位置闭环控制。
六自由度平台主要参数:转动幅值10°平动幅值0.4 m,频率范围0.01~35 Hz,静载荷2 t,可以进行正弦扫频振动、激励谱(路面谱、海浪谱等)复现。试验对象为图4a中的28 m桁架式喷杆及其摆式悬架,悬架机构如图2原理图所示,带有两对弹簧、阻尼的摆式悬架,摆杆长度1.1 m,喷杆两侧喷臂由两段组成:内臂质量248.6 kg,长度6.3 m;外臂质量125.7 kg,长度6.83 m,内、外喷臂通过液压缸进行折叠/展开。通过安装夹具将悬架支座固定于Stewart六自由度运动模拟平台上,以动平台的运动模拟喷雾机车体的扰动激励,动平台运动姿态(平动、转动)实时反馈给工控机,图4b为喷杆动力学模拟分析软件。
如图5所示喷杆的倾角(绕X轴)通过2个高精度超声波传感器(Banner,U-GAGE U45Q)测算,响应时间可调节范围为40~1 280 ms,最高响应频率为25 Hz,满足悬架动力学测试频响要求。喷杆的相对摆杆PQ滑动位移使用顶杆式线位移传感器(linear variable differential transformer,LVDT)位移传感器测得,分体式阻尼器(bosch rexroth)的动行程使用分体式LVDT位移传感器(soway,SDVG20-250)测得,使用东华测试的DH5902无线动力学采集系统进行数据采集。
4.2 瞬态响应仿真与验证
ANTHONIS等采用提拉法对喷杆缆绳悬架进行瞬态响应试验,并以此验证悬架数学模型准确性[12]。喷杆摆振提拉法试验具体方法:在喷杆展开状态下,利用行车提拉喷杆一侧,将喷杆倾斜至5.7°,自由释放喷杆,同时使用超声波高度传感器,记录喷杆两端测点高度变化,计算得到喷杆侧倾角随时间衰减历程,瞬态响应的峰值时间为2.25 s,超调量为2.24°,到达3.36 s时刻喷杆倾角衰减到初始值的10%以内。在Matlab中采用四五阶龙格—库卡塔算法求解二阶微分方程5,得到仿真曲线与曲线如图6a虚线所示,二者变化趋势一致,均方根误差为0.072,可知描述喷杆翻滚运动的数学模型精度较高,可以用于系统动力学特性的分析。
在Matlab环境中,改变悬架旋转阻尼系数进行3组仿真分析,喷杆倾角变化如图6b,可以看出阻尼系数对动力学响应的峰值影响比较大,增大阻尼,系统振荡性能减弱,即最大超调量和振荡次数都减小。但阻尼系数过大,悬架峰值时间增加,响应速度变慢。改变悬架旋转刚度系数进行3组数值分析,喷杆倾角变化如图6c,可知弹簧刚度对响应峰值影响相对较小,刚度系数越大,悬架的瞬态响应峰值越大,峰值时间越小,系统的响应越快。
喷杆垂向振动提拉法试验具体方法:通过门式行车提拉喷杆中心位置,将喷杆整体提升0.1 m,自由释放喷杆,使用超声波高度传感器,记录喷杆垂向高度变化历程如图7a所示,峰值时间0.69 s,超调量为0.018 m,2.2 s之后喷杆回到平衡位置。在Matlab中求解微分方程14,得到仿真曲线与试验曲线如图7a虚线所示,仿真曲线与试验曲线的均方根误差为0.046,可知描述喷杆垂向运动的数学模型精度较高,可以用于系统垂向动力学特性的分析。由图7b和7c可知阻尼系数和刚度系数对垂直方向瞬态动力学特性影响规律与翻滚方向一致。
4.3 翻滚运动频响特性分析
喷杆翻滚运动的频响特性试验:使Stewart动平台绕轴按指定频率输出正弦往复摆动,多次试验发现激励频率大于2 Hz后喷杆运动幅值非常小,随着频率增大,测得的喷杆倾角与动平台倾角的幅值比迅速衰减一个稳定值,同时,从式(13)和(16)所述的频响函数也可以看出,该摆式悬架属二阶系统,对输入激励起到二阶低通滤波的作用,随着频率增大,幅值比存在极限值。因此,试验过程中缩小了测试频率范围,在包含共振区的低频段0.01~2.4 Hz取18个频率点,依次进行试验,记录喷杆达到稳态后的倾角幅值,计算出每个试验频率对应的幅值比(喷杆倾角幅值与动平台倾角幅值之比),绘制角位移频响曲线如图8a所示,采用对数坐标系,试验曲线与数学模型仿真进行比对,两者的变化趋势一致,试验值与预测值的均方根误差为0.146。当激励频率小于0.07 Hz时,测得侧倾角的幅值比接近水平且保持在0.87左右,说明喷杆能够随机架的低频摆动而摆动,适应长波段的地形变化。当激励频率为0.22 Hz时,幅值比最大为1.74,可知当频率大于0.3 Hz时,进入隔振区,振动幅值比小于1,并逐渐减小,频率为1.2 Hz(截止频率)时,幅值比衰减到极小值0.135 6,悬架的截止频率越低,从机身传递到喷杆的高频振动越少。
从图8b不同阻尼系数悬架幅频曲线可以看出:峰值频率与阻尼无关,幅频曲线的峰值受阻尼变化影响较大,阻尼愈小峰值处的幅值比越大,悬架将来自车体的振动进行了放大。从图8c不同弹簧刚度系数下幅频曲线可以看出:弹簧刚度对幅值比峰值影响相对较小,刚度系数越大,悬架的幅频特性峰值越大,同时固有频率增大,系统响应的快速性越好。
通过调节阻尼器上节流阀的开度,调节螺钉从最外侧依次旋入2圈,阻尼由小增大,幅频特性曲线如图9所示,阻尼小对应节流阀完全打开;阻尼中对应阻尼调节螺钉旋入2圈,阻尼大对应阻尼调节螺钉旋入4圈,调节螺钉旋入6圈阻时尼器锁死;幅频特性受系统阻尼系数影响下的变化规律与图8b模型预测一致。
4.4 垂向振动频响特性分析
喷杆垂向振动频响特性试验:利用六自由度平台模拟作业时喷雾机上下起伏运动,使动平台沿轴输出正弦往复运动,频率在0.01~18 Hz范围内取18个频率点,依次进行试验,将位移传感器测得的喷杆相对位移与动平台位移叠加,即喷杆绝对位移。记录喷杆运动达到稳态后的幅值,计算出每个试验频率对应的幅值比(喷杆运动幅值与动平台运动幅值之比),绘制幅频曲线如图10a中所示,在Matlab中建立公式(14)~(16)所述数学模型,分析垂向频响特性,模型预测值与试验值的均方根误差为0.203。当激励频率为0.59 Hz时,幅值比最大为1.50。当激励在0.1至1.04 Hz之间为悬架系统的共振区,位移传递率大于1;当激励频率大于1.05 Hz时为隔振区,随之频率增加传递率减小。从图10b和10c可以看出阻尼系数和刚度系数对垂直方向瞬态动力学行为影响规律与喷杆翻滚运动幅频特性一致。
5 结 论
1)对大型喷杆摆式减振悬架的基本结构和减振原理进行了分析,建立了描述喷杆-悬架系统翻滚运动、垂向运动的数学模型,并在MATLAB环境中进行了瞬态响应分析、频率响应分析。
2)以某大型喷杆-摆式悬架为试验对象,通过六自由度运动模拟平台分别产生垂向、翻滚运动激励,采用超声波距离传感器、LVDT位移传感器等进行数据分析,测得喷杆瞬态动力学响应及频率响应特性,验证了数学模型的精度,其中翻滚运动频响特性模型预测值与试验值均方根误差为0.146,垂向频响特性均方根误差为0.203。
3)通过振动频响试验确定了被测摆式悬架减振系统的频率响应峰值及共振频率,研究表明摆式悬架可以有效隔离源于地表不平度造成的高频振动;阻尼系数愈小频响特性特性曲线峰值越大;刚度系数越大悬架的频响特性曲线峰值越大。
[1] 贾卫东,张磊江,燕明德,等. 喷杆喷雾机研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 中国农机化学报,2013,34(4):19-22. Jia Weidong, Zhang Leijiang, Yan Mingde, et al. Current situation and development trend of boom sprayer[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2013, 34(4): 19-22.
(in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] Langenakens J J, Clijmans L, Ramon H, et al. The effects of vertical sprayer boom movements on the uniformity of spray distribution[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 1999, 74(3): 281-291.
[3] Lardoux Y, Sinfort C, Enfält P, et al. Test method for boom suspension influence on spray distribution, part I. experimental study of pesticide application under a moving boom[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2007, 96(1): 29-39.
[4] Lardoux Y, Sinfort C, Enfält P, et al. Test method for boom suspension influence on spray distribution, part II: validation and use of a spray distribution model[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2007, 96(2): 161-168.
[5] Tahmasebi M, Rahman R A, Mailah M, et al. Active force control applied to spray boom structure[J]. Applied Mechanics & Materials, 2013, 315: 616-620.
[6] Tahmasebi M, Rahman R A, Mailah M, et al. Roll movement control of a spray boom structure using active force control with artificial neural network strategy[J]. Journal of Low Frequency Noise Vibration & Active Control, 2013, 32(32): 189-202.
[7] Georgiou G, Verros G, Natsiavas S. Multi-objective optimization of quarter-car models with a passive or semi-active suspension system[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2007, 45(1): 77-92.
[8] Sun W, Gao H, Kaynak O. Finite frequency, control for vehicle active suspension systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2011, 19(2): 416-422.
[9] Nation H J. The design and performance of a gimbal-type mounting for sprayer booms 1: Optimization model and validation[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 1987, 36(4): 247-260.
[10] Frost A R, O’Sullivan J A. Verification of a mathematical model for a passive spray boom suspension[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 1986, 34(3): 245-255.
[11] Anthonis J, Kennes P, Ramon H. Design and evaluation of a low-power mobile shaker for vibration tests on heavy wheeled vehicles[J]. Journal of Terra Mechanics, 2000, 37(4): 191-205.
[12] Anthonis J, Audenaert J, Ramon H. Design optimization for the vertical suspension of a crop sprayer boom[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2005, 90(2): 153-160.
[13] Anthonis J, Ramon H. Design of an active suspension to suppress the horizontal vibrations of a spray boom[J]. Journal of Sound & Vibration, 2003, 266(3): 573-583.
[14] Kennes P, Ramon H, Baerdemaeker J D. Modelling the effect of passive vertical suspensions on the dynamic behaviour of sprayer booms[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 1999, 72(3): 217-229.
[15] Deprez, K, Anthonis, J, & Ramon, H. System for vertical boom corrections on hilly fields. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2003, 266: 613-624.
[16] Deprez K, Anthonis J, Ramon H, et al. Development of a slow active suspension for stabilizing the roll of spray booms-part 1: Hybrid modelling[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2002, 81(2): 185-191.
[17] Ooms D, Ruter R, Lebeau F, et al. Impact of the horizontal movements of a sprayer boom on the longitudinal spray distribution in field conditions. Crop Protection, 2003, 22(6): 813-820.
[18] Ooms D, Lebeau F, Ruter R, et al. Measurements of the horizontal sprayer boom movements by sensor data fusion[J]. Computers & Electronics in Agriculture, 2002, 33(2): 139-162.
[19] Wilkerson J B, Womac A R, Hart W E, et al. Sprayer boom instrumentation for field use[J]. Transactions of the American Society of Agricultural Engineers, 2004, 47(3): 659-666.
[20] Garciaramos F J, Vidal M, Boné A, et al. Methodology for the regulation of boom sprayers operating in circular trajectories[J]. Sensors, 2011, 11(4): 4295-4311.
[21] 张际先. 喷雾机悬架的优化设计[J]. 农业机械学报,1995,26(1):50-55. Zhang Jixian. Optimal design of boom sprayer suspensions[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 1995, 26(1): 50-55. (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] 张际先. 喷雾机喷臂悬架性能的动态分析[J]. 农业机械学报,1996,27(增刊1):138-142. Zhang Jixian. Dynamic analysis of the suspension performance of sprayer boom[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 1996, 27(Supp.1): 134-138.
[23] Sun J, Miao Y. Modeling and simulation of the agricultural sprayer boom leveling system[C]// International Conference on Measuring Technology & Mechatronics Automation. IEEE, 2011: 613-618.
[24] 吴吉麟,苗玉彬. 不同激励源下宽幅喷雾机喷杆的动态特性分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(4):39-44. Wu Jilin, Miao Yubin. Dynamic characteristic analysis of boom for wide sprayer with different exciting sources[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(4): 39-44. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 邱白晶,杨宁,徐溪超,等. 喷雾机前后轮相继激励下喷杆理想运动响应提取[J]. 农业机械学报,2012,43(2):55-60. Qiu Baijing, Yang Ning, Xu Xichao, et al. Ideal spray boom response extraction with front and rear tires excited by step track[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2012, 43(2): 55-60. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 何耀杰,邱白晶,杨亚飞,等. 基于有限元模型的喷雾机喷杆弹性变形分析与控制[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(6):28-36. He Yaojie, Qiu Baijing, Yang Yafei, et al. Deformation analysis and control of elastic deformation for spray boom based on finite element model[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(6): 28-36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 陈树人,韩红阳,陈刚,等. 喷杆喷雾机机架动态特性分析与减振设计[J]. 农业机械学报,2013,44(4):50-53,20. Chen Shuren, Han Hongyang, Chen Gang, et al. Dynamic characteristic analysis and vibration reduction design for sprayer frame[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2013, 44(4): 50-53, 20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] Zhang J X, Li H. Optimization design on dynamic characteristics and fatigue life of automotive suspension system[J]. Journal of Vibroengineering, 2015, 17(5): 25-47.
[29] Ma Z Y, Song Z Q. Nonlinear Dynamic characteristic analysis of the shaft system in water turbine generator set[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2009, 22(1): 124-131.
[30] Shen P H, Lin S W. Mathematic modeling and characteristic analysis for dynamic system with asymmetrical hysteresis in vibratory compaction[J]. Meccanica, 2008, 43(5): 505-515.
[31] 王军,杨勇,罗诗风,等. 基于PMAC运动控制卡的六自由度运动平台控制系统开发[J]. 机床与液压,2012,40(9):77-80.
Wang Jun, Yang Yong, Luo Shifeng, et al. Development of the stewart platform motion control system based on PMAC controller[J]. Machine Tool & Hydraulics, 2012, 40(9): 77-80. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 王山山,杨振宇. 重力坝动力特性测试方法模型试验研究[J]. 振动与冲击,2012,31(10):1-3.
Wang Shanshan, Yang Zhenyu. Model testing method for dynamic properties of gravity dam[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2012, 31(10): 1-3. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Analysis and test of dynamic characteristics of large spraying boom and pendulum suspension damping system
Cui Longfei1,2, Xue Xinyu1※, Ding Suming1, Qiao Baiyu1, Le Feixiang1
(1.210014,;2.212013,)
To increase the yield in agriculture, plants must be protected against diseases and need to be provided with fertilizers. One of the most important methods to spread agro-chemicals is by using spray booms. The efficiency of the chemicals is highly correlated with the uniformity of the spray distribution pattern, and as spray boom motions play a dominant role on the spray distribution pattern, spray boom stability is important. Moreover, with the stable boom, the distance between the nozzles and the target can be reduced, and then the drift losses are less important. Boom movements are due to ground irregularities that are transformed and more or less amplified depending on the mechanics features of the boom suspension. In order to reduce the unevenness in spray deposit, the majority of current agricultural sprayers are equipped with a suspension system to attenuate the roll of the boom. The suspension tries to keep the boom at right angles by isolating the boom from vibrations of the tractor or trailer which are induced by unevenness of the ground. Therefore, the suspension system should act as a system that attenuates undesired machine movement. The most important vibration, affecting the spray distribution pattern, is rolling (rotational motion around an axis along the driving direction) that causes spray boom motions in the vertical plane. However, the correlation between the dynamic behavior of the spray boom and suspension parameters are still unclear and the design principles and methods of the pendulum boom suspension are also missing or imperfect, which restrict the improvement of spray quality and operation efficiency. In order to understand the effect of the dynamic parameters of pendulum suspension system on the dynamic behavior of the spray boom, an analytical mathematical model of this pendulum suspension is established by using the second kind of Lagrange equations and the necessary transfer function. The dynamic characteristics of the pendulum suspension are derived, and the behavior such as the rolling movement and vertical movement of the passive suspension can be most conveniently described by its complex frequency response function. Transient response analysis and frequency response analysis are carried out in MATLAB/Simulink, and the effects of dynamic parameters on the characteristics of the suspension are studied. On the basis of this, taking a large spray boom and its pendulum suspension as the test object, the boom rolling movement and vertical movement excitations were outputted by using the six degrees of freedom motion simulation platform, and the boom suspension was instrumented with ultrasonic distance sensor, LVDT (linear variable differential transformer) displacement sensor, and so on. The transient dynamic response and frequency response characteristics of spray boom were measured, and then the accuracy of the mathematical model was verified. The root mean square error between the mathematical model predictive value and test value was 0.146 for rolling frequency response, and 0.203 for vertical oscillation frequency response. Peak value of the amplitude frequency curve and the corresponding frequency were determined by the sweep frequency vibration test, and the influence of damping and stiffness coefficients on the vibration characteristics of the boom was analyzed. In a certain range, increasing the damping could reduce the system oscillation and increase the stiffness, which was beneficial to increase the response speed and natural frequency of the suspension, but natural frequency could not be too high since beyond this frequency the suspension started to suppress the disturbances. Through research, we get to know that this kind of pendulum suspension with springs and dampers can enable the boom to follow low frequency ground undulations so remaining parallel to the ground beneath it, while providing isolation from the rapid motion of the spray vehicle as it travels over rough terrain. This study also provides a theoretical basis and test method for the parameters configuration of large boom, and it is beneficial to perfect the test method and test standard of the dynamic characteristics of large scale spraying boom (over 12 m) in China.
mechanization; models; experiments; boom sprayer; spray boom movement; pendulum suspension; dynamic characteristics
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.09.008
S49
A
1002-6819(2017)-09-0061-08
2016-10-14
2017-04-08
国家自然科学基金资助项目(51605236);国家重点研发计划:地面与航空高工效施药技术及智能化装备(2016YFD0200700);江苏省农业科技自主创新资金(CX(16)1043);
崔龙飞,男(汉族),河南巩义人,助理研究员,博士生,主要从事机械系统动力学研究。南京 农业部南京农业机械化研究所,210014。Email:cuilong.fei@163.com
薛新宇,女(汉族),江苏苏州人,研究员,博士,博士生导师,主要从事植保机械技术研究。南京 农业部南京农业机械化研究所,210014。Email:735178312@qq.com
崔龙飞,薛新宇,丁素明,乔白羽,乐飞翔. 大型喷杆及其摆式悬架减振系统动力学特性分析与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(9):61-68. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.09.008 http://www.tcsae.org
Cui Longfei, Xue Xinyu, Ding Suming, Qiao Baiyu, Le Feixiang. Analysis and test of dynamic characteristics of large spraying boom and pendulum suspension damping system[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(9): 61-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.09.008 http://www.tcsae.org

