晚期非小细胞肺癌患者化疗过程中体内血浆D-二聚体及纤维蛋白原水平临床分析
仲立新 孙红辉
晚期非小细胞肺癌患者化疗过程中体内血浆D-二聚体及纤维蛋白原水平临床分析
仲立新 孙红辉
目的 检测晚期非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)患者化疗前和化疗过程中体内血浆D-二聚体及纤维蛋白原(fibrinogen,FIB)水平,研究二者浓度变化与化疗效果和无进展生存期(progression-free survival,PFS)的关系。方法 选取晚期非小细胞肺癌患者120例,收集并记录患者第1、2、3次化疗前血浆D-二聚体及纤维蛋白原水平、肿瘤病理类型、分期及无进展期。同时收集60例健康人员的血浆D-二聚体及纤维蛋白原水平作对照。结果 血浆D-二聚体及纤维蛋白原水平的异常升高与晚期非小细胞肺癌患者的年龄、性别、肿瘤分期及病理类型均无相关性。对照组D-二聚体和FIB水平分别为0.47 mg/L和3.76 g/L,明显低于化疗前晚期NSCLC患者的(0.96 mg/L和4.32 g/L),差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。化疗两个周期后,有效(PR+SD)的晚期NSCLC患者D-二聚体和FIB水平分别为0.65 mg/L和2.74 g/L,无效患者分别为1.72 mg/L和4.65 g/L,对比差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。晚期NSCLC患者的PFS中位数为5.4个月,化疗前D-二聚体和FIB阴性的患者PFS明显长于阳性患者,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。将3次化疗前患者的D-二聚体和FIB水平进行对比,虽在不断降低,但差异无统计学意义(P均>0.05)。结论 晚期非小细胞肺癌患者化疗前D-二聚体和FIB水平异常升高,能够提示肺癌的诊断。治疗过程中要监测肿瘤进展情况,及时调整治疗方案,延长患者PFS。
晚期非小细胞肺癌;化疗;D-二聚体;纤维蛋白原;无进展生存期
(ThePracticalJournalofCancer,2017,32:382~385)
肺癌是最常见的肺原发性恶性肿瘤,大多数起源于支气管黏膜上皮,又称支气管肺癌。肺癌的发病率和死亡率占所有肿瘤之首,吸烟人数的增加以及工业的快速发展对城市造成的污染都是导致肺癌发病率不断升高的主要原因[1-3]。2015年调查数据显示,全球肺癌新增病人180万,仅我国就有接近60万的新发病例。预计到2025年,我国肺癌患者将突破100万,成为世界上肺癌患者最多的国家[4-5]。肺癌的生存率极低,有研究表明肺癌患者的5年生存率仅为16%。肺癌对人们的身体健康和生活质量都造成了严重的不良影响,因此对肺癌治疗方法的研究成为了医疗领域热门的课题[6-7]。目前在肺癌治疗领域我国已经取得了比较大的进展,患者的生存率得到了明显提高,生存质量也有所改善。由于肺癌的早期症状不明显,难以发现,因此如果能够对早期肺癌患者进行有效的评估与诊断,这对肺癌的治疗具有重要的意义[8-10]。本研究通过检测晚期非小细胞肺癌患者化疗前和化疗过程中体内血浆D-二聚体及纤维蛋白原水平,研究二者浓度变化与化疗效果和无进展生存期的关系,探讨二者在诊断肿瘤进展和预测化疗效果中的意义。
1 材料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取2013年1月至2015年12月间在我院住院治疗的晚期非小细胞肺癌患者120例,其中男性80例,女性40例,平均年龄(41.26±3.25)岁,年龄21~58岁。对照组健康人员60例,男性32例,女性28例,平均年龄(39.75±4.15)岁,年龄18~56岁。两组年龄、性别间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。本研究获我院伦理委员会批准,患者或近亲属对研究方案签署知情同意书。
1.2 入选标准
患者年龄>18岁;经组织学或细胞学诊断确诊为非小细胞肺癌;处于非小细胞肺癌晚期;预计生存期大于3个月;无其他肿瘤及肾类疾病;患者自愿参与本次研究。
1.3 排除标准
非晚期肺小细胞癌患者;病情严重,预计生存期较短;除肺癌外患有其他栓塞性疾病;严重的免疫缺陷或自身免疫病;患者不同意参与此次研究。
1.4 化疗方法
前两次化疗均进行一线化疗,第3次化疗前通过影像学检查评估患者肿瘤进展及转移情况。
1.5 疗效评定
按照国际统一标准,疗效评定结果分为完全缓解(complete response,CR)、部分缓解(partial response,PR)、病情稳定(stable disease,SD)及肿瘤进展(progress disease,PD),本次研究中未出现CR现象,因此认定PR+SD为有效组,PD为无效组。有效组患者继续进行原化疗方案,无效组患者改变治疗方案。
1.6 统计学方法
应用SPSS 20.0统计学软件对实验所得所有数据进行处理和分析,组内和组间数据比较采用t检验,P<0.05视为差异具有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 血浆D-二聚体及纤维蛋白原水平与肺癌临床病理特征的关系
血浆D-二聚体及纤维蛋白原水平的异常升高与晚期非小细胞肺癌患者的年龄、性别、肿瘤分期及病理类型均无相关性,P均>0.05,见表1。
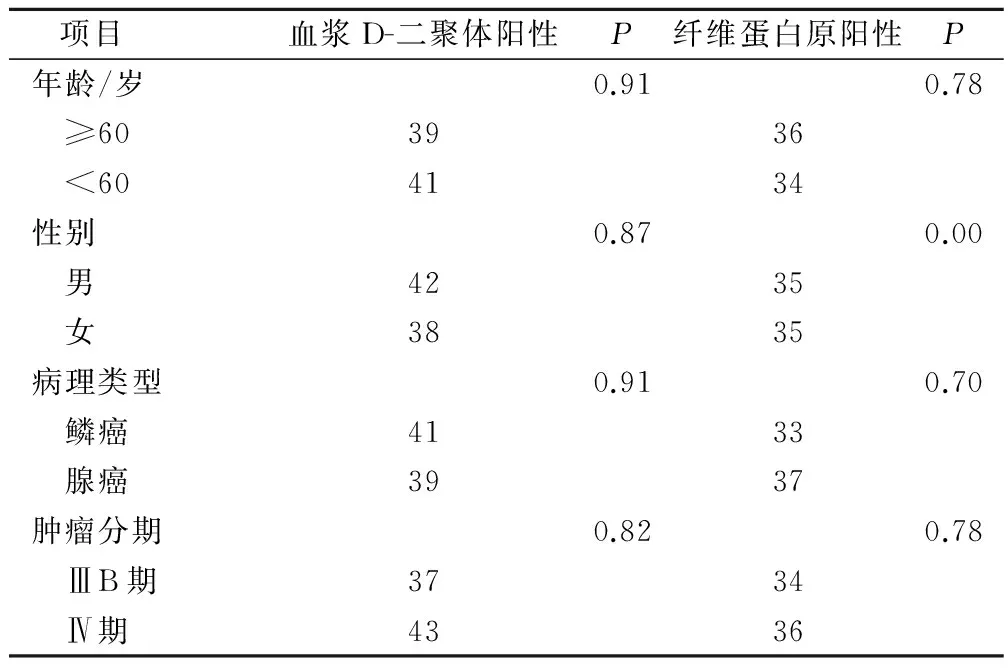
表1 血浆D-二聚体及纤维蛋白原水平与肺癌临床病理特征关系/例
2.2 NSCLC组与对照组D-二聚体和FIB水平比较
对照组D-二聚体和FIB水平分别为0.47 mg/L和3.76 g/L,明显低于化疗前晚期NSCLC患者的0.96 mg/L和4.32 g/L,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。
2.3 血浆D-二聚体和FIB水平与化疗效果的关系
化疗2个周期后,有效(PR+SD)的晚期NSCLC患者D-二聚体和FIB水平分别为0.65 mg/L和2.74 g/L,无效患者为1.72 mg/L和4.65 g/L,对比差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。
2.4 血浆D-二聚体和FIB阳性与PFS的关系
晚期NSCLC患者的PFS中位数为5.4个月,化疗前D-二聚体和FIB阴性患者PFS明显长于阳性患者,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。
2.5 三次化疗前后患者的D-二聚体和FIB水平对比
将三次化疗前患者的D-二聚体和FIB水平进行对比,虽在不断降低,但差异无统计学意义(P均>0.05)(表2)。

表2 三次化疗前后患者的D-二聚体和FIB水平对比
3 讨论
D-二聚体是纤维蛋白单体经活化因子XIII交联后,再经纤溶酶水解所产生的1种特异性降解产物,是1个特异性的纤溶过程标记物。D-二聚体来源于纤溶酶溶解的交联纤维蛋白凝块[11-13]。纤维蛋白原是1种由肝脏合成的具有凝血功能的蛋白质。纤维蛋白是在凝血过程中,凝血酶切除血纤蛋白原中的血纤肽A和B而生成的单体蛋白质[14-15]。临床上通过对D-二聚体和FIB水平进行测定来评价患者的凝血状态,大量研究表明,肿瘤与凝血系统之间存在相互影响作用。因此对D-二聚体和FIB水平进行测定也可以作为恶性肿瘤诊断的依据,对肿瘤的早期治疗具有重要意义[16-18]。这一诊断方法目前已经被应用于对非小细胞肺癌的诊断,并且在晚期非小细胞肺癌的临床治疗中发挥出巨大作用。
本研究主要检测晚期非小细胞肺癌患者化疗前和化疗过程中体内血浆D-二聚体及纤维蛋白原水平,研究二者浓度变化与化疗效果和无进展生存期的关系,结果发现:血浆D-二聚体及纤维蛋白原水平的异常升高与晚期非小细胞肺癌患者的年龄、性别、肿瘤分期及病理类型均不相关,P值均大于0.05。对照组D-二聚体和FIB水平分别为0.47 mg/L和3.76 g/L,明显低于化疗前晚期NSCLC患者的0.96 mg/L和4.32 g/L,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。进行两个周期的化疗后,有效(PR+SD)的晚期NSCLC患者D-二聚体和FIB水平分别为0.65 mg/L和2.74 g/L,无效患者为1.72 mg/L和4.65 g/L,对比差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。晚期NSCLC患者的PFS中位数为5.4个月,化疗前D-二聚体和FIB阴性的患者PFS明显长于呈阳性的患者,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。将三次化疗前患者的D-二聚体和FIB水平进行对比,虽在不断降低,但差异无统计学意义(P均>0.05)。血浆D-二聚体和FIB与肿瘤间存在着互相影响的作用,两者浓度的异常升高暗示着肿瘤的进展情况,因此对患者血浆D-二聚体和FIB水平的检测可以作为晚期非小细胞肺癌的诊断依据,这对患者的早期治疗具有重要意义。
综上所述,晚期非小细胞肺癌患者化疗前D-二聚体和FIB水平异常升高,能够提示肺癌的诊断。治疗过程中要监测肿瘤进展情况,及时调整治疗方案,延长患者PFS。
[1] 何 圆,尤长宣.非小细胞肺癌免疫治疗进展〔J〕.中国肺癌杂志,2014,46(3):277-281.
[2] Sequist LV,Haber DA,Lynch TJ.Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in non-small cell lung cancer:predicting clinical response to kinase inhibitors.〔J〕.Clin Cancer Res,2015,11(16):5668-5670.
[3] 宋 勇,杨 雯.2014年晚期非小细胞肺癌内科治疗进展〔J〕.解放军医学杂志,2015,40(1):10-15.
[4] Reck M,Popat S,Reinmuth N,et al.Metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC):ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis,treatment and follow-up.〔J〕.Ann Oncol,2014,25 (Suppl 3):27-39.
[5] Reguart N,Rosell R,Cardenal F,et al.Phase I/II trial of vorinostat (SAHA) and erlotinib for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations after erlotinib progression ☆〔J〕.Lung Cancer,2014,84(2):161-167.
[6] Eberhardt WE,De Ruysscher D,Weder W,et al.2nd ESMO Consensus Conference in Lung Cancer:locally-advanced stage III non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).〔J〕.Ann Oncol,2015,26(8):1573-1788.
[7] Loong HH,Mok TS.Lung cancer:dropping bars or rising hoops--phase III outcomes of NSCLC.〔J〕.Nat Rev Clin Oncol,2014,11(7):381-382.
[8] Pallis AG.Management of elderly patients with NSCLC;updated expert's opinion paper:EORTC Elderly Task Force,Lung Cancer Group and International Society for Geriatric Oncology.〔J〕.Ann Oncol,2014,25(7):1270-1283.
[9] Oh SB,Hwang CJ,Song SY,et al.Anti-cancer effect of tectochrysin in NSCLC cells through overexpression of death receptor and inactivation of STAT3〔J〕.Cancer Lett,2014,353(1):95-103.
[10] Rolfo C,Giovannetti E,Hong DS,et al.Novel therapeutic strategies for patients with NSCLC that do not respond to treatment with EGFR inhibitors〔J〕.Cancer Treat Rev,2014,40(8):990-1004.
[11] 蔡 军,尹 杰,张 军,等.胃癌患者血浆D-二聚体检测的临床意义〔J〕.临床和实验医学杂志,2014,5(11):894-896.
[12] 张亚雷,何绮华,杨海虹,等.广泛期小细胞肺癌血浆纤维蛋白原、D-二聚体水平及血小板计数与患者近期疗效的相关性研究〔J〕.赣南医学院学报,2015,35(3):379-382.
[13] 贵立政.AECOPD急性加重患者血清CRP、FIB、PA和D-二聚体检测的临床意义〔J〕.河北医药,2014,4(2):195-197.
[14] Johnson KR.Evaluating surrogacy metrics and investigating approval decisions of progression-free survival (PFS) in metastatic renal cell cancer:A systematic review.〔J〕.Ann Oncol,2014,26(3):126-131.
[15] Hendifar A,Hingorani S,Harris W,et al.LBA-02High Response Rate and PFS with PEGPH20 added to Nab-Paclitaxel/Gemcitabine in Stage IV Previously Untreated Pancreatic Cancer Patients with High-HA Tumors:Interim Results of a Randomized Phase 2 Study〔J〕.Ann Oncol,2015,26(4):1225-1227.
[16] Errico A.Melanoma:CheckMate 067-frontline nivolumab i- mproves PFS alone or in combination with ipilimumab.〔J〕.Nat Rev Clin Oncol,2015,12(8):435.
[17] Mcarthur GA,Larkin J,Dréno B,et al.Impact of baseline genetic heterogeneities on progression-free survival (PFS) in patients (pts) with advanced BRAFV600-mutated melanoma treated with cobimetinib (COBI)+vemurafenib (VEM) in the phase 3 coBRIM study〔J〕.Eur J Cancer,2015,51(5):722-723.
[18] K.E.Oliver,Brady WE,Birrer MJ,et al.An evaluation of progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) of ovarian cancer patients with clear cell carcinoma vs serous carcinoma treated with platinum therapy:A Gynecologic Oncology Group (GOG) experience〔J〕.Gynecol Oncol,2014,133(9):26-27.
(编辑:吴小红)
Clinical Analysis of Plasma D-dimer and Fibrinogen Levels in Patients with Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer During Chemotherapy
ZHONG Lixin,SUN Honghui.
The First People’s Hospital of Nanyang,Nanyang,473010
Objective To study the changes of plasma D-dimer and fibrinogen (FIB) in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) before and after chemotherapy,and to investigate the effect of chemotherapy on the concentration of D-dimer and fibrinogen And progression-free survival (PFS),and to explore their significance in the diagnosis of tumor progression and prognosis of chemotherapy.Methods 120 patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who were hospitalized in our hospital from January 2013 to December 2015 were enrolled in this study.Plasma D-dimer and fibrin were measured before and after the first,Original level,tumor pathological type,stage and no progression.The plasma D-dimer and fibrinogen levels of 60 healthy people were collected as controls,and the relationship between plasma D-dimer and fibrinogen level and the progress of lung cancer and the therapeutic effect were studied.Results Abnormal elevation of plasma D-dimer and fibrinogen levels was not associated with age,sex,tumor stage and pathological type of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer,P values were greater than 0.05.The levels of D-dimer and FIB in the control group were 0.47 mg/L and 3.76 g/L,respectively,which were significantly lower than those of the patients with NSCLC before chemotherapy (0.96 mg/L and 4.32 g/L,P<0.05 ).D-dimer and FIB levels were 0.65 mg/L and 2.74 g/L,1.72 mg/L and 4.65 g/L,respectively,in patients with advanced NSCLC who were treated with both cycles of chemotherapy (PR + SD),The difference was statistically significant (P<0.05).In patients with advanced NSCLC,the median PFS was 5.4 months.PFS was significantly longer in D-dimer and FIB-negative patients before chemotherapy than in patients with positive results (P<0.05).The levels of D-dimer and FIB were compared before and after chemotherapy,but the differences were not statistically significant (P>0.05).Conclusion D-dimer and FIB levels in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) are abnormally high before chemotherapy,which may be helpful for the diagnosis of lung cancer.The course of treatment to monitor tumor progression,timely adjustment of treatment programs to extend the patient PFS.
Advanced non-small cell lung cancer;Chemotherapy;D-dimer;Fibrinogen;Progression-free survival
473010 南阳市第一人民医院
10.3969/j.issn.1001-5930.2017.03.010
R734.2
A
1001-5930(2017)03-0382-04
2016-10-09
2016-11-04)

